Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
GIS test two, satellites
front 1 What is an orbit? (think very generally) | back 1 the repeating path that one object takes around another |
front 2 What is an orbit cycle? | back 2 The interval of time required for a satellite to pass a point on Earth’s surface directly below the satellite for a second time. |
front 3 What is revisit time? | back 3 The interval of time between observations of the same point on Earth by a satellite |
front 4 Why can the revisit time of a satellite differ from its orbit cycle? | back 4 because satellites can look off-nadir and therefor pass a point twice without imaging it both times. |
front 5 What is a Geostationary Orbit? | back 5 An orbit that matches the speed and direction of |
front 6 What would be some uses of a satellite in geostationary orbit (2) | back 6 Continuous data collection over one location for weather, communication satellites |
front 7 Decreasing the revisit time of a satellite _____________ the temporal resolution of its images. Geostationary satellites have a ________ temporal resolution. | back 7 decreases, high |
front 8 What is a near-polar orbit? | back 8 An orbit path close to the North and South Poles |
front 9 What is a sun-synchronous orbit? What is the advantage of this? | back 9 An orbital path set so the satellite crosses the |
front 10 What is a satellite swath? | back 10 The width of the ground area a satellite images |
front 11 What is an Across-track scanner? What is the other name it's referred to as? | back 11  A scanning method that uses a rotating mirror to collect data by moving back and forth, also referred to as a whiskbroom scanner. |
front 12 What is an Along-track scanner? What is the other name it's referred to as? | back 12  A scanning method that uses a linear array to collect data directly on a satellite’s path, also referred to as a pushbroom scanner. |
front 13 What is relief displacement? | back 13  When objects towards the edge of an image appear to lean away from the centre of the image |
front 14 What is Tangential scale distortion? | back 14  The compression of image features located further away from nadir |
front 15 What is Off-Nadir viewing? | back 15 The capability of a centre to look off nadir |
front 16 What do we use to track satellites? | back 16 Receiving stations |
front 17 The U of L Satellite Receiving Station is owned by which company currently? | back 17 Planet labs |
front 18 What is the spatial resolution of a satellite? | back 18 The smallest unit of area the sensor can collect |
front 19 What is the Radiometric resolution of a satellite? | back 19 The sensor’s ability to determine fine |
front 20 What is the Spectral resolution of a satellite? | back 20 The number and width of bands measured by a |
front 21 What is the Temporal resolution of a satellite? | back 21 The revisit time, or time between images in the |
front 22 ___________ has over _____ years of continuous monitoring and is considered the gold standard due to its quality data and longevity. | back 22 Landsat, 50 |
front 23 When was Landsat 1 launched? | back 23 1972 |
front 24 With which satellite did Landsat switch from across track to along track sensors? | back 24 Landsat 8 |
front 25 Landsat satellites have progressed from ___ bit with Landsat 1 to ___ bit with Landsat 8 and 9. | back 25 6 bit, 12 bit |
front 26 A _______________ sensor measures one broad range of wavelengths | back 26 Panchromatic |
front 27 What is pansharpening? | back 27 The process of merging high-resolution panchromatic and lower resolution multispectral imagery to create a single-coloured image |
front 28 What does SWIR stand for? What does NIR stand for? | back 28 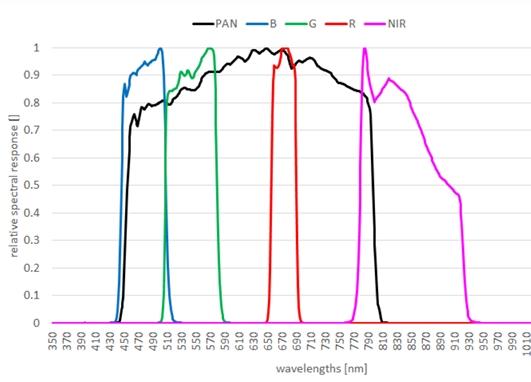 SWIR = short wavelength infrared NIR = near infrared |
front 29 What broke on Landsat 7 that corrected for forward motion? | back 29  The Scan Line Corrector (SLC) |
front 30 What are the two new bands added to Landsat 8 and 9? What are they used to detect? | back 30 Band 1: ultra-blue- to detect chlorophyl concentrations (ocean
colour) in coastal Band 9: cirrus band- to detect cirrus clouds by measuring reflected NIR energy |
front 31 ________ is the 2nd longest-running Earth Observation mission (37 years) but has a ________________ orientation instead of an experimental one. | back 31 SPOT, commercial |
front 32 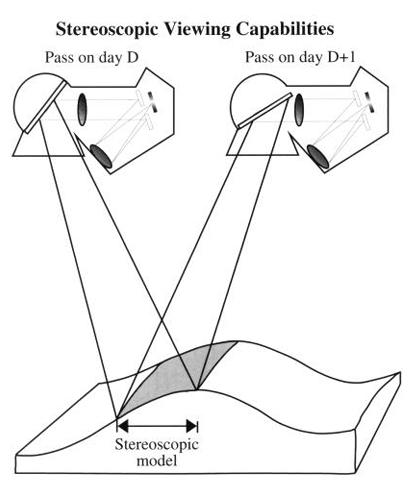 SPOT is capable of off-nadir viewing which | back 32 parallax, digital elevation models |
front 33 SPOT orbits the world from pole to pole and revisits points on earth at the same local time each time it passes over them. Which two terms apply to SPOT's orbits? | back 33 Near-polar and sun-synchronous |
front 34 Sentinel, operated by the European Space Agency (ESA), has three main uses. What are they? | back 34 Land Monitoring (information on land cover like vegetation state and the water cycle), Emergency management (information for the management of natural disasters, man-made emergency situations and humanitarian crises), and Security (border and maritime surveillance) |
front 35 Why was the company Digital Globe revolutionary? | back 35 They produced the first public collection of high-resolution imagery that rivalled military technology with the satellite IKONOS-2. |
front 36 Why was the company WorldView revolutionary? | back 36 They produced the world’s first 50 cm resolution commercial satellite. |
front 37 What is the goal of Maxar’s WorldView Legion? | back 37 To support US national security through surveillance and monitoring |
front 38 Planet labs has three satellite types that make up their constellation. What are they? | back 38 • Dove |
front 39 Why were Dove satellites so different in a practical sense from the norm of the time? (2) | back 39
|
front 40 Of the three satellite types that made up the Planet labs constellation which was retired? | back 40 RapidEye |