Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 11/12 Cell Communication Mastering AP Biology
front 1 Which of these is NOT a carcinogen?Which of these is NOT a carcinogen? A. Cigarette smoke B. Testosterone C. UV light D. Fat E. All of the above are carcinogens | back 1 E. All of the above are carcinogens |
front 2 _____ is a carcinogen that promotes colon cancer._____ is a carcinogen that promotes colon cancer. A. Fat B. UV light C. Estrogen D. A virus E. Testosterone | back 2 A. Fat |
front 3 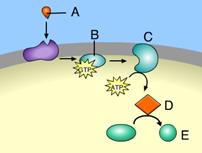 Which of these acts as a second messenger? A. B B. A C. C D. D E. E | back 3 D. D |
front 4 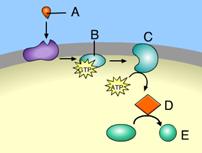 Which of these is responsible for initiating a signal transduction pathway? A. A B. B C. C D. D E. E | back 4 A. A |
front 5 What role does a transcription factor play in a signal transduction pathway? A. By binding to a plasma membrane receptor it initiates a cascade. B. It relays a signal from the cytoplasm to the plasma membrane. C. It activates relay proteins. D. By binding to DNA it triggers the transcription of a specific gene. E. It is a plasma membrane protein that binds signal molecules. | back 5 D. By binding to DNA it triggers the transcription of a specific gene. |
front 6 Which of these is a membrane receptor? A. A B. B C. C D. D E. E | back 6 B. B |
front 7 A signal transduction pathway is initiated when a _____ binds to a receptor. A. G protein B. Tyrosine kinase C. Calmodulin D. Signal molecule E. Cyclic AMP | back 7 D. Signal molecule |
front 8 Which of these acts as a second messenger? A. G-protein-linked receptor B. Cyclic AMP C. G protein D. Protein kinase E. Adenylyl kinase | back 8 B. Cyclic AMP |
front 9 Calcium ions that act as second messengers are stored in _____. A. Endoplasmic reticula B. Peroxisomes C. Lysosomes D. Chloroplasts E. Mitochondria | back 9 A. Endoplasmic reticula |
front 10 _____ catalyzes the production of _____, which then opens an ion channel that releases _____ into the cell's cytoplasm. A. Phospholipase C ... IP3 .... Ca2+ B. Adenylyl cyclase ... IP3 .... Ca2+ C. Protein kinase ... PIP2 ... Na+ D. Adenylyl cyclase ... cyclic AMP ... Ca2+ E. Phospholipase C ... cyclic AMP ... Ca2+ | back 10 A. Phospholipase C ... IP3 .... Ca2+ |
front 11 A protein kinase activating many other protein kinases is an example of _____. A. Sensitization B. Deactivation C. Amplification D. A cellular response E. Mutualism | back 11 A. Amplification |
front 12 The cleavage of glycogen by glycogen phosphorylase releases _____. A. Cellulose B. Fructose-1-phosphate C. Glucose-1-phosphate D. Galactose-1-phosphate E. Nothing: glycogen phosphorylase cannot cleave glycogen | back 12 C. Glucose-1-phosphate |
front 13 Epinephrine acts as a signal molecule that attaches to _____ proteins. A. Nuclear receptor B. Ion-channel receptor C. Intracellular receptor D. G-protein-linked receptor E. Receptor tyrosine kinase | back 13 D. G-protein-linked receptor |
front 14 Which of these is a receptor for calcium ions? A. G protein B. PIP2 C. Adenylyl cyclase D. Calmodulin E. IP3 | back 14 D. Calmodulin |
front 15 Which of these is NOT correct? A. Ion channels are found on both the plasma membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum. B. Tyrosine-kinase receptors consist of two polypeptides that join when activated by a signal molecule. C. Kinases are enzymes that phosphorylate other molecules. D. Phospholipase C catalyzes the formation of IP3. E. Cyclic AMP binds to calmodulin. | back 15 E. Cyclic AMP binds to calmodulin. |
front 16 A toxin that inhibits the production of GTP would interfere with the function of a signal transduction pathway that is initiated by the binding of a signal molecule to _____ receptors. A. G-protein-linked B. Steroid C. Intracellular D. Ion-channel E. Receptor tyrosine kinase | back 16 A. G-protein-linked |
front 17 Which of these is a logical signal transduction pathway? A. An intracellular receptor activates phospholipase C, which cleaves a membrane protein to form IP3, which then activates the opening of an ER channel protein, which releases cyclic AMP into the cytoplasm, where it binds to an intracellular enzyme that carries out a response. B. A receptor tyrosine kinase activates adenylyl cyclase, which activates phospholipase C, which converts ATP into cyclic AMP, which binds to an intracellular enzyme that carries out a response. C. A G-protein-linked receptor activates G protein, which activates phospholipase C, which cleaves a membrane lipid to form IP3, which binds to a calcium channel on the ER, which opens to release calcium ions into the cytoplasm, which bind to an intracellular enzyme that carries out a response. D. An ion-channel receptor opens, allowing a steroid hormone to enter the cell; the steroid hormone then activates protein kinases that convert GTP to GDP, which binds to an intracellular enzyme that carries out a response. | back 17 C. A G-protein-linked receptor activates G protein, which activates phospholipase C, which cleaves a membrane lipid to form IP3, which binds to a calcium channel on the ER, which opens to release calcium ions into the cytoplasm, which bind to an intracellular enzyme that carries out a response. |
front 18 An environmental substance that is known to cause cancer is called a what? A. Teratogen B. Carcinogen C. Mutagen D. Mitogen | back 18 B. Carcinogen |
front 19 Radiation emitted from which of the following two sources are most alike? A. X-rays and microwaves B. Microwaves and cellphones C. Cellphones and cosmic rays D. Cosmic rays and light bulbs | back 19 B. Microwaves and cellphones |
front 20 You are trying to discover if the pesticide atrazine is a mutagen. Where are you looking for mutations? A. DNA B. RNA C. Mitochondria D. Glucose molecules | back 20 A. DNA |
front 21 Which of the following is true? A. A cancer-causing substance always directly damages DNA. B. No substance has ever been determined to cause cancer. C. A cancer-causing substance never directly damages DNA. D. Cancer-causing substances work in many different ways. | back 21 D. Cancer-causing substances work in many different ways. |
front 22 Which of the following best summarizes current scientific opinion regarding cellphones and brain cancer? A. While most studies indicate that cellphones cause brain cancer, the studies are not statistically sound. B. While most studies indicate that cellphones do not cause brain cancer, more research needs to be done as cellphone use increases. C. Cellphones do not cause brain cancer. D. Cellphones cause brain cancer. | back 22 A. While most studies indicate that cellphones do not cause brain cancer, more research needs to be done as cellphone use increases. |
front 23 Nucleoli are present during _____. A. Prometaphase B. Metaphase C. Interphase D. Prophase E. Anaphase | back 23 C. Interphase |
front 24 Cytokinesis often, but not always, accompanies _____. A. Interphase B. Telophase C. Prometaphase D. Anaphase E. Metaphase | back 24 B. Telophase |
front 25 Chromosomes become visible during _____. A. Interphase B. Prometaphase C. Prophase D. Anaphase E. Metaphase | back 25 C. Prophase |
front 26 Centromeres divide and sister chromatids become full-fledged chromosomes during _____. A. Telophase B. Anaphase C. Interphase D. Metaphase E. Prometaphase | back 26 B. Anaphase |
front 27 Spindle fibers attach to kinetochores during _____. A. Interphase B. Anaphase C. Telophase D. Metaphase E. Prometaphase | back 27 E. Prometaphase |
front 28 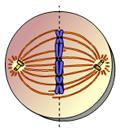 This animation illustrates the events of _____. A. Metaphase B. Telophase C. Interphase D. Anaphase E. Prophase | back 28 D. Anaphase |
front 29 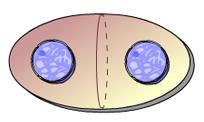 This animation illustrates the events of _____. A. Cytokinesis as it occurs in plant cells B. Cytokinesis as it occurs in animal cells C. Metaphase D. Prometaphase E. Prophase | back 29 B. Cytokinesis as it occurs in animal cells |
front 30 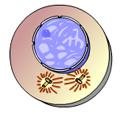 This animation illustrates the events of _____. A. Telophase B. Anaphase C. Prometaphase D. Interphase E. Prophase | back 30 E. Prophase |
front 31 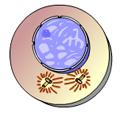 This animation illustrates the events of _____. A. Metaphase B. Anaphase C. Prometaphase D. Telophase E. Prophase | back 31 A. Metaphase |
front 32  This animation illustrates the events of _____. A. Interphase B. Anaphase C. Cytokinesis as it occurs in plant cells D. Prometaphase E. Metaphase | back 32 D. Prometaphase |
front 33  This animation illustrates the events of _____. A. Anaphase B. Prometaphase C. Prophase D. Metaphase E. Cytokinesis as it occurs in plant cells | back 33 E. Cytokinesis as it occurs in plant cells |
front 34 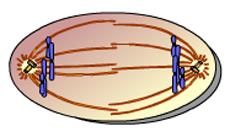 This animation illustrates the events of _____. A. Prophase B. Anaphase C. Telophase D. Prometaphase E. Metaphase | back 34 C. Telophase |
front 35 During prophase a homologous pair of chromosomes consists of _____. A. One chromosome and four chromatids B. Four chromosomes and two chromatids C. One chromosome and two chromatids D. Two chromosomes and two chromatids E. Two chromosomes and four chromatids | back 35 E. Two chromosomes and four chromatids |
front 36 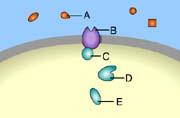 Which of these is a receptor molecule? A. D B. A C. B D. E E. C | back 36 C. B |
front 37 A signal transduction pathway is initiated when a _____ binds to a receptor. A. Tyrosine kinase B. G protein C. Signal molecule D. Cyclic AMP E. Calmodulin | back 37 C. Signal molecule |
front 38 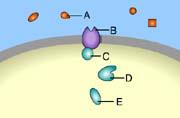 Which of these is a signal molecule? A. A B. B C. D D. C E. E | back 38 A. A |
front 39 A signal molecule is also known as a(n) _____. A. Initiator B. Key C. Ligand D. Receptor E. Protein | back 39 C. Ligand |
front 40 Which of these is the second of the three stages of cell signaling? A. Gene activation B. Reception C. Binding of a neurotransmitter to a plasma membrane receptor D. Transduction E. Cell response | back 40 D. Transduction |
front 41 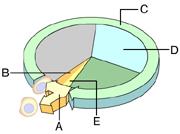 Which of these phases encompasses all of the stages of mitosis? A. C B. E C. D D. B E. A | back 41 B. E |
front 42 During _____ both the contents of the nucleus and the cytoplasm are divided. A. The mitotic phase B. Mitosis C. G1 D. S E. G2 | back 42 A. The mitotic phase |
front 43 During _____ the cell grows and replicates both its organelles and its chromosomes. A. Mitosis B. Cytokinesis C. Interphase D. S E. G1 | back 43 C. Interphase |