Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Infectious Diseases Manifesting in the Genitourinary System
front 1 urinary tract infections causative agents | back 1 E.coli, staphylococcus saprophyticus, enterococcus |
front 2 urinary tract infections mode of transmission | back 2 opportunism: transfer from GI tract (community-acquired) or environment or GI tract (via catheter) |
front 3 urinary tract infection culture/diagnosis | back 3 usually culture-based; antimicrobial susceptibilities always checked |
front 4 urinary tract infection prevention | back 4 hygiene practices; in case of CA-UTIs, limit catheter usage |
front 5 E. coli (urinary tract infection) virulence factors | back 5 adhesions, motility |
front 6 staphylococcus saprophyticus (urinary tract infection) treatment | back 6 usually nitrofurantoin |
front 7 E. coli (urinary tract infection) treatment | back 7 usually nitrofurantoin |
front 8 E. coli (urinary tract infection) epidemiological features | back 8 causes 90% of community UTIs and 50-70% of CA-UTIs |
front 9 staphylococcus saprophyticus (urinary tract infection) epidemiological features | back 9 causes small percentage of community UTIs and even lower percentage of CA-UTIs |
front 10 enterococcus (urinary tract infection) treatment | back 10 based on susceptibility testing; vancomycin-resistant enterococcus is in serious threat category in CDC antibiotic resistance report |
front 11 enterococcus (urinary tract infection) epidemiological features | back 11 frequent cause of CA-UTIs |
front 12 urinary tract infection disease table | back 12 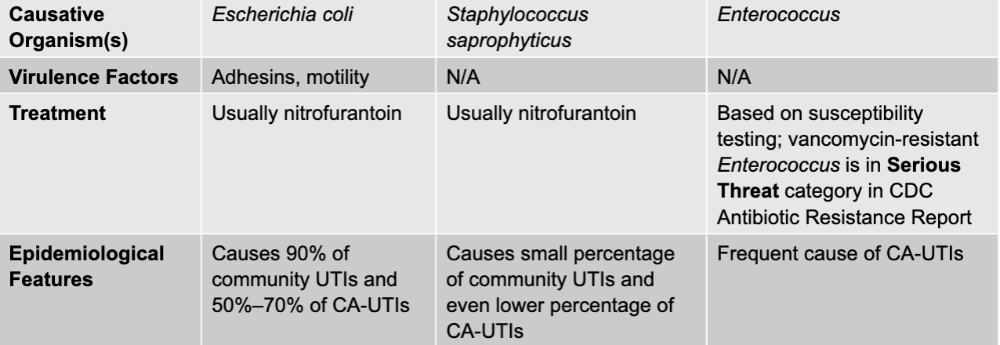 |
front 13 leptospirosis disease table | back 13 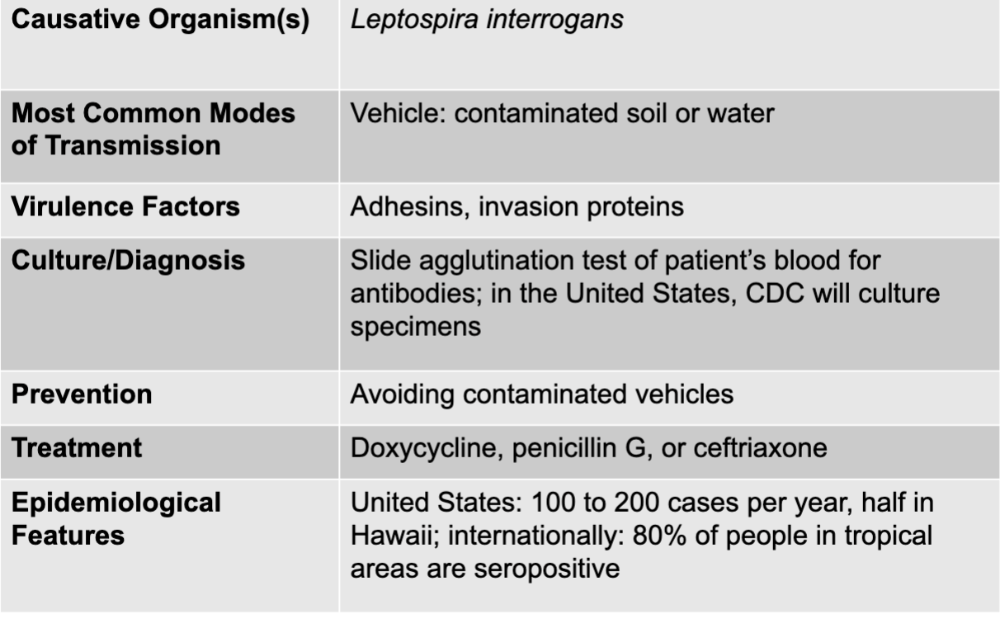 |
front 14 leptospirosis causative agent | back 14 leptospira interrogans |
front 15 leptospirosis mode of transmission | back 15 vehicle: contaminated soil or water |
front 16 leptospirosis virulence factors | back 16 adhesions, invasion proteins |
front 17 leptospirosis culture/diagnosis | back 17 slide agglutination test of patient's blood for antibodies; in the US, CDC will culture specimens |
front 18 leptospirosis prevention | back 18 avoiding contaminated vehicles |
front 19 leptospirosis treatment | back 19 doxycycline, penicillin G, or ceftriaxone |
front 20 leptospirosis epidemiological features | back 20 US: 100 to 200 cases per year, half in Hawaii; internationally: 80% of people in tropical areas are seropositive |
front 21 urinary schistosomiasis disease table | back 21  |
front 22 urinary schistosomiasis causative agent | back 22 schistosoma haematobium |
front 23 urinary schistosomiasis mode of transmission | back 23 vehicle; contaminated water |
front 24 urinary schistosomiasis virulence factors | back 24 antigenic "cloaking," induction of granulomatous response |
front 25 urinary schistosomiasis culture/diagnosis | back 25 identification of eggs in urine, PCR methods |
front 26 urinary schistosomiasis prevention | back 26 avoiding contaminated vehicles |
front 27 urinary schistosomiasis treatment | back 27 praziquantel |
front 28 urinary schistosomiasis epidemiological features | back 28 endemic in africa, middle east, india, and turkey, in sub-saharan african: 120 million infected |
front 29 vaginitis disease table | back 29 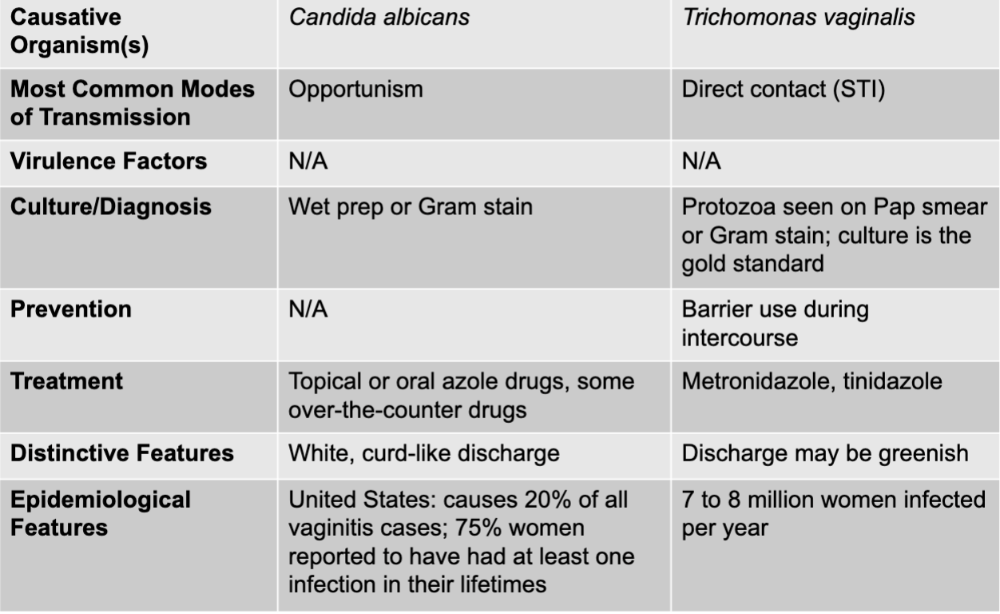 |
front 30 vaginitis causative agents | back 30 candida albicans and trichomonas vaginalis |
front 31 vaginitis (candida albicans) mode of transmission | back 31 opportunism |
front 32 vaginitis (candida albicans) culture/diagnosis | back 32 wet prep or gram stain |
front 33 vaginitis (candida albicans) treatment | back 33 topical or oral azole drugs, some over-the-counter drugs |
front 34 vaginitis (candida albicans) distinctive features | back 34 white, curd-like discharge |
front 35 vaginitis (candida albicans) epidemiological features | back 35 US: causes 20% of all vaginitis cases; 75% women reported to have had at least one infection in their lifetimes |
front 36 vaginitis (trichomonas vaginalis) mode of transmission | back 36 direct contact (STI) |
front 37 vaginitis (trichomonas vaginalis) culture/diagnosis | back 37 protozoa seen on pap smear or gram stain; culture is the gold standard |
front 38 vaginitis (trichomonas vaginalis) prevention | back 38 barrier use during intercourse |
front 39 vaginitis (trichomonas vaginalis) distinctive features | back 39 discharge may be greenish |
front 40 vaginitis (trichomonas vaginalis) epidemiological features | back 40 7 to 8 million women infected per year |
front 41 vaginosis disease table | back 41 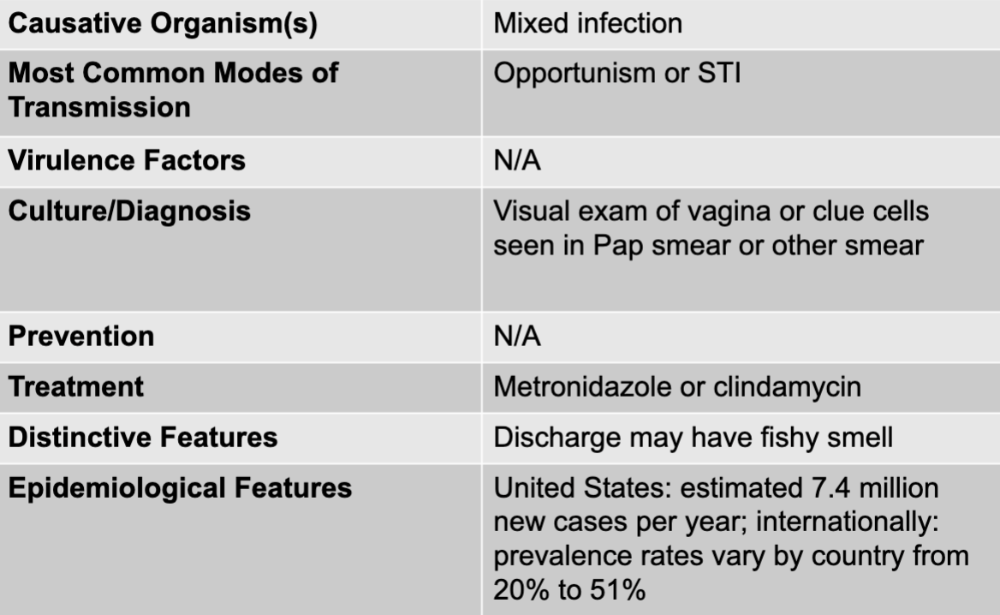 |
front 42 vaginosis causative organisms | back 42 mixed infection |
front 43 vaginosis mode of transmission | back 43 opportunism or STI |
front 44 vaginosis culture/diagnosis | back 44 visual exam of vagina or clue cells seen in pap smear or other smear |
front 45 vaginosis treatment | back 45 metronidazole or clindamycin |
front 46 vaginosis distinctive features | back 46 discharge may have fishy smell |
front 47 vaginosis epidemiological features | back 47 US: estimated 7.4 million new cases per year; internationally: prevalence rates vary by country from 20% to 51% |
front 48 prostatitis disease table | back 48 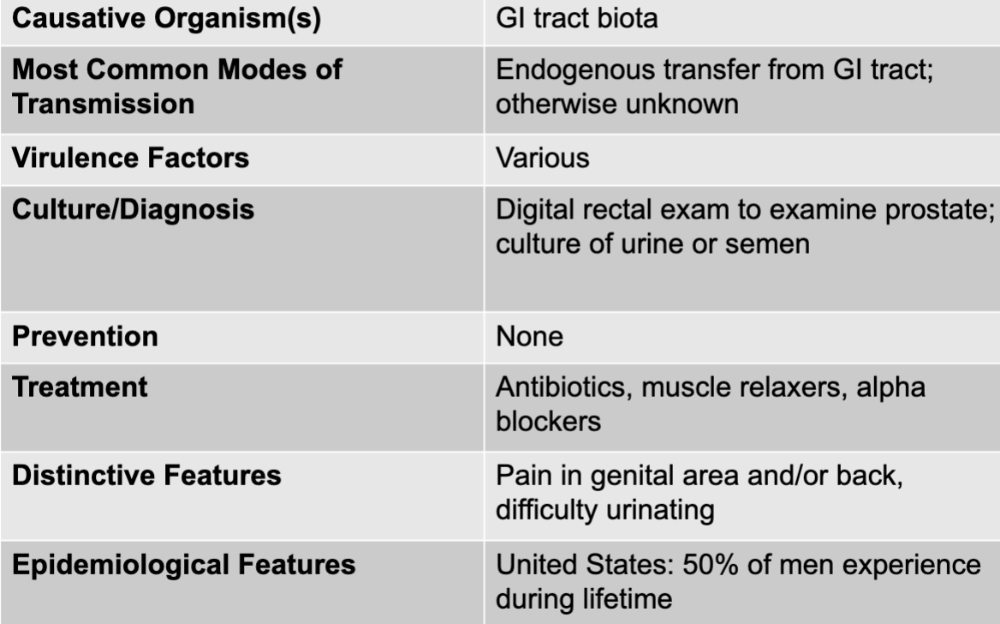 |
front 49 prostatitis causative agent | back 49 GI tract biota |
front 50 prostatitis mode of transmission | back 50 endogenous transfer from GI tract; otherwise unknown |
front 51 prostatitis virulence factors | back 51 various |
front 52 prostatitis culture/diagnosis | back 52 digital rectal exam to examine prostate; culture or urine or semen |
front 53 prostatitis treatment | back 53 antibiotics, muscle relaxers, alpha blockers |
front 54 prostatitis distinctive features | back 54 pain in genital area and or/back, difficulty urinating |
front 55 prostatitis epidemiological features | back 55 US: 50% of men experience during lifetime |
front 56 gonorrhea disease table | back 56 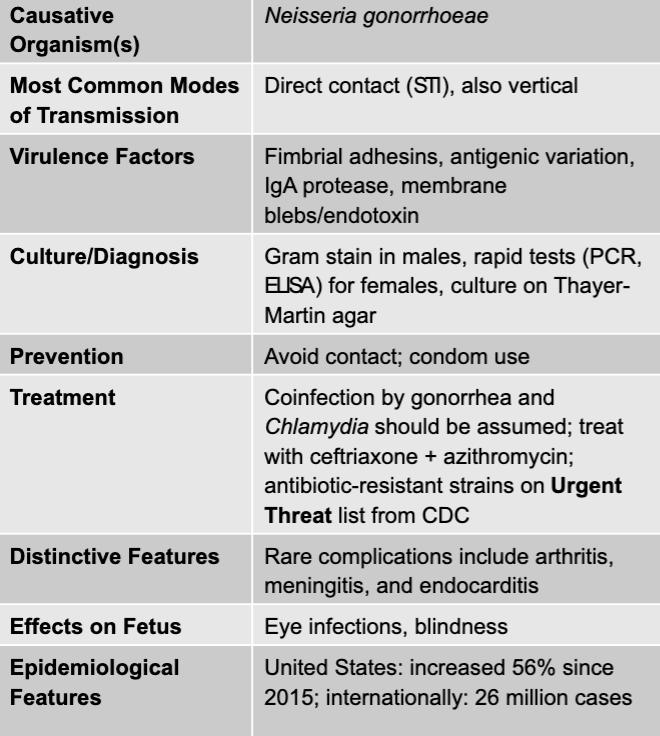 |
front 57 chlamydia disease table | back 57  |
front 58 gonorrhea causative agent | back 58 neisseria gonorrhoeae |
front 59 gonorrhea mode of transmission | back 59 direct contact (STI), also vertical |
front 60 gonorrhea virulence factors | back 60 fimbrial adhesins, antigenic vvariation, IgA protease, membrane blebs/endotoxin |
front 61 gonorrhea culture/diagnosis | back 61 gram stain in males, rapid tests (PCR, ELISA) for females, culture on thayer-martin agar |
front 62 gonorrhea prevention | back 62 avoid contact; condom use |
front 63 gonorrhea treatment | back 63 coinfection by gonorrhea and chlamydia should be assumed; treat with ceftriaxone + azithromycin; antibiotic-resistant strains on urgent threat list from CDC |
front 64 gonorrhea distinctive features | back 64 rare complications include arthritis, meningitis, and endocarditis |
front 65 gonorrhea effects on fetus | back 65 eye infections, blindness |
front 66 gonorrhea epidemiological features | back 66 US: increased 56% since 2015; internationally: 26 million cases |
front 67 chlamydia causative agent | back 67 chlamydia tranchomatis |
front 68 chlamydia mode of transmission | back 68 direct contract (STI), vertical |
front 69 chlamydia virulence factors | back 69 intracellular growth resulting in avoiding immune system and cytokine release, unusual cell wall preventing phagolysosome fusion |
front 70 chlamydia culture/diagnosis | back 70 PCR or ELISA, can be followed by cell culture |
front 71 chlamydia prevention | back 71 avoid contact; condom use |
front 72 chlamydia treatment | back 72 coinfecction by chlamydia and gonorrhea should be assumed; treat with doxycycline or azithromycin |
front 73 chlamydia distinctive features | back 73 more commonly asymptomatic than gonorrhea |
front 74 chlamydia effects on fetus | back 74 eye infections, pneumonia |
front 75 chlamydia epidemiological features | back 75 US: 92% increase since 2009; internationally: eye infection (trachoma) has 90% prevalence rate in developing world |
front 76 syphilis disease table | back 76 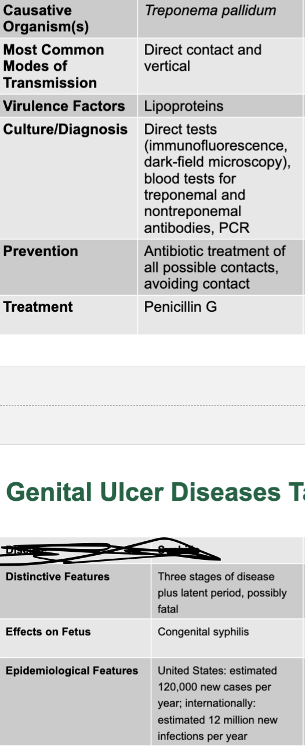 |
front 77 chancroid disease table | back 77 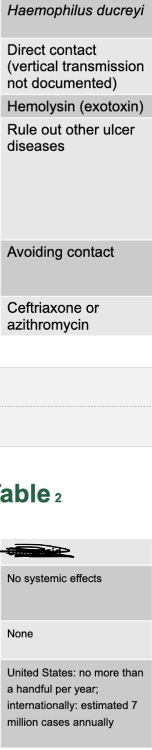 |
front 78 herpes disease table | back 78  |
front 79 syphilis causative agent | back 79 treponema pallidum |
front 80 syphilis mode of transmission | back 80 direct contact and vertical |
front 81 syphilis virulence factors | back 81 lipoproteins |
front 82 syphilis culture/diagnosis | back 82 direct tests, blood tests for treponemal and nontreponemal antibodies, PCR |
front 83 syphilis prevention | back 83 antibiotic treatment of all possible contacts, avoiding contact |
front 84 syphilis treatment | back 84 penicillin G |
front 85 syphilis distinctive features | back 85 three stages of disease plus latent period, possibly fatal |
front 86 syphilis effects on fetus | back 86 congenital syphilis |
front 87 syphilis epidemiological features | back 87 US: estimated 120,000 new cases per year; internationally; estimated 12 million new infections per year |
front 88 chancroid causative agent | back 88 haemophilus ducreyi |
front 89 chancroid mode transmission | back 89 direct contact (vertical transmission not documented) |
front 90 chancroid virulence factors | back 90 hemolysin (exotoxin) |
front 91 chancroid culture/diagnosis | back 91 rule out other ulcer diseases |
front 92 chancroid prevention | back 92 avoiding contact |
front 93 chancroid treatment | back 93 ceftriaxone or azithromycin |
front 94 chancroid distinctive features | back 94 no systemic effects |
front 95 chancroid effects of fetus | back 95 none |
front 96 chancroid epidemiological features | back 96 US: no more than a handful per year; internationally: estimated 7 million cases annually |
front 97 herpes causative agent | back 97 herpes simplex 1 and 2 |
front 98 herpes mode of transmission | back 98 direct contact, vertical |
front 99 herpes virulence factors | back 99 latency |
front 100 herpes culture/diagnosis | back 100 clinical presentation, PCR, Ab tests, growth of virus in cell culture |
front 101 herpes prevention | back 101 avoiding contact, antivirals can reduce recurrences |
front 102 herpes treatment | back 102 acyclovir and derivatives |
front 103 herpes distinctive features | back 103 ranges from asymptomatic to frequent recurrences |
front 104 herpes effects on fetus | back 104 blindness, disseminated herpes infection |
front 105 herpes epidemiological features | back 105 US: 25% prevalence in adults; internationally: estimated 536 million infected in 15-49 age group |
front 106 wart diseases causative agents | back 106 HPV and molluscum contagiosum |
front 107 HPV disease table | back 107 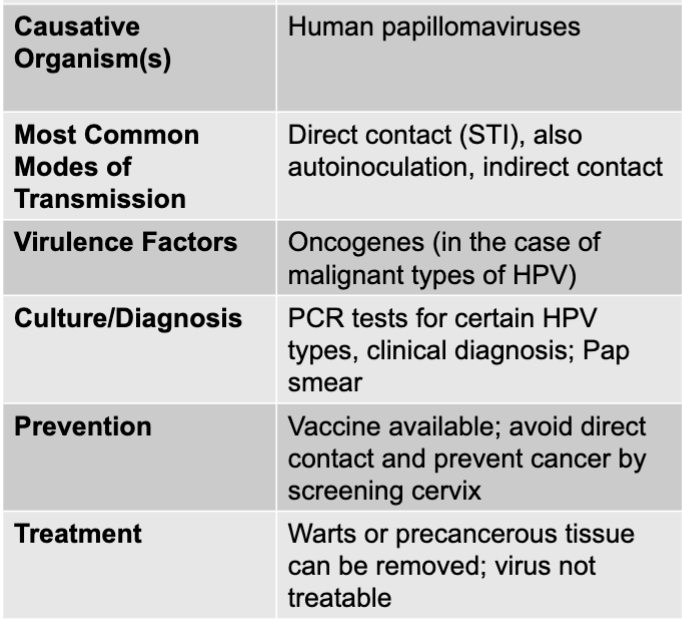 |
front 108 molluscum contagiosum disease table | back 108  |
front 109 HPV causative agent | back 109 human papillomaviruses |
front 110 HPV mode of transmission | back 110 direct contact (STI), also auto inoculation, indirect contact |
front 111 HPV virulence factors | back 111 oncogenes (in the case of malignant types of HPV) |
front 112 HPV culture and diagnosis | back 112 PCR tests for certain HPV types, clinical diagnosis; pap smear |
front 113 HPV prevention | back 113 vaccine available; avoid direct contact and prevent cancer by screening cervix |
front 114 HPV treatment | back 114 warts or precancerous tissue can be removed; virus not treatable |
front 115 HPV distinguishing features | back 115 infection may or may not results in warts; infection may result in malignancy |
front 116 HPV effects on fetus | back 116 may cause laryngeal warts |
front 117 HPV epidemiological features | back 117 US: estimated 6 million new infections per year, 12,000 new cases of HPV-associated cervical cancer |
front 118 molluscum contagiosum causative agent | back 118 poxvirus, sometimes called the molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV) |
front 119 molluscum contagiosum mode of transmission | back 119 direct contact (STI), also indirect and autoinoculation |
front 120 molluscum contagiosum culutre/diagnosis | back 120 clinical diagnosis, also histology, PCR |
front 121 molluscum contagiosum prevention | back 121 avoid detection contact |
front 122 molluscum contagiosum treatment | back 122 warts can be removed; virus not treatable |
front 123 molluscum contagiosum distinguishing features | back 123 wart-like growths are only known consequence of infection |
front 124 molluscum contagiosum epidemiological features | back 124 US: affects 2-10% of children annually |
front 125 group b streptococcus disease table | back 125 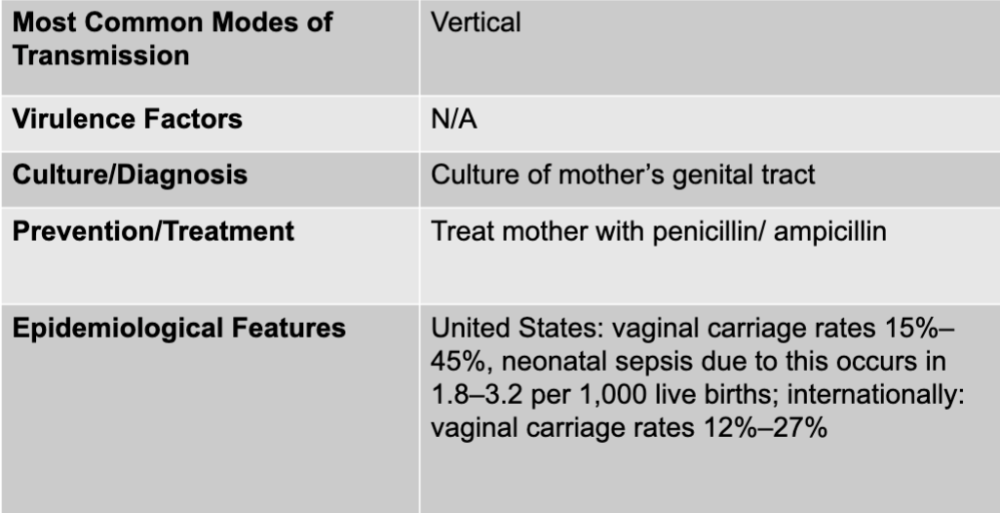 |
front 126 group b streptococcus mode of transmission | back 126 vertical |
front 127 group bstreptococcus culture/diagnosis | back 127 culture of mother's genital tract |
front 128 group b streptococcus prevention/treatment | back 128 treat mother with penicillin/ampicillin |
front 129 group b streptococcus epidemiological features | back 129 US: vaginal carriage rates 15%-45%, neonatal sepsis due to this occurs in 1.8-3.2 per 1,000 live births; internationally: vaginal carriage rates 12%-27% |
front 130 gram-positive bacteria | back 130 saphylococcus saprophyticus group b stretococcus |
front 131 gram-negative bacteria | back 131 E. coli enterococcus leptospira interrogans neisseria gonorrhoeae chlamydia trachomatis treponema pallidum haemophilus ducreyi |
front 132 DNA viruses | back 132 herpes simplex viruses 1 and 2 human papillomaviruses pox viruses |
front 133 fungi | back 133 candida albicans |
front 134 protozoa | back 134 trichomonas vaginalis |
front 135 helminth-trematode | back 135 schistosoma haematobium |