Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Unit 5 - Transformation
front 1 rx-axis | back 1 (x, - y) x is lazy & doesn't change |
front 2 ry-axis | back 2 (-x, y) y is lazy & doesn't change |
front 3 ry=x | back 3 (y,x) switch order |
front 4 ry = - x | back 4 (-y, -x) switch & negate |
front 5 RO,90 | back 5 (- y, x) |
front 6 RO, 180 | back 6 (-x, -y) |
front 7 RO, 270 | back 7 (y, -x) |
front 8 Ta,b | back 8 (x+a, y+b) |
front 9 rorigin | back 9 (-x,-y) |
front 10 Golden Rule for Rigid Motion Explanation as to why 2 triangles are congurent | back 10 A series of rigid motions (you list the specific ones you did in the problem) MAPS shape 1 onto shape 2. Rigid motions preserve segment length and angle measure, therefore the image is congruent to the pre-image. |
front 11 Line reflection | back 11 is the Perpendicular Bisector of the line segment connecting each pre-image point to its image. |
front 12 Orientation | back 12 The arrangement (or how you name the shape) of the points before and after a transformation. If it is preserved, the order and direction will be the same in the pre-image and the image. |
front 13 Orientation NOT is preserved for what type of transformation? | back 13 a line reflection |
front 14 what does the line x = # look like? | back 14 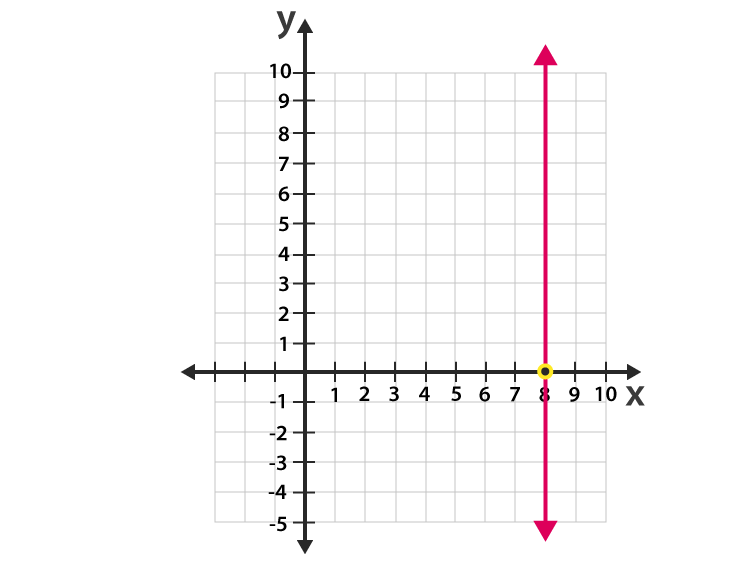 a Vertical line |
front 15 what does the line y = # look like? | back 15 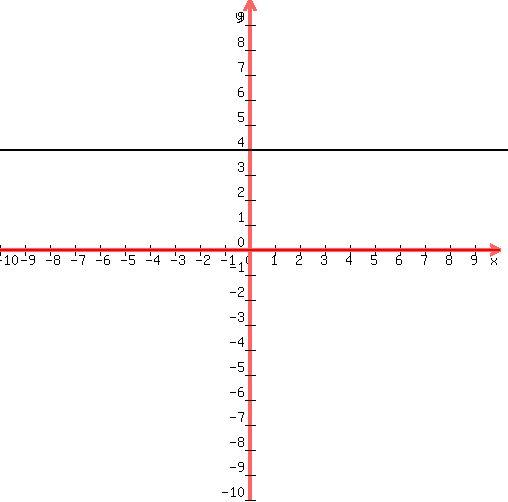 a Horizontal line |
front 16 Rotation notation must have three things: CDD | back 16 C: Center of Roation D: Direction of Rotation ( + = Counter clockwise (CCW) & - = clockwise (CW)) D: Degree of Rotation EX: RO,-90 |
front 17  | back 17 Theta = angle measurement symbol |
front 18 Regular Polygons | back 18 A shape with ALL SIDES CONGRUENT & ALL ANGLES CONGRUENT |
front 19 Regular Pentagon | back 19 5 sides |
front 20 Regular HeXagon | back 20 siX sides |
front 21 Regular Heptagon | back 21 7 sides |
front 22 Regular Octogon | back 22 8 sides |
front 23 Regular Nonagon | back 23 9 sides |
front 24 Regular Decagon | back 24 10 sides |
front 25 Regular Dodecagon | back 25 12 sides |
front 26 Point Symmetry | back 26 If you turn a shape upside down (or RO, 180) and it looks the same, then it has point symmetry |
front 27 Roational Symmetry | back 27 The number of degrees less than 360 it takes to map a shape onto itself. If your shape is a regular polygon then the formula to find the rotational symmetry is: 360/ n (where n is the number of sides) |
front 28 Line Symmetery | back 28 the "Fold Line" that divides a shape into 2 identical halves |
front 29 Composition Notation | back 29 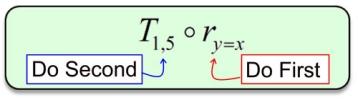 **Work Backwards** |