Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
(OTD 515) Special Senses: Vision, Audition, and Olfaction Overview
front 1 Cranial Nerve VIII | back 1 Transmits auditory information from cochlea. |
front 2 Sound Waves | back 2 Vibrations characterized by frequency and amplitude. |
front 3 Frequency | back 3 Pitch measured in Hertz (Hz) of oscillations. |
front 4 Amplitude | back 4 Loudness determined by magnitude of oscillations. |
front 5 Cochlea | back 5 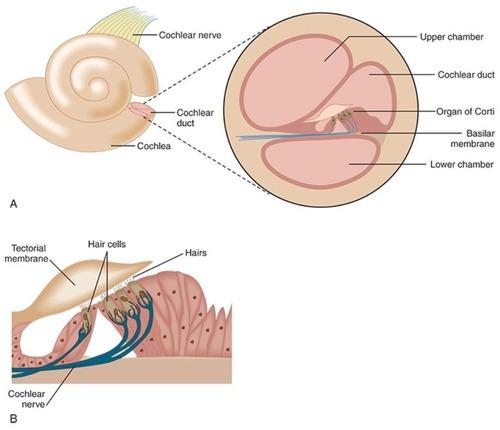 auditory structure |
front 6 Organ of Corti | back 6 coverts mechanical energy from sound waves into neural signals |
front 7 Basilar Membrane | back 7
|
front 8 Hair Cells | back 8 Sensory cells that generate neural signals. |
front 9 Auditory Pathway (from choclear nuceli) | back 9 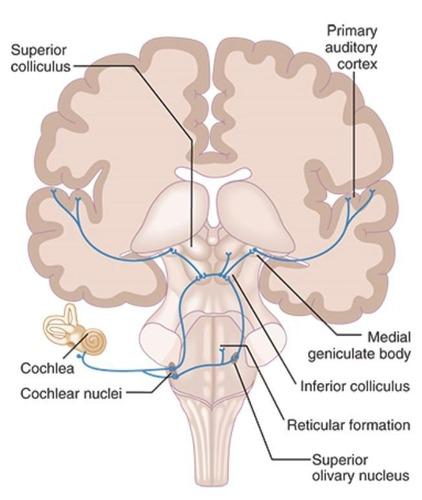 reticular formation --> inferior colliculus --> medial geniculate body |
front 10 Cochlear Nuclei | back 10 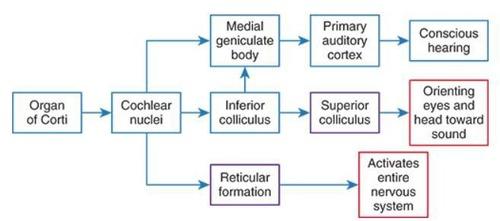 First relay station for auditory signals. |
front 11 Inferior Colliculus | back 11 Integrates auditory information from both ears. |
front 12 Medial Geniculate Body | back 12 Thalamic relay for auditory signals to cortex. |
front 13 Primary Auditory Cortex | back 13 Processes complex sounds, sound localization, selective attention to specific sounds, discrimination of auditory patterns, performance of difficult auditory tasks |
front 14 Auditory Patterns | back 14 Recognition and discrimination of sound sequences. |
front 15 Round Window | back 15 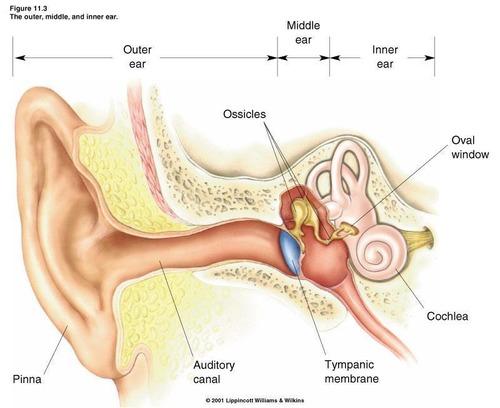 Flexible membrane that relieves cochlear pressure. |
front 16 Oval Window | back 16 Membrane transmitting vibrations from stapes to cochlea. |
front 17 Reticular Formation | back 17 Regulates arousal and attention to auditory stimuli. |
front 18 Auditory Nerve | back 18 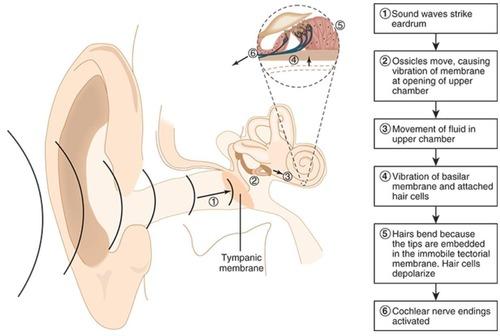 Transmits signals from cochlea to brainstem. |
front 19 Olfactory receptors | back 19 Hair cells in nostrils detecting odors. |
front 20 Olfactory pathway | back 20 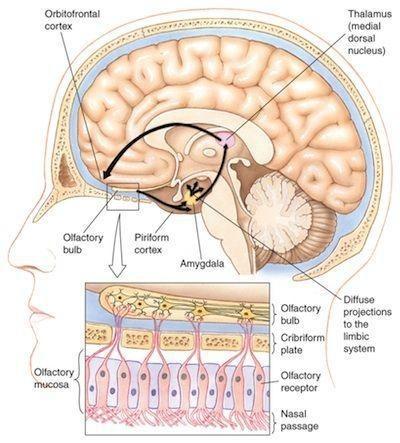 olfactory receptors --> olfactory bulb --> Primary olfactory cortex/amygdala/parahippocampal gyrus |
front 21 Amygdala sends olfactory information to (3 places) | back 21
|
front 22 Primary olfactory cortex | back 22 Initial processing area for olfactory signals. |
front 23 Orbitofrontal cortex | back 23 Processes value judgments of odors. |
front 24 Visual system | back 24 System responsible for sight and visual processing. |
front 25 Eye movement control | back 25 Regulates movements for visual targeting. |
front 26 Lens | back 26 Refracts light before it enters the pupil. |
front 27 Pupil | back 27 Opening for light entry, controlled by ciliary bodies. |
front 28 Retina | back 28 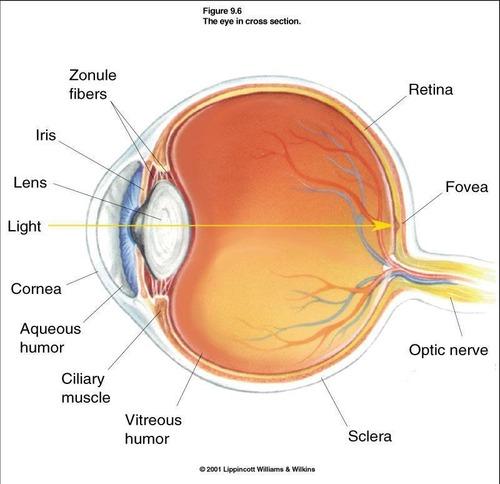 Receptors that convert light into neural signals |
front 29 Optic nerve (CN II) | back 29 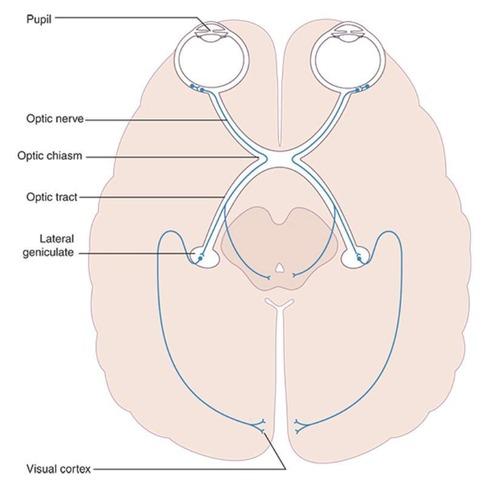 First order neuron in visual pathway. |
front 30 Visual pathway | back 30 Sequence of neural connections for vision. |
front 31 Optic chiasm | back 31 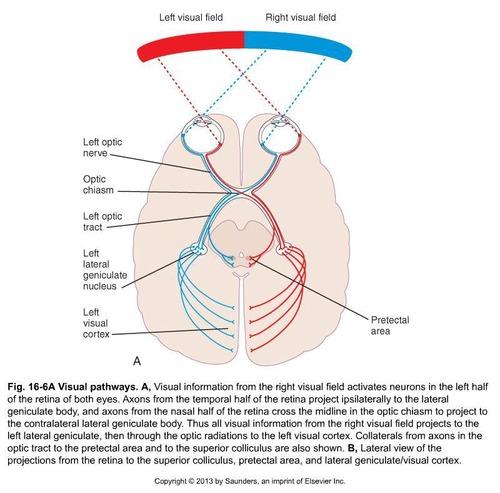 Point where retinal axons cross to opposite cortex. |
front 32 Lateral geniculate nucleus | back 32 Thalamic relay for visual information. |
front 33 Primary visual cortex | back 33 Processes basic visual features like shape. |
front 34 Dorsal stream | back 34 Visual pathway for action and movement adjustments. |
front 35 Ventral stream | back 35 Visual pathway for object recognition. |
front 36 Tectal system | back 36  Midbrain structure for auditory and visual reflexes. |
front 37 Eye movement system | back 37
|
front 38 Conjugate Movements | back 38 Both eyes move in the same direction. |
front 39 Vergence Movements | back 39 Eyes move toward or away from midline. |
front 40 Gaze Stabilization | back 40 Maintains stable vision during head movements. |
front 41 Nystagmus | back 41 Involuntary oscillating movements of the eyes. |
front 42 Optokinetic Nystagmus | back 42 Reflex elicited by moving moving visual stimuli. |
front 43 Physiologic Nystagmus | back 43 Normal response elicited by head rotation or stimulation. |
front 44 Saccades | back 44 Fast eye movements between visual targets. |
front 45 Smooth Pursuits | back 45 Eye movements tracking a moving object. |
front 46 Convergence | back 46 Eyes aim at midline for closer objects. |
front 47 Optic Nerve Lesion | back 47 Causes total vision loss in ipsilateral eye. |
front 48 Optic Chiasm Lesion | back 48 Results in bitemporal hemianopia. |
front 49 Complete Optic Tract Lesion (before LGN) | back 49 Leads to contralateral homonymous hemianopia. |
front 50 Incomplete Optic Tract Lesion (after LGN) | back 50 Causes partial vision loss in contralateral field. |
front 51 Ciliary Muscles | back 51 Contract to increase lens curvature for focus. |
front 52 Frontal Eye Fields | back 52 Involved in voluntary eye movement control. |
front 53 Superior Colliculus | back 53 Processes visual information for saccades. |
front 54 Eye movement system objectives | back 54
|
front 55 Eye movements are either | back 55
|