Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
ochem II lab quizzes
front 1 What is meant by the term bumping? | back 1 Sudden and uncontrolled boiling of liquid |
front 2 What is the best technique for removing a round bottom flask from an oil bath? | back 2 Wearing heat-resistant gloves, raise the clamp to lift the flask out of the oil bath. Allow the flask to cool for a while, then use a paper towel to wipe any oil from the bottom of the flask. |
front 3 Identify items that can be used to control the boiling when heating liquid in a round bottom flask. | back 3 A stir bar and stir plate Boiling chips or stones |
front 4 According to Markovnikov's rule of the electrophilic addition to an alkene, the electrophile, usually a proton, is more likely to add to the ______ in a double bond. This arrangement places the intermediate carbocation on the _______, which stabilizes it with the presence of ______. In the major product of a reaction following Markovnikov's rule, the _______ will then end up on the more-substituted carbon in a double bond. | back 4 less-substituted carbon more-substituted carbon more substituents neutrophile |
front 5 Determine whether each alcohol could be a major product of the acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene. | back 5 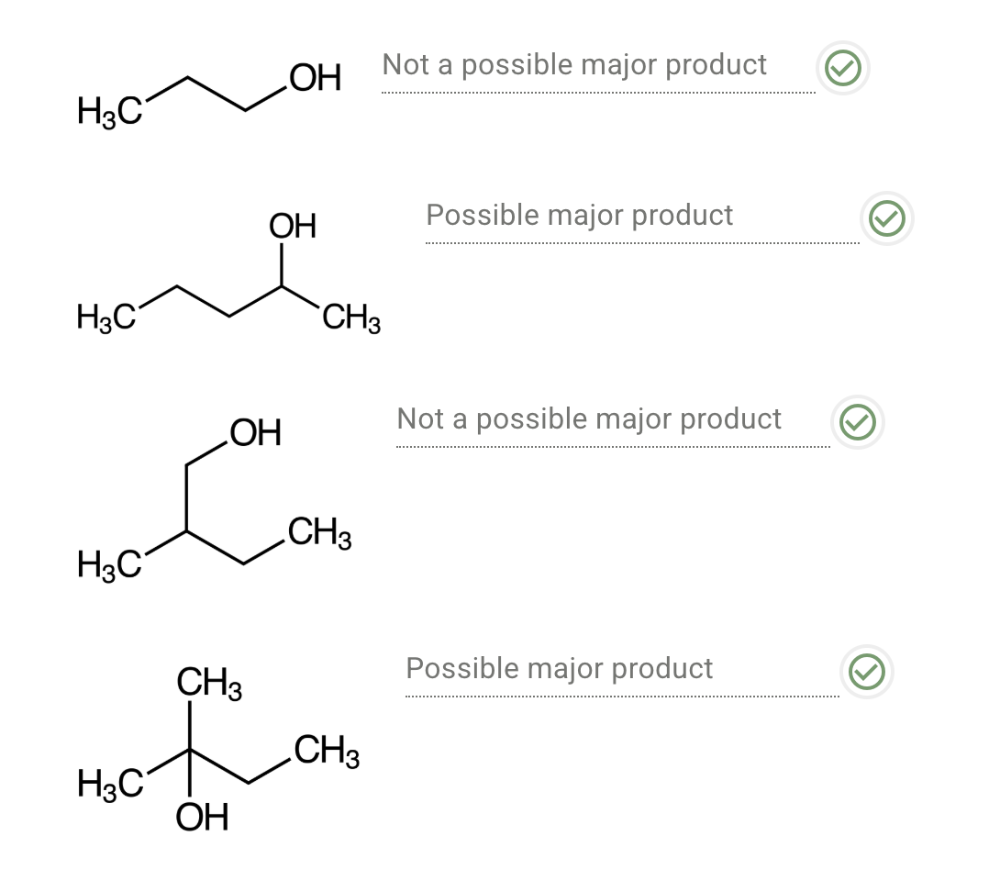 |
front 6 Determine the order of steps in the mechanism of acid-catalyzed hydration of propene. First step | back 6 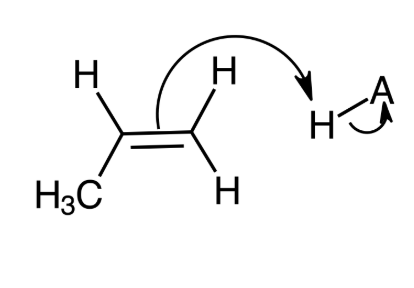 |
front 7 Determine the order of steps in the mechanism of acid-catalyzed hydration of propene. Second step | back 7 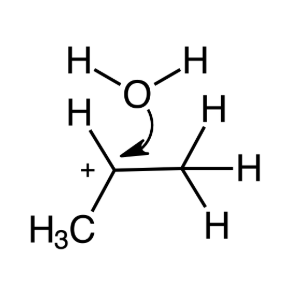 |
front 8 Determine the order of steps in the mechanism of acid-catalyzed hydration of propene. Third step | back 8 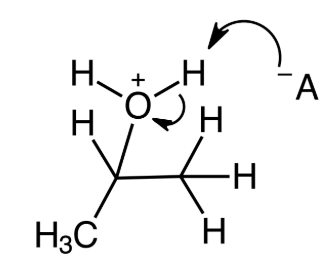 |
front 9 In general, what are the possible products of an acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene? | back 9 Primary alcohol secondary alcohol tertiary alcohol |
front 10 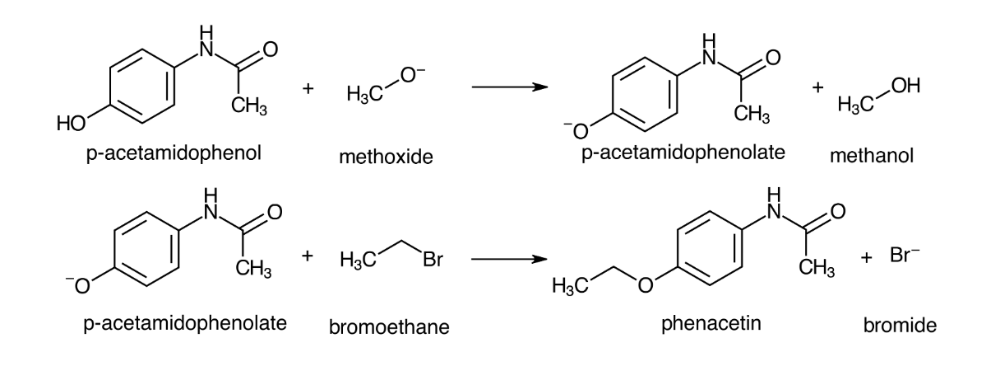 Consider the mechanism of forming phenacetin from p-acetaminophenol, bromoethane, and methoxide. Identify the species that performs each listed role in the reaction. Acid____ Base____ Leaving group ____ | back 10 Acid: p-Acetamindophenol Base: Methoxide Leaving group: Bromide Nucleophile: p-Acetamindophenolate |
front 11 In Williamson ether synthesis, you start by adding a base like methoxide to deprotonate a phenol so the deprotonated phenolate can act as nucleophile. The moles of base should be ____ the moles of phenol. Less base might result in the phenol ______. More base might result in the base_____. | back 11 Equal to not reacting completely acting as the nucleophile |
front 12 The SN2 mechanism occurs in _____ with the nucleophile attacking _____ the leaving group leaves. Therefore, unsubstituted electrophiles react _____ than substituted electrophiles due to the ______. | back 12 one step, at the same time Faster, decreased crowding |
front 13 During a recrystallization, the goal is to form purified crystals of a solid out of solution. However, you might form an oil instead. How should you respond if an oil forms during your recrystallization? | back 13 Add more of the recrystallization solvent to form a solution before cooling again |
front 14 What is the recommended order of measurements to report the most accurate melting point possible? Use slow heating to carefully observe melting_____ Use slow heating to confirm the careful measurement_____ Use quick heating to estimate the melting point_____ | back 14 second step third step first step |
front 15 What characteristics should a good sample for melting point determination have? | back 15 Solid phase small particles thoroughly dry |
front 16 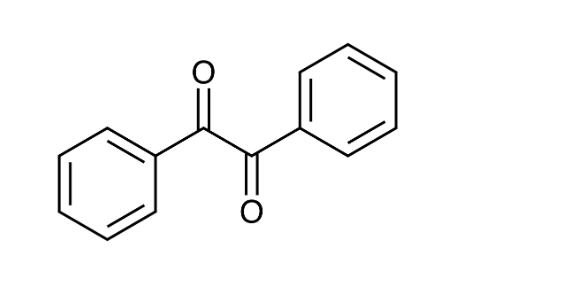 Consider the structure of benzil and its reduction. The functional group reduced in benzil is ___. An appropriate reducing agent for this reaction is _____ | back 16 a ketone sodium borohydride |
front 17 Is often the ending point of an arrow in a mechanism____ | back 17 proton |
front 18 Is often the starting point of an arrow in a mechanism____ | back 18 hydride |
front 19 Can act as a nucleophile | back 19 hydride |
front 20 Can act as an electrophile | back 20 proton |
front 21 Can act as a reducing agent | back 21 hydride |
front 22 Can act as an oxidizing agent | back 22 proton |
front 23 Suppose you notice a solid impurity in a small liquid sample with a volume less than 10 mL. What technique can you use to remove the solid impurity? | back 23 Filter the sample through a Pasteur pipet with glass wool in it |
front 24 What statements about the possible hazards of sodium borohydride are correct? | back 24 Sodium borohydride is corrosive. Sodium borohydride is flammable. Sodium borohydride can have a violent reaction with acids |