Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Graph theory
front 1 Graph | back 1 consists of points (called vertices or nodes) which are connected by lines (edges or arcs) |
front 2 Weighted graph / network | back 2 A graph where the edges have associated values (weights) |
front 3 Vertex set | back 3  A, B, C, D, E, F, the vertices within a graph |
front 4 Edge set | back 4  AD, AE, BA, BC, CE, CF, DE, EF, the edges within the graph (G) |
front 5 Subgraph of G | back 5 A graph, each of whose vertices belong to the original graph (G) and each of whose edges belong to G. It is simply a part of the original graph. |
front 6 Degree, Order, or Valency of a vertex | back 6  The no. of edges incident to the vertex A: 3, B: 2 etc. |
front 7 Even vertex | back 7 vertex with an even degree |
front 8 Odd vertex | back 8 vertex with an odd degree |
front 9 Walk | back 9 A route through a graph along edges and from one vertex to another (can be multiple vertices and edges) |
front 10 Path | back 10 A walk where no vertex is visited more than once |
front 11 Trail | back 11 A walk where no edge is visited more than once |
front 12 Cycle | back 12 A walk where the end vertex is the same as the start vertex and no vertex is visited more than once |
front 13 Hamiltonian cycle | back 13 A cycle which includes every vertex. |
front 14 Connected graph | back 14 Where every vertex is connected, in some way, to the graph. (Vertices are connected when there is an arc connecting them) |
front 15 Loop | back 15 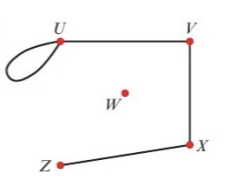 Edge that starts and finishes at the same vertex |
front 16 Simple graph | back 16 A graph with no loops and up to one arc connecting the same two vertex |
front 17 Directed graph | back 17 Graphs where direction is associated to each arc, often shortened to digraph |
front 18 The Handshake Lemma | back 18 Th sum of the degrees of the vertices is equal to 2x the number of edges, as a consequence the number of vertices must be even. This is known as Euler's Handshake Lemma. |