Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Biology 101
front 1 Metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules | back 1 Catabolic Pathways |
front 2 Pinocytosis or Receptor-mediator Endocytosis is nonselective in the molecules it brings into the cell. | back 2 Pinocytosis |
front 3 ATP made during glycolysis is generated by what? | back 3 Substrate-level phosphorylation |
front 4 Oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event? | back 4 Accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain |
front 5 During cellular respiration, acetyl CoA accumulates in which location? | back 5 Mitochondrial matrix |
front 6 The molecule that functions as the reducing agent (electron donor) in a redox or oxidation-reduction reaction... | back 6 Loses electrons and loses potential energy |
front 7 When a molecule of NAD+ gains a hydrogen atom, not a proton, the molecule becomes _____. | back 7 Reduced |
front 8 Which process in eukaryotic cells will proceed normally whether oxygen (O2) is present or absent? | back 8 Glycolysis |
front 9 During glycolysis, when each molecule of glucose is catabolized to two molecules of pyruvate, most of the potential energy contained in glucose is... | back 9 Retained in the two pyruvate |
front 10 Carbon Dioxide (CO2) is released during which of the stages of cellular respiration? | back 10 Oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA and the Citric Acid Cycle |
front 11 The proteins of the electron transport chain are located where | back 11 Mitochondrial Inner Membrane |
front 12 In cellular respiration, the energy for most ATP synthesis is supplied by... | back 12 A proton gradient across a membrane |
front 13 Primary role of oxygen in cellular respiration is to... | back 13 Act as an acceptor for electron and hydrogen, forming water |
front 14 Inside an active mitochondrion, most electrons follows which pathway? | back 14 Citric Acid Cycle -> NADH-> Electron Transport Chain -> Oxygen |
front 15 In chemiosmosis, what is the most direct source of energy that is used to convert ADP + i to ATP? | back 15 Energy released from movement of protons through ATP synthase, down their electrochemical gradient |
front 16 Energy released by the electron transport chain is used to pump H+ into which location in eukaryotic cells? | back 16 Mitochondrial Intermembrane Space |
front 17 ATP synthase is located where in the mitochondrion? | back 17 Inner Membrane |
front 18 The force provided by a transmembrane hydrogen ion gradient | back 18 Proton-motive force |
front 19 Along with glycolysis, where does fermentation take place in eukaryotic cell? | back 19 Cytosol |
front 20 Without oxygen, yeast cells can obtain energy by fermentation, resulting in the production of... | back 20 ATP, CO2, and ethanol (ethyl alcohol) |
front 21 The final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain that functions in aerobic oxidative phosphorylation is ____. | back 21 Oxygen |
front 22 Formation of acetyl CoA takes place in the _____. | back 22 Mitochondrial Matrix |
front 23 The citric Acid Cycle Takes place in the ______. | back 23 Mitochondrial Matrix |
front 24 Oxidative Phosphorylation occurs where? | back 24 Inner Mitochondrial Membrane |
front 25 Name the net input for oxidative phosporylation | back 25 NADH, ADP, O2 |
front 26 Name the net output for oxidative phosporylation | back 26 ATP, NAD+, Water |
front 27 Net input involved in Citric acid Cycle | back 27 CoA, NAD+, ADP |
front 28 Net output involved in citric acid cycle | back 28 NADH, ATP, coenzyme A |
front 29 Pyruvate, NAD+, coenzyme A are my inputs Acetyl CoA, NADH, CO2 are my outputs who am I | back 29 Acetyl CoA |
front 30 My net inputs are ADP glucose, and NAD+ My net outputs are ATP, NADH, and pyruvate what am I | back 30 Glycoysis |
front 31 The reactions of cellular respiration can be broken down into four stages... | back 31 1. Glycolysis 2. Acetyl CoA (Coenzyme A) 3. Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle) 4. Oxidative Phosphorylation |
front 32 When a compound donates (loses) electrons, that compound becomes _______. Such compound is often referred to as an electron donor. | back 32 Oxidized |
front 33 In glycolysis, the carbon-containing compound that functions as the electron donor is _______. | back 33 Glucose |
front 34 Once the electron donor is glycolysis gives up its electrons, it is oxidized to a compound called... | back 34 Pyruvate |
front 35 _____ is the electron acceptor in glycolysis | back 35 NAD+ |
front 36 Reduced form of electron acceptor in glycolysis is _______ | back 36 NADH |
front 37 What compounds in glycolysis which compounds can be used in other biological reactions? | back 37 Pyruvate, ATP, NADH |
front 38 In lactate, what is the product of pyruvate metabolism? | back 38 Fermentation in human muscle |
front 39 In ethanol what is the product of pyruvate metabolism? | back 39 Fermentation in yeast and bacteria |
front 40 Main purpose of combined processes of glycolysis and cellular respiration | back 40 Transformation of the energy in glucose and related molecules in a chemical form that cells can use for work |
front 41 Electrons shipped from glucose in cellular respiration end up in which compound? | back 41 Water |
front 42 What results from an unequal sharing of electrons betweens atoms? | back 42 Polar Covalent Bonds |
front 43 A covalent bond is likely to be polar when | back 43 One of the atoms sharing electrons is much more electronegative than the other atom |
front 44 What charge does a proton have? | back 44 +1 charge |
front 45 What charge does a neutron have? | back 45 0 charge |
front 46 What charge does an electron have? | back 46 -1 charge |
front 47 Which subatomic particles both have masses of about 1 amu? | back 47 proton and neutron |
front 48 What determines the types of chemical reactions that an atom participates in? | back 48 The number of electrons in the outermost electron shell |
front 49 What type of bond is one in which electron pairs are shared? | back 49 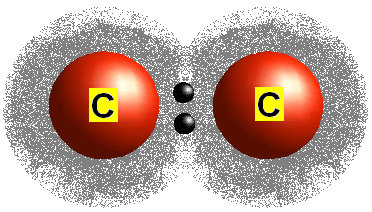 Covalent Bond |
front 50 ______ refers to two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds | back 50 molecule |
front 51 An ionic bond involves an attraction between ions of | back 51 opposite charge |
front 52 Atoms with the same number of protons but with different electrical charges are _______ | back 52 Different ions |
front 53 In salt, what is the nature of the bond between sodium and chloride | back 53 Ionic |
front 54 The type of bonding and the numbers of covalent bonds an atoms can form with other atoms is determined by _____ | back 54 The number of unpaired electrons in the valence shell |
front 55 What type of bond do atoms with similar electronegativities have? | back 55 Non-polar covalent |
front 56 What bond is formed when one atom transfers an electron to another atom? | back 56 Ionic Bond |
front 57 Hydrogen bonding is most often seen when hydrogen is... | back 57 covalently bonded to an electronegative atom |
front 58 Tendency of dissimilar particles/ surfaces to cling to one another | back 58 Adhesion |
front 59 The attraction between like molecules (water forms drops on table) | back 59 Cohesion |
front 60 Resistance of the surface of a liquid of stretching or breaking | back 60 Surface tension |
front 61 Resists change is pH by accepting hydrogen ions when acids are added to the solution and donating hydrogen ions when bases are added | back 61 A buffer |
front 62 Buffers minimize the change in the ____ of a solution | back 62 pH |
front 63 What forms when two atoms transfer or share outer electrons to complete their outer shells? | back 63 Chemical bond |
front 64 Most organic compounds contain which two elements? | back 64 Hydrogen and Carbon |
front 65 Large diversity of shapes of biological molecules is possible because of the extensive presence of ______ in the molecule. | back 65 Carbon |
front 66 Chemical energy is a form of _____ energy | back 66 Chemical energy |
front 67 Process that converts chemical energy found in glucose into chemical energy found in ATP. | back 67 Cellular respiration |
front 68 What are 3 by-products of cellular respiration? | back 68 Heat, carbon dioxide, and water |
front 69 In a cell, what is usually the immediate source for an endergonic reaction? | back 69 ATP |
front 70 A reaction in which the net input of energy is required from its surroundings | back 70 Endergonic |
front 71 In an endergonic reaction, the _______ have more potential energy than the ______. | back 71 Products Reactants |
front 72 In an exergonic reaction the ______ have less potential energy than the _______. | back 72 Products Reactants |
front 73 ADP + P --> ATP is a.... | back 73 Endergonic reaction |
front 74 The energy released by an exergonic reaction can be used to... | back 74 drive an endergonic reaction |
front 75 What is the fate of the phosphate group that is removed when ATP is converted to ADP? | back 75 It is acquired by a reactant in an endergonic reaction |
front 76 The use of energy released form an exergonic reaction to drive an endergonic reaction | back 76 Energy coupling |
front 77 Conservation of energy | back 77 Energy cannot be created nor destroyed but can be converted from one form to another |
front 78 What reaction breaks the bonds that join the phosphate group in an ATP molecule? | back 78 Hydrolysis |
front 79 Anabolism | back 79 Building of complex molecules from simple ones |
front 80 Energy needed or produced from a catabolic or anabolic process is stored where? | back 80 Intermediate energy carrying molecules such as ATP |
front 81 A catabolic/ anabolic process requires energy. | back 81 Anabolic process |
front 82 A catabolic/ anabolic process generates energy. | back 82 Catabolic process |
front 83 In general, enzymes are what kind of molecules? | back 83 Proteins |
front 84 How do enzymes work? | back 84 By reducing the energy of activation |
front 85 Enzymes are proteins that behave as... | back 85 Catalysts |
front 86 After involvement in an reaction, an enzymes results are changed. | back 86 False |
front 87 For a reaction to proceed, ________ must be overcome. | back 87 Energy of Activation |
front 88 The name given to a reactant in an enzymatically catalyzed reaction. | back 88 Substrate |
front 89 Generally, how many active sites at which catalysis can occur in an enzyme? | back 89 one |
front 90 The movement of glucose into a cell against a concentration gradient is most likely to be accomplished by... | back 90 Co-transport of the glucose with a proton or sodium ion that was pumped across the membrane using the energy of ATP hydrolysis |
front 91 What type of molecules are the major structural components of the cell membrane? | back 91 Phospholipids and proteins |
front 92 Singer and Nicolson's fluid mosaic model of the membrane produced that membranes... | back 92 Consist of protein molecules embedded in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids |
front 93 The presence of cholesterol in the plasma membranes of some animals | back 93 enables the membrane to stay fluid more easily when cell temperature drops |
front 94 The primary function of polysaccharides attached to the glyclo-proteins and glycolipids and animal cell membranes is... | back 94 To mediate cell-to-cell recognition |
front 95 What kinds of molecules pass through a cell membrane most easily? | back 95 Small and hydrophobic |
front 96 True/ False Diffusion is a passive process in which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration | back 96 True |
front 97 Pinocytosis/ Receptor-mediator Endocytosis is nonselective in the molecules it brings into the cell. | back 97 Pinocytosis |
front 98 Pinocytosis/ Receptor-mediator Endocytosis offers more selectivity in the cells it brings into the cells | back 98 Receptor-mediator Endocytosis |
front 99 A bacterium engulfed by a white blood cell through phagocytosis will be digested by enzymes contained in... | back 99 Lysosomes |
front 100 Substance that acts at a long distance from the site at which it is secreted. | back 100 Hormone |
front 101 Advantage of light microscopy over electron microscopy is that... | back 101 Light microscopy allows one to views dynamic processes in living cells |
front 102 ____ are surfaces appendages that allow a bacterium to stick to a surface | back 102 Fimbriae |
front 103 What is the function of a bacterium's capsule? | back 103 Protection |
front 104 Where is a bacterial cell's DNA found? | back 104 Nucleoid region |
front 105 In bacterium where are proteins synthesized? | back 105 Ribosomes |
front 106 The rigid structure, found outside the plasma membrane, that surrounds and supports the bacterial cell? | back 106 Cell wall |
front 107 The bacterial structure that acts as a selective barrier, allowing nutrients to enter the cell and wastes to leave the cell | back 107 Plasma membrane |
front 108 What clue tells if a cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic? | back 108 Whether or not the cell is partitioned by internal membranes |
front 109 What are the two domains of prokaryotes? | back 109 1. Bacteria 2. Archaea |
front 110 What is the first of the two main steps of proteins synthesis? | back 110 Transcription |
front 111 Large numbers of ribosomes are present in cells that specialize in producing what molecule? | back 111 Proteins |
front 112 Which structure is the site of the synthesis of proteins that may be exported from the cell? | back 112 Rough ER |
front 113 Which polymers are composed of amino acids? | back 113 Proteins |
front 114 Which monomers make up RNA? | back 114 Nucleotides |
front 115 What happens between the formation of polypeptides from amino acids? | back 115 a bond forms between the carboxyl functional group of one amino acid and the amino functional group of the other amino acid |
front 116 Which molecule is not a carbohydrate? cellulose, glycogen, lipid, starch | back 116 Lipid |
front 117 What is the function of cellulose? | back 117 It is the structural component of plant cell walls |
front 118 Glycogen is _______ | back 118 A polysaccharide found in animals |
front 119 _______ is the most abundant organic compound on Earth | back 119 Cellulose |
front 120 Lactose, the sugar in milk, is a _____ because it can be split into two monosaccharides | back 120 Disaccarides |
front 121 Phospholipids are composed of a ____, ____, and a ____. | back 121 Phosphate group, a glycerol, and fatty acids |
front 122 The sequence of amino acids in a protein | back 122 Primary structure |
front 123 The pattern of hydrogen bonds of the protein, such as alpha-helices and beta sheets, that are observed in an atomic resolution structure | back 123 Secondary structure |
front 124 Achieved when a protein folds into a compact, three-dimensional shape, stabilized by interactions between side chain "R-groups" of amino acids | back 124 Tertiary structure |
front 125 The result of two or more protein subunits assembling to form a larger, biologically active protein complex | back 125 Quartermary Structure |
front 126 Two strands of a DNA double helix are held together by _____ that form between pairs of nitrogenous bases | back 126 Hydrogen |
front 127 Which linkage forms the backbone of a nucleic acid? | back 127 Sugar-phosphate linkage |
front 128 List the levels of biological organization from the most wide to the most specific | back 128 1. Biosphere 2. Ecosystems 3. Communities 4. Populations 5. Organisms 6. Organs and Organ Systems 7. Tissues 8. Cells 9. Organelles 10. Molecules |
front 129 Approach of reducing complex systems to simpler components that are more manageable to study | back 129 Reductionism |
front 130 5 themes that help organize biological information and help understand life better. | back 130 1. Organization 2. Information 3. Energy 4. Interaction/ communication 5. Evolution |
front 131 Descent with modification; the idea that living species are descendants if ancestral species that were different from the present-day ones; the change in the genetic composition of a population from generation to generation | back 131 Evolution |
front 132 New properties arise with each step upward in the hierarchy of life, owing to the arrangement and interactions of parts as complexity increases. | back 132 Emergent properties |
front 133 A cell with a membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles | back 133 Eukaryotic cell |
front 134 Eukaryotic/ Prokaryotic cells protists, plants, fungi, and animals | back 134 Eukaryotic cells |
front 135 A cell lacking a membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles | back 135 Prokaryotic cell |
front 136 Eukaryotic/ Prokaryotic cells bacteria and archaea | back 136 Prokaryotic cells |
front 137 Discrete unit of hereditary information consisting of a specific nucleotide sequence in DNA or RNA | back 137 Genes |
front 138 Process by which information encoded in DNA directs the synthesis of proteins or, in some cases, RNAs that are not translated into proteins and instead function as RNAs | back 138 Gene expression |
front 139 Genetic material of an organism of virus; the complete complement of an organisms genes along with its nucleic acid sequences | back 139 Genome |
front 140 Name the three domains | back 140 Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya |
front 141 Which two of the three domains are prokaryotic? | back 141 Bacteria and Archaea |
front 142 What domain includes three kingdoms of multicellular eukaryotes, what are the three kingdoms? | back 142 Eukarya; Plantae, Fungi, and Animalia |
front 143 Mostly unicellular eukaryotes and some relatively simple multicellular relatives | back 143 Protists |
front 144 What kingdom consists of terrestrial multicellular eukaryotes (land plants) that carry outs photosynthesis, the conversion of light energy to the chemical energy in food | back 144 Kingdom Platae |
front 145 Which kingdom is defined in part by the nutritional mode of its members (such as this mushroom) which absorb nutrients from outside their bodies | back 145 Kingdom Fungi |
front 146 Explain natural selection | back 146 Process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits |
front 147 Search for information, often focusing on specific questions | back 147 Inquiry |
front 148 Type of logic in which generalizations are based on a large number of specific observations | back 148 Inductive Reasoning |
front 149 True/ False A hypothesis is narrower in scope than a theory | back 149 True |
front 150 Type of logic in which specific results are predicted from a general premise | back 150 Deductive reasoning |
front 151 An experiment in which an experimental group is compared with a control that varies only in the factor being tested | back 151 Controlled experiment |
front 152 Explanation that is broader in scope than a hypothesis, generates new hypothesis and is supported by a large body of evidence | back 152 Theory |
front 153 All the organisms in a given area as will as the abiotic factors with which they interact; one or more communities and the physical environment around them | back 153 Ecosystem |
front 154 A group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area and interbreed, producing fertile offpring | back 154 Population |
front 155 All the organisms that inhabit a particular area; an assemblage of populations of different species living close enough together for potential interaction | back 155 Community |
front 156 An organisms basic unit unit of structure and function | back 156 A cell |
front 157 Qualitative data is information with the use of... | back 157 Descriptions rather than measurements |
front 158 Quantitative data is information with the use of... | back 158 Recorded measurements which are sometimes organized into tables and graphs |