Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Shock and Sepsis Chapter 14
front 1 Which abnormal laboratory finding would be indicative of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) associated with septic shock? Increased platelet count Decreased D-dimer levels Short prothrombin time Decreased amount of fibrinogen | back 1 Decreased amount of fibrinogen |
front 2 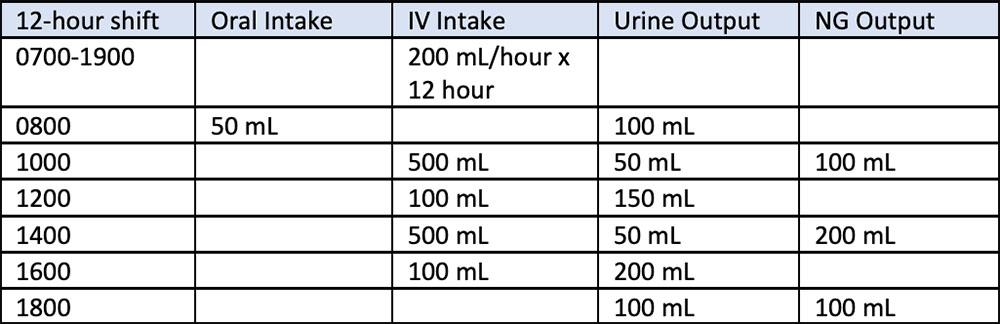 The nurse is calculating the shift intake for an unstable patient who is in septic shock. What is the final intake total? Enter the numeral only. | back 2 3650 |
front 3 While caring for a patient with burns and excessive loss of fluids, the nurse is concerned that the patient is in the compensatory stage of shock. Which assessment finding would cause the nurse to think this? Select all that apply. Anuria Cool, pale skin Lethargy Weak pulses Hypotension | back 3 Cool, pale skin Weak pulses |
front 4 Which statement would accurately describe the role of aldosterone during shock states? Aldosterone is released when blood pressure is too high. Aldosterone causes an increased excretion of sodium. Aldosterone results in water retention to increase blood pressure. Aldosterone causes glucose to be released by the body for energy. | back 4 Aldosterone results in water retention to increase blood pressure. |
front 5 The nurse is caring for a patient in the emergency department who has been admitted for septic shock as a result of a urinary tract infection. The patient weighs 187 pounds. How many milliliters per hour of lactated Ringer’s would the nurse administer over the next 3 hours? Record as a whole number. | back 5 850 |
front 6 Which physiologic change would result in increased cardiac output? Decreased contractility Increased afterload Decreased heart rate Increased preload | back 6 Increased preload |
front 7 The nurse identifies that a patient in cardiogenic shock has poor cardiac contractility. What medication should the nurse request from the provider? Dobutamine Nitroglycerin Phenylephrine Vasopressin | back 7 Dobutamine |
front 8 The trauma nurse is preparing to care for a patient who was involved in a motor vehicle accident and has massive blood loss. Which item should the nurse have prepared in the room before the patient arrives? Select all that apply. IV start kits with 20-gauge needles Bags of 0.9% NaCl Central venous catheter insertion kit High-flow oxygen delivery devices Intubation equipment | back 8 Bags of 0.9% NaCl Central venous catheter insertion kit High-flow oxygen delivery devices Intubation equipment |
front 9 The nurse observes that a patient is in the late stage of septic shock. Which assessment supports the nurse’s conclusion? Temperature of 101.2ᵒF (38.4ᵒC) Lethargy and coma Bounding pulses Warm, flushed skin | back 9 Lethargy and coma |
front 10 The nurse is assessing a patient at risk for shock. Vital signs include: Temperature 97.8ᵒF (36.5ᵒC), HR 87 beats per minute, respirations 16 breaths per minute, blood pressure 110/75, oxygen saturation 95%. Which stage of shock do these vital signs reflect? Initial stage Refractory stage Progressive stage Compensatory stage | back 10 Initial stage |
front 11 When assessing the cardiovascular system of a patient experiencing hypovolemic shock, which assessment finding would the nurse anticipate? Hypertension Bradycardia Wide pulse pressure Weak, thready pulses | back 11 Weak, thready pulses |
front 12 The nurse is caring for a postoperative patient after a ruptured spleen was removed. Which assessment change is most concerning? Hypertension A bulb drain in the lower abdomen with 50 mL serous fluid Jugular venous distention with the head of the bed at a 45-degree angle A central venous pressure (CVP) of 1 cm H2O | back 12 A central venous pressure (CVP) of 1 cm H2O |
front 13 The nurse is caring for an older adult patient admitted a week ago with pneumonia and a urinary tract infection. Blood cultures were positive upon admission, and the patient has been unstable since admission. The nurse notes that the serum creatinine and liver enzymes are increasing. Which conclusion can be made? The infection is worsening and has spread to other organs. The patient’s condition has stabilized. The patient is developing complications from the sepsis. Treatments have been effective. | back 13 The patient is developing complications from the sepsis. |
front 14 The nurse is talking to a critical patient’s family about hypovolemic shock. Which statement made by the significant other indicates an understanding of the teaching? Select all that apply. “Hypovolemic shock can occur from severe blood loss or fluids.” “Vomiting is the most common cause of hypovolemic shock.” “If dehydration is treated quickly, shock can be prevented.” “If he had taken antibiotics as prescribed, shock would not have occurred.” “I should have taken him to the hospital when he first became confused.” | back 14 “Hypovolemic shock can occur from severe blood loss or fluids.” “If dehydration is treated quickly, shock can be prevented.” “I should have taken him to the hospital when he first became confused.” |
front 15 Which hemodynamic alteration would the nurse expect when caring for a patient diagnosed with cardiogenic shock resulting from myocardial infarction? Increased central venous pressure Increased cardiac output Bradycardia and hypotension Decreased systemic vascular resistance | back 15 Increased central venous pressure |
front 16 When caring for a patient diagnosed with severe cardiogenic shock whose family has decided to withdraw life support, which nursing intervention would be appropriate? Administer pain medications on a set schedule. Continue obtaining blood samples in case the family changes their mind. Titrate vasopressor medications to maintain blood pressure within set parameters. Educate the family members about the dying process. | back 16 Educate the family members about the dying process. |
front 17 The nurse is admitting a patient with severe diarrhea related to Clostridium difficile colitis. Which type of shock is the patient at the greatest risk for? Obstructive shock Distributive shock Cardiogenic shock Hypovolemic shock | back 17 Hypovolemic shock |
front 18 While treating a patient, the nurse finds that the patient has extensive shunting of blood away from nonessential organs. The patient shows symptoms of lethargy and has severe metabolic acidosis. Which stage of shock is the patient experiencing? Progressive Compensatory Initial Refractory | back 18 Progressive |
front 19 The healthcare provider is administering spinal anesthesia to a patient before surgery. Which assessment change is most concerning? Heart rate of 52 beats per minute Blood pressure of 135/78 mm Hg SvO2 of 65% Central venous pressure (CVP) of 8 cm H2O | back 19 Heart rate of 52 beats per minute |
front 20 Which physical assessment finding will the nurse report during hand-off when the patient is in the compensatory stage of shock? Bradypnea Oliguria Hypertension Decreased cardiac output | back 20 Oliguria |
front 21 Which abnormal laboratory finding would help the nurse confirm a suspected diagnosis of septic shock? Lactate 1.8 mg/dL Serum pH 7.51 PaCO2 40 mm Hg Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 18 mg/dL | back 21 Serum pH 7.51 |
front 22 The nurse is caring for a patient in cardiogenic shock after a cardiac arrest. The patient is placed on an intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP). The chest x-ray shows that the tip of the catheter is just below the aortic arch, about 2 cm from the left subclavian artery. Which action should the nurse take? Have the chest x-ray repeated for better visualization. Confirm that the catheter is secured in that location. Call the provider to adjust the catheter placement. Confirm the waveform demonstrates accurate placement. | back 22 Confirm that the catheter is secured in that location. |
front 23 The nurse is caring for a patient receiving a continuous infusion of dobutamine for the treatment of cardiogenic shock. Which assessment is the priority for the nurse to perform? Potassium levels Respiratory status Chest pain level Urine output | back 23 Potassium levels |
front 24 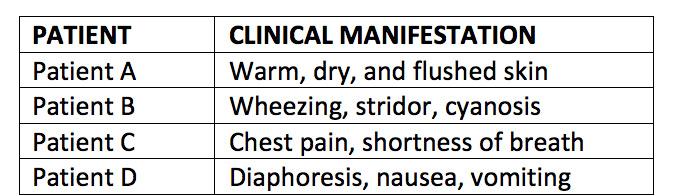 The nurse received a hand-off report on each of these four patients. Which patient is demonstrating signs of anaphylactic shock? Patient A Patient B Patient C Patient D | back 24 Patient B |
front 25 The nurse is treating a patient who received burns over 40% of his lower body in a flash fire incident 2 hours ago. Which order is the highest priority in the first 30 minutes? Select all that apply. Obtain blood cultures Administer vasopressors Initiate broad-spectrum antibiotics Measure central venous pressure (CVP) Measure lactate levels | back 25 Obtain blood cultures Initiate broad-spectrum antibiotics Measure lactate levels |
front 26 Arrange the order of progression of septic shock.
| back 26 1.Infection 2.Systemic inflammatory response 3.Sepsis 4.Early septic shock 5.Late septic shock 6.Multiorgan dysfunction syndrome |
front 27 The nurse is teaching a student nurse about the different kinds of shock and asks the student to list a cause of obstructive shock. Which example by the student nurse would be correct? Anaphylaxis Gastrointestinal bleeding Neurogenic shock Pulmonary embolism | back 27 Pulmonary embolism |
front 28 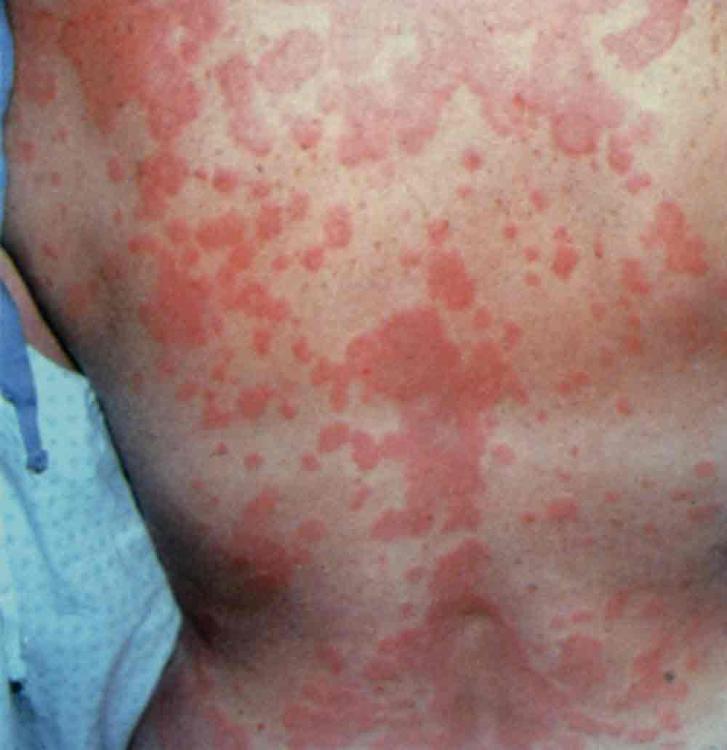 The nurse administers the first dose of IV ampicillin. Ten minutes later, the patient calls the nurse and says, “I feel funny.” The nurse observes the rash shown. Which action should the nurse take next? Select all that apply. Obtain a full set of vital signs. Stop the antibiotic infusion. Notify the provider. Place the patient on oxygen at 4 L/min per nasal cannula. Auscultate the lungs | back 28 Obtain a full set of vital signs. Stop the antibiotic infusion. Notify the provider. Auscultate the lungs |
front 29 Obtain a full set of vital signs.Stop the antibiotic infusion.Notify the provider.Place the patient on oxygen at 4 L/min per nasal cannula.Auscultate the lungs Dopamine Epinephrine Norepinephrine Nitroglycerin Vasopressin | back 29 Dopamine Epinephrine Norepinephrine Vasopressin |
front 30 A patient recently had mediastinal chest tubes removed after surgery and is experiencing obstructive shock from cardiac tamponade. Which assessment change would the nurse observe? Weak peripheral pulses Increased urine output Increased bowel sounds Valvular click | back 30 Weak peripheral pulses |
front 31 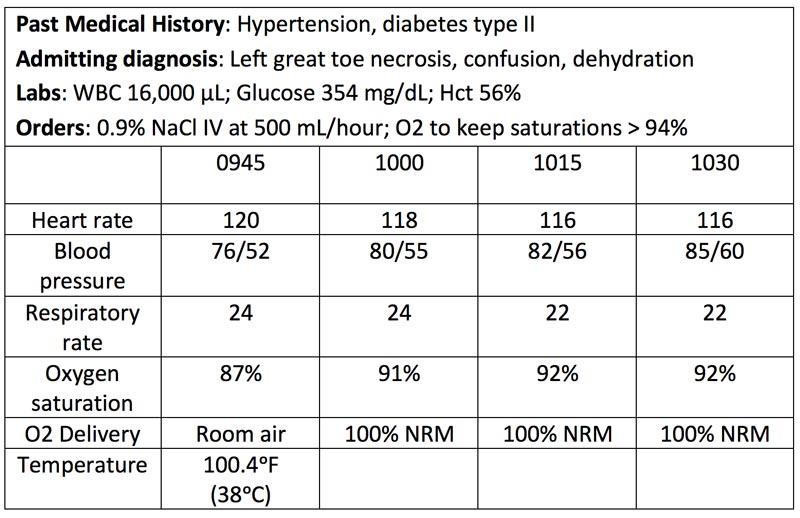 The nurse in the emergency department is caring for a newly admitted patient. Analyze the information and determine which statement is correct. The patient’s condition is improving from the medical interventions provided. The patient is in the compensatory stage of shock. Additional intervention with fluids and medications is not needed. Wound culture and IV antibiotics are the priority medical interventions. | back 31 The patient’s condition is improving from the medical interventions provided. |
front 32 Which nursing intervention would be appropriate for a patient experiencing cardiogenic shock and with a pulmonary artery catheter? Keep the inflation port locked at all times. Maintain clean technique when handling the catheter. When obtaining a blood sample, withdraw slowly through the distal port. Take all readings at the end of respiratory inspiration. | back 32 When obtaining a blood sample, withdraw slowly through the distal port. |