| back 1 nutrients are used as raw materials for synthesizing essential compounds |
| back 2 decomposes substances to provide energy cells need to function |
| back 3 -requires two essential ingredients
-
Oxygen
-
Organic molecules ( such as
carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) broken down by
intracellular enzymes
|
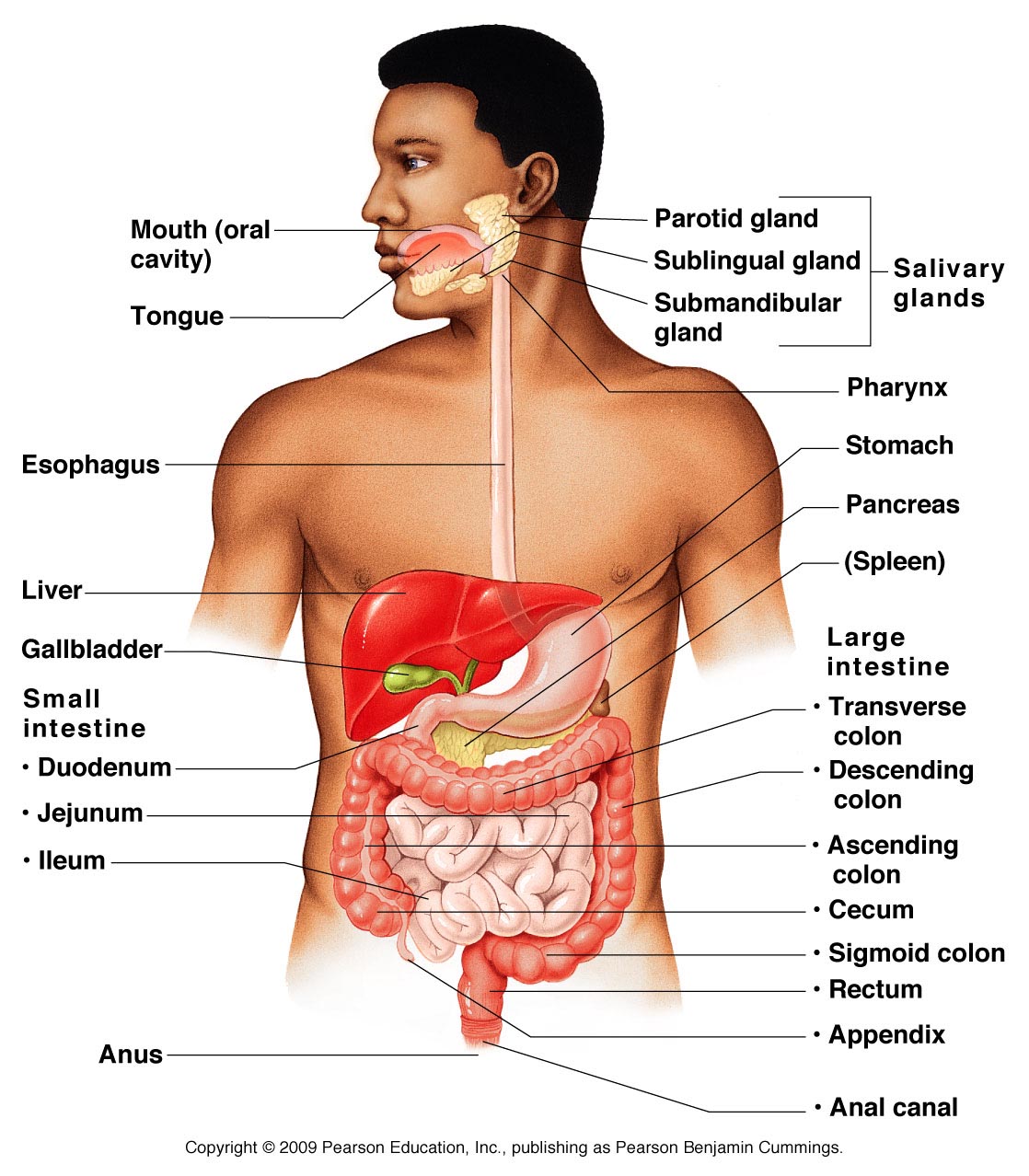
| back 4 - aka the gastrointestinal (GI) tract or alimentary canal
- is a muscular tube
- includes the mouth, pharynx,
esophagus, stomach, and small and large intestines
- extends
from the oral cavity to the anus
|
front 5 Accessory Digestive Organs | back 5 - teeth
- tongue
- salivary glands
- liver
- gallbladder
- pancreas
|
front 6 6 Functions of the Digestive System | back 6 - Ingestion
- Mechanical Processing
- Digestion
- Secretion
- Absorption
- Excretion
|
| back 7 - takes place when materials
enters the oral cavity
|
| back 8 - crushing and shearing, making materials easier to move along
the digestive tract
|
| back 9 - the chemical breakdown of food into small organic fragments for
absorption by digestive epithelium
|
| back 10 - the release of water, acids, enzymes, buffers, and salts by the
epithelium of the digestive tract & glandular organs
|
| back 11 - the movement of organic substrates, electrolytes, vitamins, and
water across digestive epithelium and into interstitial fluid of the
digestive trace
|
| back 12 the removal of wastes from the body
*defecation |
| back 13 ejection of wastes from the digestive tract eliminating them as feces |
front 14 Serosa or Visceral Peritoneum | back 14 covers organs within peritoneal cavity |
| back 15 lines inner surfaces of body wall |
| back 16 - produced by the serous membrane lining
- provides
essential lubrication
- separates parietal and visceral
surfaces, allowing sliding without friction or irritation
|
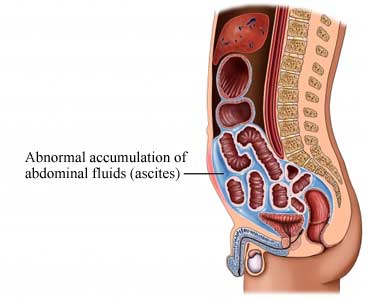
| back 17 - excess peritoneal fluid causing abdominal swelling
|
| back 18 - double sheets of peritoneal membrane
- suspend portions
of the digestive tract within the peritoneal cavity by sheets of
serous membrane that connect parietal and visceral peritoneum
- stabilize positions of attached organs
- prevent
intestines from being entangled
|
front 19 Areolar Tissue Between Mesothelial Surfaces | back 19 -provides an access route to and from the digestive tract for passage
of blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels |
| back 20 - fat skin
- stabilizes the position of the stomach
- provides an access route for blood vessels and other structures
entering or leaving the liver
- attaches stomach to
liver
|
| back 21 - helps stabilize the position of the liver, relative to the
diaphragm and abdominal wall
|
| back 22 - enlarges to form an enormous pouch, called the greater
omentum
|
| back 23 - extends inferiorly between the body wall and the anterior
surface of the small intestine
- hangs like an apron, from
the inferior and lateral borders of the stomach
|
front 24 Adipose Tissue in the Greater Omentum | back 24 - conforms to shapes of surrounding organs
- provides
padding & protection
- insulates to reduce heat loss
- stores lipid energy reserves
|
| back 25 - suspends all but the first 25 cm of small intestine
- thick mesenterial sheet
- provides stability, but permits
SOME independent movement
- associated
with the duodenum and pancreas
- fuses with posterior
abdominal wall, locking structures in position
|
front 26 Four Layers of the Digestive Tract | back 26 - mucosa
- submucosa
- muscularis externa
- serosa
|
| back 27 - the inner lining of digestive tract
- mucous
membrane
- consists of epithelium, moistened by glandular
secretions
- lamina propria of areolar tissue
|
| back 28 - mucosal epithelium is either simple or stratified depending on
the location, function, and stresses
|
front 29 Lined with Stratified Squamous | back 29 - oral cavity
- pharynx
- esophagus
|
front 30 Lined with Simple Columnar Epithelium | back 30 -
for absorption
- stomach
- small intestine
- most of the large
intestine
- contains mucous cells
|
| back 31 - scattered amongst columnar cells of the digestive tract
- secrete hormones that coordinate the activities of the digestive
tract
|
front 32 Lining of the Digestive Tract | back 32 - appears as longitudinal folds, which disappears as the tract
fills
- folding increases the surface area available for
absorption
|
| back 33 - layer of areolar tissue
- contains:
- blood
vessels
- sensory nerve ending
- lymphatic
vessels
- smooth muscle cells
- scattered areas of
lymphoid tissue
|
| back 34 - narrow sheet of smooth muscle and elastic fibers in lamina
propria
- cells are arranged in two concentric layers
|
| back 35 - layer of dense irregular connective tissue
- binds the
mucosa to the muscularis externa
- has numerous blood and
lymphatic vessels
- some regions contains exocrine glands
that secrete buffers and enzymes into the lumen of the digestive
tract
|
| back 36 - aka Meissner plexus
- network of intrinsic nerve fibers
and scattered neurons
- contains sensory neurons,
parasympathetic ganglionic neurons, and sympathetic postganglionic
fibers
|
| back 37 - smooth muscles dominates this region
- cells are
arranged in circular layer and outer longitudinal layer
|