Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
FInal Exam
front 1 A prokaryotic cell will not have a) chloroplasts b) mitochondria c) nuclei d) all of the above | back 1 d) all of the above |
front 2 The golgi apparatus is a) a membraneous structure b) a very large cell compartment c) Associated with processing and export material d) A and B e) A and C | back 2 a) a membraneous structure |
front 3 Which of the following would be useful in visualizing a living prokaryotic cell a) a compound light microscope b) a scanning electron microscope c) a transmission electron microscope d) a microwave scope | back 3 b) a scanning electron microscope |
front 4 When studying a typical eukaryotic cell -an object that is 2 microns in size is most likely a) subcellular b) cellular c) existential d) ethereal | back 4 a) subcellular |
front 5 The typical yeast strain used for making bread or beer is a) Prokaryotic b) Eukaryotic c) Archean | back 5 b) Eukaryotic |
front 6 The metabolism of hydrogen peroxide is probably occurring in a) the nucleus b) the lysosome c) the chloroplast d) the peroxisome | back 6 d) the peroxisome |
front 7 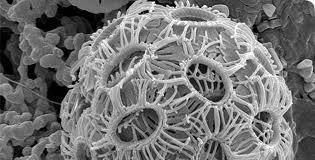 The above image was generate using a) a fluorescent microscope b) a scanning electron microscope c) a transmission electron microscope d) a microwave scope | back 7 b) A scanning electron microscope |
front 8 Endosymbiotic theory suggests that a) mitochondria are derived from an ancestral prokaryote b) the nucleus is derived from an ancestral prokaryote c) the chloroplast is derived from an ancestral prokaryote d) A and B e) A and C | back 8 e) A and C |
front 9 Na+ is considered one of the major groups of biological molecules a) true b) false | back 9 b) false |
front 10 The reactive group -C=O is a) a carbonyl b) basic c) weakly polar d) A and B e) A and C | back 10 d) A and B |
front 11 You have isolated an organism that can catabolize polysaccharides that are connected by an alpha 1,4 linkage. Which of the following would be a good carbon source for this organism a) fructose b) amylose c) cellulose d) palmitic acid | back 11 c) cellulose |
front 12 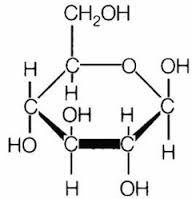 The above molecule is a) a sugar b) a lipid c) an amino acid d) A and B | back 12 a) a sugar |
front 13 Fructose and Glucose are a) monosaccharides b) lipids c) isomers d) both a and b e) both a and c | back 13 e) both a and c |
front 14 Which of the following is a good example of an amphipathic molecule a) glucose b) a glycolipid c) a lipid d) a protein | back 14 a) glucose |
front 15 If a phospholipid is added to water the molecules with produce micelles. Which part of the phospholipid will associate with the water molecules? a) hydrocarbon tails b) phosphate c) a and b d) the nitrogen atoms | back 15 b) phosphate |
front 16 In the reaction A + B <---> C + D the (delta) G will be positive and the rate will be largely a) to the left (toward A + B) b) to the right (toward C + D) c) at equilibrium d) stopped | back 16 b) to the right (toward C + D) |
front 17 Isoprene are often subunits of a) steroids b) carotenoids c) bile and salts d) A and B e) All of the above | back 17 a) steroids |
front 18 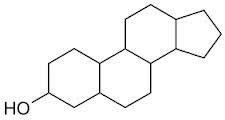 The above molecule is a) a protein b) a sugar c) a steroid d) a sphingolipid | back 18 c) a steroid |
front 19 Nucleic acids contain a sugar as a portion of the molecule a) true b) false | back 19 a) true |
front 20 The 5-prime carbon of most nucleic acids often is associated with a) adenine b) purines c) phosphates d) hydroxyl groups | back 20 b) purines |
front 21 In the following formula regarding free energy ( G=H-TS), S is defined as a) free energy b) temperature c) stored energy d) entropy | back 21 d) entropy |
front 22 ATP: when used in many biological reactions often results in a) Increased S b) a positive (delta) G c) a negative (delta) G d) Production of Adenosine | back 22 d) production of adenosine |
front 23 In the reaction A + B <---> C + D: increasing the amount of A and B will probably shift the (delta) G to a) zero b) negative c) positive d) no change | back 23 b) negative |
front 24 An enzyme defined as a kinase is involved with a) most biological reactions b) transfer of a sugar c) transfer of a phosphate d) production of dihydroxyacetone phosphate | back 24 c) transfer of a phosphate |
front 25 What enzyme associated with gluconeogensis is necessary to reverse the step associated with pyruvate kinase in glycolysis a) phophooenolpyruvate carboxykinase b) phosphofructokinase c) enolase d) fructose- 1,6-diphosphate phosphatase | back 25 c) enolase |
front 26 When using yeast to make bread there is probably an increase in a) sugar b) oxygen c) acetaldehyde d) lactate | back 26 a) sugar |
front 27 The metabolism of fatty acids in a typical eukaryotic cell occurs a) in the mitochondria b) with a degrading of two carbon units at a time c) with the direct production of NADH2 d) A and B e) all of the above | back 27 d) A and B |
front 28 Low oxygen levels will result in a) a slow down of the TCA cycle because of high levels of NADH b) a slow down of the TCA cycle because of low levels of NADH c) an increase in the TCA cycle because of high levels of NADH d) an inquired in the TCA cycle because of low levels of NADH | back 28 a) a slowdown of the TCA cycle because of high levels of NADH |
front 29 The TCA cycle occurs a) in the cytosol b) in the mitochondria c) in the chloroplasts d) in the nucleus | back 29 b) in the mitochondria |
front 30 In biological systems the cleavage of a protein to its amino acids and a starch to its monosaccharides is a process of a) condensation b) polymerization c) hydrolysis d) ATP utilization | back 30 c) hydrolysis |
front 31 In a typical eukaryotic cell, glycolysis occurs in a) the mitochondria b) the cytosol c) both a and b d) none of the above | back 31 b) the cytosol |
front 32 (GRE) Glucose is a simple sugar with the formula C6H12O6. If two glucose molecules are joined to form a disaccharide the molecular formula would be a) C6H12O6 b) C12H24O12 c) C12H23O11 d) C12H22O11 | back 32 d) C12H22O11 |
front 33 (GRE) Glycogen is a polymer of which of the following? a) Fructose b) Glucose c) Sucrose d) Cellulose e) Galactose | back 33 b) Glucose |
front 34 You and your lab partner have found a living organism and it contains membranes and DNA. You would classify this organism as a a) prokaryote b) eukaryote c) you cannot classify the organism based on this information d) plant | back 34 c) you cannot classify the organism based on this information |
front 35 The DNA in your skin cells is found in a) the nucleus b) the mitochondria c) the chloroplast d) A and C e) A and B f) A, B, and C | back 35 b) the mitochondria |
front 36 Where does the glycolysis occur in a eukaryotic cell a) cytoplasm b) mitochondria c) nucleus d) all of the above e) A and B | back 36 a) cytoplasm |
front 37 You and your lab partner are growing a cell line in the presence of glucose. When your lab partner adds a drug that mimics the presence of citrate it will a) inhibit the conversion of dihydroxyacetone to glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate b) directly inhibit electron transport c) decrease activity of phosphofructokinase d) increase activity of phosphofructokinase | back 37 d) increase activity of phosphofructokinase |
front 38 FADH2 is produced during a) glycolysis b) TCA cycle c) Fatty Acid Metabolism d) A and B e) B and C f) all of the above | back 38 b) TCA cycle |
front 39 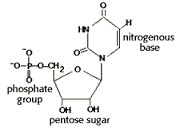 The above molecule is found in a) DNA b) polysaccharides c) fats d) all of the above e) none of the above | back 39 a) DNA |
front 40 Metabolism of fats in a typical human cell involves a) production of acetyl CoA b) mitochondria c) A and B d) None of the above | back 40 c) A and B |
front 41 The hydrolysis of ATP in the cytoplasm a) has a very positive (delta) G b) has a very negative (delta) G c) has a (delta) G of zero d) (delta) G can not be measured for this reaction | back 41 b) has a very negative (delta) G |
front 42 How many acetyl CoA molecules are produced from one glucose following glycolysis a) one b) two c) three d) four | back 42 b) two |
front 43 How many CO2 molecules are produced during lactate fermentation a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3 | back 43 c) 2 |
front 44 Where does the TCA cycle occur in a typical eukaryotic cell a) cytoplasm b) mitochondria c) chloroplasts d) a and b e) a, b, and c | back 44 b) mitochondria |
front 45 Which of the following is NOT a direct product of fatty acid metabolism a) Acetyl CoA b) NADH c) FADH2 d) ATP e) None of the above | back 45 d) ATP |
front 46 Which of the following molecules is transported into the mitochondria a) acetyl CoA b) fatty acids c) pyruvate d) a and b e) b and c f) all of the above | back 46 e) b and c |
front 47 A typical eukaryotic cell is about a) 2000 micrometers b) 200 micrometers c) 20 micrometers d) 0.2 micrometers | back 47 c) 20 micrometers |
front 48 A symport is a) two substances transported together in the same direction b) two substances transported together in opposite directions c) a simple pore for ion transport d) an example of simple diffusion | back 48 a) two substances transported together in the same direction |
front 49 Which is the following part of the glycocalyx a) a glycolipid b) a glycoprotein c) a phospholipid d) A and B e) A,B, and C | back 49 d) A and B |
front 50 The most common lipid in a human cell is a) sphingosine b) glycosphingolipids c) phospholipid d) cholesterol | back 50 c) phospholipid |
front 51 Isolation of the molecule chlorophyll is probably best accomplished with a a) polar solvent b) nonpolar solvent | back 51 b) nonpolar solvent |
front 52 You have isolated a membrane that contains a voltage gated transporter. Which of the following is probably carried by this transporter? a) lipids b) proteins c) ions d) sugars | back 52 c) ions |
front 53 You have homogenized a plasma membrane and mixed it with oil and water. You would expect the fatty acids to orient with the a) oil layer b) water layer c) not in either layers d) gated transporters | back 53 a) oil layer |
front 54 Which of the following may increase membrane fluidity a) a decrease in cholesterol b) a decrease in fatty acid length c) an increase in unsaturation d) a and b e) all of the above | back 54 a) a decrease in cholesterol |
front 55 Photosynthetic electron transport occurs a) in the stroma b) in the intermembrane space c) on the inner envelope membrane d) on the thylakoid membrane e) in the outer envelope membrane | back 55 d) on the thylakoid membrane |
front 56 The CO2 membrane transporter is more prevalent in cells that line the lung a) true b) false | back 56 b) false |
front 57 Chloroplasts contain a reducible lipid in the membrane. Which of the following is a similar molecule in a mitochondrion? a) cytochrome c b) plastocyanin c) ubiquinone d) ferridoxin | back 57 d) ferridoxin |
front 58 A typical mitochondrion is about a) .01 microns b) 1 micron c) 100 microns d) 1000 microns | back 58 b) 1 micron |
front 59 Chlorophyll is a protein a) true b) false | back 59 b) false |
front 60 Which of the following will not passively cross a typical cell membrane a) H+ b) water c) Cl- d) O2 e) A and C f) B and D | back 60 e) A and C |
front 61 Which of the following has a higher concentration outside a typical plant cell a) K+ b) H+ c) Na+ d) A and B e) B and C | back 61 b) H+ |
front 62 Most of the ATP for a typical animal cell is produced a) from glycolysis b) from the TCA cycle c) in a mitochondrion d) from photosynthesis | back 62 a) from glycolysis |
front 63 Carotenes and xanthophylls are considered to be a) reaction center pigments b) accessory pigments c) electron transfer molecules d) oxygen donors to light induced electron transfer | back 63 a) reaction center pigments |
front 64 Two protons of light are used to drive photosynthesis in most eukaryotes. This is because a) a reaction center has two chlorophylls b) carotenoids absorb one and xanthophyll the other c) there are two linked photosystems d) NADPH picks up two photons | back 64 c) there are two linked photosystems |
front 65 Glucose transport into and out of the liver can be described as a) facilitated diffusion b) simple diffusion c) glycogen associated transport d) ATP driven | back 65 a) facilitated diffusion |
front 66 Sodium transport from sweat glands can be described as a) voltage gated transport b) ligand gated transport c) stress gated transport d) light gated transport | back 66 b) ligand gated transport |
front 67 The electrons acquired from NADH in a mitochondrion are derived from a) acetyl CoA produced from pyruvate b) acetyl CoA produced from fatty acid metabolism c) acetyl CoA produced from RUBISCO d) A and B e) All of the above | back 67 a) acetyl CoA produced from pyruvate |
front 68 In comparison to cytoplasm plant vacuoles usually contain a) elevated Na+ b) elevated K+ c) elevated H+ d) decreased H+ e) decrease K+ | back 68 c) elevated H+ |
front 69 The final electron acceptor in electron transport in mitochondria is a) CO2 b) O2 c) NADH d) FADH2 e) C and D | back 69 b) O2 |
front 70 Passive transport may utilize a protein a) true b) false | back 70 a) true |
front 71 Both O2 and CO2 are either produced or used in mitochondria. How are they transported into this organelle? a) CO2 moves out and O2 moves in via antiproton mechanism b) CO2 and O2 move across by diffusion c) CO2 moves in and O2 moves out via a antiport mechanism d) CO2 moves out and O2 moves in via a symport mechanism | back 71 b) CO2 and O2 move across by diffusion |
front 72 ELVISLIVES is an example of a) primary b) secondary c) tertiary d) quarternary e) misguided old rocking rollers living a lie | back 72 a) primary |
front 73 A denatured protein has a) lost conformation b) gained conformation c) increased tertiary structure d) increased solubility | back 73 a) lost conformation |
front 74 Chaperons are a) lipids that facilitate protein folding b) proteins that facilitate protein folding c) protein transporter d) people that make sure no hanky pinky occurs | back 74 b) proteins that facilitate protein folding |
front 75 The recognition of a foreign molecule by your immune system is an example of a) protein ligand interaction b) protein-protein interaction c) protein substrate interaction d) all of the above e) none of the above | back 75 a) protein ligand interaction |
front 76 Cysteine is important for establishing a) primary structure b) secondary structure c) quaternary structure d) hydrophillic behavior | back 76 c) quaternary structure |
front 77 An antiport is a) two substances transported together in the same direction b) two substances transported together in opposite directions c) a simple pore for ion transport d) an example of simple diffusion | back 77 b) two substances transported together in opposite directions |
front 78 You have isolated a solution containing 1 mole of a functional protein. When you denature by gentle heating the solution you can isolate 4 moles of a given polypeptide. Your conclusion is a) you have cleaved the amino acid backbone and created four peptides b) you have disrupted the quaternary structure c) you have increased enzyme activity d) this result is not possible | back 78 b) you have disrupted the quaternary structure |
front 79 In the formula RATE=Vmax[S/(S+Km)] the letter S is defined as a) entropy b) enzyme activity c) substrate concentration d) substrate synthesis | back 79 c) substrate concentration |
front 80 End product inhibition is usually the result of competition of the end product and the substrate for the active site of the enzyme a) true b) false | back 80 a) true |
front 81 You have isolated enzyme A which catalyzes the conversion of x to y. This reaction is not directly associated with ATP as a substrate but when you add a chemical that inhibits all protein kinase function the activity of enzyme A decreases. This is probably due to a) Inactivation of enzyme A because it is a protein kinase b) inactivation of enzyme A because its activity is positively regulated by a protein kinase c) reconversion of y to x d) over production of ATP | back 81 b) inactivation of enzyme A because its activity is positively regulated by a protein kinase |
front 82 Where do you typically find cholesterol in a cell? a) within the plant vacuole b) on the outer surface of an animal cell c) embedded in an animal membrane d) all of the above | back 82 c) embedded in an animal membrane |
front 83 The inner membrane of the chloroplast envelope is permeable to which of the following molecules a) O2 b) CO2 c) H+ d) Cl- e) A and B f) C and D g) All of the above | back 83 e) A and B |
front 84 Integral membrane proteins can make pores a) true b) false | back 84 a) true |
front 85 You have isolated a drug that digests carbohydrate chains but has the side effect of gastrointestinal distress. This is probably due to a) disruption of sodium transport of glucose b) disruption of ATPase transporters c) Disruption of K+ transport d) disruption of glycocalyx structure | back 85 d) disruption of glycocalyx structure |
front 86 Coupled transporters always require ATP hydrolysis a) true b) false | back 86 b) false |
front 87 Increasing the soil of pH for a typical plant will result in a) an increase in Mg++ uptake b) a decrease in Mg++ uptake c) an increase in the activity of the sodium potassium ATPase pump d) A and C e) B and C | back 87 b) a decrease in Mg++ uptake |
front 88 You have isolated a drug that inhibits the sodium potassium ATPase pump in an animal cell line. When you treat cells with the drug there is an immediate inhibition of pyruvate into the cytoplasm but there is a lag before there is an inhibition of pyruvate uptake into the mitochondrion. This is probably due to a) a lack of ATP production b) A build up of citrate c) A depletion of pyruvate in the cytoplasm d) inhibition of the mitochondrial membrane carrier for pyruvate | back 88 c) A depletion of pyruvate in the cytoplasm |
front 89 The acetylcholine receptor discussed in lecture is an example of a) ATPase pump b) a gated transporter c) a ligand bound H+ transporter d) all of the above e) none of the above | back 89 b) a gated transporter |
front 90 Ribosomes are found in a) the cytoplasm b) the matrix c) the stroma d) all of the above | back 90 d) all of the above |
front 91 The molecule Q has a higher affinity for electrons compared to NADH dehydrogenase a) true b) false | back 91 a) true |
front 92 The H+ potential across the inner membrane of an active mitochondrion can be a) ten-fold b) 100-fold c) 1000-fold d) 10000-fold | back 92 a) ten-fold |
front 93 Neutrophil attack at an infection site is mediated by a) protein kinase activity b) ATP hydrolysis c) Glycocalyx interactions d) Actin driven | back 93 c) Glycocalyx interactions |
front 94 Glucose transport into and out of the liver can be described as a) facilitated diffusion b) simple diffusion c) glycogen associated transport d) ATP driven | back 94 a) facilitated diffusion |
front 95 Passive transport may utilize a protein a) true b) false | back 95 a) true |
front 96 In comparison to the cytoplasm the vacuoles in plants usually contain a) elevated Na+ b) elevated K+ c) elevated H+ d) decreased H+ e) decreased K+ | back 96 c) elevated H+ |
front 97 Disulfide bonds in a protein often result in stabilization of a) primary structure b) secondary structure c) tertiary structure d) peptide bond formations | back 97 c) tertiary structure |
front 98 Where in a plant cell will the pH decrease in response to exposure to sunlight a) the cytoplasm b) the stroma c) the thylkoid d) the lysosome e) the matrix f) the inter membrane space | back 98 c) the thylkoid |
front 99 You isolated molecules from spinach leaves using a buffer that creates an organic phase and a water phase. Where in the isolation would you find chlorophyll? a) neither phase b) water phase c) organic phase d) both phases | back 99 c) organic phase |
front 100 A signal sequence can best be described as a) cAMP b) DAG c) A stretch of amino acids typically 15-60 subunits in length d) A and B | back 100 c) A stretch of amino acids typically 15-60 subunits in length |
front 101 Transport of a newly synthesized protein into a nucleus requires a) movement through a membrane translocator b) movement through a nuclear pore c) a symporter d) an anitporter | back 101 b) movement through a nuclear pore |
front 102 Proteins transported from the cytoplasm to the chloroplast matrix are a) unfolded b) moved in the folded state via a porin c) moved via a symporter d) moved via an antiporter e) c and d | back 102 a) unfolded |
front 103 The N- terminal end of a functional chloroplast matrix protein has the same N- terminus as the cytosolic form a) true b) false | back 103 b) false |
front 104 Deletion of a mitochondrial signal sequence will probably result in a) a nuclear protein b) a secreted protein c) a cytosolic protein d) no protein | back 104 c) a cytosolic protein |
front 105 You have mutated a gene so that one of three stop transfer sequences of the protein product is eliminated. This will most like result in a) a lumen protein b) a cytosolic protein c) misplacement of the protein in the membrane d) a mitochondrial protein | back 105 b) a cytosolic protein |
front 106 You have recently discovered a way to label vesicles that are leaving the ER. Where do you hypothesize that the label will appear next as cell development progresses? a) the membrane b) the cis-golgi c) the trans-golgi d) the endosome e) the nucleus | back 106 b) the cis-golgi |
front 107 You have created an antibody that binds the protein clathrin. When you use this antibody to purify material from a cell culture what would you expect to isolate? a) nuclei b) mitochondria c) newly formed vesicles d) A and B e) all of the above | back 107 c) newly formed vesicles |
front 108 V-snares are found on a) targets b) vesicles c) organelles d) ribosomes | back 108 b) vesicles |
front 109 A cell that constantly secretes a hormone can best be described as a) busy b) regulated c) constitutive d) steroidal | back 109 c) constitutive |
front 110 You stick your finger with a pin. The inflammation that results is an example of a) endocrine signal b) paracrine signal c) neuronal signal d) contact-dependent signal | back 110 b) paracrine signal |
front 111 An example of a slow response to an extracellular signal is a) synthesis of a membrane protein b) production of mRNA c) Ca++ release d) GTP binding e) A and B f) C and D | back 111 f) C and D |
front 112 An example of a fast response to an extracellular signal is a) synthesis of a membrane protein b) production of mRNA c) Ca++ release d) GTP binding e) A and B f) C and D | back 112 c) Ca++ release |
front 113 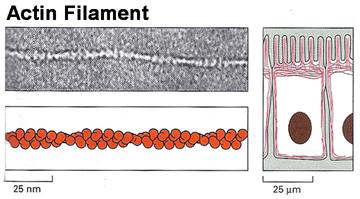 The above figure represents structures produced by a) intermediate filaments b) microtubules c) actin d) sacromeres | back 113 c) actin |
front 114 Which of the following compounds will disrupt the formation of these structures a) phalloidin b) taxol c) cytochalasins d) relaxin | back 114 c) cytochalasins |
front 115 RAS is a) a protein b) a lipid c) a second messenger d) an ion channel | back 115 a) a protein |
front 116 Receptors for the steroid-type hormones occur largely a) at a seven pass receptor b) at RAS c) at a cytoplasmic receptor d) in the nucleus | back 116 d) in the nucleus |
front 117 Active G proteins may target | back 117 adenylate cyclase |
front 118 Most G proteins are in the "on" position when bound to | back 118 GTP |
front 119 A-kinase | back 119 adds phosphates to target proteins |
front 120 Enzyme linked receptors a) often are associated with growth regulation b) are considered a tyrosine regulation c) often autophosphorylate d) all of the above | back 120 d) all of the above |
front 121 The three components of the cytoskeleton are | back 121 intermediate, filaments, actin filaments, microtubules |
front 122 The structure of the nucleus is associated with | back 122 Lamins |
front 123 Hair and feathers are | back 123 Keratins |
front 124 The tensile strength given to human skin is largely associated with | back 124 intermediate filaments |
front 125 a drug that destroys centrosomes will probably alter | back 125 Ciliary movement |
front 126 The flanking region of a sarcomere is | back 126 a Z-disc |
front 127 In a non-contracting skeletal muscle cell the Ca++ levels are elevated on | back 127 troponin |
front 128 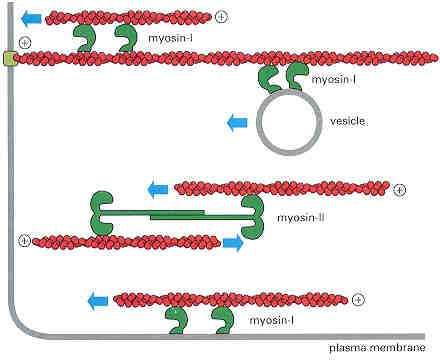 Know the actin filament and Myosin I | back 128 no data |
front 129 In a DNA double helix a) the strands contain a sugar-phosphate backbone b) adenine equals thymine c) adenine equals cytosine d) the two DNA strands run parallel e) both A and B | back 129 e) both A and B |
front 130 Semiconservative replication can best be described as | back 130 each daughter DNA molecule consists of one strand from the parent DNA molecule |
front 131 Which of the following is true of RNA polymerase | back 131 It has a higher error rate in comparison to DNA polymerase |
front 132 Which of the following statements is true of DNA replication in a cell | back 132 DNA synthesis begins with the production of an RNA primer |
front 133 Which of the following makes RNA A) RNA polymerase B) single stranded binding protein C) Primase D) A and B E) A and C | back 133 E) A and C |
front 134 A gene from a human is inserted into a bacterial cell. However, the gene product is not produced. Which of the following may explain this lack of activity a) the gene may contain introns b) the gene has an incorrect promoter c) A and B | back 134 c) A and B |
front 135 You have developed a drug that crosslinks (covalently links) signal stranded binding protein to DNA. When you add this drug to a replication cell you would expect most of the single stranded binding protein to be connected to a) the leading strand b) the lagging strand c) both strands | back 135 b) the lagging strands |
front 136 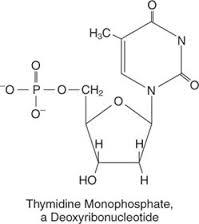 The above molecule is a) a DNA molecule b) RNA c) Both DNA and RNA d) neither | back 136 b) RNA |
front 137 You have discovered a mutant form of DNA polymerase in which there is no proof reading function. Which of the following properties do you expect the mutant polymerase to have? a) it will polymerize in both the 5' to 3' direction and function as a nuclease in the 3'-5' direction b) it will polymerize more slowly than normal c) to replicate the same amount of DNA it will hydrolyze fewer deoxyribonucleotides compared to the normal polymerase d)to replicate the same amount of DNA it will hydrolyze more deoxyribonucleotides compared to the normal polymerase | back 137 to replicate the same amount of DNA it will hydrolyze fewer deoxyribonucleotides compared to the normal polymerase |
front 138 Your skin is exposed to elevated levels of UV light from the sun. If you have progeny what percentage might contain a mutation because of the exposure | back 138 0% |
front 139 Which of the following is found as part of fully processed mRNA found in the cytoplasm? a) a poly A tail b) a 5' methyl G c) introns d) A and B | back 139 d) A and B |
front 140 Snurps are a) RNA protein complexes responsible for splicing together exons b) RNAs responsible for splicing together exons c) protein complexes responsible for splicing together eons | back 140 a) RNA protein complexes responsible for splicing together exons |
front 141 A chromosome is | back 141 a dna molecule and associated proteins |
front 142 DNA Polymerase makes few errors when replicating DNA. This is because | back 142 it has a 3'-5' exonuclease |
front 143 Your DNA is reacting with water and the guanine bases are being removed. this is known as | back 143 depurination |
front 144 A major difference between a prokaryotic gene and eukaryotic gene is | back 144 RNA polymerase in a eukaryotic cell interacts with a protein platform |
front 145 Which of the following proteins are most abundant at the replication fork? | back 145 single-stranded binding protein |
front 146 Which bases are found in DNA | back 146 A G C T |
front 147 the human genome is composed of about | back 147 3 X 109 base pairs |
front 148 application of sunscreen to your skin prior to sun exposure hopefully prevents | back 148 thymine dimers |
front 149 Which of the following is not found on a messenger RNA | back 149 the TATA box |
front 150 The codon usage for the amino acid proline is CC and then any other base. This is an example of | back 150 wobble |
front 151 Messenger RNA is produce by | back 151 RNA polymerase II |
front 152 How many aminoacyl tRNA synthases are there in a typical eukaryotic cell | back 152 20 |
front 153 Some portions of DNA during replication contain uracil. This is a result of | back 153 RNA primers |
front 154 the amino acid is attached to a tRNA at | back 154 the 3' end |
front 155 An example of signal transduction could be | back 155 a hormone signal converter to a change in gene expression |
front 156 a paracrine signal is an example of | back 156 short distance communication |
front 157 cell signals can be | back 157 peptides, amino acids, steroids |
front 158 Cell communication across a synapse is associated with | back 158 neuronal signal transduction |
front 159 Steroid hormones usually bind to | back 159 interior receptors |
front 160 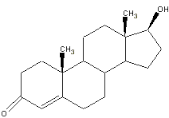 The above molecule is an example of | back 160 a steroid cell signal |
front 161 three common types of cell receptors are | back 161 Ion channel, G protein-linked, enzyme-linked |
front 162 the largest class of cell surface receptors is | back 162 enzyme linked receptors |
front 163 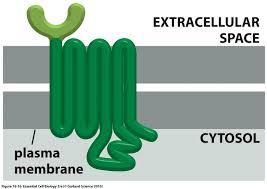 the above receptor is | back 163 a seven pass receptor |
front 164 which of the following are examples of G-protein targets | back 164 Ion Channels |
front 165 Adenylate cyclase results in | back 165 cAMP |
front 166 Phospholipase C results in | back 166 inositol triphosphate and diacylglycerol |
front 167 The advantages of cAMP and inositol triphosphate in a message cascade is that they are | back 167 small molecules that diffuse rapidly, are synthesized so that they can be amplified by producing large amounts of the product, and are lipophilic |
front 168 cAMP levels are regulated by the following | back 168 a phosphodiesterase and adenylate cyclase |
front 169 Hormone>>>Seven-Pass Receptor>>> G-protein>>> adenylate cyclase>>> ***>>> gene regulatory protein>>> transcription factor. Fill in the *** | back 169 A-Kinase |
front 170 the substrate for adenylate cyclase is | back 170 cAMP |
front 171 second messengers can result in elevated cytoplasmic calcium. The calcium is usually supplied by | back 171 the ER |
front 172 Calcium levels in the cell may alter directly or indirectly the activity of the following protein kinases | back 172 CaM Kinase |
front 173 Calmodulin binds | back 173 Calcium |
front 174 Enzyme linked receptors when functional usually exist as | back 174 activated monomers and self phosphorylating enzymes |
front 175 the receptor for initiation of the RAS cascade is | back 175 a tyrosine kinase |
front 176 RAS binds to | back 176 GTP |
front 177 High tensile strength, diameter of 10nm, and associated with most animal cells describes | back 177 intermediate filaments |
front 178 your hair is similar to | back 178 microtubules |
front 179 Keratins are | back 179 intermediate filaments |
front 180 during prophase the nuclear membrane "breakdown. this is due to | back 180 a change in the lamin phosphorylation |
front 181 Microvilli are composed of | back 181 actin filaments |
front 182 as microtubules age | back 182 GTP is hydrolyzed |
front 183 Kinesins are associated with movement along | back 183 a microtubule from - to + |
front 184 You have treated a cell with taxol and find that a specific cell movement is inhibited. This movement is associated with | back 184 microtubules |
front 185 The motor proteins associated with flagella are | back 185 myosin |
front 186 Movement of a flagellum in a unicellular organism is similar to the function of muscle cell movement in animals. true or false? | back 186 true |
front 187 actin is not found in plant cells. true or false? | back 187 false |
front 188 in the cell cortex region, you would expect to find very high levels of thymosin. true or false? | back 188 false |
front 189 troponin is a calcium binding protein. true or false? | back 189 true |
front 190 Telemers are located | back 190 at the end of your chromosome |
front 191 nucleosomes | back 191 are protein structures the eukaryotic DNA can wrap around |
front 192 replication of origins often have a segment of DNA that is | back 192 AT rich |
front 193 the number of replication origins in a human cell is | back 193 thousands |
front 194 a codon represent DNA for | back 194 one amino acid |
front 195 Okazaki fragments are found | back 195 on the lagging strand |