Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Science 6 Trees and Forests
front 1  Abiotic | back 1 The non-living part of the environment that includes temperature, water (or lack thereof) day/night, etc. |
front 2  Adaptation | back 2 The modification of alteration of an organism so that it adjusts to a new or altered environment. |
front 3  Allowable Cut | back 3 The amount of trees which can be taken from the forest annually without significantly altering the balance of the ecosystem. |
front 4  Bark | back 4 The visible outer covering of a tree which helps to protect the inside of the tree. |
front 5  Biodiversity | back 5 The many different species living in balance within a specific area or environment. |
front 6  Biotic | back 6 The living components of an environment. |
front 7  Cambium | back 7 The growing part of the tree where cells form actual wood. |
front 8  Canopy | back 8 The top branches and leaves of the trees in a forest. |
front 9  Carbon Dioxide | back 9 CO2 A gas composed of carbon and oxygen that is produced when humans and living things exhale. |
front 10  Carnivore | back 10 A meat eating organism. |
front 11  Chlorophyll | back 11 The green substance found in leaves of plants that traps light energy used in photosynthesis. |
front 12  Respiration | back 12 The process of releasing energy from sugar and other organic molecules by combining it with O2 to produce CO2 and H2O as waste. |
front 13  Clear cutting | back 13 A method of harvesting trees where ALL standing trees are removed from a section of forest at one time regardless of whether they are usable or not. |
front 14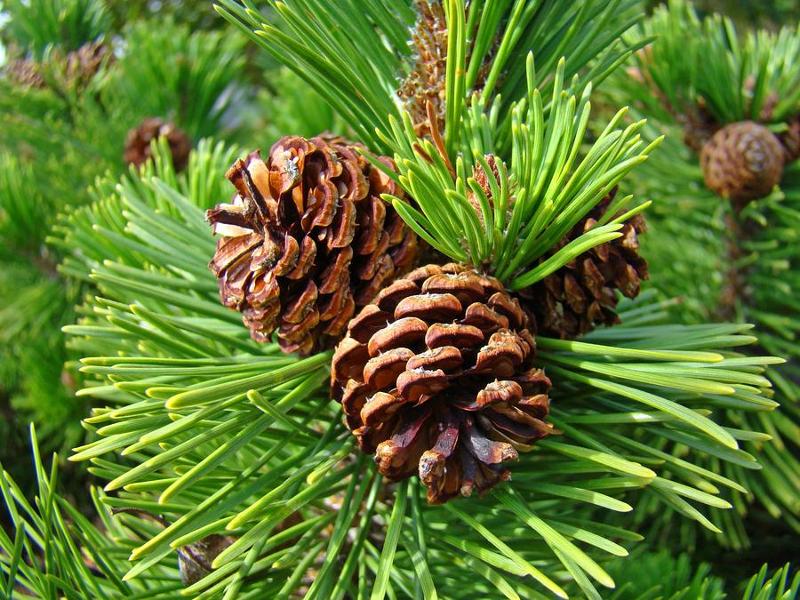  Cones | back 14 Small, woody structures of coniferous trees which produce the seeds (a baby tree). |
front 15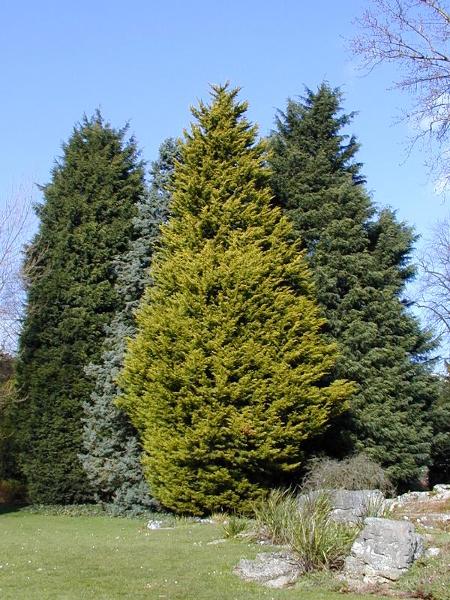  Conifer | back 15 A tree which bears cones and has needles as leaves. Some examples are pine, spruce, fir or cedars. They are often referred to as evergreens. |
front 16  Consumer | back 16 An organism which feeds on other organisms in an ecosystem: herbivores, carnivores and omnivores are part of this group. |
front 17  Crown | back 17 The top of a tree that forms the canopy. |
front 18  Deciduous | back 18 Trees which lose their leaves every autumn or a broadleaf tree. |
front 19 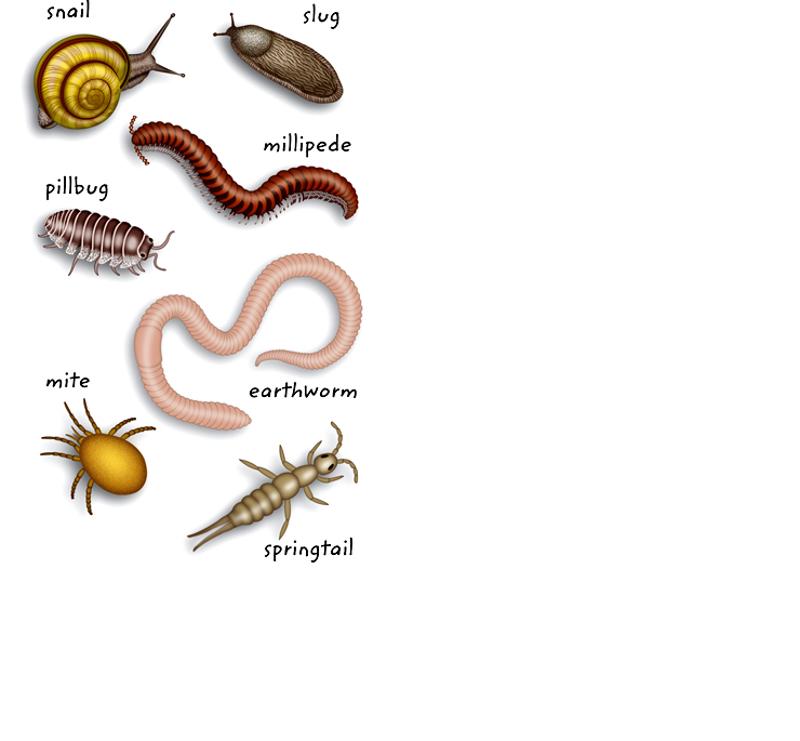 Decomposer | back 19 An organism which breaks down material and litter - the forest floor cleaners! |
front 20  Direct Seeding | back 20 Putting seeds directly into the forest floor rather than planting seedlings. |
front 21  Ecosystem | back 21 An area of living and non-living components which form an environment. |
front 22  Evergreen | back 22 A tree which does not lose its leaves and has needles instead of broadleaves. |
front 23 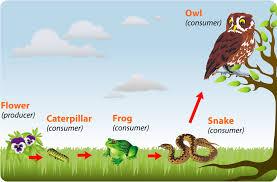 Food Chain | back 23 A transfer of energy from the sun from one living thing to another. |
front 24 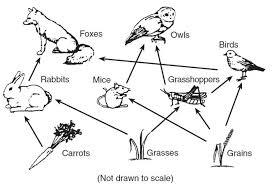 Food Web | back 24 The feeding relationships in an ecosystem. It shows how all organisms are connected in a specific ecosystem. |
front 25  Forest | back 25 A group of trees. You had all better get this one CORRECT!! |
front 26  Forest Floor | back 26 The area around the base of trees, usually covered with leaves, moss and other plants. |
front 27  Forest Management | back 27 The care and use of forests - it works to protect the forest. |
front 28  Forest Products | back 28 Things that are made from trees. |
front 29  Forestry | back 29 The practice of managing, conserving and creating forests. |
front 30  Growth Ring | back 30 Rings that are present when you look at a tree cookie which are used to determine the age of the tree. |
front 31 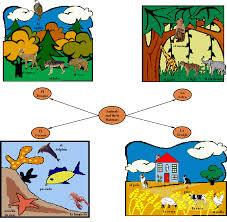 Habitat | back 31 A preferred place where an animal or plant lives. or, in simpler terms, an animal's home. |
front 32  Harvesting | back 32 The removal of trees for a variety of uses- logging. |
front 33  Heartwood | back 33 The non-living wood, right in the middle of the trunk, making up most of a tree truck which gives the truck strength. |
front 34  Herbivore | back 34 A plant eating organism. |
front 35  Inner Bark | back 35 The inner layer which serves to take food from the leaves to parts of the tree. |
front 36  Interdependence | back 36 The state of being dependent upon each other for survival - being interconnected. |
front 37  Log | back 37 The trunk of a tree after its been felled (cut down). |
front 38  Logging | back 38 The cutting and transporting of trees to the mill to make products. A very important industry in Alberta. |
front 39 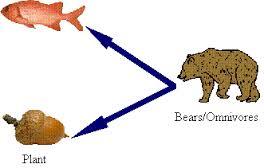 Omnivore | back 39 An organism which eats both plants and animals. |
front 40  Park | back 40 A specially designated area used for recreation. |
front 41 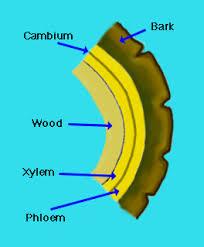 Phloem | back 41 The inner bark tissue that transports nutrients down to the roots and back up to the canopy. |
front 42 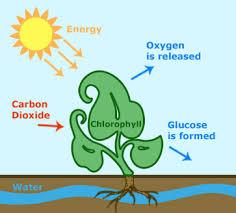 Photosynthesis | back 42 The process by which a tree produces its own food (sugar) using sunlight. |
front 43  Producer | back 43 Any organism which uses energy from the sun to produce its own food. These are generally ALL green. |
front 44  Reforestation | back 44 The building of a new forest by replanting or reseeding - usually done after an area has been logged or damaged by fire. |
front 45  Regeneration | back 45 The process of growing back what has been lost. Forests usually do this after a fire with the growth of new seedlings. |
front 46 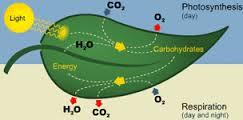 Respiration | back 46 When trees "sweat" - trees release water back into the atmosphere. |
front 47  Sap | back 47 The fluid part of a tree rich in sugar and starch which moves up and down the tree in the phloem tissue of the bark - maple syrup is one of these (yummmy!) |
front 48  Sapling | back 48 Code word for a young tree. |
front 49  Sapwood | back 49 The softer outer layer of the wood in the truck between the cambium and heartwood - responsible for nutrient transportation. The live part of the trunk. |
front 50  Seedling | back 50 Code word for a baby tree. |
front 51  Selective Harvesting | back 51 A method of harvesting trees where certain trees are slelected for cutting and ONLY these trees are taken. |
front 52  Shrub | back 52 A low-growing perennial plant. |
front 53  Snags | back 53 A standing tree which has begun to decay or a tree which has been felled but has caught itself on the way down. These are great for knocking over - but be careful of hornet nests inside the rotting truck. |
front 54 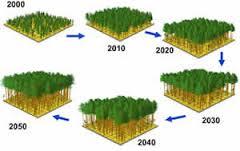 Stand | back 54 A group of trees in a given area. |
front 55 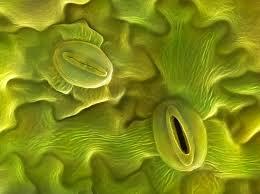 Stomata | back 55 Little holes on the underside of leaves which allow the tree to "sweat". |
front 56  Strip-Cutting | back 56 A method of harvesting a forest in strip-like sections. |
front 57 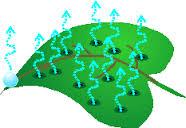 Transpiration | back 57 The loss of water through the stomata of the leaves. |
front 58  Tree | back 58 A perennial plant that has a wood trunk and a self-supporting truck. |
front 59 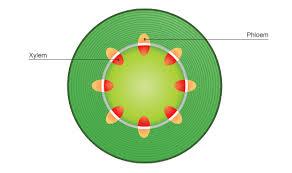 Xylem | back 59 Microscopic tubes running throughout the trunk of a tree that transports water and minerals up from the roots. |
front 60  Your teacher | back 60 The most awesome person you know! |