Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Bones of the skeleton
front 1 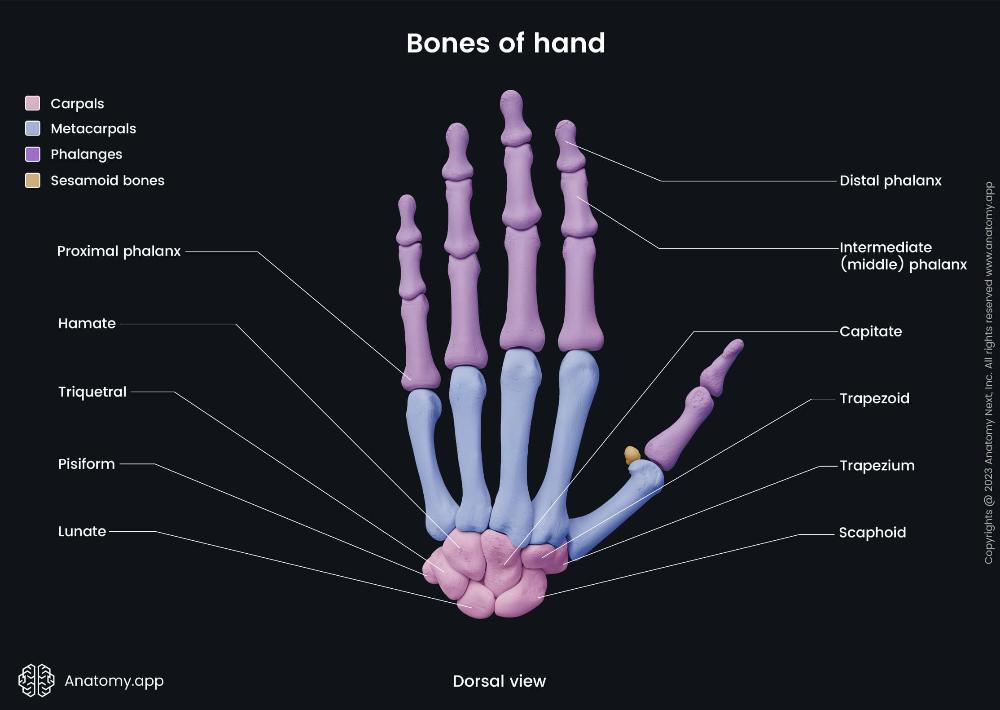 Hand (distal phalanx) | back 1 Articulates with the middle phalanx at the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint and features a rough, horseshoe-shaped tuberosity on the palmar side. |
front 2  Hand (intermediate phalanx) | back 2 Its main features include a base with two concave articular facets to connect with the proximal phalanx. |
front 3  Hand (proximal phalanx) | back 3 The main features of the proximal phalanx are its structure, which includes a base, a diaphysis (body), and a head, and its specific articulations at each end |
front 4  Hand (Hamate) | back 4 Wedge-shaped carpal bone with a hook; articulates with capitate, triquetral, 4th and 5th metacarpals; forms ulnar carpal tunnel boundary. |
front 5  Hand (triquetral) | back 5 Pyramidal carpal bone; articulates with pisiform, lunate, and hamate; on ulnar side; forms part of wrist joint capsule. |
front 6  Hand (Capitate) | back 6 Largest carpal bone; centrally located; articulates with third metacarpal, scaphoid, lunate, trapezoid, and hamate bones. |
front 7  Hand (Trapezoid) | back 7 Small wedge-shaped carpal bone; articulates with second metacarpal, trapezium, capitate, and scaphoid; located lateral to capitate. |
front 8  Hand (Trapezium) | back 8 Saddle-shaped carpal bone; articulates with first metacarpal, scaphoid, and trapezoid; allows thumb opposition and mobility. |
front 9  Hand (Scaphoid) | back 9 Boat-shaped carpal bone; articulates with radius, lunate, trapezium, and capitate; has tubercle; commonly fractured bone. |
front 10  Hand (Pisiform) | back 10 Small pea-shaped sesamoid bone; lies in flexor carpi ulnaris tendon; articulates only with triquetral; palpable on wrist. |
front 11  Hand (Lunate) | back 11 Crescent-shaped carpal bone; articulates with radius, scaphoid, triquetral, and capitate; central wrist bone aiding flexion-extension. |
front 12 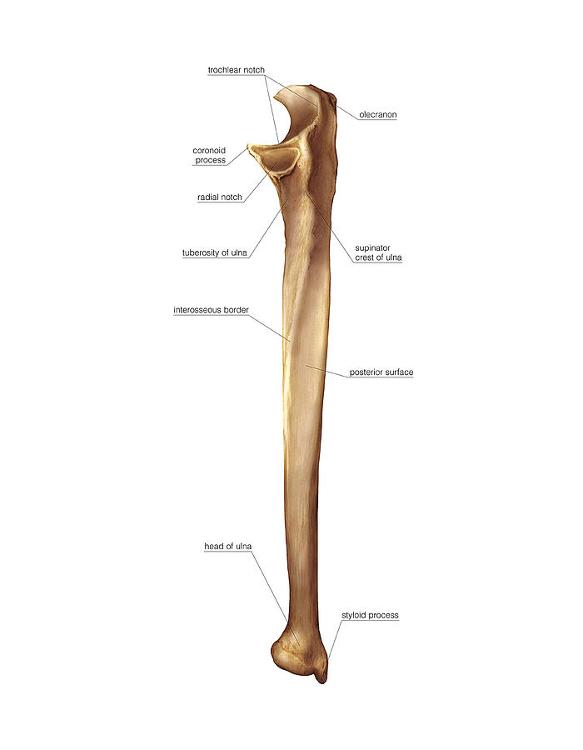 Ulna (Trochlear notch) | back 12 Large curved notch of ulna; articulates with humeral trochlea; enables elbow hinge movement (flexion and extension). |
front 13  Ulna (Olecranon) | back 13 Proximal ulna prominence; forms elbow tip; articulates with humerus trochlea; attachment for triceps tendon; enables elbow extension leverage. |
front 14  Ulna (Coronoid process) | back 14 Anterior ulna projection; fits humeral trochlea; stabilizes elbow; attachment for brachialis and ulnar collateral ligament. |
front 15  Ulna (Styloid Process) | back 15 A small, pointed projection at the distal end of the ulna, providing attachment for ligaments of the wrist. |
front 16  Ulna (Head) | back 16 The distal, rounded end of the ulna; articulates with the ulnar notch of the radius |
front 17  Ulna (Posterior surface) | back 17 The back surface of the ulna shaft, providing attachment for several forearm muscles. |
front 18  Ulna (Interosseous border) | back 18 The sharp ridge along the lateral side of the ulna where the interosseous membrane attaches, connecting the ulna to the radius |
front 19  Ulna (Supinator crest) | back 19 A ridge located below the radial notch; attachment site for part of the supinator muscle. |
front 20  Ulna (Tuberosity) | back 20 A roughened area just below the coronoid process; site of attachment for the brachialis muscle. |
front 21  Ulna (Radial notch) | back 21 A small depression on the lateral side of the coronoid process where the head of the radius articulates with the ulna. |
front 22 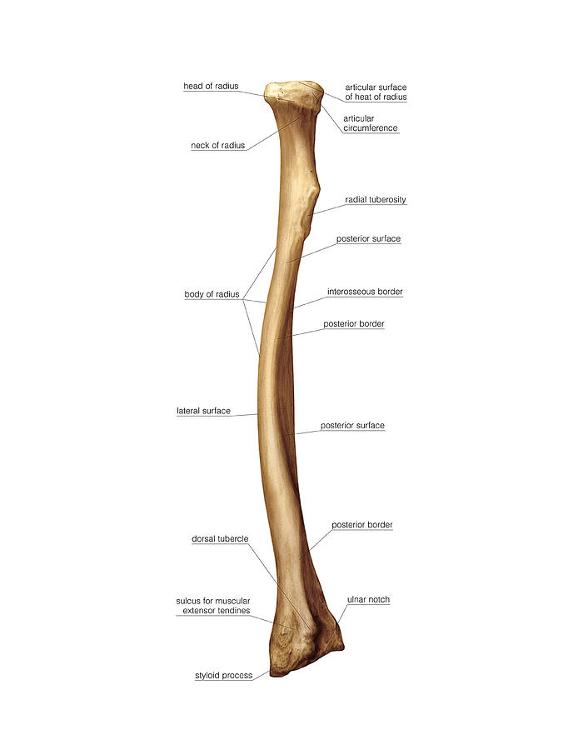 Radius (Head) proximal end | back 22 The disc-shaped top part that articulates with the capitulum of the humerus and the radial notch of the ulna. |
front 23  Radius (Articular surface of head of radius ) proximal end | back 23 The concave superior surface of the head that articulates with the capitulum of the humerus. |
front 24  Radius (Articular circumference ) proximal end | back 24 The smooth, rounded area around the edge of the head that articulates with the radial notch of the ulna, allowing rotation. |
front 25  Radius (Neck) proximal end | back 25 The narrow area just below the head; it supports the head and serves as an attachment site for ligaments. |
front 26  Radius (Radial tuberosity) proximal end | back 26 A bony prominence below the neck on the medial side; attachment site for the biceps brachii tendon. |
front 27  Radius (shaft) of radius body | back 27 The long, central portion of the bone. |
front 28  Radius (Lateral surface) body | back 28 The outer surface; relatively smooth and gives attachment to muscles such as the supinator. |
front 29  Radius (Posterior surface) body | back 29 The back surface of the shaft; gives attachment to the abductor pollicis longus and extensor muscles. |
front 30  Radius (Interosseous border) body | back 30 The sharp medial ridge where the interosseous membrane attaches, connecting the radius and ulna. |
front 31  Radius (Styloid process) Distal End | back 31 The pointed projection on the lateral side of the distal radius; provides attachment for ligaments of the wrist. |
front 32  Radius (ulnar notch) Distal end | back 32 The concave depression on the medial side of the distal radius that articulates with the head of the ulna |
front 33 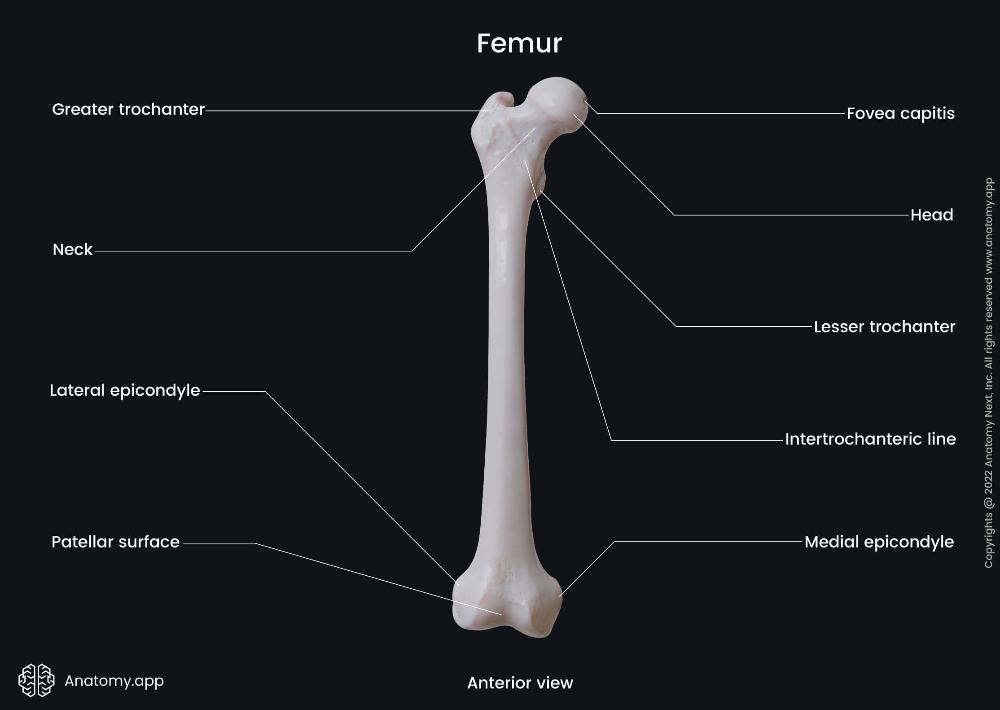 Femur (Head) Proximal End | back 33 The rounded, smooth portion that articulates with the acetabulum of the pelvis to form the hip joint. |
front 34  Femur (Neck) Proximal End | back 34 The constricted region just below the head; connects the head to the shaft and allows range of motion at the hip. |
front 35  Femur (Greater trochanter) Proximal End | back 35 The large, lateral projection that serves as an attachment site for gluteal muscles (gluteus medius, minimus, and piriformis). |
front 36  Femur (Lesser trochanter) Proximal End | back 36 The smaller, posteromedial projection where the iliopsoas muscle attaches. |
front 37  Femur (Lateral epicondyle) Distal End | back 37 A projection on the outer side of the distal femur; provides attachment for the lateral collateral ligament of the knee. |
front 38  Femur (Medial epicondyle) Distal End | back 38 A projection on the inner side of the distal femur; provides attachment for the medial collateral ligament of the knee. |
front 39 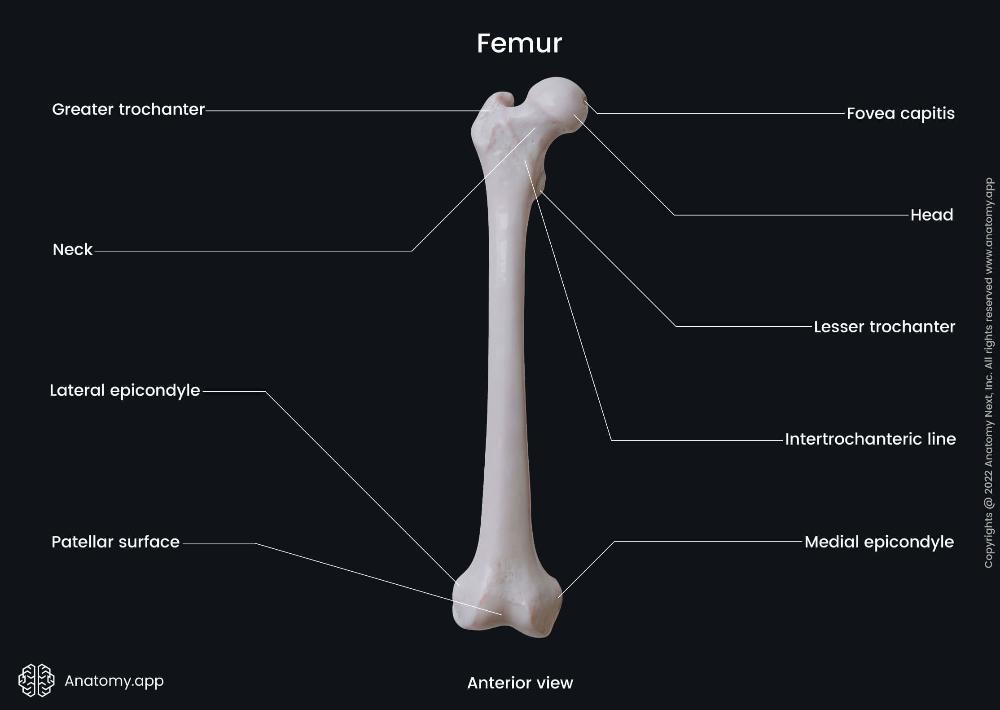 Femur (Patellar surface) Distal End | back 39 The smooth anterior surface between the condyles where the patella (kneecap) articulates with the femur. |
front 40 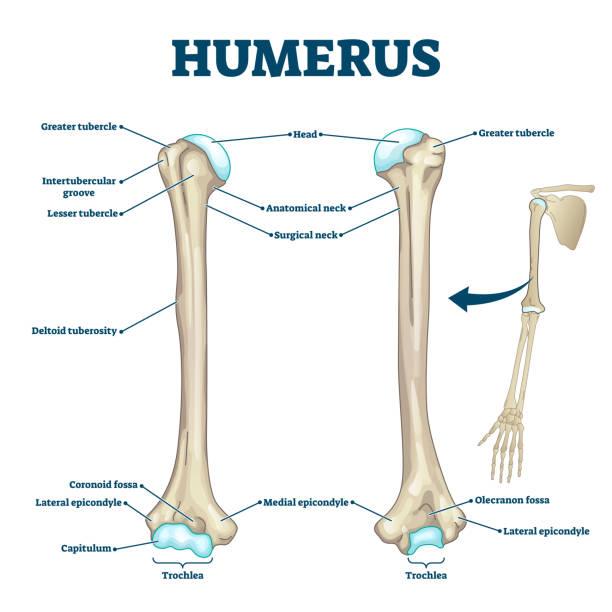 Humerus (Head) Proximal End | back 40 <p data-start="295" data-end="430">The rounded upper part of the humerus that articulates with the glenoid cavity of the scapula, forming the shoulder joint.</p> <br> |
front 41  Humerus (Greater tubercle) Proximal End | back 41 Large projection on the lateral side of the humerus; attachment site for supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres minor muscles |
front 42  Humerus (Lesser tubercle) Proximal End | back 42 Smaller projection on the anterior surface; attachment site for the subscapularis muscle. |
front 43  Humerus (Intertubercular groove) Proximal End | back 43 The groove between the greater and lesser tubercles where the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii runs. |
front 44  Humerus (Deltoid tuberosity) Body | back 44 Roughened area on the lateral surface of the shaft; insertion point for the deltoid muscle. |
front 45  Humerus (Medial epicondyle) Distal End | back 45 Large projection on the medial side; attachment site for forearm flexor muscles. |
front 46  Humerus (Lateral epicondyle ) Distal End | back 46 Smaller projection on the lateral side; attachment site for forearm extensor muscles |
front 47  Humerus (Capitulum) Distal End | back 47 Rounded knob on the lateral side of the distal humerus that articulates with the head of the radius. |
front 48  Humerus (Trochlea) Distal End | back 48 Spool-shaped surface on the medial side that articulates with the trochlear notch of the ulna |
front 49  Humerus (Coronoid fossa ) Distal End | back 49 Depression above the trochlea on the anterior side; receives the coronoid process of the ulna during elbow flexion. |
front 50  Humerus (Olecranon fossa ) Distal End | back 50 Large depression on the posterior side; receives the olecranon of the ulna when the elbow is extended. |
front 51 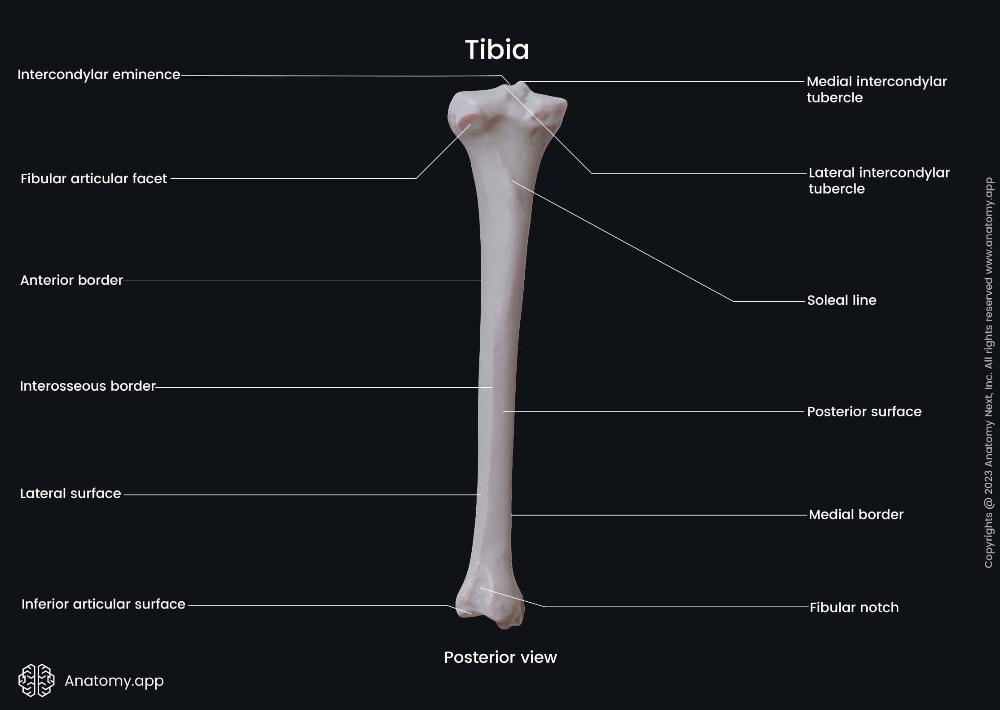 Tibia Proximal End | back 51 intercondylar eminence – The raised ridge between the medial and lateral condyles; provides attachment for the cruciate ligaments and menisci of the knee. Medial intercondylar tubercle – A prominence on the medial side of the intercondylar eminence; attachment site for ligaments and menisci. Lateral intercondylar tubercle – A prominence on the lateral side of the intercondylar eminence; also serves as a ligament and meniscus attachment point. |
front 52  Tibia Body | back 52 Anterior border (shin) – The sharp ridge along the anterior surface; easily palpable under the skin (the “shin bone”). Posterior surface – The back surface of the tibial shaft; provides attachment for several leg muscles, including the popliteus. Medial border – The inner ridge of the tibial shaft, forming the medial contour of the leg. Lateral surface – The outer surface of the shaft; attachment site for muscles like the tibialis anterior. |
front 53  Tibia Distal End | back 53 Inferior articular surface – The smooth surface at the bottom of the tibia; articulates with the talus bone of the ankle join Fibular notch – A shallow depression on the lateral side of the distal tibia; articulates with the distal end of the fibula to form the tibiofibular joint. |
front 54  scapula features | back 54 Spine of scapula – The prominent ridge running across the posterior surface of the scapula; divides it into the supraspinous and infraspinous fossae. Acromion – The broad, flat projection extending laterally from the spine; articulates with the clavicle to form the acromioclavicular (AC) joint. Coracoid process – A hook-like projection on the anterior surface of the scapula (visible from posterior in part); provides attachment for muscles like the pectoralis minor, short head of biceps brachii, and coracobrachialis. Scapular notch (suprascapular notch) – A small indentation on the superior border; allows passage of the suprascapular nerve. |
front 55 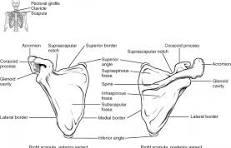 scapula (Fossae Depressions)) | back 55 Supraspinous fossa – The shallow depression above the spine; origin site for the supraspinatus muscle Infraspinous fossa – The larger depression below the spine; origin site for the infraspinatus muscle. |
front 56 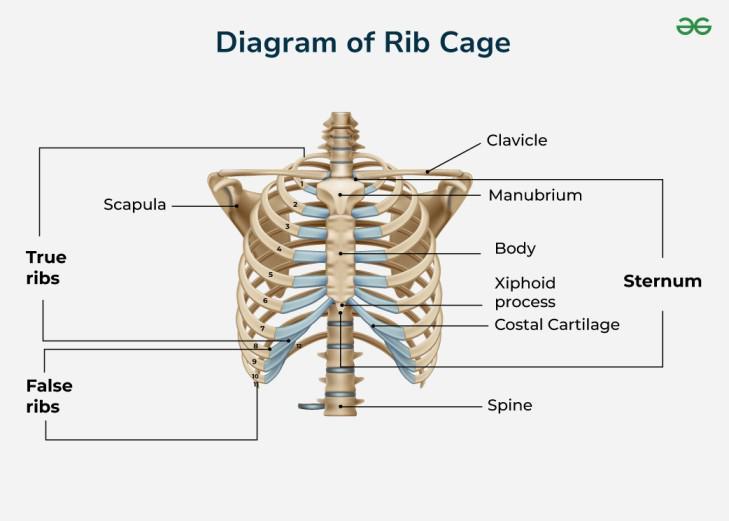 Ribs (sternum) | back 56 Located in the center of the chest; it connects to the ribs via costal cartilages. |
front 57  Ribs (Manubrium) | back 57 Upper part of the sternum; articulates with the clavicles (collarbones) and first pair of ribs. |
front 58  Ribs (Body) | back 58 The long, middle portion; articulates with ribs 2–7 via costal cartilages. |
front 59  Ribs (Xiphoid Process) | back 59 Small, cartilaginous lower tip that ossifies (turns to bone) with age. |
front 60  Ribs (True Ribs (1–7) | back 60 Attach directly to the sternum through their own costal cartilages. |
front 61  Ribs (False Ribs (8-10) | back 61 Attach indirectly to the sternum via the cartilage of the rib above them. |
front 62  Ribs (Floating Ribs (11-12) | back 62 A subset of false ribs that do not attach to the sternum at all; they end in the posterior abdominal wall. |
front 63 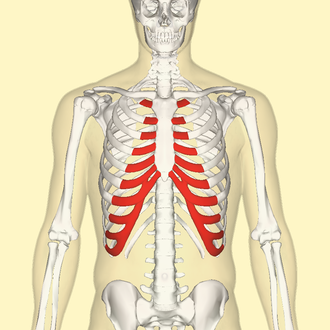 Costal Cartilage | back 63
|
front 64  Rib Cage Function | back 64
|
front 65 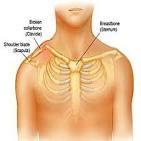 Clavicle (Collarbone) | back 65 The clavicle is a long, S-shaped bone that connects the arm to the trunk, with key features including its S-shape, two ends, and lack of a medullary cavity |
front 66 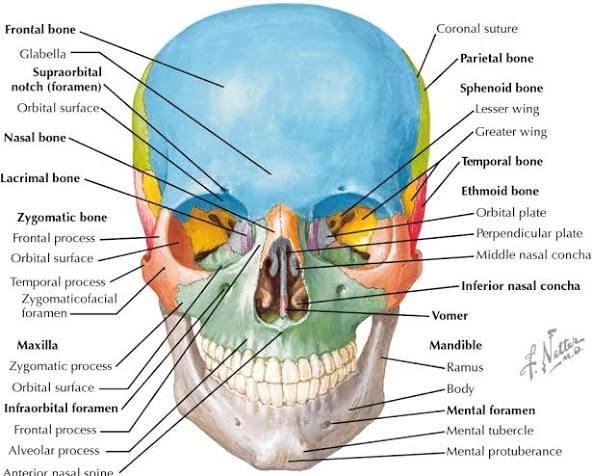 Maxilla | back 66 Upper jaw; alveolar process, infraorbital foramen, palatine process. |
front 67  Zygomatic | back 67 Cheekbone; temporal, frontal, maxillary processes, zygomatic arch. |
front 68  Nasal | back 68 Bridge of nose; forms upper nasal structure. |
front 69  Lacrimal | back 69 Medial orbit wall; lacrimal fossa for tear duct. |
front 70  Palatine | back 70 Posterior hard palate; horizontal and perpendicular plates. |
front 71  Vomer | back 71 Lower nasal septum; thin vertical plate. |
front 72  Mandible | back 72 Lower jaw; body, ramus, condylar process, mental foramen. |
front 73 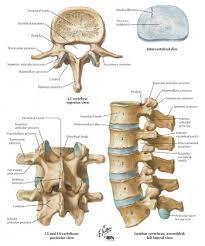 <p data-start="73" data-end="178">Cervical Vertebrae (C1–C7)</p> <br> | back 73 –Small body, transverse foramen, bifid spinous process (except C1, C7). |
front 74  Atlas (C1) – | back 74 No body; anterior/posterior arches; supports skull. |
front 75  <ul> <li data-start="253" data-end="316">Axis (C2) – Dens (odontoid process) for head rotation.</li> </ul> <br> | back 75 Dens (odontoid process) for head rotation. |
front 76  Thoracic Vertebrae (T1–T12) | back 76 Heart-shaped body; costal facets for ribs; long spinous process. |