Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Micro Lab Final
front 1 What is the tool used for spreading plates? | back 1 Glass spreader or hockey stick |
front 2 What do we use to inoculate semi-solid media | back 2 inoculation needle |
front 3 Bacteria used in bacteriophage lab | back 3 Streptomyces greseus |
front 4 How do you calculate titer/VCN? | back 4 (# of colonies x dilution factor)/mL pipetted |
front 5 What is a plaque and how are they formed? | back 5 A plaque is a clearing in a bacterial lawn caused by a bacteriophage eating the nutrients on the agar and reproducing |
front 6 What type of plaques are formed in the lysogenic and lytic cycle? | back 6 Lysogenic produces cloudy plaques whereas lytic produces clear plaques |
front 7 Define coliphage and bacteriophage | back 7 coliphage: a bacteriophage that specifically infects e.coli bacteriophage: a virus that infects bacteria |
front 8 What does PFU stand for? | back 8 Plaque forming units |
front 9 What is an obligate intracellular parasite? | back 9 an organism that can only reproduce inside of a host cell |
front 10 lytic cycle stages | back 10 attachment, penetration, biosynthesis, maturation, and lysis |
front 11 Are coliforms gram negative or positive and what do they ferment? | back 11 Gram negative and lactose fermenting rods |
front 12 Two advantages of colisure test | back 12 Quick results: in under 24 hours color change: easy to interpret |
front 13 What is the principle indicator organism in fecal contamination | back 13 e.coli |
front 14 wavelength of light used to interpret colisure test | back 14 365 nm |
front 15 Name of enzyme in coliforms (all)? | back 15 B-Galactosidase |
front 16 Name of enzyme in e.coli? | back 16 B-Glucuronidase |
front 17 Principle behind oxidase test | back 17 Prescence of enzyme cytochrome c oxidase |
front 18 Name of indicator in developing oxidase test | back 18 TMPD |
front 19 What organism tested positive for the oxidase test | back 19 Pseudomonas Vibrioionaceae |
front 20 What tested negative for oxidase test | back 20 Enterobacteriae |
front 21 Review Rhizopus on plate | back 21 Black and tan and fuzzy |
front 22 Review Aspergillus on plate | back 22 Solid black plate with little white |
front 23 Media used for growing fungi in lab | back 23 SDA: sabouraud dextrose agar |
front 24 define dimorphic fungi | back 24 produce anitbiotics ie.penicillium produces penicillin |
front 25 What is lichen? How do they help each other? | back 25 Algae and fungi engaging in a symbiotic relationship Algae provides carbohydrates and fungi provides structure, moisture, and protection |
front 26 Enzyme that detoxifies hydrogen peroxide how do you test for it | back 26 Catalase bubbles |
front 27 What organism was negative for catalase test? positive? | back 27 n= streptococcus species p= staphlyococcus aureus |
front 28 What reagent was used for oxidase test | back 28 Hydrogen peroxide |
front 29 Two stages of protozoa | back 29 Trophozoite: active, feeding, motile Cyst: dormant, resistant stage |
front 30 Two characteristics of protozoa | back 30 Unicellular eukaryotes motile |
front 31 4 classes of protozoa | back 31 Mastigophora: motile using flagella Ciliophora: motile using cilia Sarcodina: move using pseudopodia Apicomplexa: non motile:glide |
front 32 What reagent in used in developing starch hydrolysis test | back 32 grams iodine |
front 33 Principle behind starch hydrolysis test | back 33 Produce amylase to break down starch |
front 34 Example of mesophile | back 34 e.coli |
front 35 example of thermophile | back 35 s. stearothermophile |
front 36 what is a pandemic and epidemic | back 36 Worldwide spread epi= increased number of cases in a specific area |
front 37 Pathogen in epidemiology experiment | back 37 pseudomonas putida |
front 38 MMWR? | back 38 Morbidity and mortality weekly report from the CDC |
front 39 p. putida requires what to grow? | back 39 toluic acid |
front 40 What is a pilus? what is a plasmid? | back 40 pilus: initiates conjugation by attaching to recipient cell plasmid: small circular dna molecule that replicates independently of chromosomal dna |
front 41 plasmid responsible for degrading toluic acid | back 41 TOL plasmid |
front 42 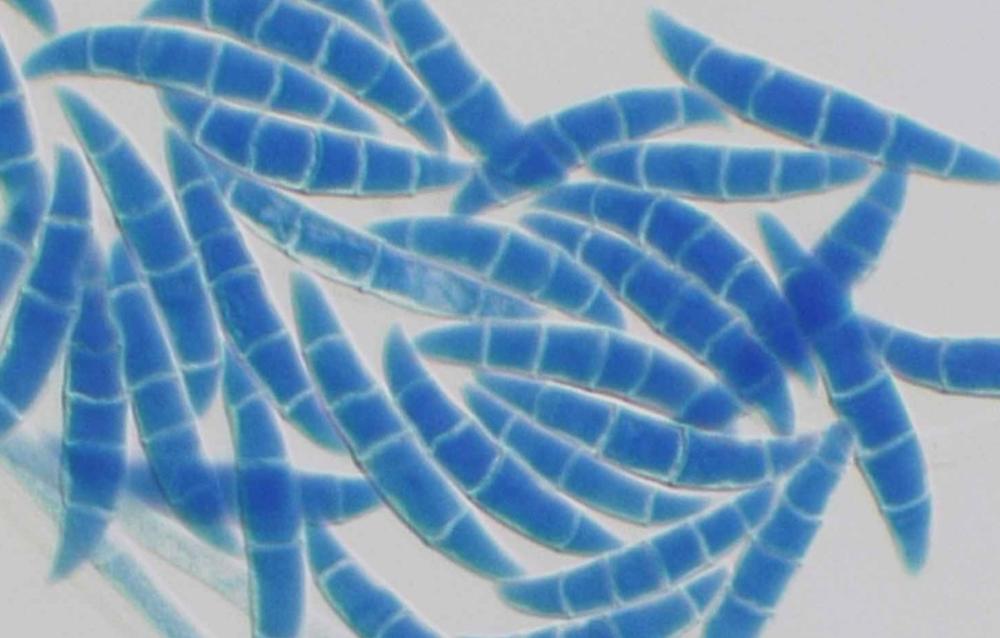 | back 42 Fusarium: fungi |
front 43 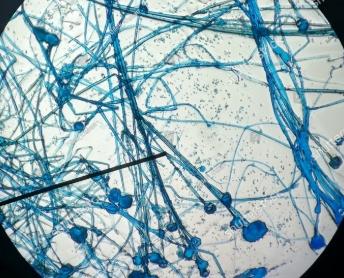 | back 43 Rhizopus stolonifer: fungi |
front 44  | back 44 Penicillium: fungi |
front 45 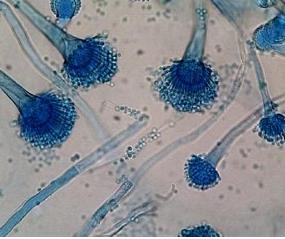 | back 45 Aspergillus: fungi |
front 46 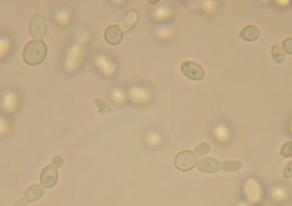 | back 46 Saccaromyces: fungi |
front 47 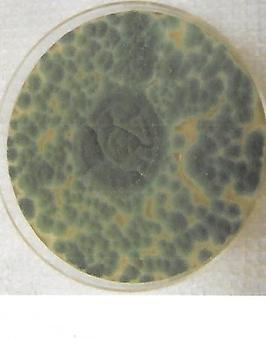 | back 47 Penicillium fungi |
front 48  | back 48 Aspergillus niger fungi |
front 49  | back 49 Rhizopus stolonifer fungi |
front 50 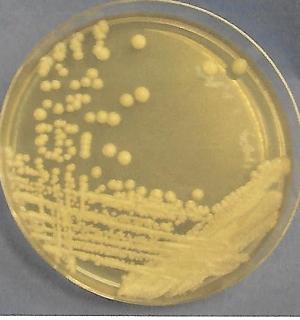 | back 50 Saccaromyces cervisiae fungi |
front 51 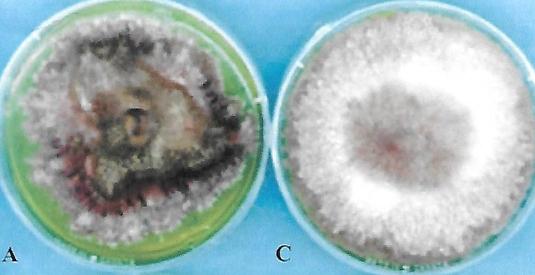 | back 51 Fusarium fungi |
front 52 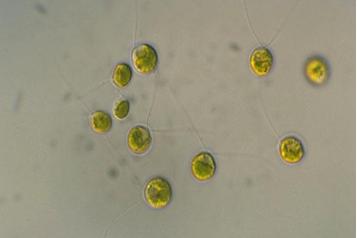 | back 52 chlamyldomonas algae |
front 53  | back 53 Spyrogira algae |
front 54  | back 54 Volvox algae |
front 55 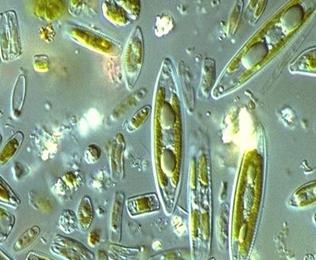 | back 55 Diatoms algae |
front 56  | back 56 Desmids algae |
front 57 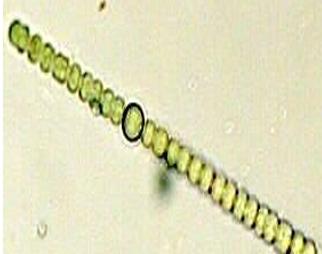 | back 57 anabaena cyanobacteria |
front 58 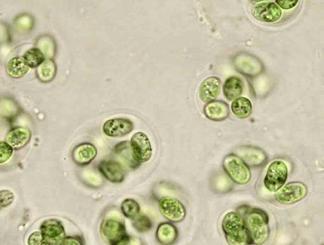 | back 58 Geleocapsa Cyanobacteria |
front 59 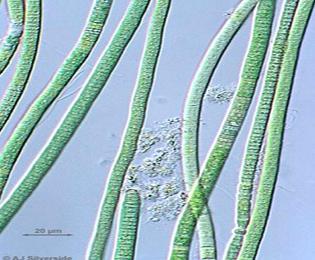 | back 59 Oscillatoria cyanobacteria |
front 60 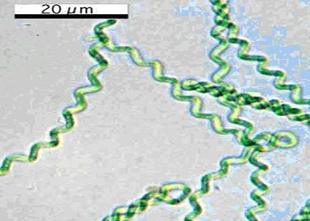 | back 60 Spirulina cyanobacteria |
front 61 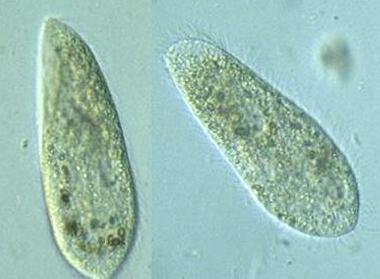 | back 61 Paramecium protozoan |
front 62 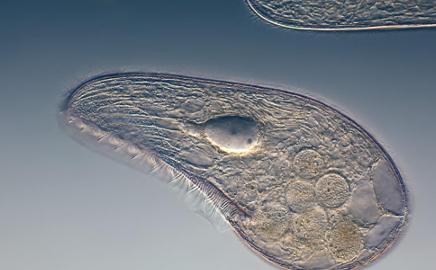 | back 62 Blepharisma protozoan |
front 63  | back 63 Vorticella protozoan |
front 64 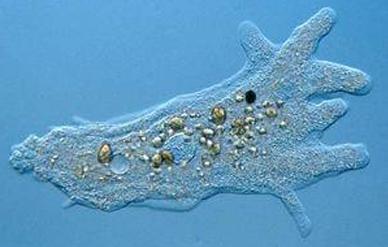 | back 64 amoeba proto |
front 65 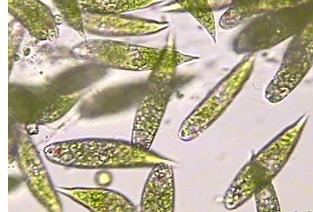 | back 65 Euglena proto |
front 66 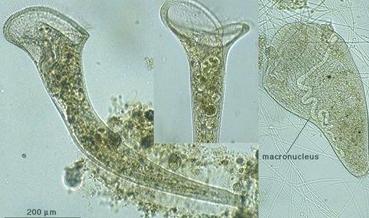 | back 66 Stentor proto |
front 67 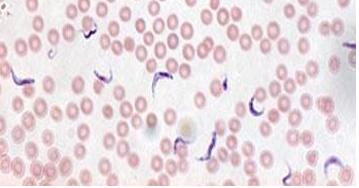 | back 67 trypanosoma proto |
front 68 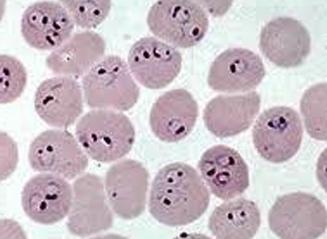 | back 68 Plasmodium (ring stage) proto |
front 69 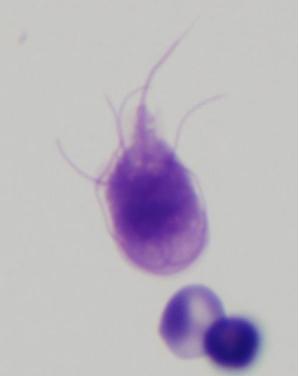 | back 69 Giardia Lambia |
front 70 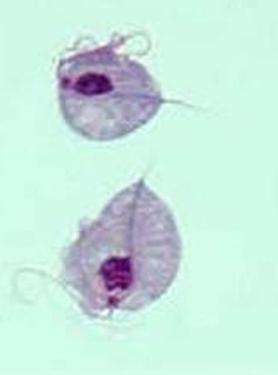 | back 70 Trichomonas vaginillis proto |
front 71 auxotroph v prototroph | back 71 auxotroph: mutant that cannot synthesize a required nutrient prototroph: wild-type organism that can synthesize all required nutrients |
front 72 One use of algae in lab | back 72 Agar |
front 73 Study of algae is called | back 73 phycology |
front 74 two modes of action for antibiotics | back 74 inhibiting cell wall synthesis and inhibiting bacterial protein growth |
front 75 Name of antibiotic susceptibility test? name of media? | back 75 Kirby bauer test and the media was mueller hinton agar |
front 76 advantage of using e-test over kirby bauer test? | back 76 Gives exact MIC (minimum inhibtory concentration) |
front 77 difference between antiseptic and disinfectant? | back 77 Antispectic is for living skin, disinfectant is for inanimate surfaces |
front 78 Structure of importance within fungi | back 78 septate hyphae |
front 79 What is the name of the red pigment produced by serratia marcescens | back 79 Prodigiosin |