Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Lab
front 1 Identify and give the function of the microscope. Condenser, iris diaphragm, objective lens, ocular lens, fine-coarse focus adjustment | back 1 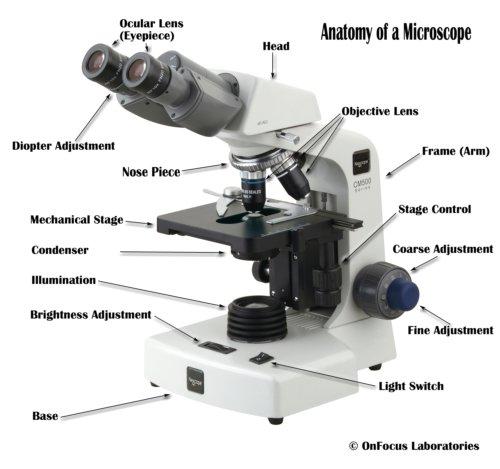 |
front 2 Terms to Understand: Resolution, depth of field, working distance, illumination | back 2 Resolution:Ability to see details of object Depth of field: Vertical distance through which the object is in focus Working Distance:Between the objective and the slide. Illumination: lighting |
front 3 Be able to calculate the total magnification of a compound light microscope. | back 3 no data |
front 4 Know the function of immersion oil | back 4 Function of immersion oil is to prevent refraction (loss) of light |
front 5 Estimate the size of an object in a microscope if you know the diameter of the field. | back 5 Example: To determine the field of view for a 40x objective (total magnification 400x) insert the values for the 10x objective (total magnification of 100x) (100) x (2mm)= (400)x (Y)= 200mm=400Y 200mm/400 = Y .5=Y |
front 6 Calculate how to prepare any volume of any culture medium, given the amount of dehydrated power used to prepare one liter. | back 6 no data |
front 7 Describe a colonys shape, size, optical properties, margin, elevation, color | back 7 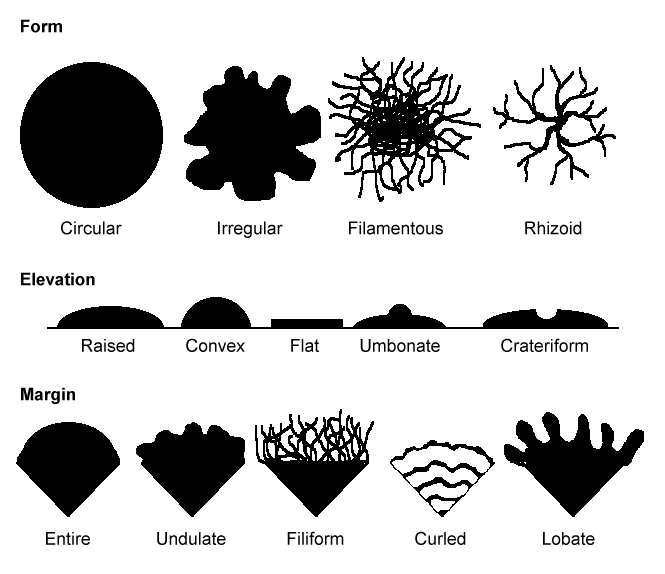 |
front 8 Use a drawing of a petri dish and words to describe how to prepare a streak plate. | back 8 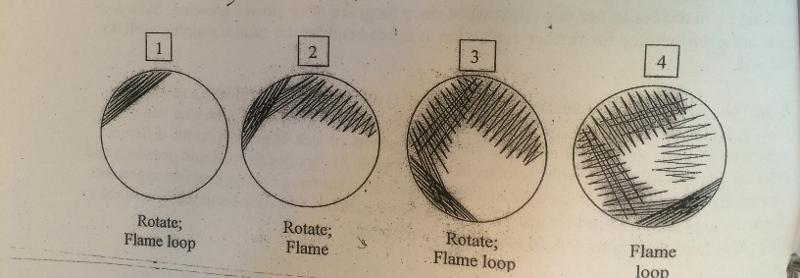 1) Aseptically load the loop once 2) streak, using a tight zig zag pattern in the first "quadrant" on SM agar plate 3) flame loop to sterilize it, can use portion of agar to cool loop 4) Reload, overlapping streaks into the 1st section 5)Repeat #3, 4 by overlapping 4-5 times into the second quadrant 6) Repeat #3, 4 by overlapping into the 3rd quadrant |
front 9 Describe the proper orientation of petri dishes in the incubator and refrigerator. | back 9 Incubator: Inverted |
front 10 why are smears heat fixed? | back 10 You heat fix the bacteria to kill it and make it adhear to the slide |
front 11 What is the difference between simple and differential stains? | back 11 Simple stains: Positive stain: dye with positive charge on colored part attached to cell wall with color. Ex: crystal violet, methylene blue, safranin Negative Stain: dye with negative charge on colored part leaves cells unstained, background colors Ex: congo red, nigrosin Differential stains: Use of 2 or may dyes After satining, one group of cells are one color; a different type of cell has a different color Example: Gram += purple; Gram -=pink |
front 12 Select the proper sequence for making smears from solid and liquid media. | back 12 no data |
front 13 What are the color of gram positive and gram negative organisms? | back 13 Gram Positive: Purple Gram Negative: Pink |
front 14 What are the reagents, in order of use, in the gram stain? | back 14 Gram's Crystal Violet, Grams Iodine, Acetone/alcohol, Gram Safrainin (Come In And Stain) |
front 15 What are the functions of the reagents? | back 15 Gram Crystal Violet- Primary stain Gram Iodine- a mordant that increases affinity between the dye and cell wall Acetone/alcohol- decolorizing agent Gram's safranin- secondary stain |
front 16 Why do some organisms stain unevenly in terms of gram positiveness? | back 16 no data |
front 17 What are the common genera of the endospore producing bacteria? | back 17 Prokaryotic |
front 18 What are the colors of the spores and cells in the methods (Schaeffer-Fulton & Gram Stain) used to stain endospores forming bacteria? | back 18 Spores stain green while the vegetative cells are red. |
front 19 What is the purpose of using heat during the endospore staining process? | back 19 Heat drives the stain into the cells. |
front 20 What are two advantages of using staining rather than positive staining? | back 20 no data |
front 21 How does negative staining differ from positive staining? | back 21 Positive stain: dye with positive charge on colored part attached to cell wall with color. Ex: crystal violet, methylene blue, safranin Negative Stain: dye with negative charge on colored part leaves cells unstained, background colors Ex: congo red, nigrosin |