Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Blood
front 1 Cardiovascular System consists of...... | back 1 -a pump (heart)
|
front 2 Blood | back 2  -a specialized fluid of connective tissue that contains cells suspended in a fluid matrix |
front 3 Important functions of blood... | back 3 -Transportation of dissolved substances
|
front 4 Whole Blood | back 4 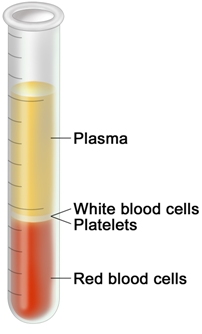 -combination of plasma and formed elements |
front 5 Plasma | back 5 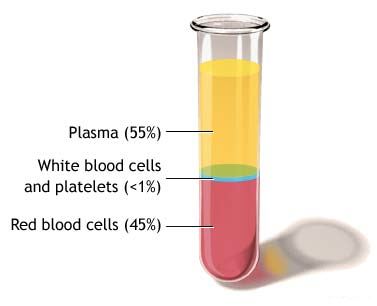 fluid matrix of blood consisting of:
|
front 6 Formed Elements | back 6 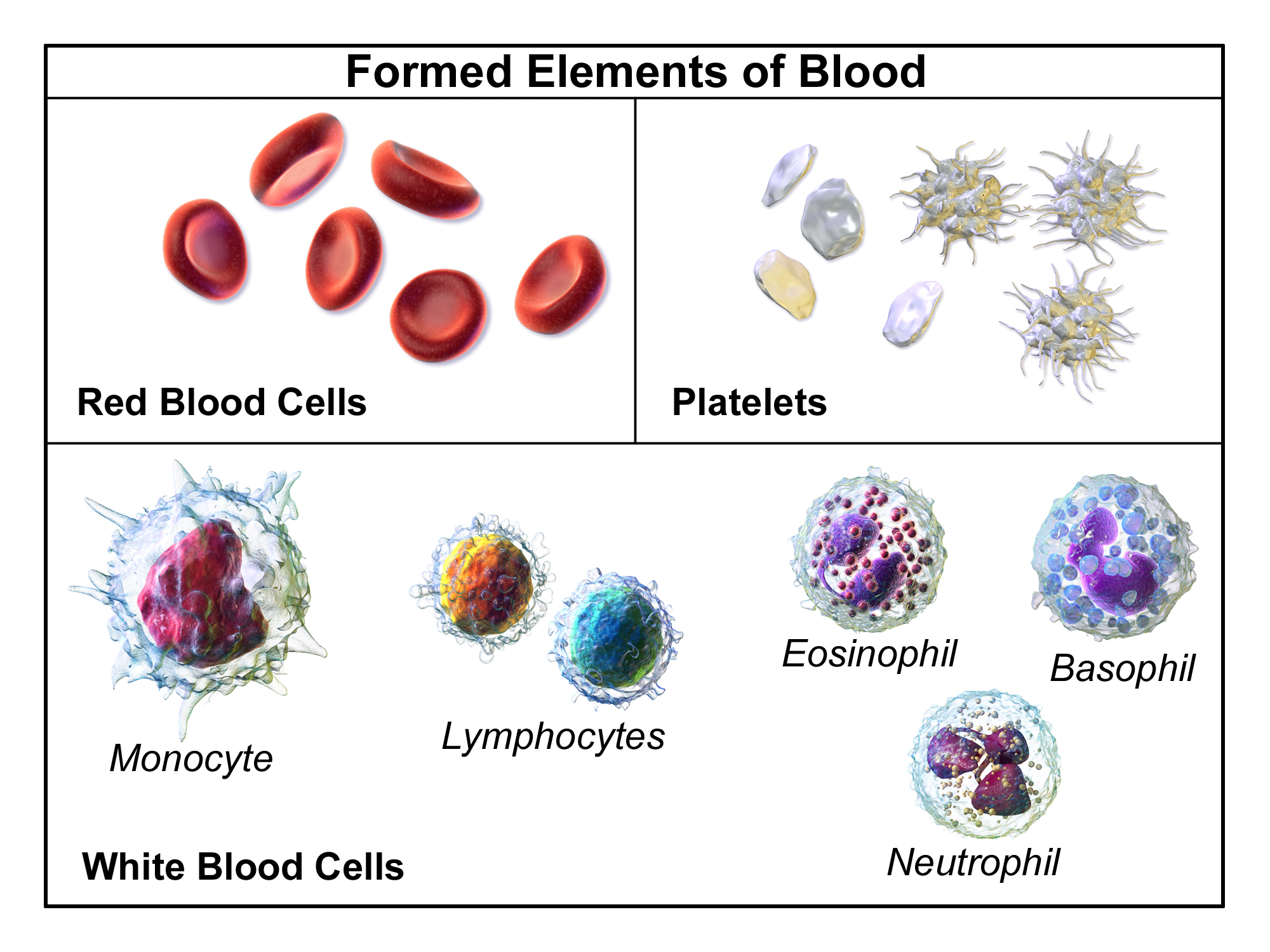 -blood cells and cell fragments that are suspended in plasma |
front 7 Three Types of Formed Elements | back 7  -red blood cells/erythrocytes
|
front 8 Red Blood Cells/Erythrocytes | back 8  -transport oxygen from lungs to tissues and carbon dioxide from tissues to lungs)
|
front 9 White Blood Cells/Leukocytes | back 9  -part of the immune system
|
front 10 Platelets/Thrombocytes | back 10  -cell fragments involved in clotting |
front 11 Hemopoiesis | back 11 -process of producing formed elements by myeloid and lymphoid stem cells |
front 12 Fractionation | back 12  -process of separating whole blood for clinical analysis |
front 13 General Characteristics of Blood | back 13 1. 38 degrees C (100.4 degress F) is normal temperature, slightly above normal body temperature
|
front 14 The Composition of Plasma | back 14  -makes up 50-60% of blood volume
|
front 15 Plasma Proteins | back 15 -Albumins (60%)
|
front 16 Albumins | back 16 -makes up 60% of the plasma proteins
|
front 17 Three Important Effects of RBC Shape on FUnction | back 17 -high surface to volume ratio (quickly absorbs and releases oxygen)
|
front 18 Globulins | back 18 --makes up 35% of the plasma proteins
|
front 19 Fibrinogen | back 19 -makes up only 4% of plasma proteins
|
front 20 Serum | back 20 -liquid part of a blood sample, in which dissolved fibrinogen has converted to solid fibrin |
front 21 Other Plasma Proteins | back 21 -1% of plasma proteins
|
front 22 Origins of Plasma Proteins | back 22 -more than 90% is made in the liver
|
front 23 Hemoglobin | back 23 -the red pigment that gives whole blood its color
|
front 24 Fetal Hemoglobin | back 24 -strong form of hemoglobin found in embryos
|
front 25 Erythropoiesis | back 25  -red blood cell formation, occurs only in myeloid tissue (red bone marrow) in adults
|
front 26 Stages of RBC Maturation | back 26  1.Myeloid stem cell
|
front 27 RBC Formation and Turnover | back 27 -1% of circulating RBCs are replaced each day
|
front 28 Hemoglobin Conversion and Recycling | back 28 -macrophages of liver, spleen, and bone marrow play a role in recycling RBC components
|
front 29 Biliverdin | back 29 -an organic compound with a green color |
front 30 Breakdown of Biliverdin | back 30 -biliverdin is converted to bilirubin |
front 31 Iron Recycling | back 31 -iron removed from heme leaving biliverdin |
front 32 Hemocytoblasts | back 32 -stem cells in myeloid tissue divide to produce:
|
front 33 Regulation of Erythropoiesis | back 33 -building red blood cells requires:
|
front 34 Pernicious Anemia | back 34 -Vitamin B12 deficiency
|
front 35 Erythropoietin (Erythropoiesis-stimulating hormone) | back 35 -secreted when oxygen in peripheral tissues is low (hypoxia) |
front 36 Hematocrit (Hct) | back 36 -percentage of formed elements in whole blood
|
front 37 Reticulocyte Count | back 37 -percentage of circulating reticulocytes
|
front 38 Hemoglobin Concentration | back 38 -concentration of hemoglobin in blood
|
front 39 Surface Antigens | back 39 -surface proteins that identify cells to immune system
|
front 40 Blood Types | back 40 -genetically determined, by presence or absence of RBC surface antigens A, B, or RH |
front 41 Four Blood Types | back 41  A, B, AB, O |
front 42 Type A (blood type) | back 42  surface antigen A
|
front 43 Type B (blood type) | back 43  surface antigen B
|
front 44 Type AB (blood type) | back 44  antigens A and B
|
front 45 Type O (blood type) | back 45  -has neither A or B antigens |
front 46 Agglutinogens | back 46  -antigens on surface of RBCs
|
front 47 Cross-Reactions in Transfusions | back 47 -plasma antibody meets its specific surface antigen, blood will clump and hemolyze
|
front 48 WBC Functions | back 48 -defend against pathogens
|
front 49 Granulocytes | back 49  -cells with abundant stained granules
|
front 50 Aggranulocytes | back 50  -few if any stained granules
|
front 51 Neutrophils | back 51 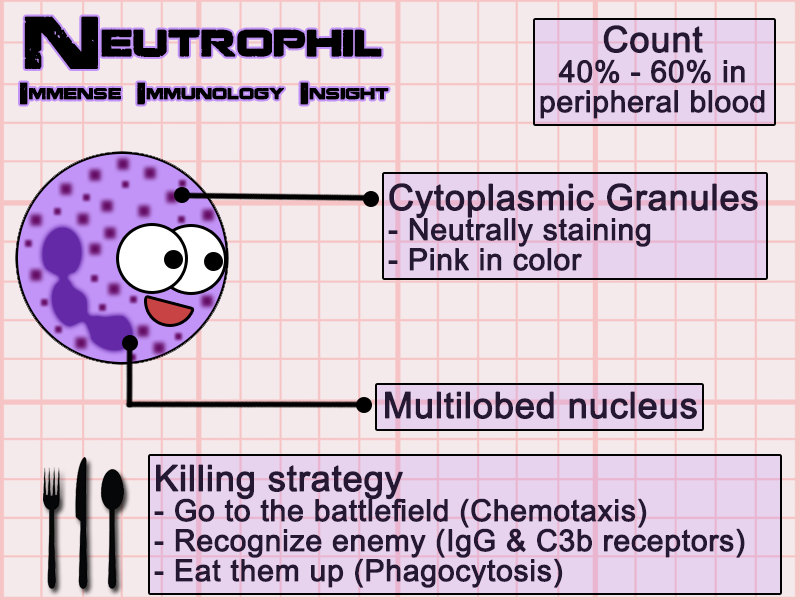 makes up 50-70% of circulating WBC
|