Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter- 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation - Part A
front 1 Which term describes the degree to which an element attracts electrons? | back 1 Electronegativity
|
front 2 Which terms describe two atoms when they form a bond in which electrons are completely transferred from one atom to the other? | back 2 Anion and cation.
|
front 3 Which of the following statements is true of the bonds in a water molecule? | back 3 Oxygen holds electrons more tightly than hydrogen does, and the net charge is zero
|
front 4 Which of the following statements is not true of most cellular redox reactions? | back 4 A hydrogen atom is transferred to the atom that loses an electron
|
front 5 What kind of bond is formed when lithium and fluorine combine to form lithium fluoride? | back 5 Ionic.
|
front 6 Gaseous hydrogen burns in the presence of oxygen to form water:
| back 6 Hydrogen, polar.
|
front 7 Which of the following best describes the main purpose of the combined processes of glycolysis and cellular respiration? | back 7 transforming the energy in glucose and related molecules in a chemical form that cells can use for work
|
front 8 In the combined processes of glycolysis and cellular respiration, what is consumed and what is produced? | back 8 Glucose is consumed, and carbon dioxide is produced.
|
front 9 Why does the oxidation of organic compounds by molecular oxygen to produce CO2 and water release free energy? | back 9 Electrons are being moved from atoms that have a lower affinity for electrons (such as C) to atoms with a higher affinity for electrons (such as O |
front 10 Which of the following statements describes the results of this reaction?
| back 10 C6H12O6 is oxidized and O2 is reduced. |
front 11 When a glucose molecule loses a hydrogen atom as the result of an oxidation-reduction reaction, the molecule becomes | back 11 oxidized. |
front 12 When a molecule of NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) gains a hydrogen atom (not a proton), the molecule becomes | back 12 reduced. |
front 13 Where does glycolysis take place in eukaryotic cells? | back 13 cytosol |
front 14 The ATP made during glycolysis is generated by | back 14 substrate-level phosphorylation |
front 15 The oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event? | back 15 accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain |
front 16 Why are carbohydrates and fats considered high energy foods? | back 16 They have a lot of electrons associated with hydrogen. |
front 17 Glycolysis
| back 17 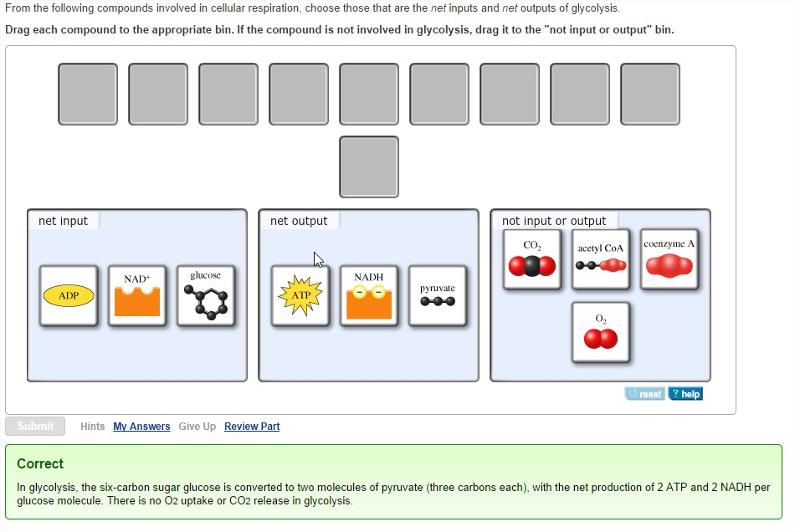 |
front 18 Acetyl CoA Formation
| back 18 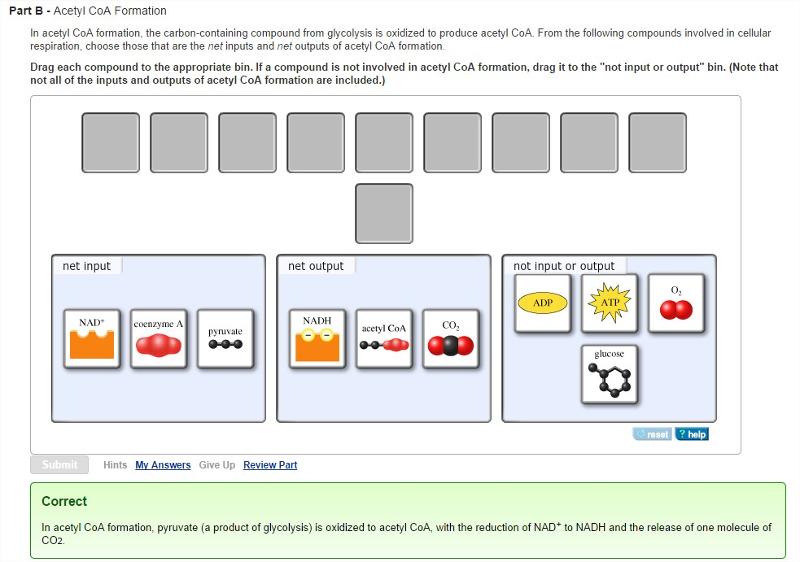 |
front 19 Oxidative Phosphorylation
| back 19 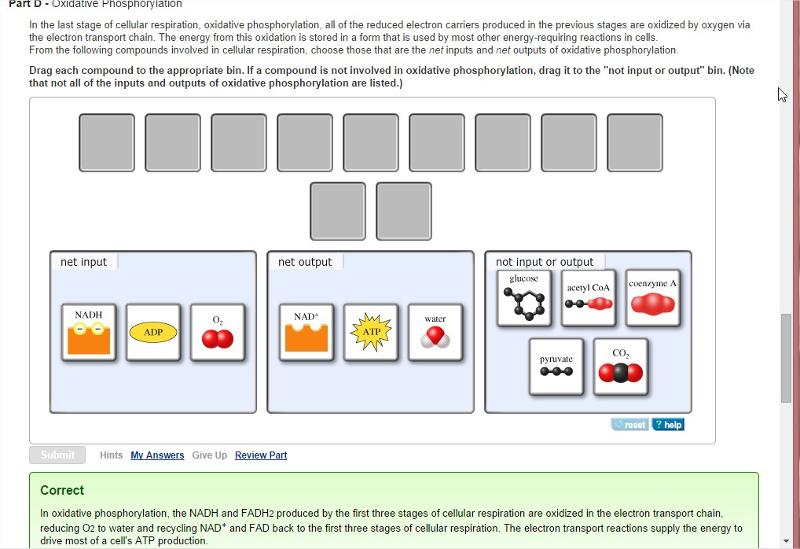 |
front 20 Cellular locations of the four stages of cellular respiration
| back 20 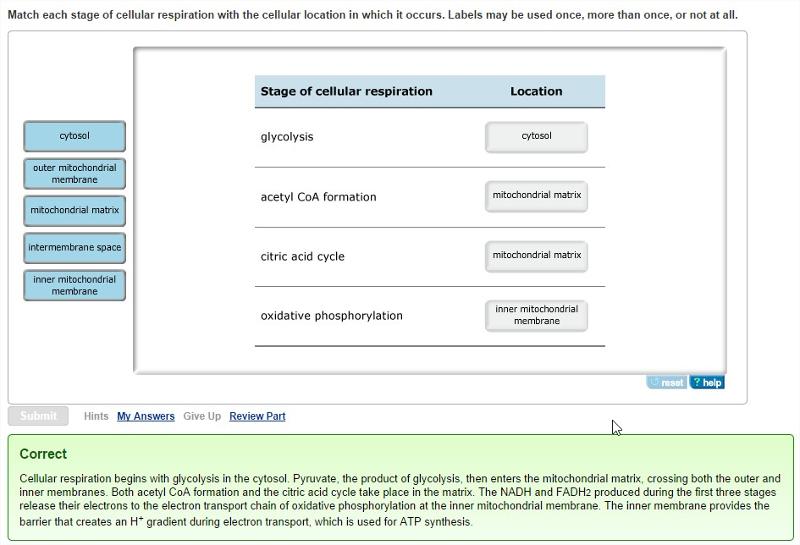 |
front 21 Citric Acid Cycle
| back 21 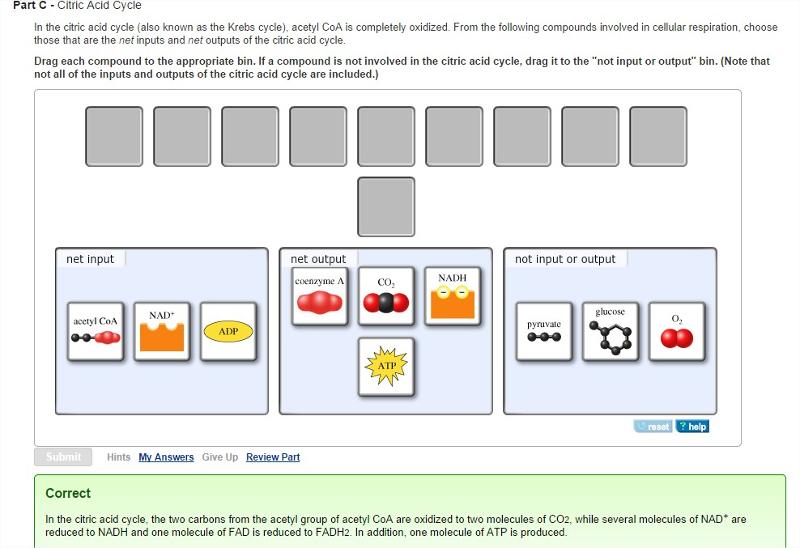 |
front 22 Redox (oxidation-reduction) reactions in glycolysis
| back 22 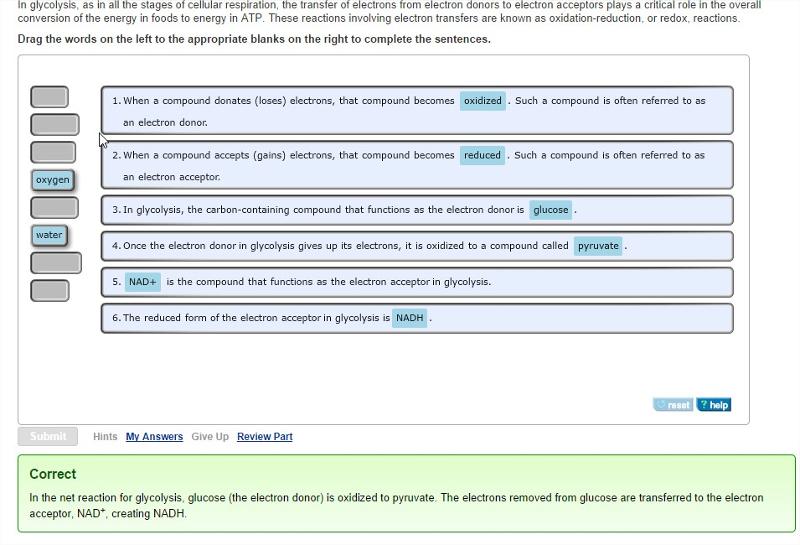 |
front 23 Energy from glycolysis
| back 23 pyruvate, ATP, and NADH
|
front 24 The ATP that is generated in glycolysis is produced by substrate-level phosphorylation, a very different mechanism than the one used to produce ATP during oxidative phosphorylation. Phosphorylation reactions involve the addition of a phosphate group to another molecule. | back 24 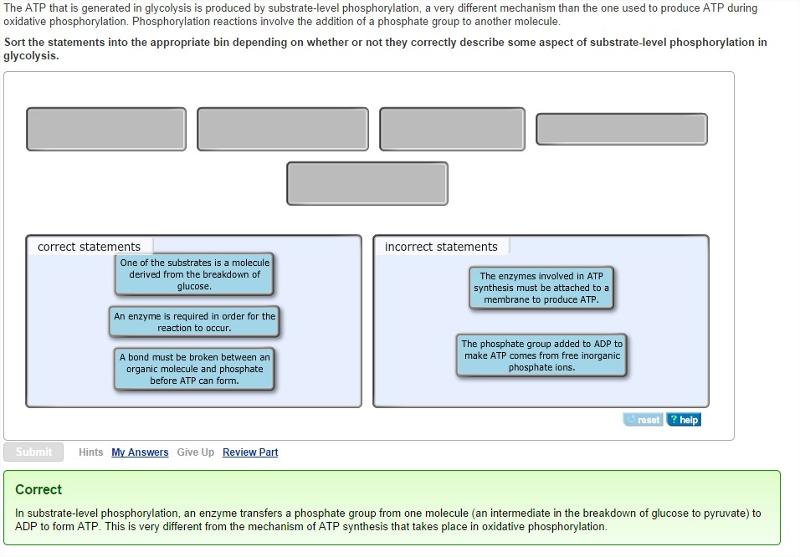 |
front 25 How many NADH are produced by glycolysis? | back 25 2
|
front 26 In glycolysis, ATP molecules are produced by _____. | back 26 substrate-level phosphorylation
|
front 27 Which of these is NOT a product of glycolysis? | back 27 FADH2
|
front 28 In glycolysis, what starts the process of glucose oxidation? | back 28 ATP
|
front 29 In glycolysis there is a net gain of _____ ATP | back 29 2
|
front 30 Glycolysis | back 30 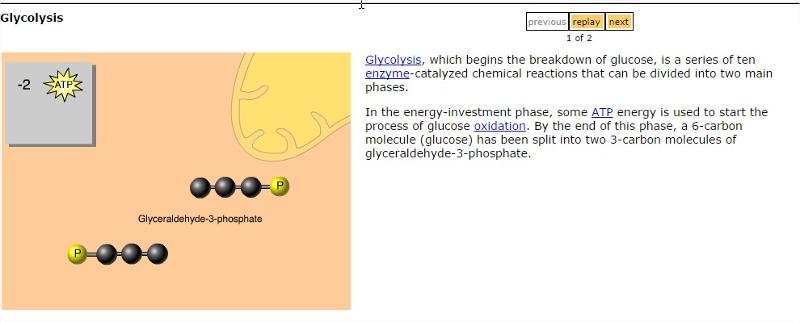 |
front 31 Which of the following describes the process of glycolysis? | back 31 It represents the first stage in the chemical oxidation of glucose by a cell.
|
front 32 Substrate-level phosphorylation accounts for approximately what percentage of the ATP formed by the reactions of glycolysis? | back 32 100% |
front 33 In addition to ATP, what are the end products of glycolysis? | back 33 NADH and pyruvate |
front 34 In glycolysis, for each molecule of glucose oxidized to pyruvate | back 34 two molecules of ATP are used and four molecules of ATP are produced. |
front 35 A molecule that is phosphorylated | back 35 has an increased chemical potential energy; it is primed to do cellular work. |
front 36 Which kind of metabolic poison would most directly interfere with glycolysis? | back 36 an agent that closely mimics the structure of glucose but is not metabolized |