Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
PreMat Stuff from My Own Notes
front 1 nerve plexuses | back 1 when a bunch of nerves come together |
front 2 anterior rami | back 2 go out to body wall and to limbs come together in a plexus mix and form the peripheral nerves that innervate the limbs |
front 3 posterior rami | back 3 just go to epaxial muscles that run along vertebral column |
front 4 describe how three separate spinal (segmental) nerves innervate skin | back 4 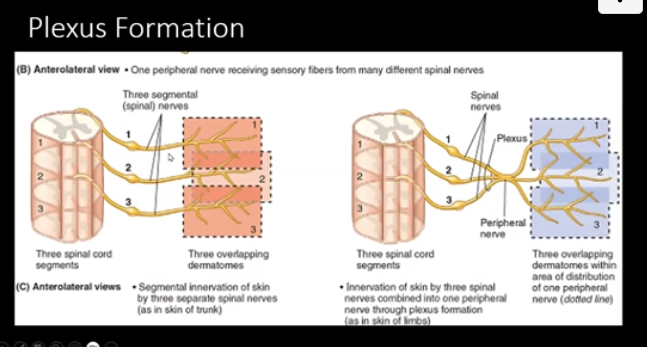 spinal segment 1 - gives off segmental nerve which goes off to dermatome 1 spinal segment 2 - gives off segmental nerve which goes off to dermatome 2 spinal segment 3 - gives off segmental nerve which goes off to dermatome 3
|
front 5 describe how three separate spinal (segmental) nerves form a plexus | back 5  spinal nerves 1, 2, and 3 come together and form a plexus and then it eventually splits into three and supply three different dermatomes
|
front 6 plexus formation | back 6
|
front 7 brachial plexus | back 7 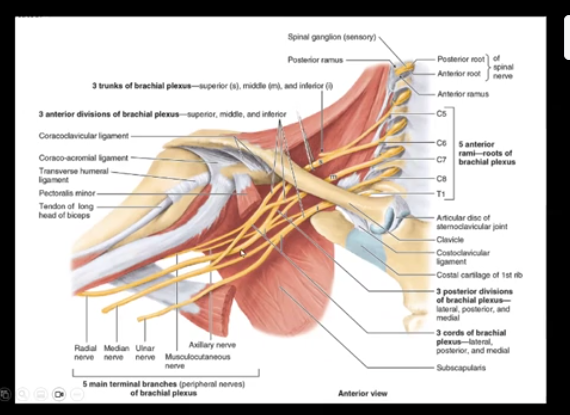
|
front 8 sympathetic nervous system | back 8
|
front 9 postganglionic neurons | back 9
|
front 10 lateral horn | back 10 column of gray matter that has preganglionic sympathetic neurons
|
front 11 sympathetic chain | back 11 is on either side of the vertebral column, ganglia at each level
|
front 12 prevertebral ganglia | back 12 on anterior aspect of aorta, can be called pre-aorta bc theyre in front of aorta |
front 13 Parietal (somatic) Somatic Distribution | back 13 Postganglionic sympathetic axons leave and do things such as innervate the arrector pilli muscles, constrict blood vessels, innervate sweat glands |
front 14 Visceral Distribution | back 14 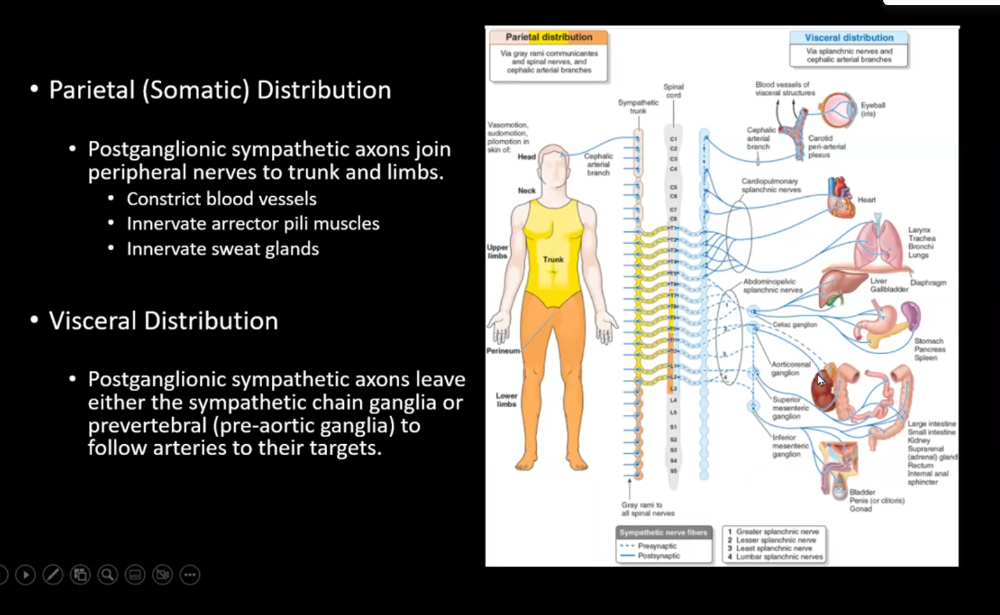 Postganglionic sympathetic axons leave either the sympathetic chain ganglia or prevertebral (pre-aortic ganglia) to follow arteries to their targets
|
front 15 parasympathetic nervous system | back 15 also called craniosacral has efferents and afferents Preganglionic neurons in nuclei of the brainstem or sacral S2-S4 spinal cord Postganglionic neurons are in ganglia in the head or associated with thoracic and abdominopelvic viscera |
front 16 Four cranial nerves have preganglionic parasympathetic nuclei or in otherwords | back 16  have parasympathetic axons that start in special nuclei in the brainstem, then travel to ganglia and control things like pupil size, saliva, and organ function read image again |
front 17 facial | back 17 superior salivatory nucleus |
front 18 glossopharyngeal | back 18 inferior salivatory nucleus |
front 19 vagus | back 19 dorsal motor nucleus |
front 20 edinger westphal nucleus | back 20 preganglionic neurons will synapse with postanglionic in the orbit behind the eye to cause pupil to constrict or when looking at near objects in midbrain, part of the brainstem |
front 21 enteric nervous system | back 21 in the GI tract, there are two interconnected plexuses that control intrinsic activity of the GI tract - submucosal plexus (Meissner's) and Myenteric plexus (Auerbach's) between the outer and inner layers of smooth muscle |
front 22 Meissner's | back 22 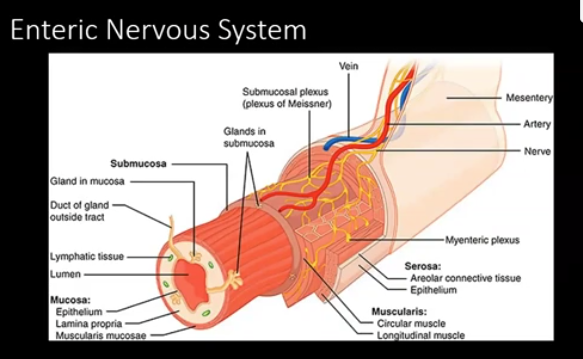 in the submucosa, has sensory and visceromotor neurons regulates mucosal events (secretion from glands or localized movement) |
front 23 Auerbach's (myenteric) | back 23  main function is peristalsis by regulating smooth muscle |
front 24 Visceral Sensation | back 24 afferents carry info from viscera to spinal cord distention - feel bladder filling, sends info back to nervous system when we're hungry or satiety visceral pain is generally poorly localized and may be referred to body wall and interpreted as somatic pain (referred pain)
|
front 25 Referred Pain | back 25 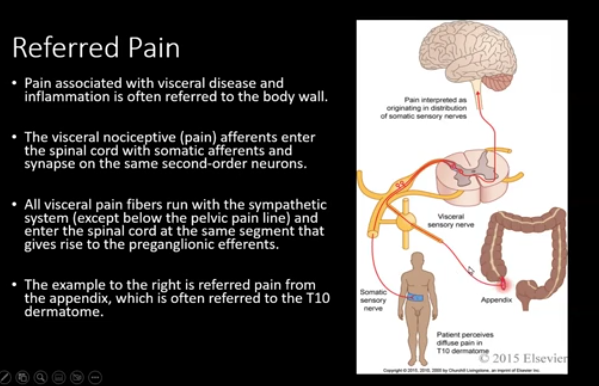 |
front 26 glaborous | back 26 smooth |
front 27 thin skin has | back 27 hair and sebaceous glands |
front 28 skin has | back 28 epidermis and dermis |
front 29 hypodermis | back 29 is superficial fascia and not part of skin |
front 30 functions of skin | back 30
|
front 31 dermis | back 31 is connective tissue |