| back 5 Anatomical term referring to the elbow (whole joint) |
| back 6 Anatomical term referring to the anterior (bending side) of the elbow |
| back 7 Anatomical term referring to the posterior (rounded) side of the elbow |
| back 8 Anatomical term referring to the wrist |
| back 9 Anatomical term referring to the hand |
| back 10 Anatomical term referring to the groin where the thigh attaches to the pelvis |
| back 11 Anatomical term referring to the posterior surface of the knee |
| back 12 Anatomical term referring to the anterior side of the leg (shaft) |
| back 13 Anatomical term referring to the posterior side of the leg (shaft) |
| back 14 Anatomical term referring to the lateral (fibula) side of the leg |
| back 15 Anatomical term referring to the ankle |
| back 16 Anatomical term referring to the heel |
| back 17 Anatomical term referring to the sole side of the foot |
| back 18 standing up straight, hands are out to the sides with the palms facing up and the thumbs facing out |
| back 19 Anatomical term referring to the ear |
front 20 ipsilateral/contralateral | back 20 ipsilateral- directional term referring to the same side of the body
contralateral- referring to body parts on opposite sides of the body |
front 21 midsagittal/parasagittal planes | back 21 midsagittal- divides the body into equal right and left halves through the midline
parasagittal- divides the body into unequal right and left sides |
| back 22 contains the cranial cavity (brain) and vertebral canal (spinal cord) |
| back 23 anterior side of the body and contains the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities |
| back 24 within the ventral body cavity
enclosed by the ribs, sternum, and vertebral column
contains the pericardial cavity (heart), 2 pleural cavities (lungs), and the mediastinum (heart, thymus gland, large blood vessels, esophogus, and trachea)
separated from the abdominopelvic region by the diaphragm |
| back 25 contains the abdominal cavity (stomach, liver, pancreas, small intestine, spleen, gallbladder, kidneys, appendix, and part of the large intestine) in the superior portion and the pelvic cavity (bladder, reproductive organs (except testes) and part of the large intestine) in the inferior portion
contains digestive and some reproductive organs
separated from the thoracic cavity by the diaphragm |
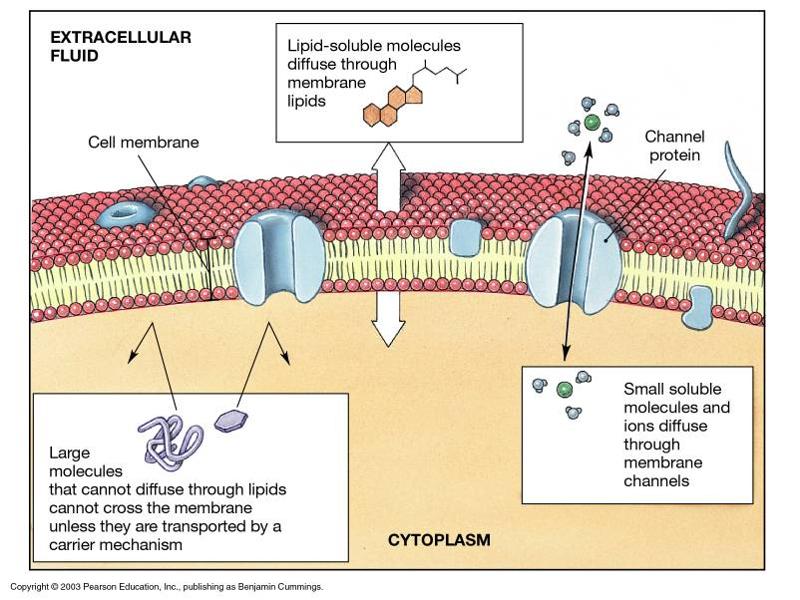
front 26 movement through the plasma membrane | back 26 Channel proteins: channels open to allow small (water soluble) things through with concentration gradients
Lipid soluble molecules (alcohol, oxygen) with concentration gradient goes right through the membrane
Large molecules that are water soluble and against concentration gradient needs carrier proteins (active transport proteins) |
front 27 Name the structure and components | back 27 typical cell (pretty active cell)
1= euchromatin: DNA being transcribed
2= nucleus (has a double membraned, nuclear envelope surrounding it)
3= nucleolus:where ribosomes and ribosomal RNA are made
4= nuclear pore: allow substances to pass in between the nucleus and cytoplasm
5= heterochromatin: DNA being repressed |
| back 28 o cell with a lot of rough ER are synthesizing proteins that need to be sequestered
keep the ribosomes separate so they don’t affect the cell (for example: digestive enzymes might eat away at the cell if they are exposed prematurely)
ribosomes are injected into rough ER as they are being made |
| back 29 packages many proteins into one container and holds them
Package proteins that were made in ribosomes and sends them off in secretory vessels for the rest of the cell/body |
| back 30 detoxifies drugs, makes fats (lipid synthesis), reduces alcohol and turns it into fat, so excessive drinking turns your whole liver into fat |
| back 31 Pancreas cells release digestive enzymes, needed for digestion
Groups amino acid chains together to make proteins
found stored in rough ER, packaged by the golgi apparatus |
| |
| back 33 membrane bound organelles that recycle old cell components
many lysosomal storage diseases are fatal because people cannot get rid of toxic waste so it builds up and kills the cells |
| back 34 A= Golgi
B= Rough ER
C=Smooth ER
D= Mitochondrion
E= Ribosomes |
front 35 name the phases of mitosis | back 35 interphase
prophase
metaphase
anaphase
telephase |
| back 36 on the surface of epithelial cells to increase surface area in places that need to absorb
• in gut and kidney (absorptive areas)
• little and stubby- hard to see on the surface (too packed together and all the same height) |
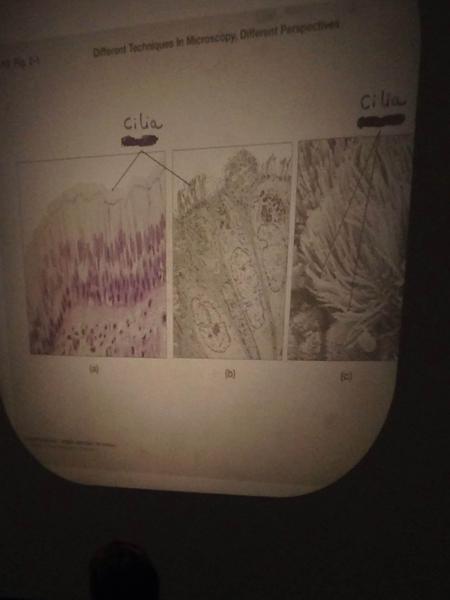
| back 37 have long molecular motors to beat and push things along
• move mucus along respiratory tract and out of the trachea and bronchi
• female reproductive tract to move the egg through the filopian tubes |
| back 38 Covers surfaces, lines cavities, forms glands.
Cells and tissue show polarity: top (apical surface- might have surface specializations like cilia or microvilli) differs from bottom (basal surface- rests on a basement membrane).
This tissue shows the most rapid turnover of all tissues, therefore most prone to cancer.
Epithelia are avascular (lack blood vessels). |
| back 39 tight junctions form a seal between cells- cells lining the stomach
• plasma membranes from opposing cells actually seal the cells together to prevent leakage
gap junctions are for communication where substances can diffuse through holes (bone cells)
desmosomes- mechanical function, helps cells stick together, kinda like Velcro (skin, heart- under a lot of mechanical stress) |
| back 40 simple squamous epithelium- single layer of cells resting on a basement membrane
• in lungs- need a really thin layer for gas exchange
• lining blood vessels- need to be smooth or blood clots will form
simple columnar epitelium
• good for absorption and secretion (microvilli and/or cilia)
• tall, column shaped, lined up with each other |
| |
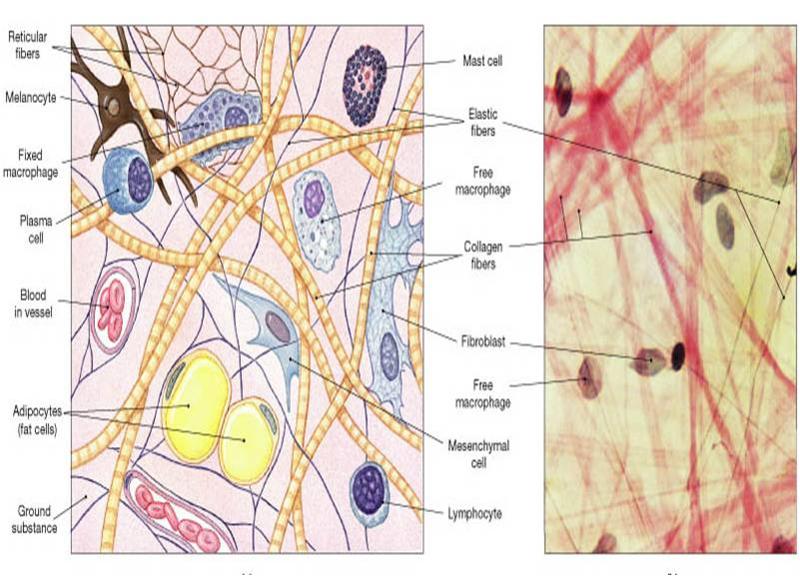
| back 42 cells (lymphocytes and fibroblasts) and fibers (collagen and elastic fibers) dispersed in an extracellular matrix
highly vascular
types: ordinary connective tissue (beneath basement membrane in all epithelium), tendons and ligaments, bone and cartilage, adipose tissue (stores energy in unlimited amounts), blood |
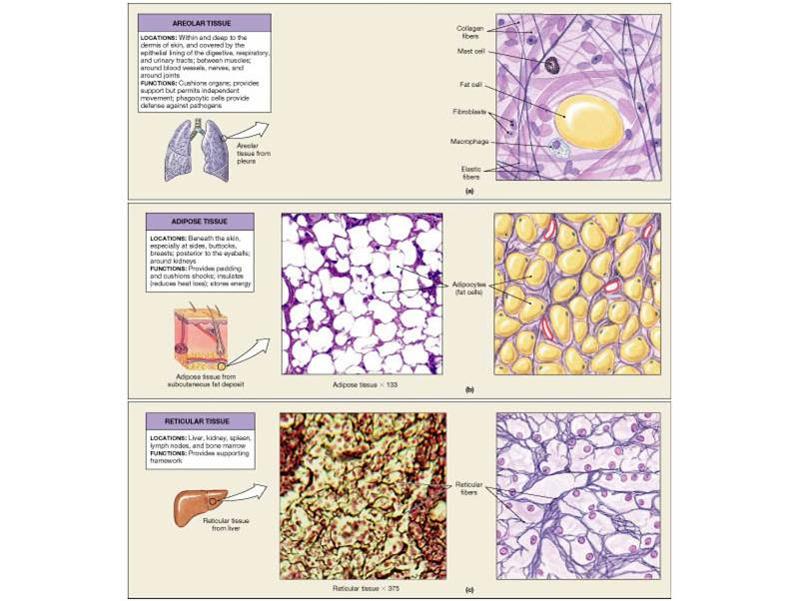
front 43 loose connective tissue types | back 43 areolar (ordinary)- beneath epithelium: binds epithelium to underlying tissues and allows nutrients to diffuse to epithelial cells
reticular- liver, spleen, lymph nodes: forms delicate support (framework, made brome more loosely bound collagen) for these soft organs
adipose- under the skin and surrounding organs: stores lipids for fuel and thermal insulation and cushions organs |
front 44 name the tissue type and structures indicated by the arrows | back 44 adipose tissue
arrows are nucleus of adipocyte |
front 45 name the types of tissues | back 45 a= Dense connective tissue
b= adipose tissue |
front 46 name the tissue in the brackets | |
front 47 label the numbers (kidney) | back 47 1= simple cuboidal epithelium
2= apical surface of a cell
3= lumen of kidney tubule
4= nucleus of a simple cuboidal cell |
front 48 label the numbers (small intestine) | back 48 1=microvilli on the apical side of the cell
2= nucleus of a cell
3= simple columnar epithelium
4= connective tissue |
front 49 label the numbers (esophagus) | back 49 1= nucleus of a squamous epithelial cell
2= stratified squamous epithelium
3= nucleus of a cell in the basal layer of the epithelium
4= connective tissue |
| back 50 1= nucleus of a transitional epithelial cell in the apical layer
2= nucleus of a transitional epithelial cell in the basal layer
3= transitional epithelium
4= connective tissue |
front 51 label the numbers (trachea) | back 51 1= nucleus of a ciliated columnar epithelial cell
2= cilia on the apical side of a columnar cell
3= pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
4= connective tissue |
front 52 label the numbers and name the tissue | back 52 areolar connective tissue
1= collagen fiber
2= elastic fiber
3= connective tissue cells (fibroblasts and lymphocytes) |
front 53 name the tissue and label the numbers | back 53 reticular connective tissue
1= reticular cell
2= reticular fiber |
front 54 name the tissue and label the numbers | back 54 dense regular connective tissue forming tendons
1= fibroblast
2= collagen fiber bundle |
front 55 name the tissue and label the numbers | back 55 dense irregular connective tissue skin
1= fibroblast
2= collagen fiber bundles running in different directions
3= parallel the collagen fiber bundles |
front 56 name the tissue and label the numbers | back 56 hyaline cartilage (trachea)
1= extracellular matrix
2= lacuna
3= nucleus of chondrocyte |
front 57 name the tissue and label the numbers | back 57 elastic cartilage (ear)
1= lacuna
2= nucleus of chondrocyte
3= elastic fibers |
| back 58 Hyaline- cells in an extracellular matrix, collagen with proteins that bind to water, ends of ribs, trachea, and long bones, because its smooth
Elastic- flexible,provides support, ear
fibrocartilage- intervertebral discs: cushions in between the vertebrae |
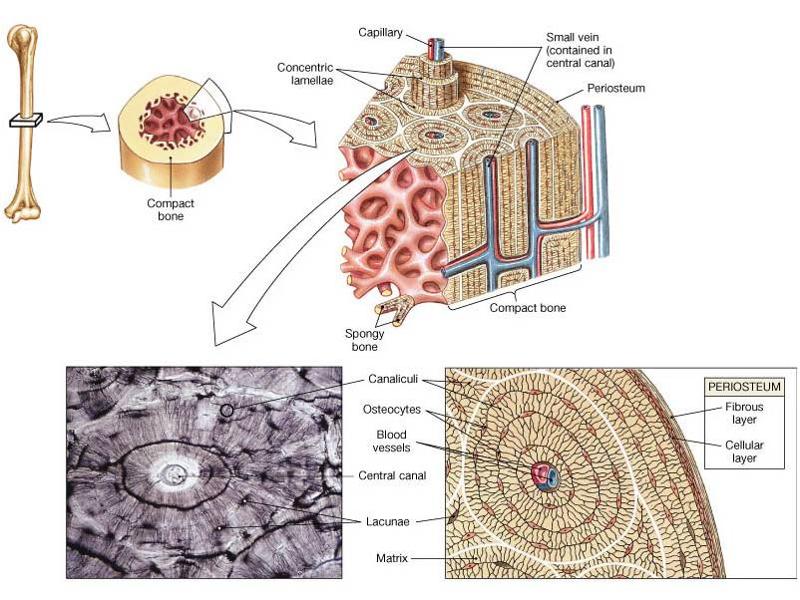
front 59 name the tissue and label the numbers | back 59 compact (cortical) bone
1= lamella
2= canaliculus
3= lacuna
4= central canal |
front 60 name the tissue and label the numbers | back 60 cardiac muscle tissue
1= width of cardiac muscle fiber
2= nucleus
3=branches of cardiac muscle fiber
4= intercalated discs
little lines are desmosomes |
front 61 name the tissue and label the numbers | back 61 skeletal muscle fibers
1= width of individual muscle fiber
2= nucleus
3= striation |
| back 62 Skeletal- for bones (sometimes skin), allows movement, voluntary control, striated
Cardiac- striated muscle found in the heart, cells are connected by gap junctions for communication (tissue goes into fibrillation if the cells do not communicate properly) and desmosomes (cells are under high mechanical stress), regulated by the CNS
Smooth- network of cells connected by gap junctions (allows a lot of communication to function smoothly), hollow organs, blood vessels |
front 63 label the tissue and the numbers and describe it | back 63 nervous tissue
1= processes
2= cell body of a mulitpolar neuron
3= nucleus |
front 64 name the structure and describe it | back 64 neuron
o very active (high euchromatin to heterochromatin ratio), polarized cells (receiving and transmitting ends) |
front 65 name the structure and describe it | back 65 nerve ganglion- collections of nerve cells |
front 66 name the tissue and label the numbers | back 66 skin
1= derma papillae
2= epidermis
3= papillary layer of the dermis (thin collagen)
4= reticular layer of the dermis (thick collagen)
5= hypodermis |
front 67 name the tissue and label the numbers
describe each layer | back 67 epidermis in thick skin
1= stratum corneum- waterproof, protective layer that is very thick (particularly in the soles of the feet and hands)
2= stratum lucidum- artifact layer
3= stratum granulosum- packages karatohyalin (from keratinocytes) into granules and chokes off the cell and kills it and the cell becomes part of the stratum corneum
4= stratum spinosum- spiny layer, held together by desmosomes, if there is a disease with desmosomes this layer forms blisters because skin can not hold together
5= stratum basale-A thin (single) layer of cells along the basement membrane which is where mitosis (cell division) occurs |
front 68 functions of the integumentary system | back 68 Physical protection- keeps moisture in, stops bacteria/other contaminants from entering
Thermoregulatory- keeps you warm, shunts blood from the surface to the internal organs when in the cold, sweats to cool
Need sun to contact skin and convert vitamin D to its active form
Elaborate sensory system to feel things
Strong immune system on skin |
front 69 name the tissue and label the numbers | back 69 epidermis
1= stratum cornueum
2= stratum granulosum
3= stratum spinosum
4= stratum basale |
front 70 name the tissue and label the numbers | back 70 thin skin with accessory structures
1= hair shaft
2= hair root
3= sebaceous gland (secretes oils that coat the hair in the follicle)
4= arrector pili muscle
5= hair follicle
6= hair bulb
7= eccrine sweat gland (reaches up to the skin's surface)
8= papilla of hair
9= apocrine sweat gland (secretion is deposited on the distal end of the hair root) |
front 71 name the tissue and label the numbers | back 71 thin skin and accessory structures
1=sebaceous gland
2= hair follicle
3= hair root
4= hair bulbs
5= papilla of hair |
| back 72 Keratinocytes- main cell type, make up most of the epidermis, keratin is responsible for the orange color in skin
Melanocytes- produce melanin which contributes to skin color (darkness of skin), have processes that reach below the basement membrane (where blood vessels and other structures are, melanoma skin cancer), everyone has the same number of melanocytes but skin color depends on the maturity of the melanocytes (more melanin steps in production= darker cells) and who much melanin is taken up by the keratinocytes, comes from neural crests
Langerhans cell- antigen presenting cell (belongs to the immune system), recognizes foreign bodies and reports back to the immune system, part of the immune function of the skin |
front 73 name and describe the structure circled | back 73 makes oil and empties into the hair follicles and lubricates hair
o only in thin skin |
front 74 name and describe the structure circled | back 74 Sweat gland is coiled and releases fluids and some waste products through a duct to the skin surface to cool the skin
occurs in all skin (not just thick or thin) |
| back 75 A=Asymmetry- one half unlike the other half
B=Border- irregular or poorly defined border
C= Varies from one shade to another. Not just brown or tan. Can be shades of red, white, or blue
D=Diameter- Unusually large diameter |
front 76 functions of bone as a tissue | back 76 reservoir for calcium that is needed for muscle contraction
production of blood cells in the bone marrow (blood cells need to be replaced every 120 days) |
front 77 functions of the skeleton | back 77 Supports body against pull of gravity
Attaches to skeletal muscles to permit movement
Protects soft body parts (like organs, brain)
Divides body into cavities or spaces |
front 78 label the parts of a long bone | back 78 1= Proximal Epiphysis
2= epiphyseal plate (growth plate, metaphysis)
3= Diaphysis
4= distal epiphysis
5= spongy (trabecular) bone
6= compact (cortical) bone
7= marrow cavity
8= articular surface |
| back 79 Osteoblasts (immature cell)- helps rebuild/remodel bones
Osteoclasts move along through bone and remove bone that needs remodeled
Osteoblasts and clasts are coupled to rebuild bone (healthy people have a good ratio of both cells, people in bed rest or in space end up with too many osteoclasts) |
front 80 label all of the features (some terms may be used twice) | back 80 1= spongy (trabecular) bone
2= trabeculae of spongy bone covered in endosteum
3= concentric lamellae
4= blood vessels
5= canaliculi
6= lacuna
7= osteocyte
8= periosteum
9= central canal
10= perforating canal
11= compact (cortical) bone
12= osteon (haversian systems)
13= compact bone
14= spongy bone
15= periosteum |
front 81 intramembranous bone development | back 81 flat bones in the skull
bone tissue develops directly from primitive connective tissue (so that is is stretchy enough to form around the brain as it grows, then turns into bone)
bones come from the neural crest (migration problems like fetal alcohol syndrome affect facial bone development) |
front 82 endochondral bone development | back 82 Most bones besides the skull, including long bones of appendicular skeleton
The growth of long bones occurs at the epiphyseal plate in between the cartilage and diaphysis where Cartilage cells divide and stack then form into bone
All cartilage is replaced by bone when growth ends, except the ends of long bones (articular cartilage)
cartilage has no blood supply, blood vessels move into the cartilage and vascularize it and bring in osteoblasts to turn the cartilage to bone |
front 83 label all the features (lateral view) | back 83 1=parietal bone
2= coronal suture
3= squamous suture
4= temporal bone (squamous part is very thin and easy to damage)
5= lamboid suture
6= occipital bone
7= frontal bone
8= sphenoid bone (very thin and easy to damage)
9= ethmoid bone
10= lacrimal bone
11= nasal bone
12= zygomatic bone
13= maxilla
14= mandible |
front 84 label the features of the skull (lateral view) | back 84 1=coronal suture
2= parietal bone
3= squamous suture
4= temporal bone (squamous part is very thin and easy to damage, petrous portion is thick to protect your inner ear)
5= lamboid suture
6= occipital bone
7= frontal bone
8= sphenoid bone (very thin and easy to damage)
9= ethmoid bone
10= lacrimal bone
11= nasal bone
12= zygomatic bone
13= maxilla
14= mandible
15= hyoid bone (elevates and compresses the larynx, but does not articulate with other bones and plays a role in speaking, swallowing) |
front 85 label the features of the skull (superior view) | back 85 1= frontal bone
2= coronal suture
3= parietal bone
4= sagittal suture
5= lamboid suture
6= occipital bone |
front 86 label the features of the skull (inferior view) | back 86 1= maxilla
2= vomer
3= sphenoid bone
4= occipital bone
5= zygomatic bone
6= palatine bone
7= parietal bone |
front 87 label the features of the skull (superior view of the floor of the cranium) | back 87 1= parietal bone
2= occipital bone
3= frontal bone
4= ethmoid bone (tumor causes loss of sense of smell, part of the nasal septum inside the nose)
5= sphenoid bone (where the pituitary gland sits)
6= temporal bone
7= lamboid suture |
front 88 label the features of the skull (anterior view) | back 88 1= parietal bone
2= sphenoid bone
3= ethmoid bone (tumor causes loss of sense of smell, part of the nasal septum inside the nose)
4= lacrimal bone
5= inferior nasal concha
6= vomer
7= frontal bone
8= temporal bone
9= nasal bone
10= zygomatic bone
11= maxilla
12= mandible |
front 89 label all the surface markings | back 89 1= supraorbital foramen
2= orbit of the eye
3= inferior orbital fissure
4= perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone (helps make up the nasal septum)
5= mental foramen
6= supraorbital margin
7= superior orbital fissure
8= middle nasal concha |
front 90 label all the surface markings | back 90 1= external auditory meatus
2= mastoid process
3= lacrimal process
4= zygomatic process of the temporal bone
5= condylar process
6= coronoid process
7= ramus of the mandible
8- body of the mandible |
front 91 label all the surface markings | back 91 1= palatine process of the maxilla
2= palatine process
3= hard palate
4= ptergoid process
5= foramen ovale
6= jugular foramen (for jugular vein)
7= occipital condyle
8= hypoglossal foramen (should be underneath the occipital condyle, above the jugular foramen)
9= mandibular fossa
10= foramen lacerum
11= carotid foramen (carotid artery)
12= stylomastoid process
13= mastoid process (has mastoid air cells to make the skull lighter. A middle ear infection can spread to those air cells and cause meningitis)
14= foramen magnum (for the spinal cord to innervate the brain) |
front 92 label all the surface markings | back 92 1= crista galli
2= olfactory foramina
3= cribriform plate
4= sella tursica (where the pituitary gland sits)
5= foramen ovale
6= internal auditory meatus (tumor causes hearing damage)
7= foramen magnum (for the spinal cord to innervate the brain)
8= lesser wing of the sphenoid
9= optic foramen (where the optic nerve passes through, damage causes vision loss)
10= greater wing of the sphenoid
11= foramen rotundum
12= foramen lacrum
13= jugular foramen |
front 93 label and describe the paranasal sinuses and define paranasal sinuses | back 93 paranasal sinus- air filled spaces that are lined wit epithelium and secrete fluid
1= frontal sinus (drains through the nose)
2= ethmoid sinus (includes the superior and middle conchi)
3= sphenoid sinus (surgeons go through the sphenoid sinus to reach the pituitary to remove tumors)
4= maxillary sinus (largest sinus, upper teeth are in the maxilla and dental infections can spread to the brain via the maxillary sinus then the orbit) |
| back 94 1= perpendicular plate of the ethmoid
2= septal cartilage
3= vomer |
front 95 label the components and give the direction of curvature for 6, 7, 8, and 9 | back 95 1= intervertebral discs
2= intervertebral foramen
6= cervical-7, anterior curvature
7= thoracic- 12, articulate with ribs, posterior curvature
8= lumbar- 5, anterior curvature
9- saccral- 5 fused vertebra, posterior curvature (below the sacrum is the coccyx which has 2-4 vertebrae) |
front 96 label the parts of the typical vertebra | back 96 1= facet of superior articular process
2= vertebral foramen
3= facet for head of rib
4= spinal cord
5= spinous process
6= transverse process
7= vertebral arch: lamina (saw through the lamina to perform a spinal fusion)
8= pedicle
9= body |
front 97 name and label the vertebra | back 97 atlas (1st cervical vertebra)- allows up/down “yes” motion
1= superior articular facet
2= transverse foramen
3= transverse process |
front 98 label and name the vertebra | back 98 axis (2nd cervical vertebra)-axis- allows side to side “no” motion- body has a ‘dens’
4= lamina
5= Dens
6= spinous process |
front 99 label and name the vertebra | back 99 typical cervical vertebra
7= body
8= transverse process
9= bifurcated spinous process
10= pedicle |
front 100 name and label the vertebra | back 100 thoracic vertebra
1= transverse process
2= facet for the articular part of the tubercle of ribs
3= superior articular facet
4= superior demifacet
5= facet for the articular part of a tubercle of rib
6= slanted spinous process
7= superior demifacet
8= inferior demifacet |
front 101 name and label the vertebra | back 101 lumbar vertebra
1= lamina
2= superior articular process
3= transverse process
4= vertebral foramen
5= body
6= hatchet-shaped spinous process
7= inferior articular facet |
| back 102 1= intervertebral foramen
2= nucleus pulposus
3= annulus fibrosus
4= intervertebral disc (made of fibrocartilage)
5= herniation
6= nucleus pulposus
7= annulus fibrosus |
front 103 name the structure and label each feature | back 103 sacrum and coccyx
1= sacral ala
2= base of sacrum
3= sacral promontory
4= sacral foramen
5= coccyx
6= sacral canal
7= superior articular facet
8= auricular surface
9= sacral hiatus |
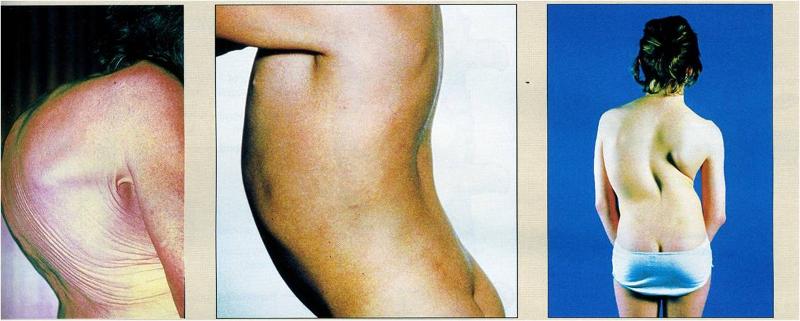
front 104 label and describe each disorder (left to right) | back 104 (left to right)
Kyphosis- abnormal thoracic curvature
Lordosis- found in obese and pregnant people, over pronunciation of the lumbar curvature
Scoliosis- correctable in children, sideways curvature of the spine, harder to correct when growth ends, affects the placement of the internal organs |
| back 105 1= suprasternal notch (jugular notch)
2= manubrium
3= body of sternum
4= xiphoid process
5= sternum
6= costal cartilage
7= sternal angle
8= true ribs
9= floating ribs
10= false ribs |
front 106 name and describe the bone and features | back 106 clavicle: keeps the upper extremity away from the trunk so the extremity can move
most commonly broken bone in the body
articulates with the scapula
1= acromial end
2= sternal end |
front 107 name the structure and label the components | back 107 scapula
3= acromion
4= coracoid process
5= glenoid cavity
6= lateral (axillary) border
7= subscapular fossa
8= medial (vertebral border)
9= supraspinous fossa
10= infraspinous fossa
11= acromion
12= spine
13= glenoid cavity |
front 108 shoulder: description and injuries | back 108 Labrum (cartilage) helps deepen the glenoid cavity (lateral cavity) which is fairly shallow to allow a wide range of mobility, and to increase the stability
Rotator cuff muscles all attach from the scapula to the humerus and allows for rotation and circumduction
separation: between the clavicle and either the acromion process of the scapula and/or the coracoid process of the scapula
dislocation: between the humerus and the scapula
when the humerus goes out of the glenoid cavity (happens inferiorly most often) |
front 109 name the bone and label components | back 109 humerus
1=greater tubercle
2= intertubercular groove
3= lesser tubercle
4= lateral epicondyle
5= capitulum
6= head
7= anatomical neck
8= deltoid tuberosity
9= coronoid fossa
10= medial epicondyle
11= trochlea
12= olecranon fossa
13= medial epicondyle
14= lateral epicondyle |
front 110 name the bones and label the components | back 110 radius (lateral- thumb side) and ulna (medial- pinky side)
1= head of the radius
2= styloid process of the radius
3= olecranon process
4= trochlear notch
5= coronoid process
6= radial notch (on ulna)
7= styloid process of ulna
styloid processes help to form the wrist joint |
| back 111 radial nerve runs along the humerus- humerus break leads to wrist drop (extensor damage, everything it flexed)
ulnar nerve runs along the medial side of the humerus- bumping the medial epicondyle of the humerus causes the "funny bone" tingling on the medial side of the hand |
| back 112 1= carpals
2= metacarpals
3= proximal phalanx V
4= middle phalanx V
5= distal phalanx V
6= capitate (most common fracture wrist bone during a fall) |
front 113 name the bone and label the components | back 113 os coxa- 3 fused bones (ilium, ischium, pubis), help support body weight and are part of the pelvis
1= ilium
2= posterior superior iliac spine
3= posterior inferior iliac spine
4= greater sciatic notch
5= ischium
6= ischium spine
7= lesser sciatic notch
8= obturator foramen
9= ischial tuberosity
10= iliac crest
11= anterior superior iliac spine
12= anterior inferior iliac spine
13= acetabulum
14= pubis |
front 114 name the structure and label the components | back 114 female (left) and male (right) pelvis- Easiest way to tell the difference between male and female pelvis is by the angle between the pubic bones (>100 degrees in females, <90 in males, models may be more exaggerated)
1= iliac crest
2= ilium
3= ischial spine
4= pelvic brim
5= pubic symphysis
6= false pelvis (holds intestines, bordered by the pelvic brim)
7= true pelvis (holds reproductive organs and bladder)
8= pubis
9= ischial spine
10= fake pelvis
11= sacroliliac joint
12= sacrum
13= coccyx
14= true pelvis (holds some reproductive organs, not the testes or penis)
15= pubis |
front 115 name and describe and label the bone | back 115 femur- femoral neck is usually what fractures in falls- tends to thin out with osteoporosis
o greater and lesser trochanters are for muscle attachment
1= head of femur
2= greater trochanter
3= neck
4= lesser trochanter
5= medial epicondyle
6= medial condyle
7= linea aspera
8= lateral epicondyle
9= lateral condyle |
front 116 name the bones and label the components | back 116 tibia (medial) and fibula (lateral)
1= lateral condyle
2= head of fibula
3= fibula
4= lateral malleolus
5= medial condyle
6= tibial tuberosity
7= anterior border (crest)
8= medial malleolus
top flat part of tibia is the tibial plateau
common fibular nerve goes along the back of the keed and causes "foot drop" when damaged. Most commonly damaged nerve |
| back 117 1= calcaneus
2= talus
3= proximal phalanx II
4= middle phalanx II
5= distal phalanx II
6= tarsals
7= metatarsals
8= phalanges |
| back 118 9= calcaneus
10= tibia
11= fibula
12= talus
13= tarsals
14= metatarsals
15= phalanges |
| back 119 1= articular bone
2= synovial fluid
3= synovial cavity
4= articular cartilage
5= fibrous capsule
6= synovial membrane
7= articular capsule |
| back 120 knee joint- hinge joint, small amount of rotation
1= articular cartilage of the femur
2= lateral (fibular) collateral ligament (gap between ligament and joint)
3= lateral meniscus
4= posterior cruciate ligament
5= anterior cruciate ligament
6= medial meniscus
7= medial collateral ligament (no gap between ligament and joint)
8= patellar ligament
9= fibrous capsule
10= articular cartilage
11= synovial fluid
12= bursae
13= infrapatellar fat pad
14= patellar ligament |
| back 121 hinge joint
Note that “tennis elbow” is due to trauma to the extensor tendon that attaches to the lateral epicondyle of the
humerus |
| back 122 “Unhappy triad”: Damage to medial meniscus, medial collateral ligament and anterior cruciate ligament
Anterior drawer syndrome: Damage to ACL allows tibia to slide forward.
Posterior drawer syndrome: Damage to PCL allows tibia to slide backward. |
| back 123 o Most commonly damaged joint
o Inversion injury (rolling your ankle) is most common- stretch the lateral ligaments (between the fibula and the talus (talofibular ligaments, or between the fibula and the calcaneus)
If asked about a inversion injury, make sure the fibular is included (lateral side of your foot)
o Eversion injuries are rare |