Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 13 Meosis & Sexual Life Cycles
front 1 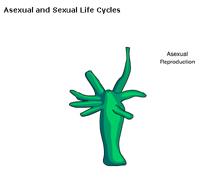 What name is given to this process? | back 1 asexual reproduction
|
front 2 Human gametes are produced by _____. | back 2 meiosis
|
front 3 Normal human gametes carry _____ chromosomes. | back 3 23 |
front 4 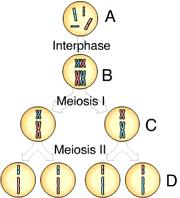 Which of these cells is (are) haploid? | back 4 C and D
|
front 5 A diploid organism whose somatic (nonsex) cells each contain 32 chromosomes produces gametes containing _____ chromosomes. | back 5 16 (half of 32) |
front 6 Asexual reproduction _____. | back 6 produces offspring genetically identical to the parent
|
front 7 What number and types of chromosomes are found in a human somatic cell? | back 7 44 autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes
|
front 8 Which is the smallest unit containing the entire human genome? | back 8 one human somatic cell |
front 9 For what purpose(s) might a karyotype be prepared? | back 9 for prenatal screening, to determine if a fetus has the correct number of chromosomes
|
front 10 In alternation of generations, what is the diploid stage of a plant that follows fertilization called? | back 10 sporophyte
|
front 11 How are sister chromatids and homologous chromosomes different from each other? | back 11 Homologous chromosomes contain the same gene loci but may have different alleles of a particular gene. Sister chromatids are identical copies of each other produced during DNA replication. |
front 12 Which of the following is a true statement about sexual vs. asexual reproduction? | back 12 In sexual reproduction, individuals transmit 50% of their genes to each of their offspring. |
front 13 Which of the following is true of a species that has a chromosome number of 2n = 16? | back 13 Each cell has eight homologous pairs. |
front 14 Which of these statements is false? | back 14 At sexual maturity, ovaries and testes produce diploid gametes by meiosis. |
front 15 Referring to a plant's sexual life cycle, which of the following terms describes the process that leads directly to the formation of gametes? | back 15 gametophyte mitosis |
front 16 Which of the following is an example of alternation of generations? | back 16 A diploid plant (sporophyte) produces, by meiosis, a spore that gives rise to a multicellular, haploid pollen grain (gametophyte). |
front 17 A triploid cell contains three sets of chromosomes. If a cell of a usually diploid species with 42 chromosomes per cell is triploid, this cell would be expected to have which of the following? | back 17 63 chromosomes in 21 sets of 3 |
front 18 Which of the following can utilize both mitosis and meiosis in the correct circumstances? | back 18 a plantlike protist |
front 19 In a human karyotype, chromosomes are arranged in 23 pairs. If we choose one of these pairs, such as pair 14, which of the following do the two chromosomes of the pair have in common? | back 19 Length, centromere position, staining pattern, and traits coded for by their genes. |
front 20 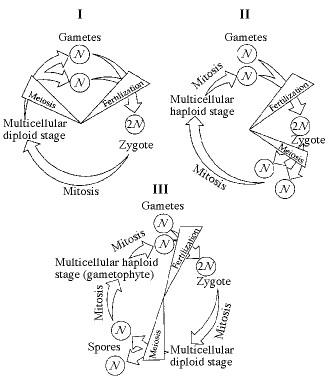 Which of the life cycles is typical for animals? | back 20 I only |
front 21 Which statement correctly describes how cellular DNA content and ploidy levels change during meiosis I and meiosis II? | back 21 DNA content is halved in both meiosis I and meiosis II. Ploidy level changes from diploid to haploid in meiosis I, and remains haploid in meiosis II. |
front 22 Meiosis I produces _____ cells, each of which is _____. | back 22 two ... haploid |
front 23 Meiosis II typically produces _____ cells, each of which is _____. | back 23 four ... haploid |
front 24 During _____ sister chromatids separate. | back 24 anaphase II
|
front 25 At the end of _____ and cytokinesis, haploid cells contain chromosomes that each consist of two sister chromatids. | back 25 telophase I |
front 26 Synapsis occurs during _____. | back 26 prophase I |
front 27 Homologous chromosomes migrate to opposite poles during _____. | back 27 anaphase I |
front 28 During _____ chromosomes align single file along the equator of a haploid cell. | back 28 metaphase II |
front 29 At the end of _____ and cytokinesis there are four haploid cells. | back 29 telophase II |
front 30 During _____ a spindle forms in a haploid cell. | back 30 prophase II |
front 31 Genetic variation occurs when chromosomes are shuffled in fertilization and what other process? | back 31 meiosis |
front 32 Heritable variation is required for which of the following? | back 32 evolution |
front 33 A human cell containing 22 autosomes and a Y chromosome is | back 33 a sperm. |
front 34 Meiosis II is similar to mitosis in that | back 34 sister chromatids separate during anaphase. |
front 35 Homologous chromosomes move toward opposite poles of a dividing cell during | back 35 meiosis I. |
front 36 Which life cycle stage is found in plants but not animals? | back 36 multicellular haploid |
front 37 If the DNA content of a diploid cell in the G1 phase of the cell cycle is x, then the DNA content of the same cell at metaphase of meiosis I would be | back 37 2x. |
front 38 If we continued to follow the cell lineage from question 5, then the DNA content of a single cell at metaphase of meiosis II would be | back 38 x. |
front 39 How many different combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes can be packaged in gametes made by an organism with a diploid number of 8 (2n = 8)? | back 39 16 |
front 40 Identify all possible products of meiosis in plant and animal life cycles. | back 40 Spores
|
front 41 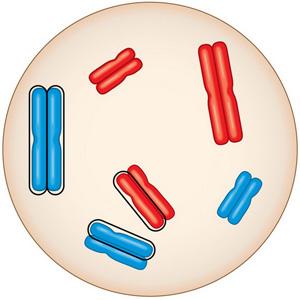 Look at the cell in the figure. Based on this figure, which of the following statements is true? | back 41 This cell is diploid. |
front 42 What is the best evidence telling you whether this cell is diploid or haploid? | back 42 The cell is diploid because it contains two sets of chromosomes. |
front 43 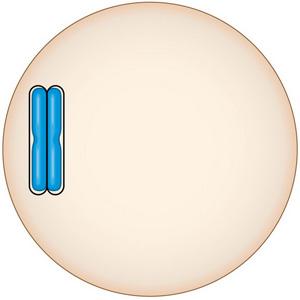 This chromosome has two chromatids, joined at the centromere. What process led to the formation of the two chromatids? | back 43 The two chromatids were formed by duplication of a chromosome. |
front 44 Two sister chromatids are joined at the centromere prior to meiosis. Which statement is correct? | back 44 Barring mutation, the two sister chromatids must be identical. |