Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Lab exam 2
front 1 Check all the statements that are true regarding the subcutaneous layer (hypodermis). | back 1 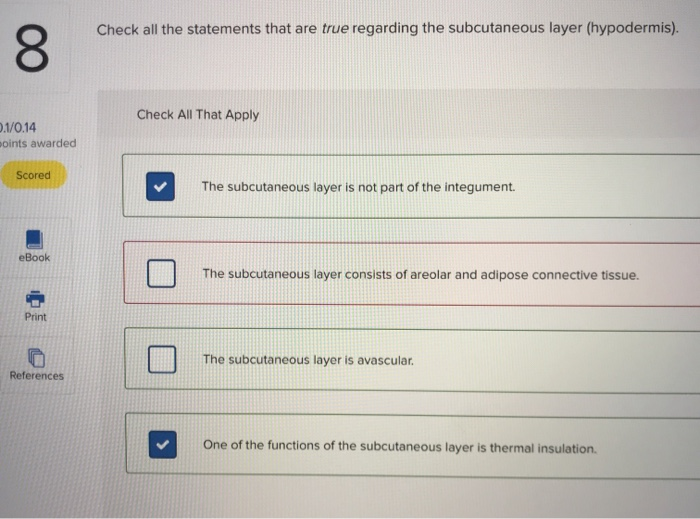 |
front 2 Check all layers that are affected by third-degree burns. | back 2 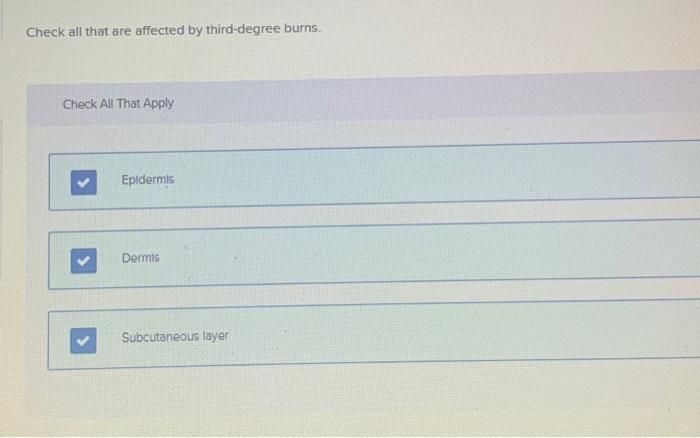 |
front 3 Click and drag each descriptive label into the appropriate category
based on whether it pertains to | back 3 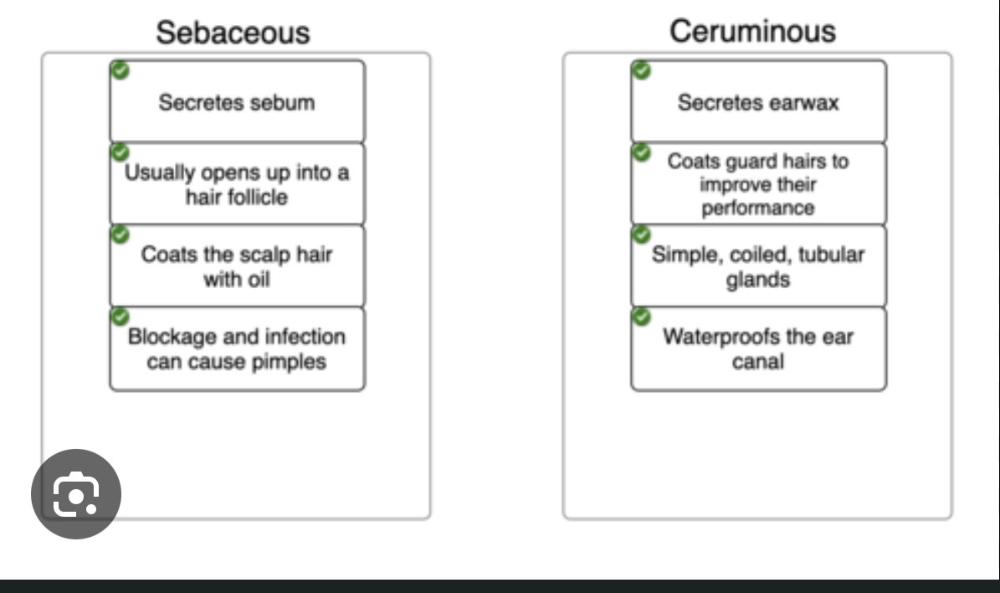 |
front 4 A gland secreting its products via a duct to the surface of the small
intestine epithelium must be an: | back 4 exocrine gland |
front 5 Which feature distinguishes a holocrine gland from a merocrine and an apocrine gland? | back 5 Secretions are released by rupture of whole cells |
front 6 Ligaments are very strong but resistant to stretching; which protein fiber probably predominates? | back 6 Collagen |
front 7 he visible part of the ear can stretch significantly and then recoil
back to its original position; which | back 7 ELASTIN |
front 8 Whether all connective tissues contain three basic components: cells,
protein fibers, and ground | back 8 TRUE |
front 9 THE specific layer of the integument from which sweat glands and sebaceous glands develop? | back 9 Reticular layer of dermis |
front 10 Click and drag the terms on the left to accurately complete the
sentences on the right. | back 10
|
front 11 Indicate whether each statement is true or false. | back 11
|
front 12 The subcutaneous layer of skin consists of | back 12 Areolar and adipose |
front 13 Keratinocytes play an important role in producing which vitamin | back 13 Vitamin D |
front 14 Milk and ear wax are not secretions. are secreted from modified sweat glands. are secreted from modified sebaceous glands. are in the blood. are synthetic substances. | back 14 are secreted from modified sweat glands. |
front 15 Another name for the skin is the _________ membrane. | back 15 cutaneous membrane |
front 16 Match these cells found in connective tissues to their functions. Cells that form fibers and ground substance in the extracellular matrix Cells that form bone Cells that are trapped in lacunae Cells that break down bone | back 16
|
front 17 The organ system that the mammary glands belong to | back 17 female reproductive system. |
front 18 Match the type of ossification (Intramembranous vs Endochondral) with
its brief | back 18 Intramembranous Ossification: Ossification that develops from mesenchyme Endochondral Ossification: Begins with a hyaline cartilage model |
front 19 Match each hormone (Calcitonin vs PTH vs Thyroid) with its
stimulatory effect on the | back 19 Calcitonin encourages calcium deposition from blood into bone, reducing blood calcium levels. Parathyroid hormone stimulates osteoclasts to resorb bone, increasing blood calcium. Thyroid hormone influences the basal metabolic rate of bone cells, affecting bone turnover. |
front 20 Match each label with the bone cell-type (Osteoprogenitor cells;
Osteoblasts; | back 20 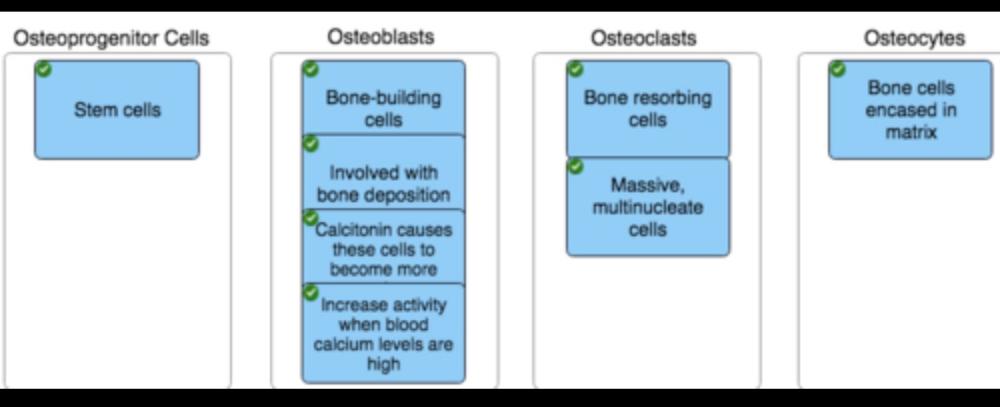 |
front 21 Classify some (4) images of specific bones into the correct bone-type they represent. | back 21 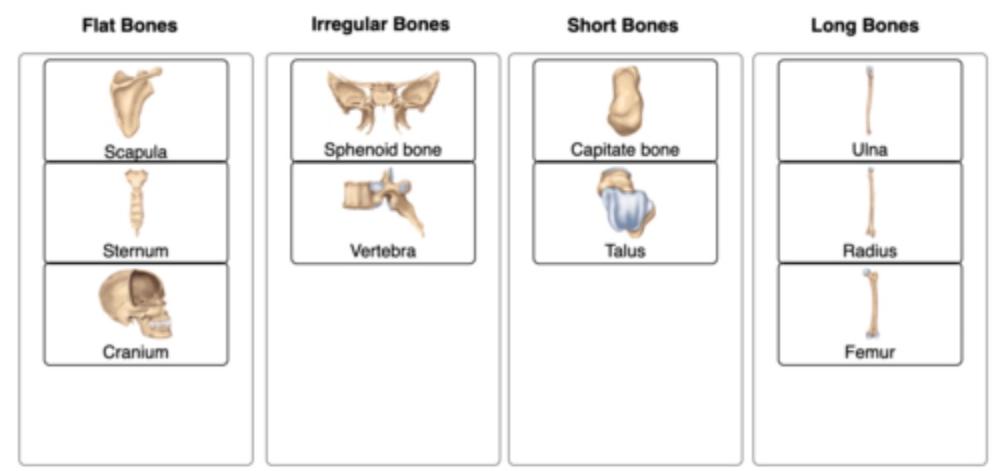 |
front 22 Correctly label the anatomical parts (3) of a flat bone image. | back 22 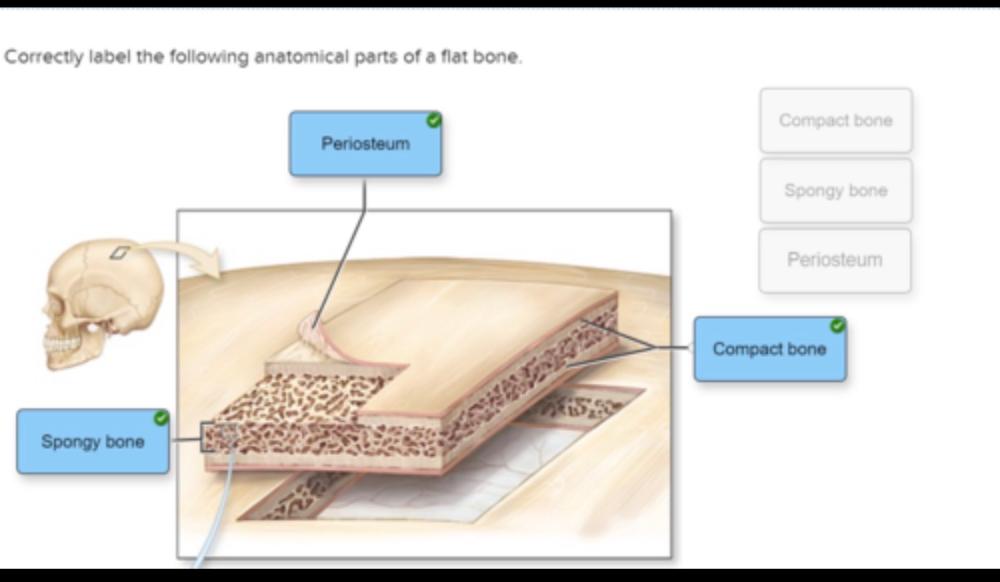 |
front 23 From a list of items (6), place each one into the correct category of
either spongy bone | back 23 Here are the answers for the questions: Question 1: Spongy Question 2: Spongy Question 3: Spongy Question 4: Compact Question 5: Compact Question 6: Compact |
front 24 Indicate whether each listed hormone (2) increases or decreases blood calcium levels. | back 24 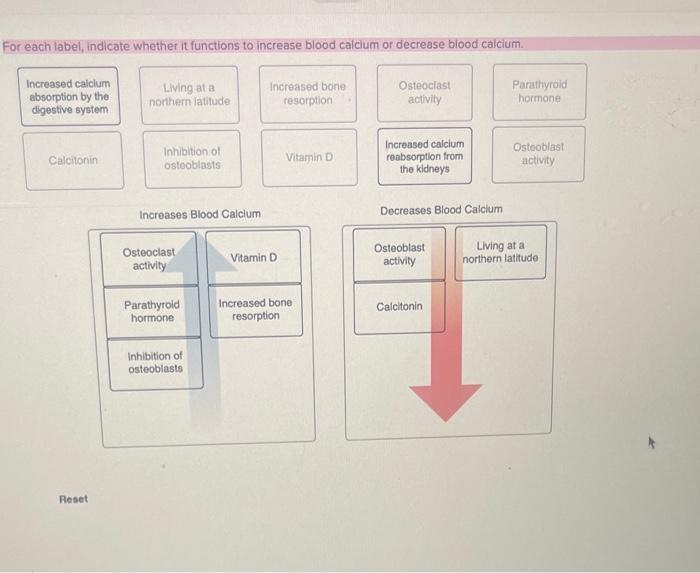 |
front 25 Place each of provided terms or examples within its correct bone
marrow type (Red | back 25  |
front 26 no data | back 26 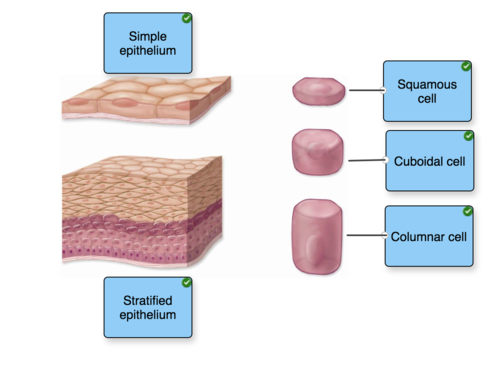 |
front 27 no data | back 27 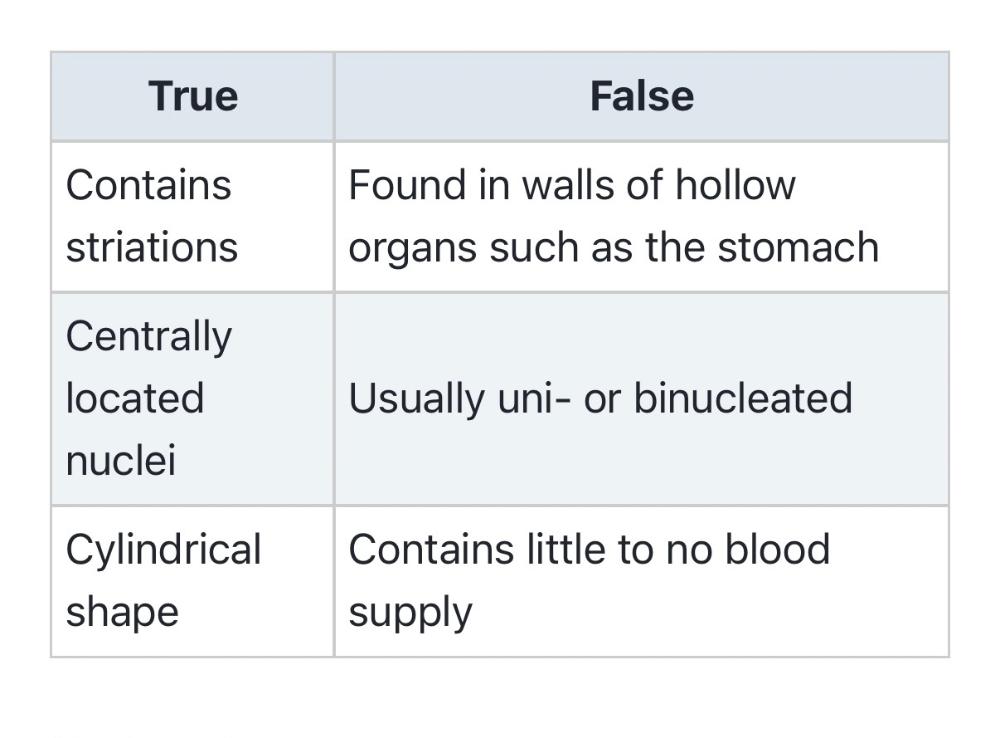 |
front 28 no data | back 28 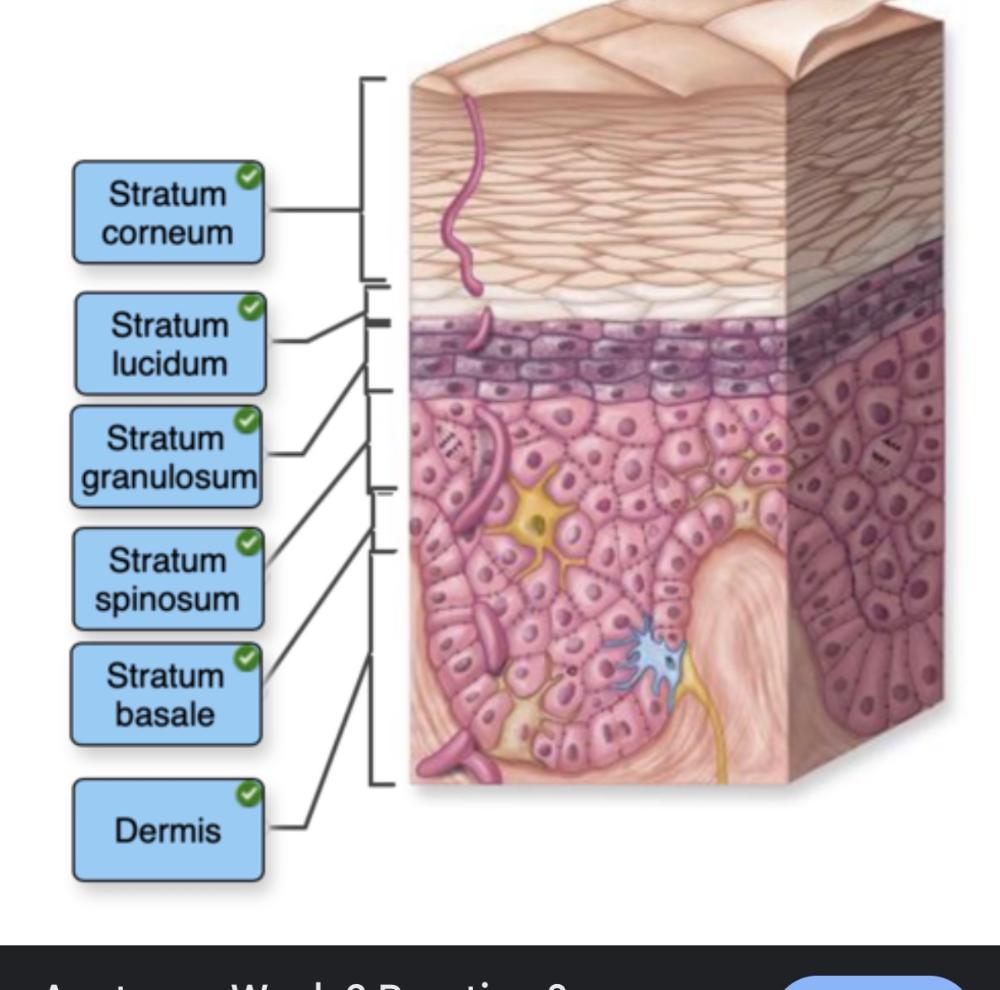 |
front 29 no data | back 29 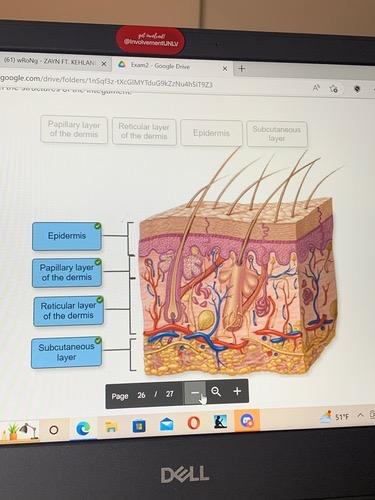 |
front 30 no data | back 30 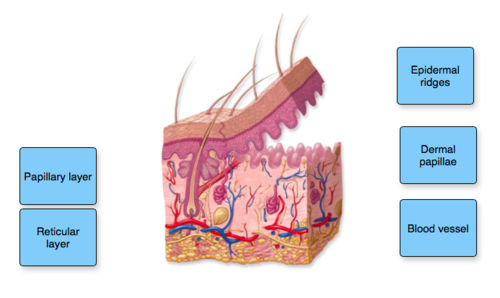 |
front 31 no data | back 31 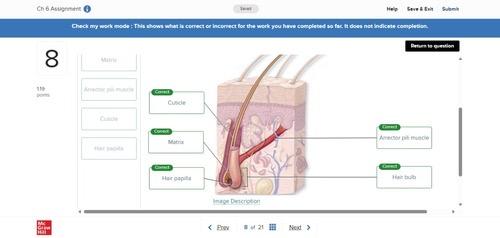 |
front 32 no data | back 32 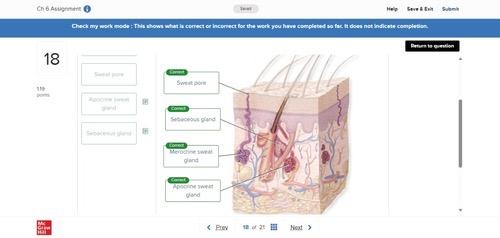 |
front 33 no data | back 33 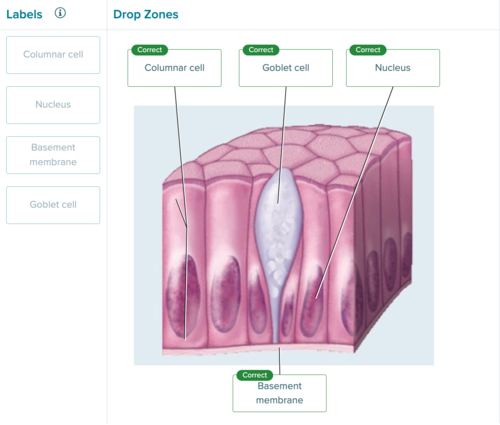 |
front 34 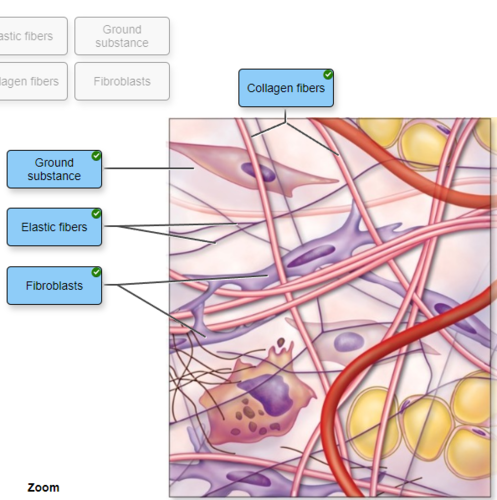 | back 34 no data |