Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
MOD 5
front 1 The concept of treating all samples, whether known or unknown, as potentially hazardous(or pathogenic) materials is known as __________. | back 1 Universal precautions |
front 2 List at least 3 observations a researcher would be sure to note while assesing an unknown microbiol sample. | back 2 1. Size and shape 2. Any observable motility 3. Gram status (positive or negative) 4. The presence of any chemical reactions 5. Changes in color localized to the organism or the surrounding media 6. Capture or draw images of any of the characteristics described above |
front 3 While observing an unknown sample of limited amounts, a researcher must determine the following observations: (1) the presence of any motility and (2) its Gram status using the same sample--the liquid sample cannot be divided. Which would you determine first and why? | back 3 I would determine first the presence of any motility. This is because gram staining requires heat fixation, which would kill the organism, making it impossible to determine if it has any motility. It is relatively easy and makes the most sense to go from a wet mount to heat fixing the sample, and in this way, we would be able to determine both motility first and then gram status. If we go the other way around, we'd be able to determine gram status, but motility because the organism would be dead. |
front 4 A faculative anaerobe is a microorganism capable of growth under what conditions? | back 4 A faculative anaerobe is capable of growth in conditions with oxygen (aerobic) or without (anaerobic). |
front 5 As Streptococcus is catalase negative, would it thrive or die in the presence of peroxides? Why? | back 5 Streptococcus would die in the presence of perioxides. This is because it is catalase negative, meaning it lacks the proper enzyme to breakdown peroxides, which are harmful. If the peroxides cannot be broken down, they will eventually cause cell death. |
front 6 Streptococcus is most often streaked onto: Chocolate agar EMB agar Blood agar Spirit blue agar | back 6 Blood agar |
front 7 True or False: The Lancefield groups are used to subdivide antigenic groups of gamma-hemolytic Streptococcus. | back 7 False-- the Lancefield groupings are used to subdivide beta-hemolytic Strep |
front 8 The distinctions for Lancefield subgroupings lie in its: (select all that apply) Hemolytic activity Catalase activity Carbohydrate composition of antigens All of the above | back 8 Carbohydrate composition of antigens |
front 9 Left untreated, strep throat can progress to _____, which displays ______ hemolytic activity. Strep. Strepticemia; gamma Strep. Pharyngitis; alpha Rheumatic fever; beta Strep. pharyngitis; beta | back 9 Rheumatic fever; beta |
front 10 True or False: Under most circumstances, staphylococcus can be found in ~80% of human population where it remains non-symptomatic. | back 10 False-- staphylococcus is only found (non-symptomatic) in ~30% of the human population |
front 11 Define commensal bacteria | back 11 Commensal bacteria are bacteria that neither benefit or harm its host from which it gets its nutrients |
front 12 Match the step of infection to its description. Invasion Evasion Transmission A. Pathogen passes through or between cells to access deeper tissues and nutrients B. Pathogen suppresses host's immune system so it can continue replicating C. Pathogen is passed to another host to restart the lifecycle | back 12 Invasion: A Evasion: B Tranmission: C |
front 13
Match the following diseases with their respective
symptoms: Infection occurs at time of birth | back 13 Folliculitis: Pus filled lesions on skin or hair |
front 14 True or False: Thr causative agent of conjunctivitis can be either bacterial or viral. | back 14 True |
front 15 True or False: An acid-fast stain is best suited to identify tuberculosis (as opposed to a Gram stain). | back 15 True |
front 16 True or False: Although TB must be inhaled and reside in the lung in order to cause infection, TB can also spread to the brain, spine, and kidneys. | back 16 True |
front 17 Identify the disease based on the following (select all that apply): It is a small, acid-fast rod usually remaining asymptomatic for up to 20 years. It affects the skin, nerves, upper respiratory tract, and eyes of infected individuals. Bacterial conjunctivitis Scalded-skin syndrome Leprosy Hansen's disease Tuberculosis | back 17 Leprosy Hansen's disease |
front 18 True or Falase: Directly ingesting costridium or its associated spores will not cause illness in adults. | back 18 True |
front 19 A 5-month-old child is given honey at breakfast and begins showing symptoms consistent with botulism. Would this child's illness be classified as foodborne, infant, or wound botulism? Explain why you chose this answer. | back 19 Infant botulism. Pediatrcians specifically tell parents not to give honey to infants younger than 6 months of age. The child described is 5-months and was given honey. The bacteria can be found in the honey, and when the child consumed it, it was able to colonize in its GI tract because it does not have adult microbiota that would prevent this (it is still in the process of developing) and produce the toxin. No wound was described, so we can rule out wound botulism, and although the honey is considered food and was consumed, we can rule out foodborne botulism because this type of botulism is commonly brought upon when canned foods are contaminated and eaten (low acid and anaerobic conditions are found in such canned foods). |
front 20 True or False: Although there is no cure for tetanus, it can be prevented through vaccination. | back 20 True |
front 21 Identify the medical condition characterized by robust carbohydrate fermentation under anaerobic conditions, swelling of the infected areas and fever. | back 21 Gas gangrene - one of the main symptoms of this medical condition is intense gas production which is caused by C. perfringens when it ferments carbohydrates under anaerobic condtions |
front 22 Why does the alpha toxin (perfringolysin) produced during an infection of gas gangrene cause cell death? | back 22 Perfringolysin perforates/forms pores in the plasma membrane of host cells. These pores in the membrane result in an uncontrolled ion flux which leads to cell lysis/death. |
front 23 You develop a fever, chills, and pneumonia after recently returning from a getaway weekend where you sat in a hot tub. What bacterial disease would a doctor suspect is causing your symptoms? Would the doctor suscpect you contracted it from another person? | back 23 Legionnaires. No, the doctor would not suscpect this because Legionella, which is the bacteria that causes legionnaires, can only be transmitted through small droplets that are inhaled. Direct with another person does not transmit this disease. |
front 24 True or False: Bubonic plague is often characterized by painfully swollen lymph nodes. | back 24 True |
front 25 Which form of the plague is the most rare? What does it target? | back 25 Septicemic plague, which targets the blood system |
front 26 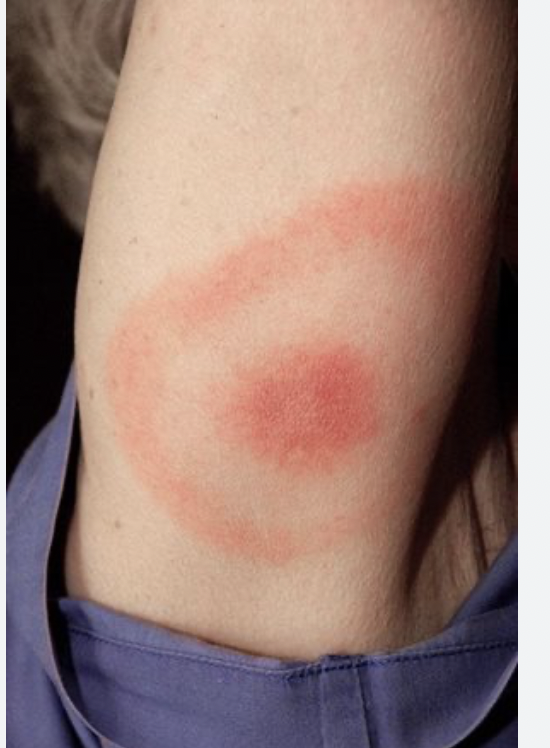 Identify the following disease: Tetanus Scaled-skin syndrome Gas gangrene Lyme disease | back 26 Lyme disease |
front 27 Syphilis is caused by: Diplococcic bacteria RNA virus Staphylococcus bacteria Diplococcic bacteria Gram-negative spirochete | back 27 Gram-negative spirochete |
front 28 True of False: Chlyamida is an obligate parasite and as such can be grown on agar plates alone. | back 28 False -- an obligate parasite requires a host (viable cells) to be present for its growth. |
front 29 Match the following diseases with their respecitve symptoms if left untreated:
Gonorrhea A. Paralysis, blindness, and dementia B. Painfully swollen lymph nodes C. Cardiac and neurological complications D. Respiratory failure associated with lock-jaw E. Infertility and pelvic inflammatory disease F. Sore throat, ocular discharge, and fever | back 29 Gonorrhea: Cardiac and neurolgocial complications |
front 30 Define the concept of universal precautions. | back 30 The concept of universal precautions means any and all samples, whether known or unknown, are to be treated as potentially hazardous (or pathogenic) materials. |
front 31 Rheumatic fever displays _____ hemolytic acitvity and occurs when _____ is left untreated. Beta; Strep. Pharyngitis Beta; Rheumatic fever Alpha; Strep. Pharyngitis Gamma; Strep. Septicemia | back 31 Beta; Strep. Pharyngitis |
front 32 True or False: Under most circumstances, staphylococcus can be found in ~30% of human population where it remains pathogenic. | back 32 False. While staphylococcus can be found in ~30% of the human population, it remains non-symptomatic. |
front 33 True or False: Only directing ingesting the pre-formed clostridium toxin (neither the bacteria nor its spores) will cause disease in adults. | back 33 True -- the mature (adult) microbiota is capable of killing the bacteria/spores |
front 34 True or False: There are currently no cures for tetanus | back 34 True |
front 35 Describe the symptoms and treatment regimen for someone infected with Clostridium perfringens. | back 35 Clostridium perfringens, which is the bacterium that causes gas gangrene. Symptoms of gas gangrene include muscle necrosis, swelling of infected areas, fever, and intense gas production. Treatment includes removal of all infected tissue, which often results in the amputation of affected areas and heavy antibiotic therapies. |
front 36 The alpha-toxin perfringolysin is associated with which medical condition caused by Gram-positive anaerobic bacteria? Tetanus Leprosy Botulism Gas gangrene | back 36 Gas gangrene |
front 37 You develop a fever, chills, and pneumonia after recently using a warm midst vaporizer in an attempt to open your sinuses. What bacterial disease would a doctor suspect is causing your symptoms? Would the doctor suspect you contracted it from touching (potentially) contaminated doorknobs? | back 37 Legionnaires. No, legionella cannot be spread by direct contact between people. Legionella can only be transmitted through small droplets that can be inhaled. |
front 38 True or False: Pneumonic plague is often characterized by painfully swollen lymph nodes. | back 38 False--pneumonic plague targets the respiratory system while bubonic targets the lymph system |
front 39 Which form of plague is highly virulent? What does it target? | back 39 Pneumonic plague. Respiratory system |
front 40 Gonnorrhea is caused by: Gram-negative spirochete Staphylococcus bacteria Diplococcic bacteria RNA virus | back 40 Diplococcic bacteria |
front 41 True or False: Chlyamida is an obligate parasite and as such can be grown on agar plates alone. | back 41 False. An obligate parasite requires a host (viable cells) to be present for its growth |