Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Unit 6: Cell Reproduction
front 1 Asexual Reproduction | back 1 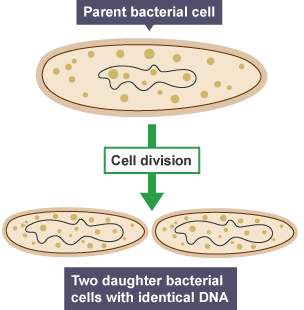 The process by which an organism produces a new, genetically identical organism without the use of gametes. Ex: binary fissions, runners in plants, budding and regeneration. |
front 2 Chromosome | back 2 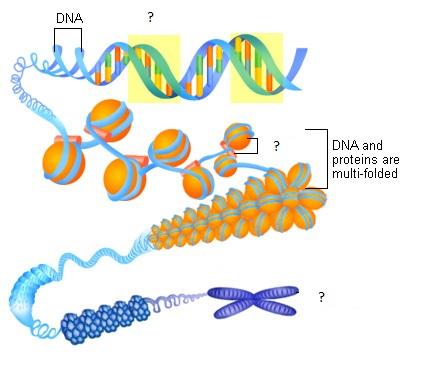 A single long molecule of DNA wound around proteins called histones. |
front 3 Genes | back 3  Segments of DNA that code for 1 protein/trait. |
front 4 Sister Chromatids | back 4 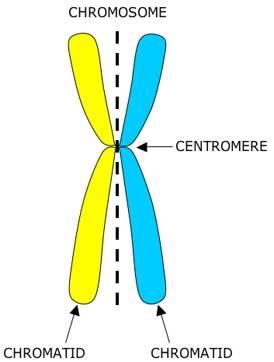 One of the two identical strands in a replicated chromosome. |
front 5 Cell Cycle | back 5 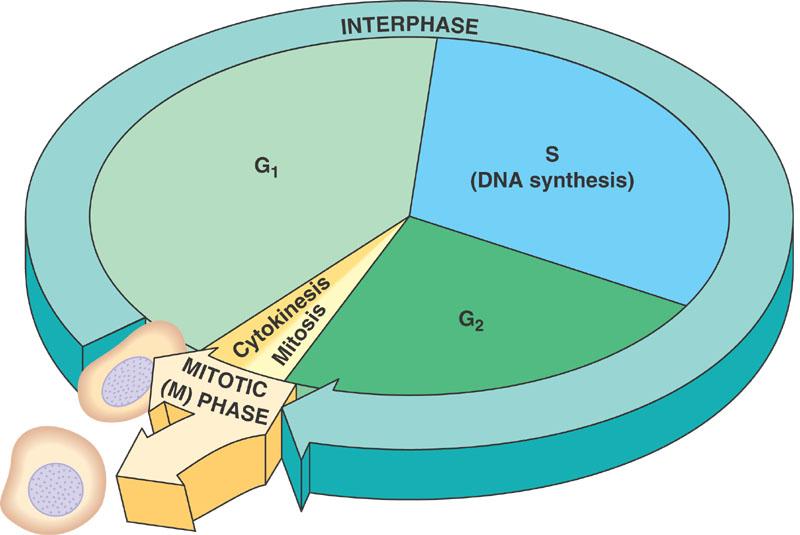 The series of events that take place in a cell during its lifetime. Phases:
|
front 6 Interphase | back 6 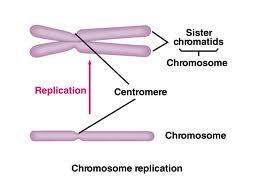 Period of cell cycle where cell grows and develops and DNA replicates. |
front 7 Centromere | back 7 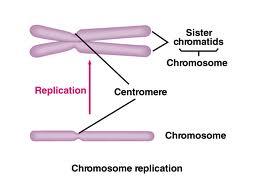 The point in the chromosome at which two chromatids are joined. |
front 8 Mitosis | back 8 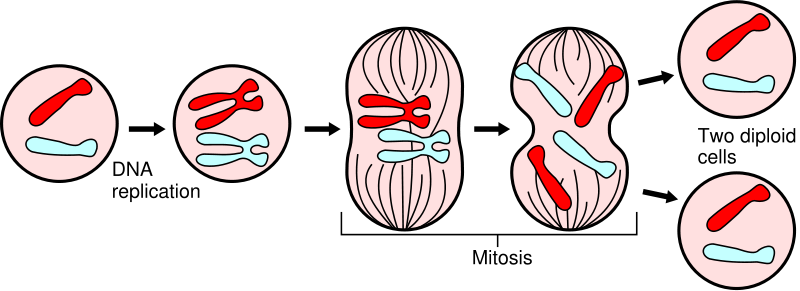 Stage of cell cycle when the nucleus divides. Phases:
|
front 9 Spindle Fibers | back 9  Microtubules that pull the sister chromatids apart during mitosis. |
front 10 Prophase | back 10 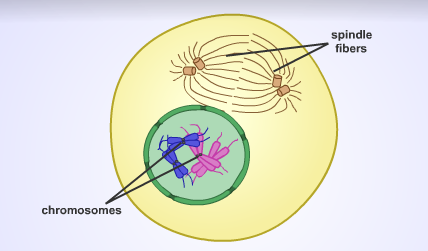 1st stage of mitosis
|
front 11 Metaphase | back 11 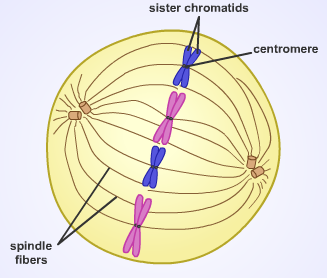 2nd stage of mitosis
|
front 12 Anaphase | back 12 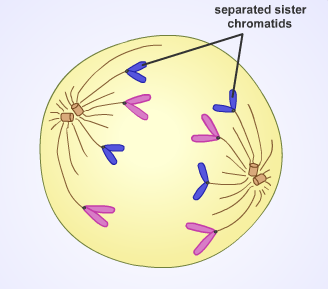 3rd stage of mitosis
|
front 13 Telophase | back 13 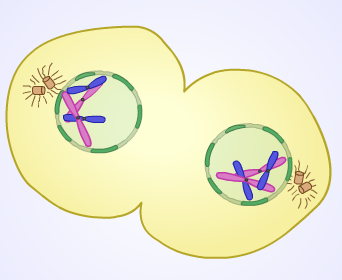 Last stage of mitosis
|
front 14 Cytokinesis | back 14 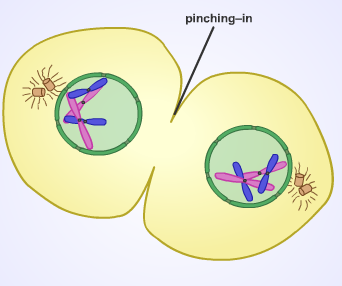 After mitosis Rest of cell divides to get 2 individual cells. |
front 15 Cell Differentiation | back 15 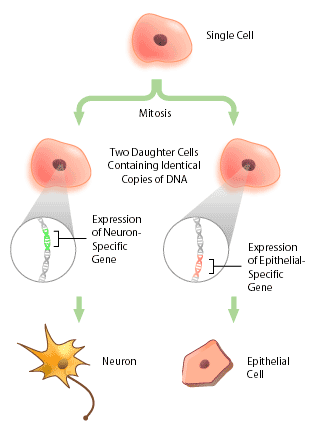 The process of cell modification to form specialized cells. Certain genes on the DNA are turned on or off. |
front 16 Stem Cells | back 16  Cells that are undifferentiated that are capable of becoming specialized cells. |
front 17 Daughter cells | back 17 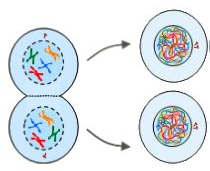 The resulting identical cells after cell division |
front 18 Somatic Cell | back 18 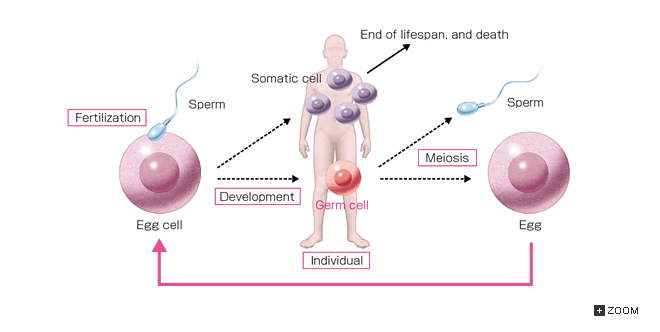 Body Cells - Any cell that forms in the body of the organism. |
front 19 DNA Replication | back 19 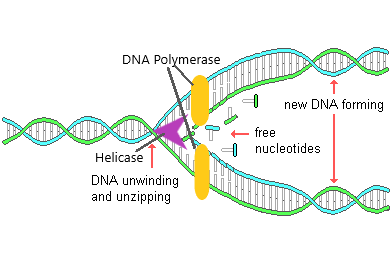 Process that makes an exact copy of DNA. Uses both strands as templates. |
front 20 Semi-conservative Replication | back 20 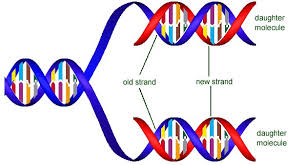 After DNA replication, the resulting DNA has 1 original strand and 1 new strand. This is due to using both strands of original DNA as templates and ensures the accuracy of the replication. |