Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
infectious disease manifesting in the cardiovascular and lymphatic systems
front 1 COVID-19 disease table | back 1 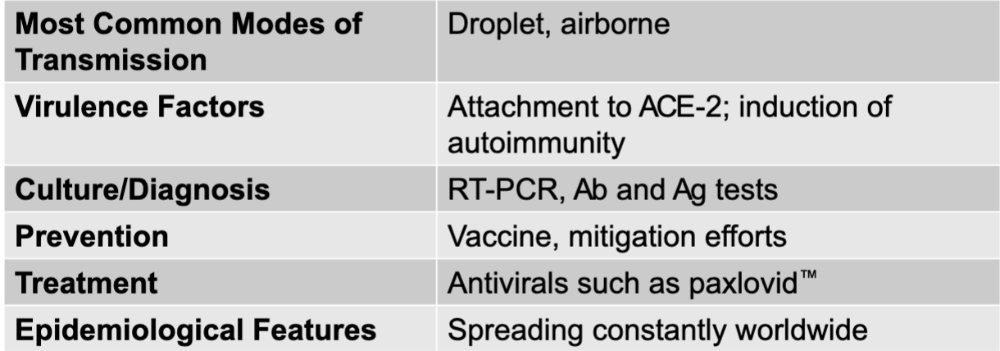 |
front 2 SARS-CoV-2 | back 2 COVID-19 causative agent |
front 3 droplet, airborne | back 3 COVD-19 mode of transmission |
front 4 attachment to ACE-2; induction of autoimmunity | back 4 COVID-19 virulence factors |
front 5 RT-PCR, Ab and Ag tests | back 5 COVID-19 culture/diagnosis |
front 6 vaccine, mitigation efforts | back 6 COVID-19 prevention |
front 7 antivirals such as paxlovid | back 7 COVID-19 treatment |
front 8 spreading constantly worldwide | back 8 COVID-19 epidemiological features |
front 9 fever, anemia, abnormal heartbeat, symptoms of heart attack, shortness of breath, and chills abdominal or side pain, Janeway lesions, and Osler's nodes | back 9 signs and symptoms of acute endocarditis |
front 10 similar to symptoms of acute endocarditis develop more slowly and are less pronounced enlarged spleen, clubbed fingers, and toes | back 10 signs and symptoms of subacute endocarditis |
front 11 acute endocarditis disease table | back 11 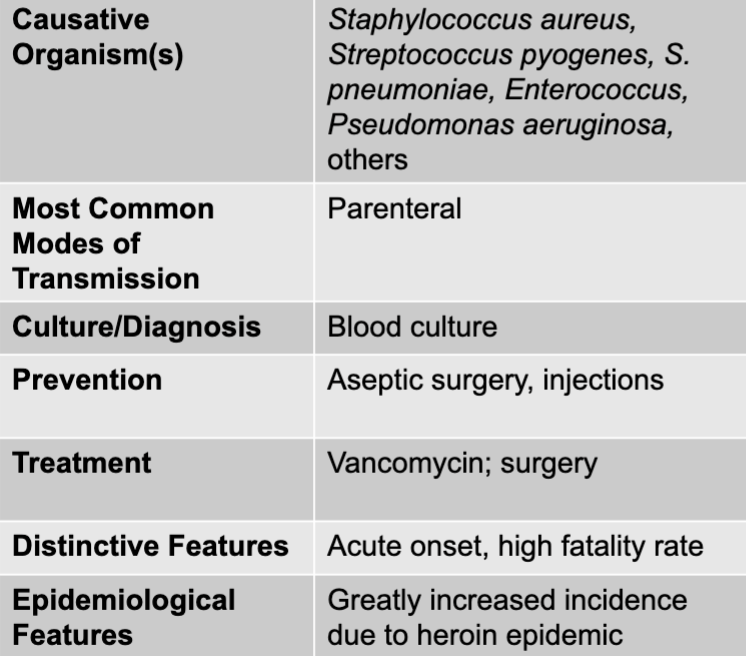 |
front 12 subacute endocarditis disease table | back 12  |
front 13 staphylococcus aureus, streptococcus pyogenes, S. pneumoniae, enterococcus, pseudomonas aeruginosa | back 13 acute endocarditis causative agent |
front 14 parenteral | back 14 acute endocarditis mode of transmission |
front 15 aseptic surgery, injections | back 15 acute endocarditis prevention |
front 16 vancomycin; surgery | back 16 acute endocarditis treatment |
front 17 acute onset, high fatality rate | back 17 acute endocarditis disntictive features |
front 18 greatly increased incidence due to heroin epidemic | back 18 acute endocarditis epidemiological features |
front 19 alpha-hemolytic streptococci, others | back 19 subacute endocarditis causative agent |
front 20 endogenous transfer of normal biota to bloodstream | back 20 subacute endocarditis mode of transmission |
front 21 blood culture | back 21 subacute endocarditis culture/diagnosis |
front 22 prophylactic antibiotics before invasive procedures | back 22 subacute endocarditis prevention |
front 23 broad-spectrum antibiotics surgery may be necessary | back 23 subacute endocarditis treatment |
front 24 slower onset | back 24 subacute endocarditis distinctive features |
front 25 fever, altered mental state, shaking chills, and gastrointestinal symptoms increased breathing rate, respiratory alkalosis, and low blood pressure resulting in loss of fluid from the vasculature | back 25 sepsis signs and symptoms |
front 26 sepsis disease | back 26 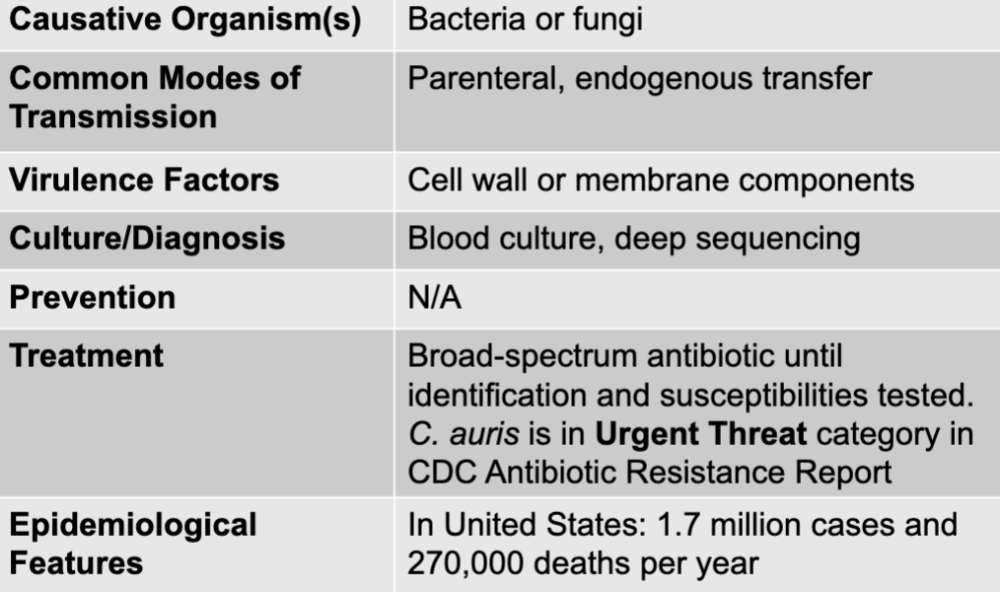 |
front 27 bacteria or fungi | back 27 sepsis causative agent |
front 28 parenteral, endogenous transfer | back 28 sepsis mode of transmission |
front 29 cell wall or membrane components | back 29 sepsis virulence factors |
front 30 blood culture, deep sequencing | back 30 sepsis culture, deep sequencing |
front 31 broad-spectrum antibiotic until identification and susceptibilities tested. C. auris is in urgent threat category in CDC antiobiotic resistance report | back 31 sepsis treatment |
front 32 in united states: 1.7 million cases and 270,000 deaths per year | back 32 sepsis epidemiological features |
front 33 plague disease table | back 33 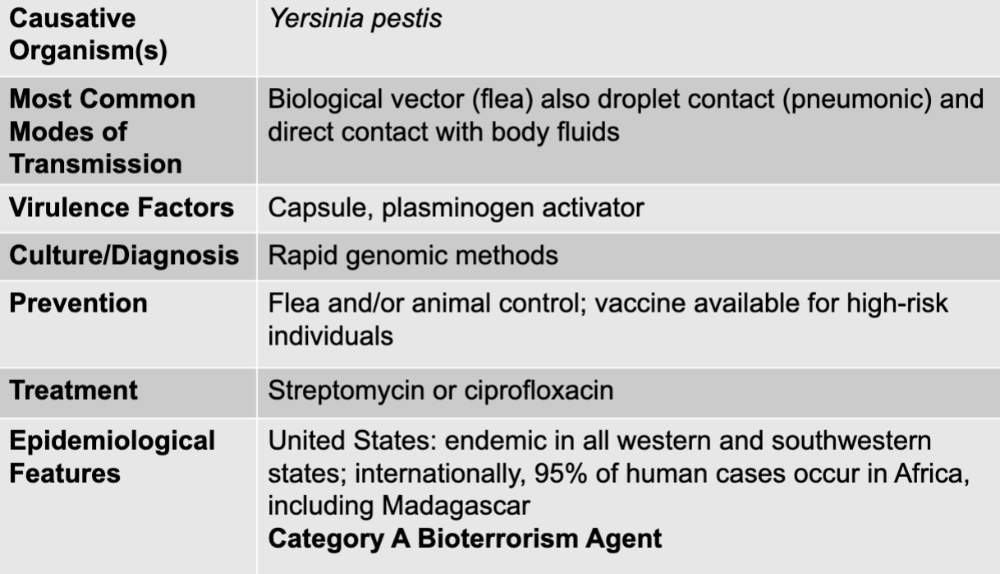 |
front 34 yersinia pestis | back 34 plague causative agent |
front 35 biological vector (flea) also droplet contact (pneumonic) and direct contact with body fluids | back 35 plague mode of transmission |
front 36 capsule, plasminogen activator | back 36 plague virulence factors |
front 37 rapid genomic methods | back 37 plague culture/diagnosis |
front 38 flea and/or animal control; vaccine available for high-risk individuals | back 38 plague prevention |
front 39 streptomycin or ciprofloxacin | back 39 plague treatment |
front 40 united states: endemic in all western and southwestern states; internationally, 95% of human cases occur in africa, including madagascar category A bioterrorism agent | back 40 plague epidemiological features |
front 41 tularemia disease table | back 41 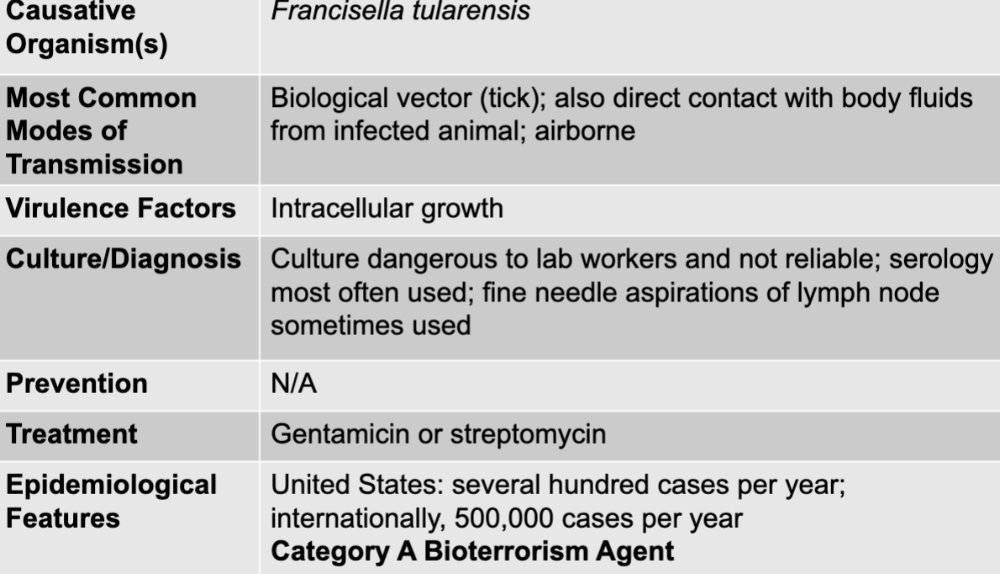 |
front 42 francisella tularensis | back 42 tularemia causative agent |
front 43 biological vector (tick); also direct contact with body fluids from infected animal; airborne | back 43 tularemia mode of transmission |
front 44 intracellular growth | back 44 tularemia virulence factors |
front 45 culture dangerous to lab workers and not reliable; serology most often used; fine needle aspirations of lymph node sometimes used | back 45 tularemia culture/diagnosis |
front 46 gentamicin or streptomycin | back 46 tularemia treatment |
front 47 united states: several hundred cases per year; internationally 500,000 cases per year category A bioterrorism agent | back 47 tularemia epidemiological features |
front 48 lyme disease table | back 48 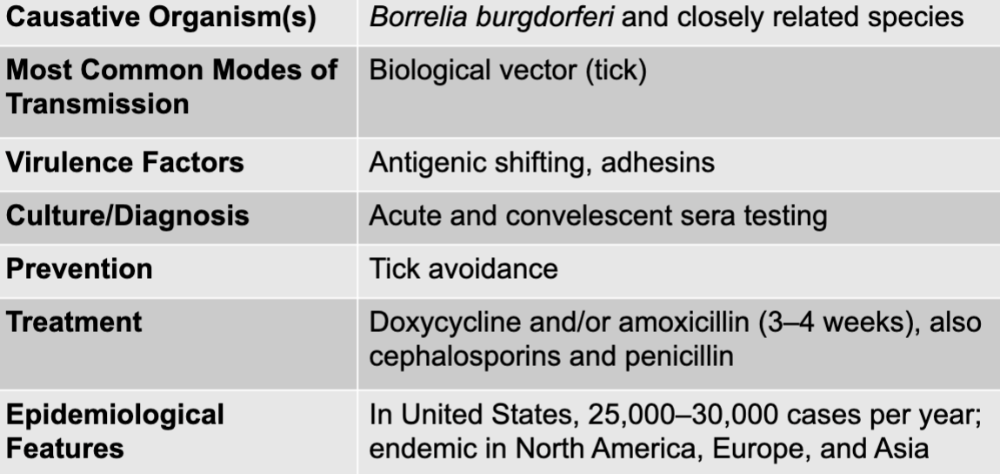 |
front 49 borrelia burgdorferi and closely related species | back 49 lyme disease causative agent |
front 50 biological vector (tick) | back 50 lyme disease mode of transmission |
front 51 antigenic shifting, adhesins | back 51 lyme disease virulence factors |
front 52 acute and convalescent sera testing | back 52 lyme disease culture/diagnosis |
front 53 doxycycline and/or amoxicillin (3-4 weeks), also cephalosporins and penicillin | back 53 lyme disease treatment |
front 54 tick avoidance | back 54 lyme disease prevention |
front 55 in US, 25,000-30,000 cases per year; endemic in north america, europe, and asia | back 55 lyme disease epidemiological features |
front 56 mono(nucleosis) disease table | back 56 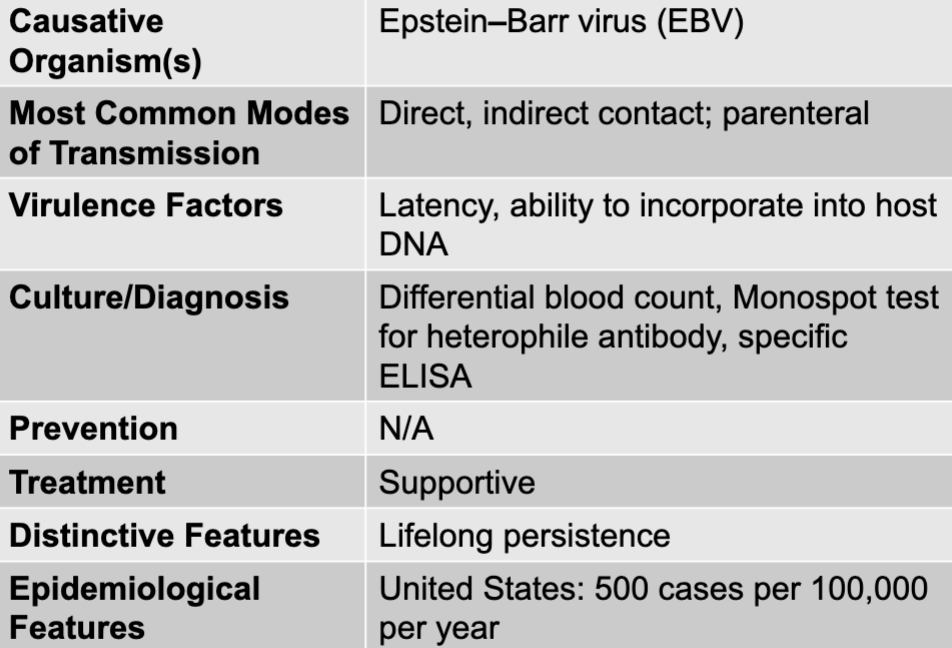 |
front 57 epstein-barr virus | back 57 mono causative agent |
front 58 direct, indirect contact; parenteral | back 58 mono mode of transmission |
front 59 latency, ability to incorporate into host DNA | back 59 mono virulence factors |
front 60 differential blood count, monospot test for heterophile antibody, specific ELISA | back 60 mono culture/diagnosis |
front 61 supportive | back 61 mono treatment |
front 62 lifelong persistence | back 62 mono distinctive features |
front 63 united states: 500 cases per 100,000 per year | back 63 mono epidemiological features |
front 64 anthrax disease table | back 64 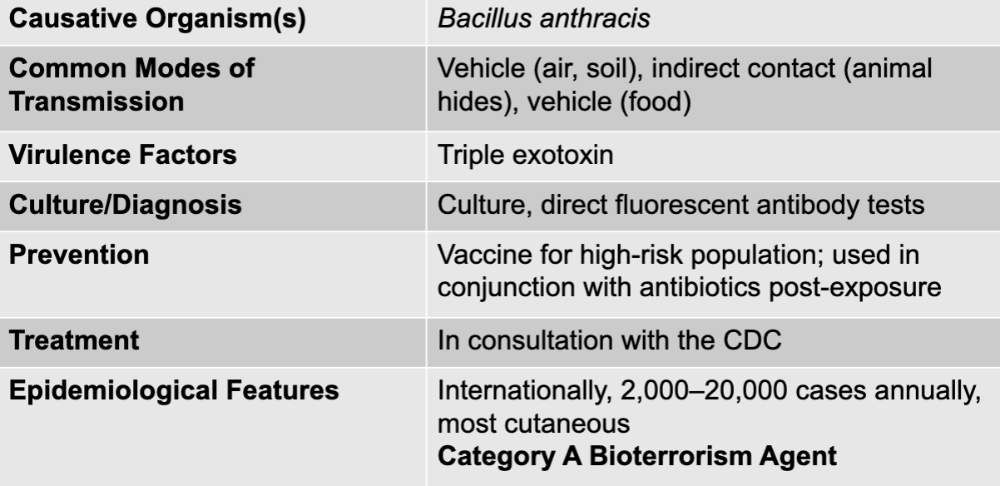 |
front 65 bacillus anthracis | back 65 anthrax causative agent |
front 66 vehicle (air, soil), indirect contact (animal hides), vehicle (food) | back 66 anthrax mode of transmission |
front 67 triple exotoxin | back 67 anthrax virulence factors |
front 68 culture, direct fluorescent antibody tests | back 68 anthrax culture/diagnosis |
front 69 vaccine for high-risk population; used in conjugation with antibiotics post-expsoure | back 69 anthrax prevention |
front 70 in consultation with the CDC | back 70 anthrax treatment |
front 71 internationally, 2,000-20,000 cases annually, most cutaneous category A bioterrorism agent | back 71 anthrax epidemiological features |
front 72 yellow fever, dengue fever, chikungunya, ebola and/or marburg, lassa fever | back 72 hemorrhagic fever diseases |
front 73 yellow fever disease table | back 73 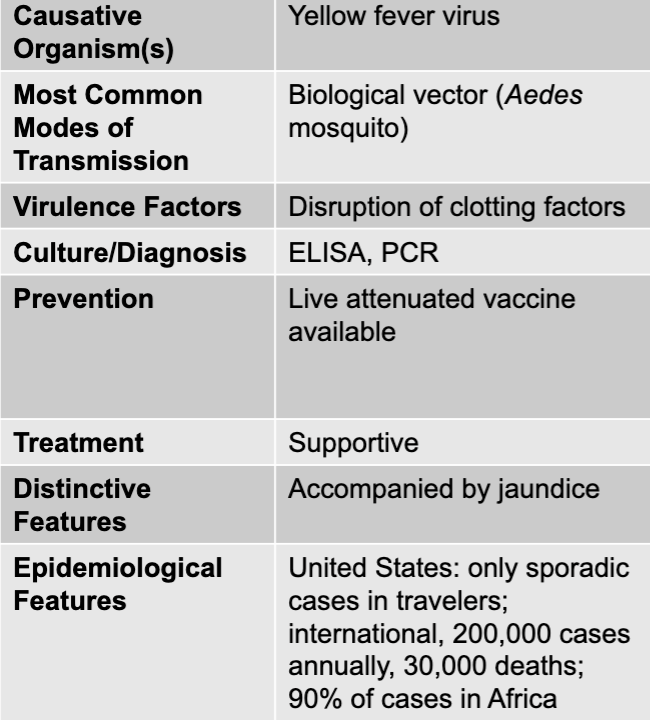 |
front 74 yellow fever virus | back 74 yellow fever causative agent |
front 75 biological vector (Aedes mosquito) | back 75 yellow fever mode of transmission |
front 76 disruption of clotting factors | back 76 yellow fever virulence factors |
front 77 ELISA, PCR | back 77 yellow fever culture/diagnosis |
front 78 live attenuated vaccine available | back 78 yellow fever prevention |
front 79 supportive | back 79 yellow fever treatment |
front 80 accompanied by jaundice | back 80 yellow fever distinctive features |
front 81 united states: only sporadic cases in travelers; international, 200,000 cases annually, 30,000 deaths; 90% of cases in africa | back 81 yellow fever epidemiological features |
front 82 dengue fever disease table | back 82  |
front 83 biological vector (Aedes mosquito) | back 83 dengue fever mode of transmission |
front 84 disruption of clotting factors | back 84 dengue fever virulence factors |
front 85 rise in IgM titers | back 85 dengue fever culture/diagnosis |
front 86 new vaccine approved in 2019 for use in children aged 9-16 with previous infection living in endemic areas in the US | back 86 dengue fever prevention |
front 87 supportive | back 87 dengue fever treatment |
front 88 "breakbone fever" - so named due to severe pain in some forms | back 88 dengue fever distinctive features |
front 89 united states: most cases in puerto rico, the us virgin islands, samoa, and guam; internationally, 50-3000 million people infected every year and tens of thousands of deaths occur, mostly among children | back 89 dengue fever epidemiological features |
front 90 chikungunya disease table | back 90 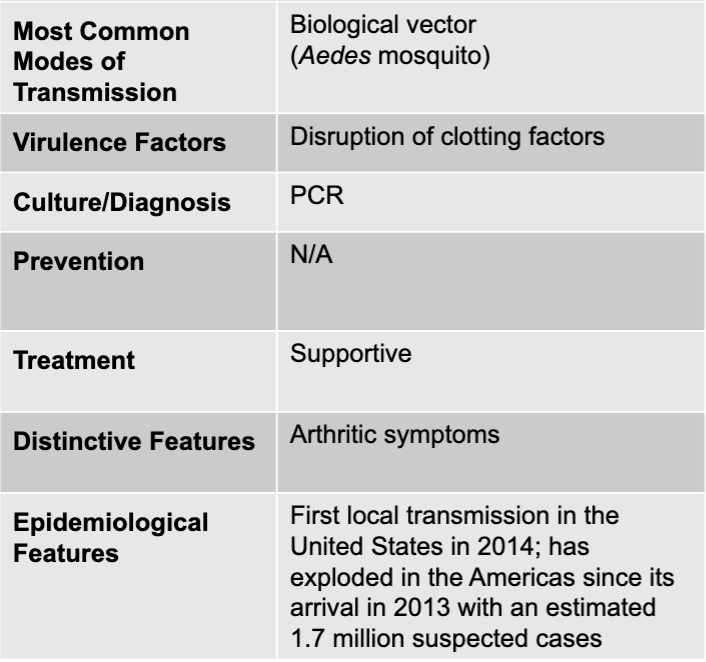 |
front 91 chikungunya virus | back 91 chikungunya causative agent |
front 92 biological vector (Aedes mosquito) | back 92 chikungunya mode of transmission |
front 93 disruption of clotting factors | back 93 chikungunya virulence factor |
front 94 PCR | back 94 chikungunya culture/diagnosis |
front 95 supportive | back 95 chikungunya treatment |
front 96 arthritic symptoms | back 96 chikungunya distinctive features |
front 97 first local transmission in the united states in 2014; has exploded in the americas since its arrival in 2013 with an estimated 1.7 million suspected cases | back 97 chikungunya epidemiological features |
front 98 ebola and/or marburg disease table | back 98  |
front 99 ebola virus, marburg virus | back 99 ebola and/or marburg causative agents |
front 100 direct contact, body fluids | back 100 ebola and/or marburg mode of transmission |
front 101 disruption of clotting factors | back 101 ebola and/or marburg virulence factors |
front 102 PCR, viral culture (conducted at CDC) | back 102 ebola and/or marburg culture/diagnosis |
front 103 new vaccine suitable for epidemic situations tested successfully in 2016 | back 103 ebola and/or marburg prevention |
front 104 new drugs developed for ongoing outbreaks in africa | back 104 ebola and/or marburg treatment |
front 105 massive hemorrhage; rash sometimes present | back 105 ebola and/or marburg distinctive features |
front 106 united states: only imported infections; internationally, sporadic outbreaks in africa; major ebola outbreak 2014-2016; category A bioterrorism agent | back 106 ebola and/or marburg epidemiological features |
front 107 lassa fever disease table | back 107 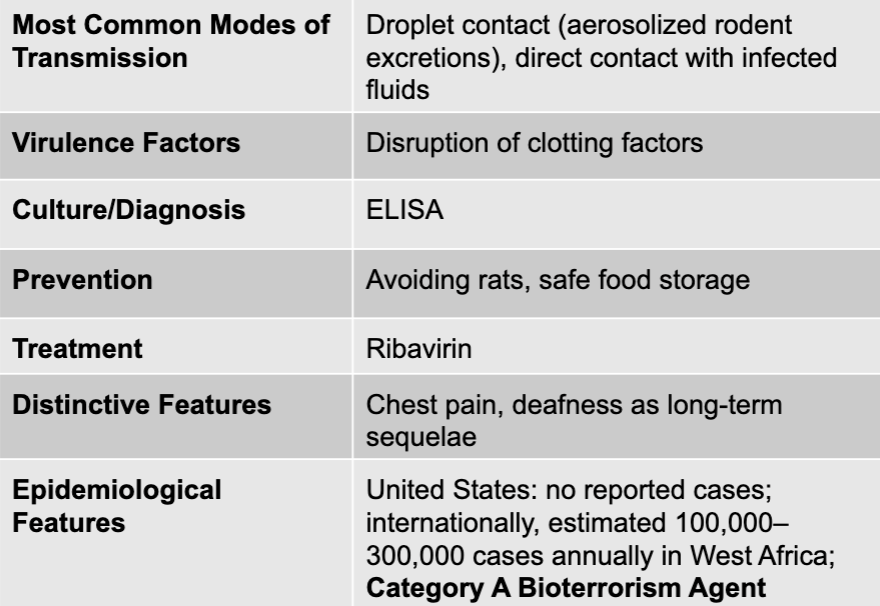 |
front 108 lassa fever virus | back 108 lassa fever causative agent |
front 109 droplet contact (aerosolized rodent excretions), direct contact with infected fluids | back 109 lassa fever mode of transmission |
front 110 disruption of clotting factors | back 110 lassa fever virulence factors |
front 111 ELISA | back 111 lassa fever culture/diagnosis |
front 112 avoiding rats, safe food storage | back 112 lassa fever prevention |
front 113 ribavirin | back 113 lassa fever treatment |
front 114 chest pain, deafness as long-term sequelae | back 114 lassa fever distinctive features |
front 115 united states: no reported cases; internationally, estimated 100,000-300,000 cases annually in west africa; category A bioterrorism agent | back 115 lassa fever epidemiological features |
front 116 brucellosis, Q fever, cat-scratch disease, trench fever, ehrilichiosis, anaplasmosis, babesiosis, spotted fever rickettsiosis | back 116 nonhemorrhagic fever |
front 117 brucellosis disease table | back 117 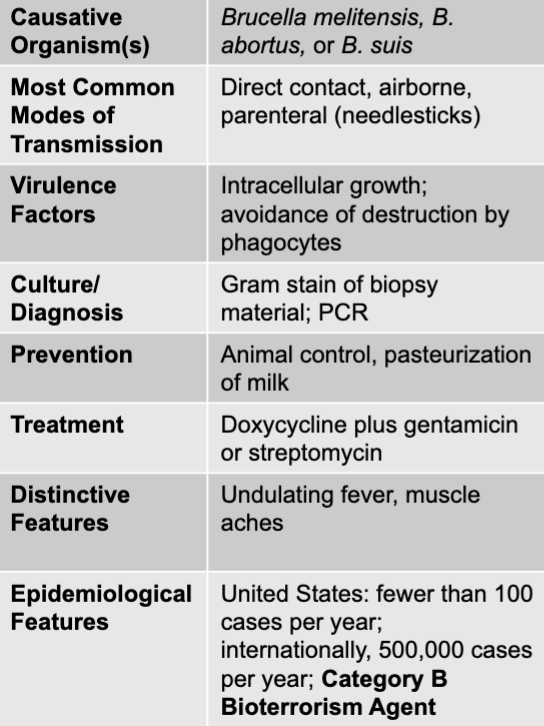 |
front 118 brucella melitensis, B. abortus, or B. suis | back 118 brucellosis causative agent |
front 119 direct contact, airborne, parenteral (needlesticks) | back 119 brucellosis mode of transmission |
front 120 intracellular growth; avoidance of destruction by phagocytes | back 120 brucellosis virulence factors |
front 121 gram stain of biopsy material; PCR | back 121 brucellosis culture/diagnosis |
front 122 animal control, pasteurization of milk | back 122 brucellosis prevention |
front 123 undulating fever, muslce aches | back 123 brucellosis distinctive features |
front 124 doxycycline plus gentamicin or streptomycin | back 124 brucellosis treatment |
front 125 united states: fewer than 100 cases per year; internationally, 500,000 cases per year; category B bioterrorism agent | back 125 brucellosis epidemiological features |
front 126 Q fever disease table | back 126 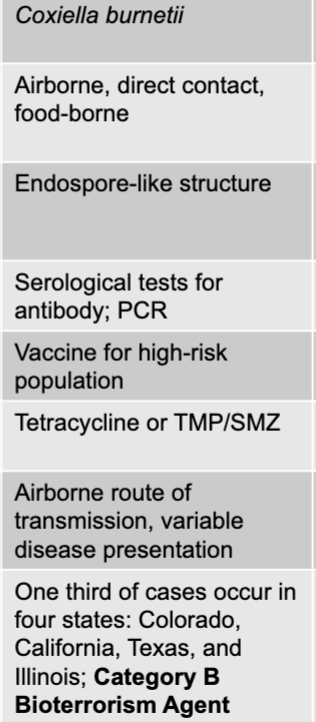 |
front 127 coxiella burnetii | back 127 Q fever causative agent |
front 128 airborne, direct contact, food-borne | back 128 Q fever mode of transmission |
front 129 endospore-like structure | back 129 Q fever virulence factors |
front 130 serological tests for antibody; PCR | back 130 Q fever culture/diagnosis |
front 131 vaccine for high-risk population | back 131 Q fever prevention |
front 132 tetracycline or TMP/SMZ | back 132 Q fever treatment |
front 133 airborne route of transmission, variable disease presentation | back 133 Q fever distinctive features |
front 134 one third of cases occur in four states: colorado, california, texas, and illinois; category B bioterrorism agent | back 134 Q fever epidemiological features |
front 135 cat-scratch disease table | back 135  |
front 136 bartonella henselae | back 136 cat-scratch causative agent |
front 137 parenteral (cat scratch or bite) | back 137 cat-scratch mode of transmission |
front 138 endotoxin | back 138 cat-scratch virulence factors |
front 139 biopsy of lymph nodes plus gram staining; ELISA (performed by CDC) | back 139 cat-scratch culture/diagnosis |
front 140 clean wound sites | back 140 cat-scratch prevention |
front 141 azithromycin or rifampin | back 141 cat-scratch treatment |
front 142 histroy of cat bite or scrath; fever not always present | back 142 cat-scratch distinctive features |
front 143 united states: estimated incidence is 9.3 cases per 100,000; internationally, seroprevalence from 0.6-37% depending on cat population | back 143 cat-scratch epidemiological features |
front 144 trench fever disease table | back 144 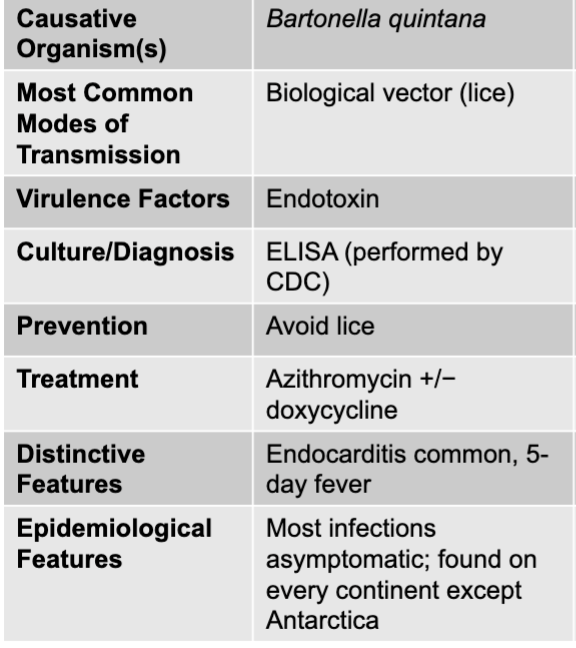 |
front 145 bartonella quintana | back 145 trench fever causative agent |
front 146 biological vector (lice) | back 146 trench fever mode of transmission |
front 147 endotoxin | back 147 trench fever virulence factors |
front 148 ELISA (performed by CDC) | back 148 trench fever culture/diagnosis |
front 149 avoid lice | back 149 trench fever prevention |
front 150 azithromycin +/- doxycycline | back 150 trench fever treatment |
front 151 endocarditis common, 5 day fever | back 151 trench fever distinctive features |
front 152 most infections asymptomatic; found on every continent except antarctica | back 152 trench fever epidemiological features |
front 153 ehrlichiosis disease table | back 153 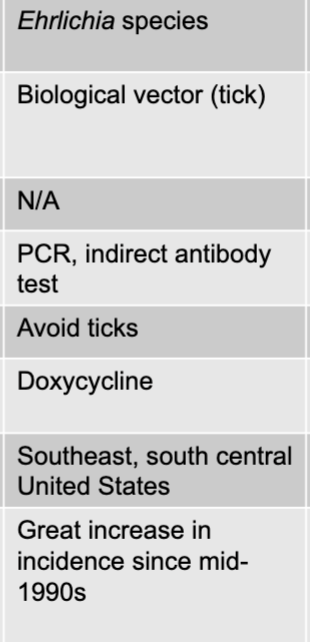 |
front 154 ehrlichia species | back 154 ehrlichiosis causative agent |
front 155 biological vector (tick) | back 155 ehrlichiosis mode of transmission |
front 156 PCR, indirect antibody test | back 156 ehrlichiosis culture/diagnosis |
front 157 doxycycline | back 157 ehrlichiosis treatment |
front 158 southeast, south central united states | back 158 ehrlichiosis distinctive features |
front 159 great increase in incidence since mid-1990s | back 159 ehrlichiosis epidemiological features |
front 160 anaplasmosis disease table | back 160 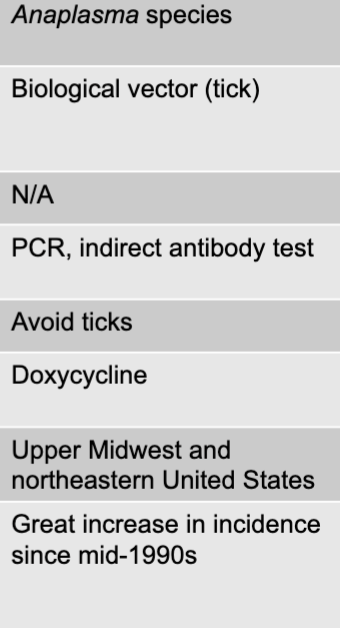 |
front 161 anaplasma species | back 161 anaplasmosis causative agent |
front 162 biological vector (tick) | back 162 anaplasmosis mode of transmission |
front 163 PCR, indirect antibody test | back 163 anaplasmosis culture/diagnosis |
front 164 avoid ticks | back 164 anaplasmosis prevention |
front 165 doxycyycline | back 165 anaplasmosis treatment |
front 166 upper midwest and northeasteern united states | back 166 anaplasmosis distinctive features |
front 167 great increase in incidence since mid-1990s | back 167 anaplasmosis epidemiological features |
front 168 babesiosis disease table | back 168 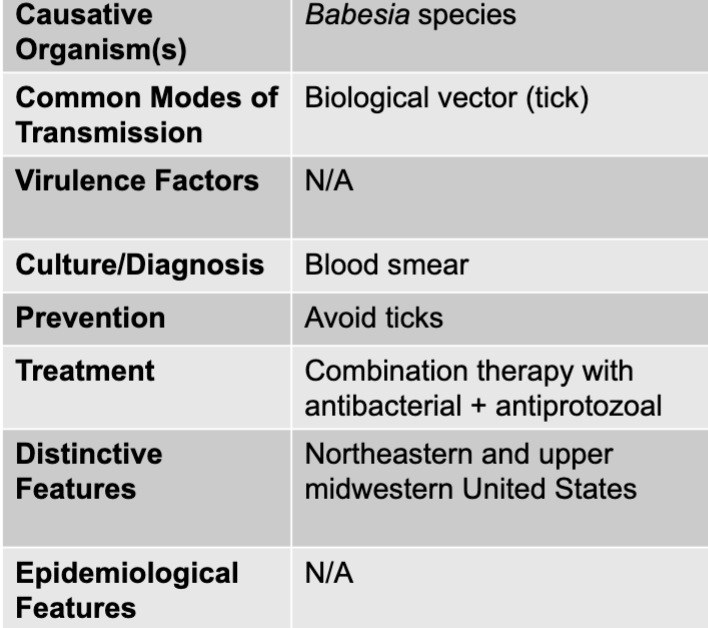 |
front 169 biological vector (tick) | back 169 babesiosis mode of transmission |
front 170 blood smear | back 170 babesiosis culture/diagnosis |
front 171 avoid ticks | back 171 babesiosis prevention |
front 172 combination therapy with antibacterial + antiprotozoal | back 172 babesiosis treatment |
front 173 northeastern and upper midwestern united states | back 173 babesiosis distinctive features |
front 174 spotted fever rickettsiosis disease table | back 174  |
front 175 rickettsia species | back 175 spotted fever rickettsiosis causative agent |
front 176 biological vector (tick) | back 176 spotted fever rickettsiosis mode of transmission |
front 177 induces apoptosis in cells lining blood vessels | back 177 spotted fever rickettsiosis virulence factors |
front 178 fluorescent antibody, PCR | back 178 spotted fever rickettsiosis culture/diagnosis |
front 179 avoid ticks | back 179 spotted fever rickettsiosis prevention |
front 180 doxycycline | back 180 spotted fever rickettsiosis treatment |
front 181 rocky mountain spotted fever is most severe of the rickettsioses | back 181 spotted fever rickettsiosis distinctive features |
front 182 only in americas; 10-fold increase since 2000 | back 182 spotted fever rickettsiosis epidemiological features |
front 183 chagas disease table | back 183 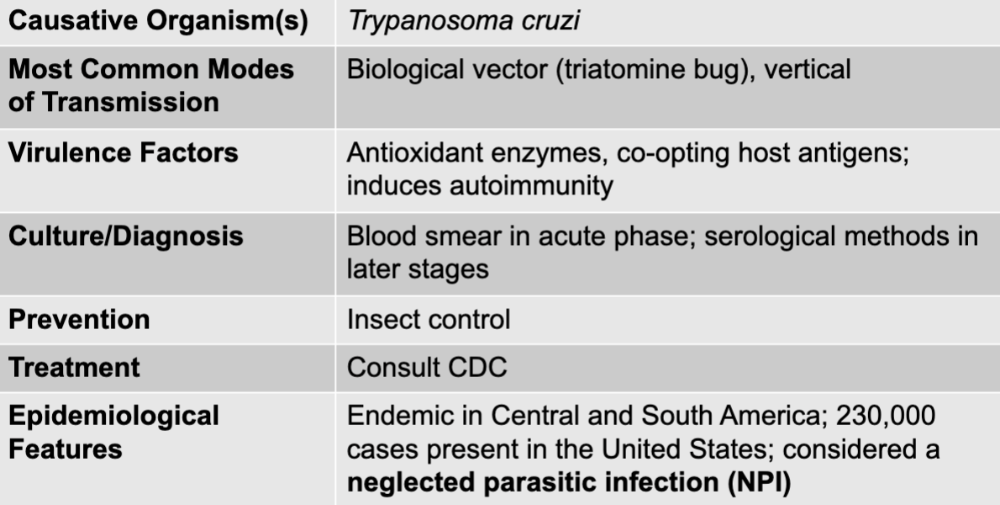 |
front 184 trypanosoma cruzi | back 184 chagas causative agent |
front 185 biological vector (tratomine bug), vertical | back 185 chagas mode of transmission |
front 186 antioxidant enzymes, co-opting host antigens; induces autoimmunity | back 186 chagas virulence factors |
front 187 blood smear in acute phase; serological methods in later stages | back 187 chagas culture/diagnosis |
front 188 insect control | back 188 chagas prevention |
front 189 consult CDC | back 189 chagas treatment |
front 190 endemic in central and south america; 230,000 cases present in the united states; considered a neglected parasitic infection | back 190 chagas epidemiological features |
front 191 malaria disease table | back 191 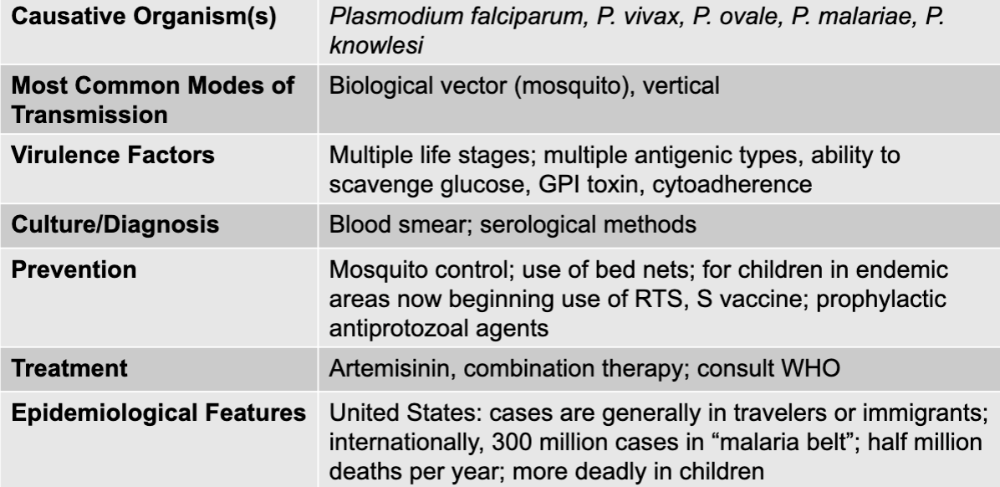 |
front 192 plasmodium falciparum, p. vivax, p. ovale, p. malariae, p. knowlesi | back 192 malaria causative agents |
front 193 biological vector (mosquito_, vertical | back 193 malaria mode of transmission |
front 194 multiple life stages; multiple antigenic types, ability to scavenge glucose, GPI toxin, cytoadherence | back 194 malaria virulence factors |
front 195 blood smear; serological methods | back 195 malaria culture/diagnosis |
front 196 mosquito control; use of bed nets; for children in endemic areas now beginning use of RTS, S vaccine; prophylactic antiprotozoal agents | back 196 malaria prevention |
front 197 arteminisin, combination therapy; consult WHO | back 197 malaria treatment |
front 198 united states: cases are generally in travelers or immigrants; internationally, 300 million cases in"malaria belt"; half million deaths per year; more deadly in children | back 198 malaria epidemiological features |
front 199 HIV and AIDS disease table | back 199 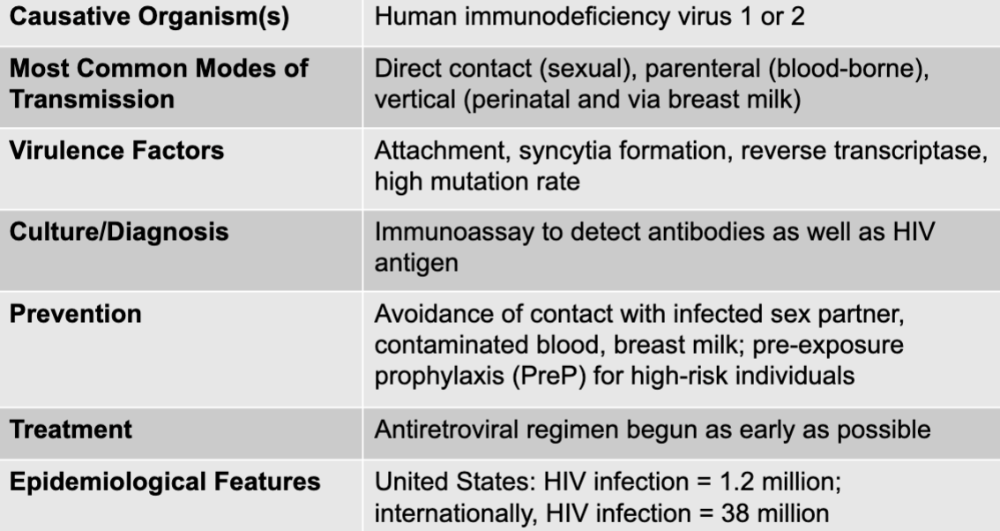 |
front 200 human immunodeficiency virus 1 or 2 | back 200 HIV causative agent |
front 201 direct contact (sexual), parenteral (blood-borne), vertical (perinatal and via breast milk) | back 201 HIV mode of transmission |
front 202 attachment, syncytia formation, reverse transcriptase, high mutation rate | back 202 HIV virulence factors |
front 203 immunoassay to detect antibodies as well as HIV antigen | back 203 HIV culture/diagnosis |
front 204 avoidance of contact with infected sex partner, contaminated blood, breast milk; pre-exposure prophylaxis (PreP) for high-risk individuals | back 204 HIV prevention |
front 205 antiretroviral regiment begun as early as possible | back 205 HIV treatment |
front 206 united states: HIV infection = 1.2 million internationally: HIV infection = 38 million | back 206 HIV epidemiological features |
front 207 gram-positive endospore-forming bacteria | back 207 bacillus anthracis |
front 208 gram-positive bacteria | back 208 staphylococcus aureus streptococcus pyogenes streptococcus pneumoniae enterococcus |
front 209 gram-negative bacteria | back 209 pseudomonas aeruginosa yersinia pestis francisella tularensis borrelia burgdorferi brucella abortus, B. suiss coxiella burnetii bartonella henselea bartonella quintana ehrlichia species anaplasma species rickettsia species |
front 210 DNA virus | back 210 epstein0barr virus |
front 211 RNA viruses | back 211 SARS-CoV-2 yellow fever virus dengue fever virus chikungunya virus ebola and marburg viruses lassa fever virus |
front 212 retroviruses | back 212 human immunodeficiency virus 1 and 2 |
front 213 protozoa | back 213 babesia species trypanosoma cruzi plasmodium falciparum, p. vivax, p. ovale, p. malariae |