Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
AERO 201 Lectures 1-5
front 1 What are the four basic aerodynamic forces | back 1 Thrust, Lift, Drag, Weight |
front 2 What is the equation of a unit vector | back 2 unit vector = vector / magnitude |
front 3 what is the dot product of two vectors | back 3 |vector a| |vector b| cos (theta) or (a1b1) + (a2b2) + (a3b3) |
front 4 what is the cross product between two vectors | back 4 |vector a| |vector b| sin (theta) |
front 5 What is Cramer's Rule | back 5 (practice problems) |
front 6 What is sheer stress and tangential stress | back 6 tangential stress is when a force acts at an angle to the surface Sheer stress is when a force acts parallel to the surface Sheer stress is always tangential stress, but not all tangential stress is sheer stress |
front 7 What are the four fundamental quantities of a fluid | back 7 Pressure, Density, Temperature, Velocity |
front 8 A fluid is a substance which ______________________. | back 8 Cannot resist an applied sheer stress |
front 9 What are the two types of fluids | back 9 Incompressible (liquid) and Compressible |
front 10 Define Pressure | back 10 The normal force per unit area P=F/A Units: N/m^2, lb/ft^2 |
front 11 Define Density | back 11 Mass per unit volume p=m/V units: kg/m^3, slug/ft^3, lbm/ft^3 |
front 12 Define Temperature | back 12 average Kinetic Energy of the particles in a gas KE=(3/2)kT where k is the Botlzmann constant (k=1.38 * 10^-23 J/K) Units: K, C, R, F |
front 13 when the flow is steady, the moving elements make fixed paths in space called ____________. | back 13 streamlines |
front 14 What is a flow field? | back 14 (search this up later) |
front 15 What is a perfect/ideal gas? | back 15 one which the intermolecular forces are negligible and where particles are widely separated (low density) |
front 16 What is the equation of state? | back 16 P=pRT R is the specific gas constant |
front 17 What is specific volume? | back 17 The volume per unit mass. It is the inverse of density |
front 18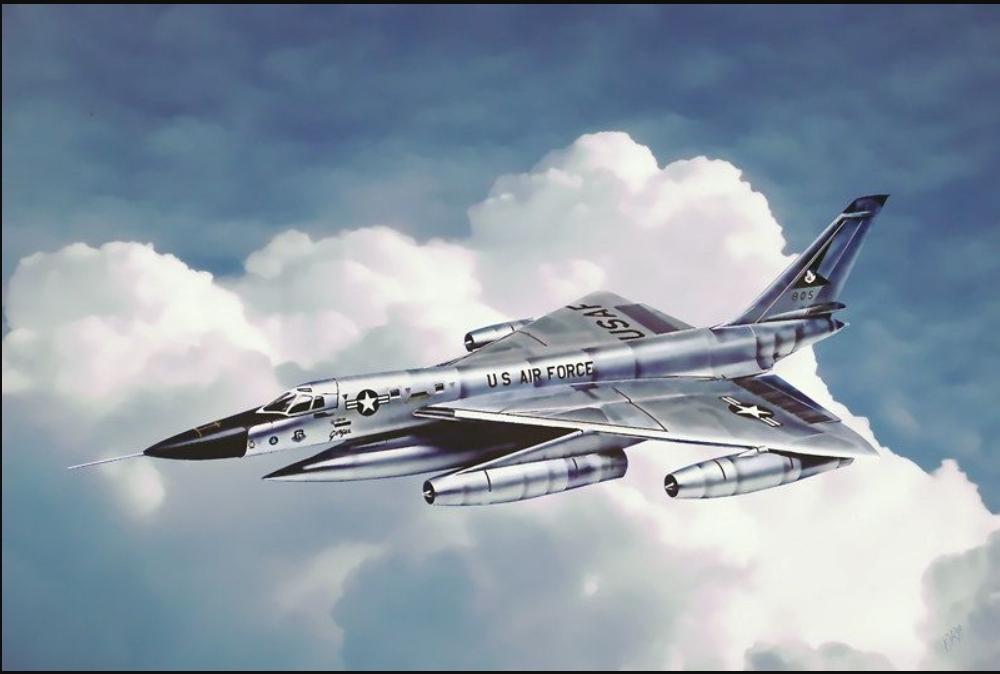  What is this plane and what is it known for? | back 18 Convair B-58 Hustler First supersonic strategic bomber capable of Mach 2 flight Delta wing |
front 19 what type of flow has a constant velocity that does not change or fluctuate with time? | back 19 A steady flow |
front 20 What do you call the path taken by a moving fluid element | back 20 a streamline |
front 21 What are the two aerodynamic forces? | back 21 Lift and Drag |
front 22 The aerodynamic force exerted by the airflow on a surface stem from two sources: | back 22 1. Pressure Distribution on the surface 2. Shear stress (friction) distribution on the surface |
front 23 What is shear stress? | back 23 the force per unit area acting tangentially (parallel) on a surface due to friction tangential force times the surface area |
front 24 What are the two types of payload? | back 24 Fixed payload (passengers, cargo, etc) drop payload (skydivers, water, dust) |
front 25 What happens when the pressure below the wing is greater than the pressure above the wing | back 25 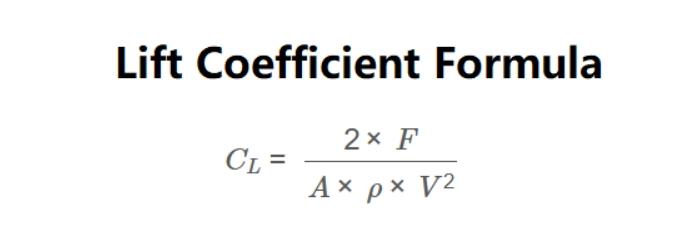 Lift! The lift coefficient equation is C_L = L / q(bar) S where q(bar) is called the dynamic pressure, and it is given by q(bar) = (1/2)pv^2 (v is the free stream velocity) |
front 26 Where does lift come from? | back 26 Lift occurs when a moving flow of fluid is turned by a solid object. The flow is turned in one direction and lift is generated in the opposite direction. if there is no motion or no fluid, then there is no lift. |
front 27 what is the difference between wind tunneling and actual flight? | back 27 Wind tunneling is when the headwinds are equal to the thrust, so the plane's speed relative to the ground is zero. When the plane is moving relative to the ground, it is called actual flight |
front 28 What are the three moves an airplane can make? | back 28 Pitch (up and down) Roll (rolling around) Yaw (left and right) |
front 29 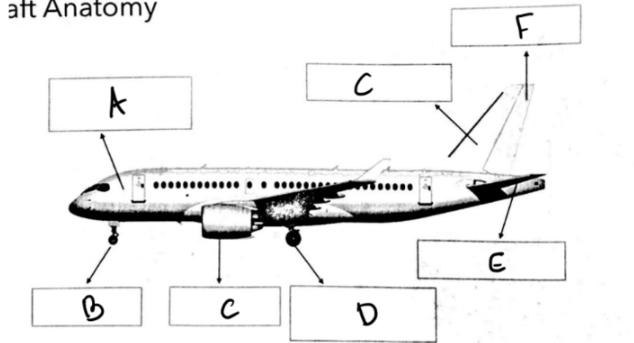 What is A? | back 29 Fuselage: Carries people, cargo, payload |
front 30  What is G? | back 30 Vertical Stabilizer: yaw stability |
front 31  What is F? | back 31 Rudder: provides yaw control (left and right motion) |
front 32  What is E? | back 32 Horizontal Stabilizer: pitch stability (up and down) H-stab, H tail |
front 33  What is the combination of E, F and G called? | back 33 Empennage |
front 34  What is D? | back 34 Main Landing Gear: supports aircraft weight on the ground (tricycle landing gear configuration) |
front 35  What is c? | back 35 Nacelle: outer covering that encloses engine |
front 36  What is B? | back 36 Nose Gear: Ground steering |
front 37 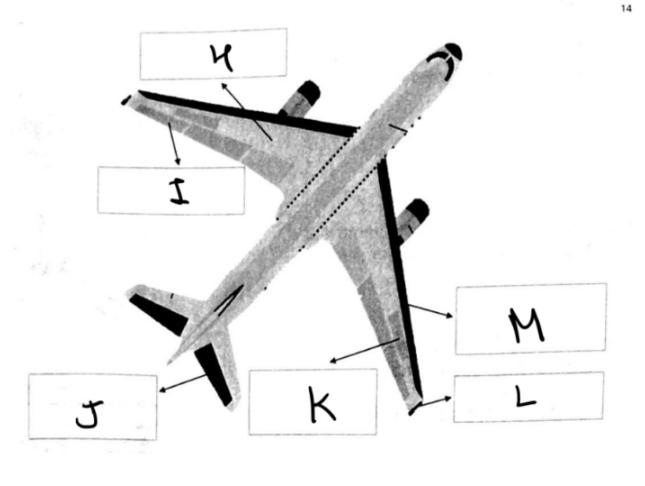 What is H? | back 37 Wings: provide lift |
front 38  What is I? | back 38 Aileron: provides roll control (left or right) (they are opposite of each other) |
front 39  What is J? | back 39 Elevators: pitch control (up and down) |
front 40  What is K? | back 40 Spoiler: Reduces lift and increases drag (independent movement of each other) |
front 41  What is L? | back 41 Winglet: reduces drag (wing vortex control) |
front 42  What is M? | back 42 Slat: aids in takeoffs and landings (increases or decreases wing surface area) |
front 43 What is the longitudinal axis called and what causes the movement along it? | back 43 The roll axis: controlled by the yoke (turn the yoke left or right to turn the ailerons up and down) Ailerons cause the movement by going up or down (located at the ends of the wings) |
front 44 What is the lateral axis called and what causes the movement along it? | back 44 The pitch axis: controlled by pushing the yoke in to dive down and pulling them up to pitch up. The elevators control the pitch by simultaneously flapping up or down |
front 45 What is the vertical axis called and what causes the movement along it? | back 45 The yaw axis: causes the aircraft to spin left or right by pushing the right or left rudder pedal. The rudder controls this movement by deflecting the airflow right or left from its position on the tail. Kind of like a shark tail. |
front 46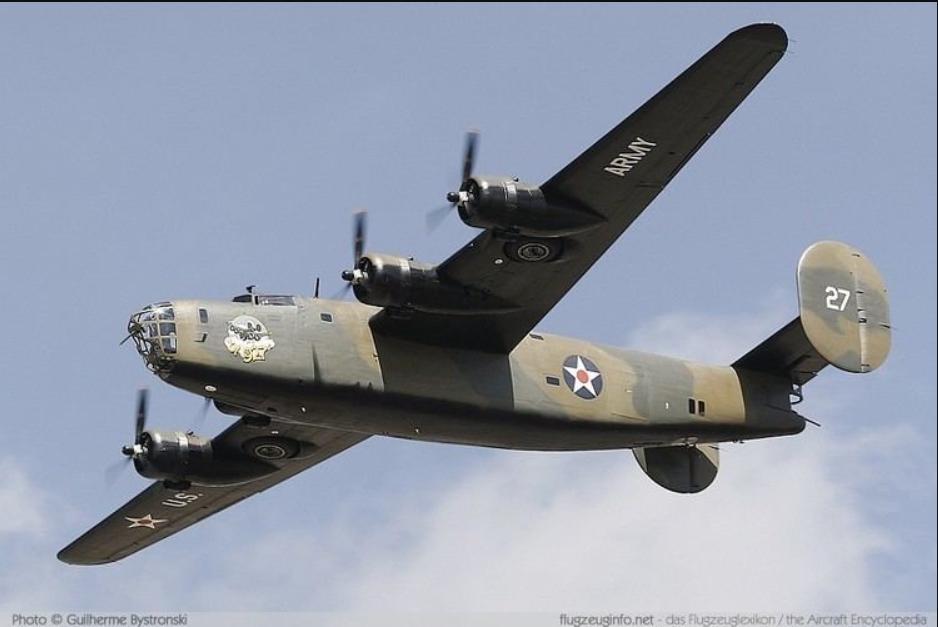  What is the manufacturer, designation, and name of this aircraft? | back 46 The Consolidated B-24 Liberator - world's most produced bomber (rapid production because of WW2) - Called the flying coffin because there was only one exit, so the pilot couldn't escape - straight (davis) wing, twin tail |
front 47 what are airplanes with 1, 2 and 3 wings called? | back 47 Monoplane (Fairchild Republic A-10), Biplane (Boeing Stearman), triplane (Fokker Dr. I) |
front 48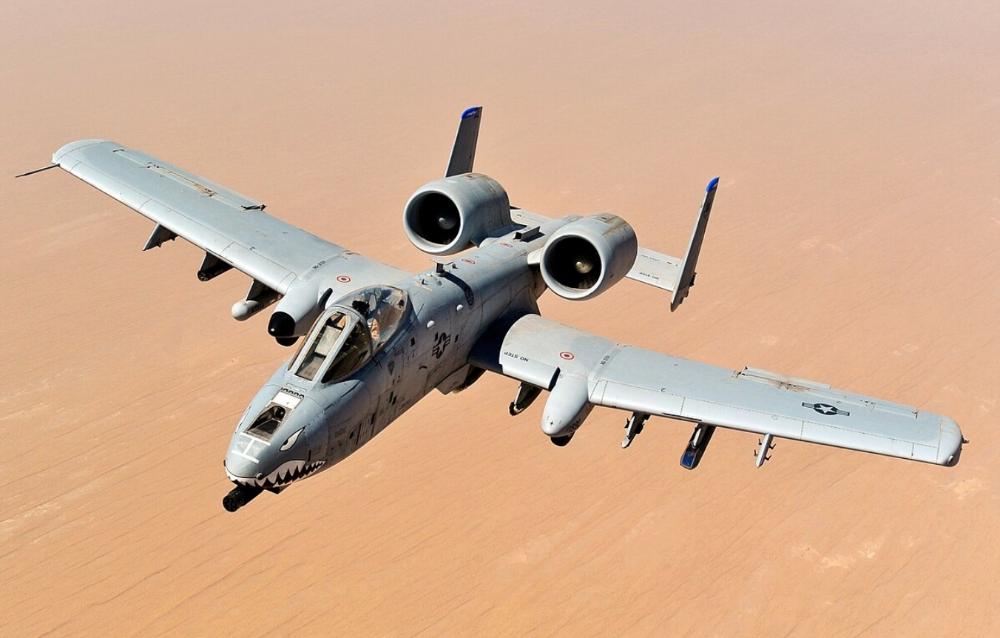  What is the name of this aircraft? | back 48 Fairchild Republic A-10 Thunderbolt - AKA A-10 Warthog -designed to provide close air support (CAS) to ground troops -the only production-built aircraft designed solely for CAS |
front 49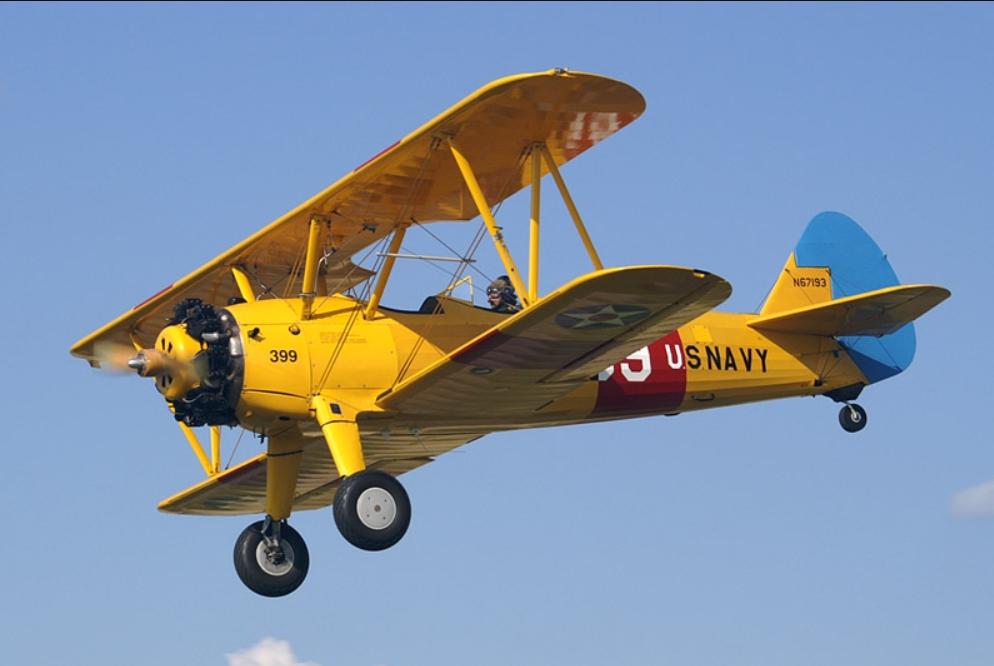  What is the name of this aircraft? | back 49 Boeing-Stearman Model 75 - military trainer aircraft - after WW2, they were sold on the civilian market and were used for crop dusting, racing, and wing walking |
front 50  What is the name of this aircraft? | back 50 Fokker Dr. I Red Baron - WW1 fighter aircraft |
front 51 What locations can the wings be placed in? | back 51 High wing (cessna 172), mid wing (f-16), low wing (Piper cherokee) |
front 52  What is the name of this aircraft? | back 52 Cessna 172 Skyhawk - more of these were built than any other aircraft -most successful aircraft in history |
front 53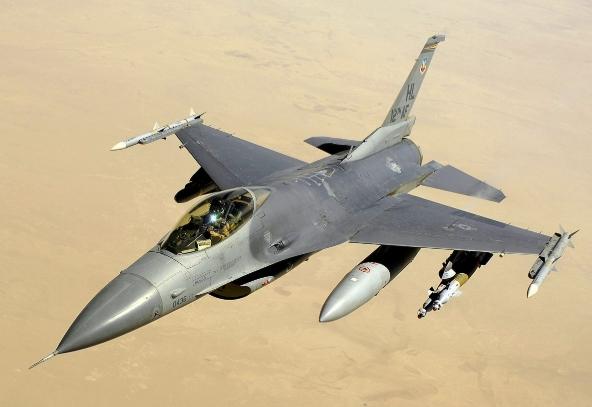  What is the name of this aircraft? | back 53 General Dynamics (aka lockheed martin) F-16 Fighting Falcon - world's most common fixed wing aircraft in the military |
front 54  What is the name of this aircraft? | back 54 Piper Cherokee - designed for flight training, taxi and personal use - 4th most produced aircraft in history |
front 55  What is the name of this aircraft? | back 55 Boeing 787 Dreamliner - swept back wings |
front 56 What are some other types of wings? | back 56 Swept back wings (boeing 787), swept forward wings (Grumman X-29A), canard at the front (Piaggio Avanti P180) |
front 57  What is the name of this aircraft? | back 57 Northrop A-9A -prototype that was passed up for the Fairchild A-10 |
front 58 What is the lift equation? | back 58 L = (1/2)pv^2SC_L or L = q(bar) S C_L |
front 59 What is the dynamic pressure formula? | back 59 q(bar) = (1/2)pv^2 |
front 60 What are the atmospheric layers (starting from bottom to top) and how does this affect atmospheric conditions? | back 60 (troposphere, tropopause, stratosphere, stratopause, Mesosphere, mesopause, Thermosphere) At the "spheres", temp changes linearly with altitude at the "pauses", temp is constant |
front 61 Hydrostatic equation | back 61 dP= -pgdhg |
front 62 What is the geometric altitude | back 62 h_g, the geometric height above sea level is |
front 63 what is the absolute altitude? | back 63 h_a the height measured from the center of the earth |
front 64 What is the equation for the absolute altitude? | back 64 h_a = h_g +r (radius of the earth) |