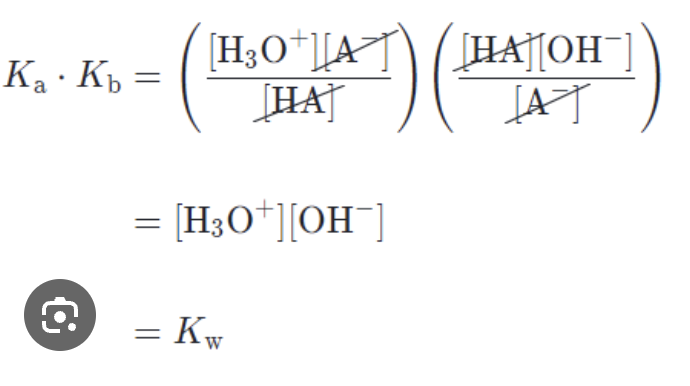front 1 Text: Measurements made in the entire visible spectrum showed that
absorbance occurred only at wavelength 625 ± 5.0 nm according to the
data in Table 1.
What is the approximate energy of a photon in the absorbed
radiation that yielded the data in Table 1?
(Note: Use 1 eV = 1.6 × 10– 19 J and
hc = 19.8 × 10– 26 J•m.)
- A.1 eV
- B.2 eV
- C.3 eV
- D.4 eV
| back 1
Be sure to pay attention to the units and the conversions
The solution is B.
- This is the energy of a photon if radiation had a wavelength
of 1250 nm.
-
The photon energy is E = hc/λ = 19.8 ×
10–26 J•m/(625 × 10–9 m) = 3.1 ×
10–19 J ≅ 2 eV.
- This is the energy of
a photon if radiation had a wavelength of 416 nm.
- This is
the energy of a photon if radiation had a wavelength of 312 nm.
|
front 2 Suppose a blood sample tested above the range (6.0 mg/dL) of the
standards used in the experiment. What modification will provide a
more precise reading by data interpolation as opposed to extrapolation
using the same standards?
- A.Increase the enzyme concentration.
- B.Increase the
oxygen pressure.
- C.Decrease the content of oxygen
acceptor.
- D.Dilute the sample with additional solvent.
| back 2
The solution is D.
- Increasing the enzyme concentration will increase the
quantity of absorber (chromogen) in solution, according to the
protocol described in the passage. This will make the resulting
absorbance value even further from the values in Table 1 and
require additional extrapolation.
- Increasing the oxygen
pressure will increase the quantity of absorber (chromogen) in
solution, according to the protocol described in the passage. This
will make the resulting absorbance value even further from the
values in Table 1 and require additional extrapolation.
- The oxygen acceptor is glucose. Removing glucose from the
solution is not feasible and defies the logic of the experiment,
which involves quantifying the amount of glucose present. One would
need to know exactly how much glucose was removed, and this would
require a separate measurement.
-
By adding solvent, the concentration of glucose will be
lowered, and the resulting absorbance will fall within the range
of the standards. This is easily accomplished, and the resulting
calculations that account for the dilution are not
difficult.
|
front 3 Which of the following reasons best explains why it is possible to
separate a 1:1 mixture of 1-chlorobutane and 1-butanol by fractional distillation?
- A.Both 1-chlorobutane and 1-butanol are polar.
- B.Both 1-chlorobutane and 1-butanol are nonpolar.
- C.The boiling point of 1-chlorobutane is substantially higher
than that of 1-butanol.
- D.The boiling point of
1-chlorobutane is substantially lower than that of 1-butanol.
| back 3
The solution is D.
- Both 1-chlorobutane and 1-butanol are polar molecules with
dipole moments that are greater than 1.5 D.
- Both
1-chlorobutane and 1-butanol are polar, not nonpolar,
molecules.
- The boiling point of 1-chlorobutane is 78°C. The
boiling point of 1-butanol is 118°C.
-
The fact that 1-chlorobutane will have a boiling point that
is substantially lower than that of 1-butanol can be rationalized
from chemical principles. The molecules have similar molecular
weights, but 1-butanol has a hydroxyl functional group that can
participate in hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding is a
particularly strong force of intermolecular
attraction.
|
front 4 Two vectors of magnitudes |A| = 8 units and
|B| = 5 units make an angle that can vary from 0° to
180°. The magnitude of the resultant vector A +
B CANNOT have the value of:
- A.2 units.
- B.5 units.
- C.8 units.
- D.12 units.
| back 4
The solution is A.
-
The magnitude of A + B is as small as 3 units (when A and B
are anti-parallel and make an angle of 180°) and as large as 13
units (when A and B are parallel and make an angle of 0°). The
magnitude of 2 units is smaller than the smallest possible
magnitude of vector A + B.
- When
A + B has 5 units, the angle
between A and B is
cos–1 (25 – 64 – 25)/(2 × 8 × 5) = 143°, thus 5 units is
a possible magnitude.
- When A + B
has 8 units, the angle between A and
B is cos–1 (64 – 64 – 25)/(2 × 8 × 5)
= 108°, thus 8 units is a possible magnitude.
- When
A + B has 12 units, the angle
between A and B is
cos–1 (144 – 64 – 25)/(2 × 8 × 5) = 46°, thus 12 units is
a possible magnitude.
|
front 5 What is the formula between frequency and time intervals? | |
front 6 What is the frequency of the pulses that deliver laser radiation to
the cornea?
- A.0.4 Hz
- B.4.0 Hz
- C.25 Hz
- D.250
Hz
| back 6
The solution is B.
- This frequency implies the pulse period is 2.5 s.
-
The frequency is 1/(250 ms) = 4 Hz.
- This
frequency implies the pulse period is 0.04 s.
- This
frequency implies the pulse period is 4 ms.
|
front 7 The index of refraction does _______ due to either a pulsed laser or
a continuous laser, because it is an intrinsic property of the tissue material. | |
front 8 All “real” molecules and atoms will exhibit __________. It is not
possible to exhibit dipole–dipole forces only. | |
front 9 What is the formula for Kb and Ka? | |
front 10 The NF-κB signaling pathway is a rapid response mechanism for cells
that are under stress. | back 10 By activating genes that promote inflammation and immune responses,
NF-κB helps the cell and surrounding tissues cope with infections,
injury, or other stressors. However, its dysregulation (e.g., constant
activation) can contribute to chronic diseases, including cancer,
autoimmune diseases, and inflammatory disorders.
The NF-κB signaling pathway is anti-apoptotic and is initiated
by degradation and release of the inhibitor binding protein IκB. |
front 11 Based on the reaction scheme in Figure 1, what is the mechanism of
substrate binding to RT?
- A.Random order
- B.Ordered
- C.Ping-pong
- D.Double-displacement
| back 11
The solution is B.
- Random order would mean either substrate could bind first,
and Figure 1 shows the TP substrate binds first and the dNTP
substrate binds second.
-
Figure 1 shows that the TP substrate binds first without any
catalysis occurring and then the dNTP substrate binds. This is an
ordered mechanism.
- In a ping-pong mechanism, no
ternary complex is formed. However, the ternary complex RT/TP/dNTP
does form.
- Double-displacement is another term for
ping-pong mechanism, which means that no ternary complex is formed.
However, the ternary complex RT/TP/dNTP does form.
|
front 12 Text: The inhibitor binding pocket contains the side chains of
Val106 and Phe227, which make the strongest
interactions with compounds 1–3.
Based on the passage, what is the primary type of interaction that
RT makes with Compound 2?
- A.Covalent
- B.Hydrogen bonds
- C.Ionic
- D.Hydrophobic
| back 12
The solution is D.
- Figure 1 shows that the interactions of the inhibitors with
RT are reversible. Covalent interactions are usually irreversible.
Also, the side chains of valine and phenylalanine cannot
spontaneously form covalent bonds with the inhibitors.
- The
passage states that the strongest RT interactions with the
inhibitors come from the side chains of valine and phenylalanine.
These side chains cannot form hydrogen bonds.
- The passage
states that the strongest RT interactions with the inhibitors come
from the side chains of valine and phenylalanine. These side chains
cannot form ionic bonds.
-
The passage states that the strongest RT interactions with
the inhibitors come from the side chains of valine and
phenylalanine. These side chains are hydrophobic, so they would
make hydrophobic interactions with the inhibitor.
|
front 13 What is the formula for absorbance? | back 13
A = εbc
c - concentration
b - path length
ε - molar solubility |
front 14 The UV–VIS spectrophotometer used by the researchers contained a
detector that had low sensitivity and was unable to measure high
absorbance samples. Which approach to the experiment makes the most
sense with this limitation in mind?
- A.The experiments done at high pH should be diluted relative
to those at low pH, or the path length of the high pH experiments
should be decreased.
- B.The experiments done at low pH
should be diluted relative to those at high pH, or the path length
of the high pH experiments should be decreased.
- C.The
experiments done at high pH should be diluted relative to those at
low pH, or the path length of the low pH experiments should be
decreased.
- D.The experiments done at low pH should be diluted
relative to those at high pH, or the path length of the low pH
experiments should be decreased.
| back 14
The solution is A.
-
To not have an absorbance reading that is below the limits
of the detector, the experiments done at pH values that result in
the highest absorptivity should be diluted. The alternative is to
decrease the path length of the experiments that have the highest
absorptivity.
- Although decreasing the path length of
the experiments that have the highest absorptivity is reasonable,
the experiments at low pH already have low absorbance relative to
the high pH samples. Thus, there is no reason to dilute them.
- Although diluting the solutions in the experiments that have the
highest absorptivity is reasonable, the experiments at low pH
already have low absorbance relative to the high pH samples. Thus,
there is no reason to decrease their path lengths.
- The
experiments at low pH already have low absorbance relative to the
high pH samples. Thus, there is no reason to dilute them or to
decrease their path lengths.
|
front 15 _____________ causes the initially plane-parallel wave-fronts of
light to change direction and partially enter the shadow region behind
the thread due to its narrowness. The overlapping of different
wave-fronts on the screen causes the pattern of dark and bright
fringes on the screen according to the phase difference between the
wave-fronts that interfere there. | |
front 16 The ionic form of which metal atom is NOT likely to be found in the
pocket of a catalytically active DNA polymerase?
| back 16
The solution is D.
- Zinc forms the divalent cation Zn2+. As shown in
Figure 1, a divalent cation is essential for DNA polymerase
catalytic activity.
- Iron forms the divalent cation
Fe2+. As shown in Figure 1, a divalent cation is
essential for DNA polymerase catalytic activity.
- Magnesium
forms the divalent cation Mg2+. As shown in Figure 1, a
divalent cation is essential for DNA polymerase catalytic
activity.
-
Sodium does not readily form a divalent cation, essential
for DNA polymerase catalytic activity as shown in Figure
1.
|
front 17 Text:
Suppose a capacitor in a portable defibrillator needs to store 400
J at 5000 V. Suppose further that half that energy is actually passed
through a patient’s chest in a time of 1.0 ms.
Roughly to what height would a 5 kg stone need to be raised in
order to have the same stored energy as the energy stored in the
defibrillator’s capacitor?
- A.4 m
- B.8 m
- C.16 m
- D.32 m
| back 17
The solution is B.
- At this height (4 m), the gravitational potential energy is
200 J, which is half the 400 J of energy stored in the
defibrillator’s capacitor.
-
The gravitational potential energy is mass × gravitational
acceleration × height. Equating 400 J = 5 kg × 9.8 m/s2
× height and solving for height leads to 400 J/(49 kg ×
m/s2) ≈ 8 m.
- At this height (16 m),
the gravitational potential energy is 800 J, which is double the 400
J of energy stored in the defibrillator’s capacitor.
- At
this height (32 m), the gravitational potential energy is 1600 J,
which is four times the 400 J of energy stored in the
defibrillator’s capacitor.
|
front 18 One company sells a defibrillator for home use that uses a 9-volt DC
battery. The battery is rated at 4.2 A•hr (amp•hour). Roughly how much
charge can the battery deliver?
- A.4.2 C
- B.38 C
- C.15,000 C
- D.136,000 C
| back 18
The solution is C.
- This is the charge delivered in one second based on the
calculation 4.2 A × 1 s = 4.2 C.
- The magnitude is computed
as an approximation of 4.2 × 9 = 37.8 ≈ 38. However, multiplying the
corresponding units V × A•hr yields J, not C.
-
The definition of current is flow of charge per unit time.
Thus, charge equals current multiplied by time, hence 4.2 A × 1 hr
= 4.2 A × 3600 s = 15,120 C ≈ 15,000 C.
- The
magnitude is computed as an approximation of 4.2 × 9 × 3600 =
136,080 ≈ 136,000. However, multiplying the corresponding units V ×
A × s yields J, not C.
|
front 19 Suppose a defibrillator successfully returns a baby’s heart to normal
beating. Suppose further that 20 g of blood enters the heart at 25
cm/s and leaves 0.10 s later at 35 cm/s. What is the estimated average
force on the 20 g of blood as it moves through the baby’s heart?
- A.0.020 N
- B.0.20 N
- C.20 N
- D.2000
N
| back 19
The solution is A.
-
According to Newton’s second law, the average force is equal
to the mass of blood multiplied by the average acceleration of the
blood. The average acceleration is (35 cm/s – 25 cm/s)/0.10 s =
100 cm/s2 = 1 m/s2. The average force is 20
g × 1 m/s2 = 0.020 kg × 1 m/s2 = 0.020
N.
- Either the mass is incorrectly used as 0.20 kg,
or the average acceleration is incorrectly computed as 10
m/s2.
- Either the mass is incorrectly used as 2.0
kg, or the average acceleration is incorrectly computed as 100
m/s2.
- Either the mass is incorrectly used as 20
kg, or the average acceleration is incorrectly computed as 1000
m/s2.
|
front 20
Passage 10 (Questions 53-56)
When a person experiences cardiac arrest, that person’s heart
undergoes what is called ventricular fibrillation. In such an event,
various parts of the heart do not beat in a coordinated way, and the
heart becomes unable to pump blood. Medical professionals often treat
a cardiac arrest patient by administering an electric shock across the
chest during which a current is passed through the heart in a
relatively short amount of time (a few milliseconds). Such a shock can
cause the heart to become temporarily paralyzed. The goal is that the
paralyzed heart will then start beating in a normal way. Occasionally,
medical professionals must administer an electric shock to a patient
more than once.
The device medical professionals use to administer electric shocks
to a patient is called a defibrillator. Portable defibrillators are
found in ambulances and are used by emergency medical personnel on
patients who could not get to the hospital. A portable defibrillator
works by storing electric energy in a capacitor. Electrodes, sometimes
called “paddles,” are placed on a patient’s chest, and current can be
passed from one electrode to the other once a switch is flipped by a
medical professional. The defibrillator must be constructed to allow
multiple uses with a minimal time delay (less than a minute) between
applications. Suppose a capacitor in a portable defibrillator needs to
store 400 J at 5000 V. Suppose further that half that energy is
actually passed through a patient’s chest in a time of 1.0 ms.
The electric field inside each of the conductors that forms the
capacitor in the defibrillator is zero. Which of the following reasons
best explains why this is true?
- A.All of the electrons in the conductor are bound to atoms,
and thus there is no way for an external electric field to penetrate
atoms with no net charge.
- B.Free electrons in the conductor
arrange themselves on the surface so that the electric field they
produce inside the conductor exactly cancels any external electric
field.
- C.Free electrons in the conductor arrange themselves
on the surface and throughout the interior so that the electric
field they produce inside the conductor exactly cancels any external
electric field.
- D.All electrons in the conductor, both free
and bound, arrange themselves on the surface so that the electric
field they produce inside the conductor exactly cancels any external
electric field.
| back 20
The solution is B.
- Conductors are characterized by the existence of free
electrons that carry current.
-
Conductors contain both atom-bound electrons and free
electrons. Free electrons arrange themselves on the surface of
conductors, and their collective electric field produced inside
the conductor cancels any external electric field. The resulting
electric field inside the conductor is zero.
- Free electrons arrange themselves only on the surface of the
conductor. If they also arranged inside, the electric field inside
the conductor would move the electrons even in the absence of a
battery.
- Bound electrons cannot arrange themselves on the
surface of the conductor due to the binding effects.
|
front 21 Cytochromes are proteins that are involved in redox reactions.
Specifically, cytochrome P450 acts as a monooxygenase, catalyzing an
oxidation reaction. | back 21
Cytochrome P450 acts as monooxygenases, where an oxygen atom
is inserted into a substrate (the drug of interest), thereby
resulting in the oxidation of the substrate. |
front 22 A defining characteristic of proteins that act as transcription factors | back 22 contain a DNA binding domain. |
front 23 Where does fatty oxidation take place? | |
front 24 As blood passes through actively contracting skeletal muscle tissue,
the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen in the muscle tissue:
- A.increases as a result of an increase in plasma
temperature.
- B.increases as a result of an increase in plasma
P O2.
- C.decreases as a result of a
decrease in plasma pH.
- D.decreases as a result of a
decrease in plasma P CO2.
| back 24
The solution is C.
- Affinity would decrease with an increase in plasma
temperature.
- Affinity would increase when P
O2 increases. However, P O2 in muscle
cells decreases with exercise.
-
Affinity would decrease with a decrease in plasma pH, and
during prolonged exercise, anaerobic respiration would decrease
the plasma pH.
- Affinity would increase with a
decrease in plasma P CO2.
|
front 25 HENRY"s LAW
A researcher measures the concentration of
CO2(aq) in a solution at equilibrium. Which
additional quantity must be measured in order to calculate the Henry’s
Law constant k H for the gas?
- A.Atmospheric pressure
- B.Volume of the solvent
- C.Partial pressure of the gas
- D.Vapor pressure of
water
| back 25
The solution is C.
- The atmospheric pressure P atm is not a
factor in the Henry’s Law constant equation.
- The volume
V of the solvent is not a factor in the Henry’s Law
constant equation.
-
The Henry’s Law constant k H relates
the solubility of a gas S to the pressure of that gas
P g above the solution and is written as
S = k H•P g.
Therefore, in addition to the concentration of
CO2(aq) in a solution at equilibrium, the
partial pressure of the gas P g must be
measured.
- The vapor pressure P
v of water is not a factor in the Henry’s Law constant
equation.
|
front 26 Text:
The A component, also known as the S1 subunit, is an ADP ribosyl
transferase. S1 is associated with the B component, which contains the
S2, S3, S4, and S5 subunits complexed in a 1:1:2:1 molar ratio (Figure
1). After the B component binds to cell surfaces, the S1 subunit is
inserted into the cytoplasm, thereby inhibiting the heterotrimeric
Gi (inhibitory G) protein, a protein that normally inhibits
adenylate cyclase.
Based on the passage, which subunit of PTx is LEAST suitable for
generation of vaccine against B. pertussis?
| back 26
The solution is A.
-
When choosing an antigen for vaccine production, there are
two aspects to consider: immunogenicity and toxicity. S1 has the
ADP ribosyl transferase activity responsible for toxicity of PTx
and therefore is least suitable for vaccine
production.
- The S2 subunit is part of the B
component of PTx that binds to the cell surface and has no toxic
activity.
- The S4 subunit is part of the B component of PTx
that binds to the cell surface and has no toxic activity.
- The S5 subunit is part of the B component of PTx that binds to
cell surface and has no toxic activity.
|
front 27 What are the sizes for prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes? | back 27 70 S -50 and 30
80S - 40 and 60 |
front 28 Which experiment can be used to investigate the transcriptional
regulation of the Cdkn1a protein?
- A.Assessing Cdkn1a mRNA levels by RT-PCR
- B.Assessing Cdkn1a mRNA levels by Southern
blotting
- C.Assessing Cdkn1a protein levels by quantitative
PCR
- D.Assessing Cdkn1a protein levels by Western
blotting
| back 28
The solution is A.
-
As the question is focused on the transcriptional
regulation, it is logical to assess the mRNA levels as opposed to
protein levels. RT-PCR is a molecular technique that measures mRNA
levels of specific protein.
- Southern blot is a
technique that analyzes genomic DNA and cannot be used to measure
the transcriptional regulation of a gene.
- Quantitative PCR
is a technique that measures the levels of DNA, not mRNA, and cannot
be used to measure the transcriptional regulation of a gene.
- Western blot is a technique that measures the translational
levels of a protein, not the transcriptional regulation of a
gene.
Khan Academy Lessons |
front 29 What are pro-inflammatory cytokines? | back 29 Pro-inflammatory cytokines are molecules that help the immune system
respond to infection or injury by promoting inflammation. They attract
immune cells to the affected area, increase blood vessel permeability,
and may cause fever to fight off pathogens. However, too many
pro-inflammatory cytokines can lead to chronic inflammation and
contribute to diseases.
*can promote apoptosis |
front 30 A peptide consisting of nine amino acids was partially hydrolysed.
Three different tripeptides were isolated. None of the tripeptides
share a common amino acid. Based on the data, what is the total number
of possible structures possible for the full-length peptide?
| back 30
The solution is C.
- Three is the number of tripeptides that were formed by
hydrolysis of the nonapeptide. This, however, is not the number of
unique possible nonapeptides that are consistent with the hydrolysis
data.
- There are more than four nonapeptides possible that are
consistent with the hydrolysis data.
-
If the sequences were ABC, DEF, and GHI, they can only be
joined in 6 different possible ways to make a nonapeptide. Each of
the tripeptides can appear in the first position and can combine
in two possible ways with the other two tripeptides: 3 × 2 =
6.
- There are nine amino acids in the full-length
peptide. These are hydrolyzed to three unique tripeptides that do
not share any amino acids in common. The product 9 × 3 = 27. This,
however, does not represent the number of unique possible
full-length sequences that are consistent with the hydrolysis
data.
|
front 31 Which of the following statements best applies to the inactive X
chromosome in mammalian females?
- A.It does not replicate.
- B.Its chromatin structure is
less condensed than that of an active X chromosome.
- C.It is
one of the last chromosomes to replicate.
- D.It is highly
transcribed.
| back 31
The solution is C.
- Both the active and inactive X chromosomes replicate.
- The chromatin of the inactivate X chromosome is more condensed
compared to the one of the active X chromosome.
-
The inactivate X chromosome is one of the last chromosomes
to replicate.
- The inactivate X chromosome is not
highly transcribed.
|
front 32 The negative control used in Experiment 1 was most likely:
- A.unconditioned media without AECs.
- B.unconditioned
media with AECs.
- C.conditioned media without AECs.
- D.conditioned media with AECs.
| back 32 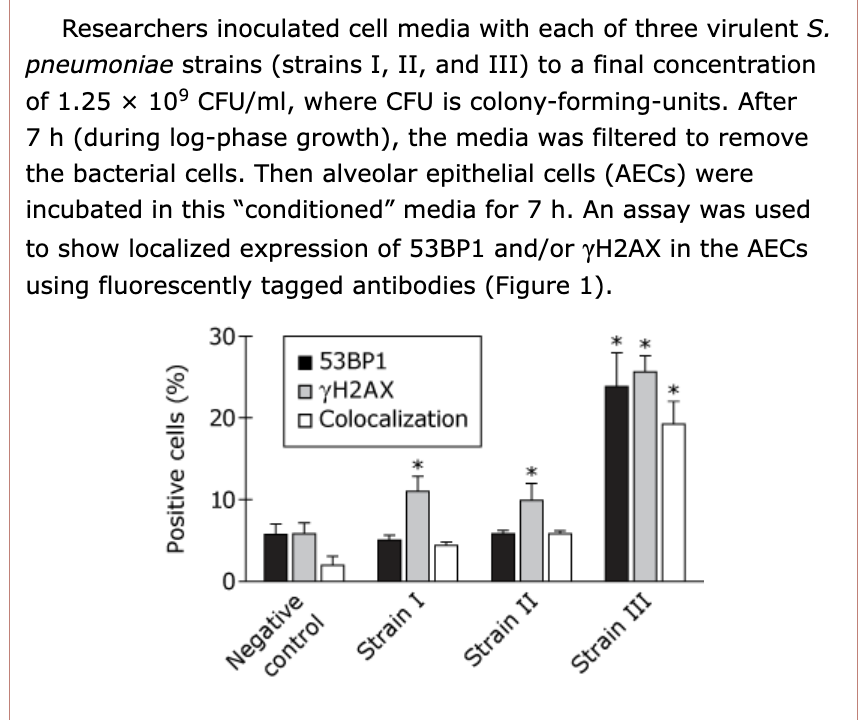
The solution is B.
- A negative control is the one that is performed in the
conditions that are not expected to give positive results. Thus,
unconditioned media will need to be used. As antibodies are highly
specific, if 53BP1 and γH2AX are detected in the negative control,
this means that AEC are present.
-
A negative control is the one that is performed in the
conditions that are not expected to give positive results. Thus,
unconditioned media will need to be used. As antibodies are highly
specific, if 53BP1 and γH2AX are detected in the negative control,
this means that AEC are present.
- A negative
control is the one that is performed in the conditions that are not
expected to give positive results. Thus, unconditioned media, not
conditioned media, will need to be used. As antibodies are highly
specific, if 53BP1 and γH2AX are detected in the negative control,
this means that AEC are present.
- A negative control is the
one that is performed in the conditions that are not expected to
give positive results. Thus, unconditioned media, not conditioned
media, will need to be used. As antibodies are highly specific, if
53BP1 and γH2AX are detected in the negative control, this means
that AEC are present.
|
front 33 Which of the following events does the release of CCK likely trigger?
- A.Relaxation of muscle in wall of gallbladder and relaxation
of hepatopancreatic sphincter
- B.Contraction of muscle in
wall of gallbladder and relaxation of hepatopancreatic
sphincter
- C.Relaxation of muscle in wall of gallbladder and
contraction of hepatopancreatic sphincter
- D.Contraction of
muscle in wall of gallbladder and contraction of hepatopancreatic
sphincter
| back 33
The solution is B.
- The passage states that in the presence of CCK, more bile is
released. For this to happen, the smooth muscles around the gall
bladder will have to contract, not relax, and the hepatopancreatic
sphincter will have to relax.
-
The passage states that in the presence of CCK, more bile is
released. For this to happen, the smooth muscles around the gall
bladder will have to contract, and the hepatopancreatic sphincter
will have to relax.
- The passage states that in
the presence of CCK, more bile is released. For this to happen, the
smooth muscles around the gall bladder will have to contract, not
relax, and the hepatopancreatic sphincter will have to relax, not
contract.
- The passage states that in the presence of CCK,
more bile is released. For this to happen, the smooth muscles around
the gall bladder will have to contract, and the hepatopancreatic
sphincter will have to relax, not contract.
|
front 34 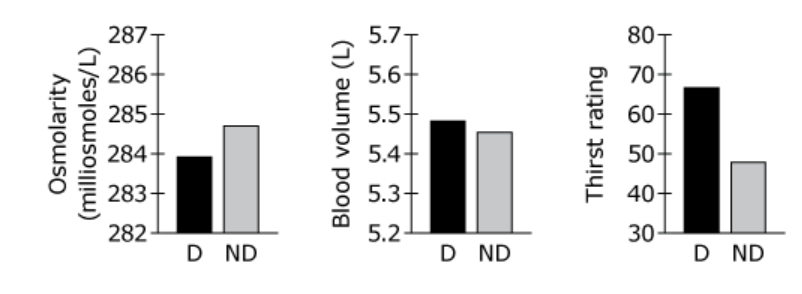 On the day of the experiment, the subjects drank about 1 L of water
on average and excreted about 400 mL of urine. The most likely
explanation for the difference between water intake and urine
excretion is that:
- A.the extra water was stored as blood.
- B.water was
consumed with the food that was eaten.
- C.the extra water
was excreted by the intestine.
- D.water was excreted via the
skin and the lungs. The solution is D.
- The extra water
cannot be stored as blood because this would increase the blood
volume.
- If the water was consumed with the food that was
eaten, then it would be absorbed and accumulate in circulation,
increasing the volume of blood.
- Extra water could be
excreted through the intestine if the subjects were having
diarrhea. As the passage does not indicate this condition, this
answer is not likely.
-
Extra water is normally excreted through skin and lungs.
The skin excretes water through the process of transpiration,
and the lungs use water to humidify the air that enters the
body.
| back 34
The solution is D.
- The extra water cannot be stored as blood because this would
increase the blood volume.
- If the water was consumed with
the food that was eaten, then it would be absorbed and accumulate in
circulation, increasing the volume of blood.
- Extra water
could be excreted through the intestine if the subjects were having
diarrhea. As the passage does not indicate this condition, this
answer is not likely.
-
Extra water is normally excreted through skin and lungs. The
skin excretes water through the process of transpiration, and the
lungs use water to humidify the air that enters the
body.
|
front 35 The osmolarity of urine in these subjects was 958 milliosmoles/L,
compared with an average blood osmolarity of 284 milliosmoles/L. The
higher osmolarity of urine suggests that:
- A.the kidneys are secreting very little Na+.
- B.the kidneys are acting to conserve water.
- C.the
subjects are on a low-protein diet.
- D.the subjects are
dehydrated.
| back 35
The solution is B.
- If the kidneys were excreting low amounts of Na+,
urine osmolarity would be lower, and the osmolarity of the blood
would be higher because there would be more Na+ in
circulation.
-
An increase in water conservation would result in higher
urine osmolarity and lower blood osmolarity.
- High levels of proteins, not low levels, result in higher urine
osmolarity.
- If the subjects were dehydrated, the osmolarity
of blood and urine would be closer.
|
front 36 Which of the following responses could maintain cardiac output under
dehydration conditions that reduce blood volume?
- A.A decrease in stroke volume
- B.A decrease in heart
rate
- C.An increase in heart rate
- D.An increase in
blood viscosity
| back 36
The solution is C.
- The stroke volume is the amount of blood that is pumped by the
left ventricle per beat. In dehydration conditions a decrease in
stroke volume will decrease, not maintain, the cardiac output.
- The heart rate is the number of heart contractions per minute. A
decrease in heart rate would decrease, not maintain, the cardiac
output.
-
The heart rate is the number of heart contractions per
minute. An increase in heart rate would maintain the cardiac
output in dehydration conditions.
- An increase in
blood viscosity would not be able to maintain cardiac output under
dehydration conditions.
|
front 37
Reverse transcriptase converts _______________ | |
front 38 According to Figure 1, as the embryo begins gastrulation, the number
of cells is between:
- A.4 and 6.
- B.6 and 40.
- C.40 and 10,000.
- D.10,000 and 100,000.
| back 38
The solution is D.
- Please note that the values on the y-axis are on
Log10. Log10 6 = 0.78 on the y-axis.
Based on the graph, the cell division is very pronounced between 4
and 6 cell stage.
- Please note that the values on the
y-axis are on Log10. Log10 40 = 1.60
on the y-axis. Based on the graph, the cell division is
still very pronounced between 6 and 40 cell stage.
- Please
note that the values on the y-axis are on Log10.
Log10 10,000 = 4 on the y-axis. Based on the
graph, the cell division starts to slow down just after the
10,000-cell stage. Gastrulation does not start before 10,000
cells.
-
Please note that the values on the y-axis are on
Log10. Based on the graph, cell division just starts to
slow down after the 10,000-cell stage, which corresponds to the
value of 4 in the y-axis of the graph. For this reason,
gastrulation should start between 10,000 and 100,000
cells.
|
front 39 The presence of which type of intercellular connections between
endothelial cells of brain capillaries results in the blood–brain barrier?
- A.Desmosomes
- B.Gap junctions
- C.Intercalated
discs
- D.Tight junctions
| back 39
The solution is D.
- Desmosomes are intercellular junctions that function as
anchors to form strong sheets of cells.
- Gap junctions are
intercellular junctions that provide cytoplasmic channels between
adjacent cells.
- Intercalated discs are specialized
intercellular junctions between cardiac muscle cells that provide
direct electrical coupling among cells.
-
Tight junctions are intercellular junctions that prevent the
movement of solutes within the space between adjacent cells. In
blood capillaries, neighboring endothelial cells form tight
junctions with one another to restrict the diffusion of harmful
substances and large molecules into the interstitial fluid
surrounding the brain.
|
front 40 If the third codon in the coding region of the Rdl GABA
receptor cDNA is replaced with an amber codon (for example, TAG) and
the modified Rdl GABA receptor cDNA is expressed in frog
oocytes, functional full-length receptors will:
- A.accumulate in the Golgi complex.
- B.accumulate in
the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
- C.not be synthesized.
- D.lose resistance to dieldrin.
| back 40 TAG is part of the coding or sense strand (" If the third codon
in the coding region ") --> mRNA is the same as the sense
strand except you replace T with U --> TAG becomes UAG which is one
of the three stop codons (UAA, UGA, UAG)
The solution is C.
- An amber codon is a stop codon. If the third codon is replaced
with a stop codon, the protein will not be synthesized, and for this
reason, it cannot accumulate in the Golgi.
- An amber codon
is a stop codon. If the third codon is replaced with a stop codon,
the protein will not be synthesized, and for this reason, it cannot
accumulate in the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
-
An amber codon is a stop codon. If the third codon is
replaced with a stop codon, the protein will not be
synthesized.
- An amber codon is a stop codon. If the
third codon is replaced with a stop codon, the protein will not be
synthesized, which will make the oocytes resistant to dieldrin
simply because the agent dieldrin reacts with is absent.
|
| back 41 In summary: when the reverse transcriptase synthesizes the cDNA, it
reads the mRNA and creates a complementary DNA strand, with U
(from RNA) replaced by T (in DNA). This is why cDNA is a
DNA copy of the mRNA sequence, with the only difference being the base
substitution: U → T.
- mRNA is like a "recipe" that tells a cell how to
make a protein. It’s made from DNA but is written in a different
"language" using letters A, U, G, and C.
- cDNA is
made by copying the mRNA. It's a DNA version of that
"recipe" but written in the DNA "language"
(which uses the letters A, T, G, and C, instead of A, U, G, and
C).
- Key difference: The main difference between mRNA and cDNA
is that where mRNA has the letter U, cDNA has a T. So, the letter U
(in RNA) is replaced by T (in DNA).
- Starting point: cDNA is made from mRNA (messenger RNA).
- Process: The mRNA is used as a template to create cDNA through a
process called reverse transcription. In this process:
- The
mRNA's "recipe" (its sequence of A, U, G, C) is read
by an enzyme.
- A complementary DNA strand is made by
replacing the U in mRNA with T
(because DNA uses T instead of U).
- End
result: The end result is cDNA, which is a DNA copy of the mRNA. So,
the mRNA (which has U's) gets transformed into a cDNA sequence
(which has T's instead of U's).
|
front 42 Endosomes are formed to transport a substance ______________ | back 42 from the outside of the cell, not inside the cell.
Endosomes are formed when the cell takes in material from outside
(through a process called endocytosis), and they play
a key role in sorting and directing these materials either to |
front 43 Which procedure would be the best negative control for endogenous
GABA-receptor function in frog oocytes?
- A.Addition of GABA to mock-transfected frog oocytes
- B.Transfection of wild-type GABA receptor into insect
oocytes
- C.Addition of excess GABA to Rdl-transfected
oocytes
- D.Transfection of wild-type GABA receptor into
Rdl-expressing oocytes
| back 43
The solution is A.
-
Transfection of GABA to mock-transfected frog oocytes would
be the best negative control for endogenous GABA-receptor
function. This procedure would ensure that the process of
transfection per se does not generate a response to
GABA.
- The insect oocytes already have the GABA
receptor, so transfection of more GABA receptors would not generate
a negative control. On the contrary, it might increase the
sensitivity to GABA.
- Addition of excess GABA to
Rdl-transfected oocytes would not be a good negative
control on the function of GABA-receptors because Rdl is not
responsive to GABA. In this case, no reaction is possible.
- Transfection of wild-type GABA receptor into
Rdl-expressing oocytes would restore sensitivity to GABA.
This method is not a negative control but a rescue experiment.
|
front 44 In Drosophila, white eyes are recessive to red eyes, and
yellow bodies are recessive to dark bodies; both genes are on the X
chromosome. The genotype of a red-eyed, dark-bodied female (XX) could
be determined by mating it with a male (XY) that has which of the
following phenotypes?
- A.Red eyes, dark body
- B.Red eyes, yellow body
- C.White eyes, dark body
- D.White eyes, yellow body
| back 44
The solution is D.
- The question tests the knowledge of the test cross. Crossing a
phenotypically dominant female with a phenotypically dominant male
(red eyes and dark body) will not allow one to determine the
genotype of the female.
- The question tests the knowledge of
the test cross. Crossing a phenotypically dominant female with a
male that is recessive for the body color (yellow body) but dominant
for the eye color (red eyes) will not allow one to determine the
genotype of the female.
- The question tests the knowledge of
the test cross. Crossing a phenotypically dominant female with a
male that is recessive for the eye color (white eyes) but dominant
for the body color (dark body) will not allow one to determine the
genotype of the female.
-
This question tests the knowledge of the test cross. This is
a method to identify if an organism that shows a dominant
phenotype is a homozygous or heterozygous. The female is red-eyed
and dark bodied, which means she has a dominant phenotype.
However, the female could also be homozygous or heterozygous for
one or both traits. Mating this type of female with a male with a
recessive phenotype for both traits (white eyes and yellow body)
would determine the genotype of the female.
|
front 45 What is involved in a test cross? | back 45 A test cross is a genetic experiment used to
determine the genotype of an individual that exhibits a dominant
trait. The basic idea is to cross the individual in question (whose
genotype is unknown) with an individual that is homozygous
recessive for the trait.
Here’s what happens in a test cross:
- Unknown Genotype (Dominant Trait): The individual you are
testing shows a dominant trait, but you don’t know whether they are
homozygous dominant (AA) or heterozygous (Aa).
- Homozygous
Recessive Partner: You cross this individual with another individual
that is homozygous recessive (aa) for the same trait. This ensures
the partner can only pass on the recessive allele (a).
- Results Interpretation:
- If the individual is
homozygous dominant (AA), all offspring will
inherit one dominant allele (A) from the parent and one
recessive allele (a) from the partner. All offspring will show
the dominant trait (genotype Aa).
- If the individual is
heterozygous (Aa), about half of the
offspring will show the dominant trait (genotype Aa), and the
other half will show the recessive trait (genotype aa). This is
because the heterozygous parent will pass on either the A or the
a allele randomly.
|
front 46 What is discriminating stimuli? | back 46 Discriminating stimuli refer to environmental cues or signals that
help an individual or organism differentiate between different
situations or responses. In behavioral psychology, they are signals
that indicate whether a specific behavior will be reinforced or punished. |
front 47 The traditional behaviorist approach does _______________. | back 47 not regard mental processes as real.
It holds that only actual outcomes of a behavior determine
whether that behavior will be repeated. |
front 48 Which statement best explains how the concept of external motivation
(used by SDT) is different from extrinsic motivation?
Compared to external motivation, extrinsic motivation:
- A.is a broader term that includes external motivation.
- B.is a narrower term that refers to external reinforcers.
- C.excludes social punishers and reinforcers.
- D.excludes
internal states that direct behavior.
| back 48
The solution is A.
-
Extrinsic motivation refers to any motivation that results
from incentives to perform a behavior that are not inherent to the
behavior itself. External motivation is described as social
pressure, which is an example of extrinsic
motivation.
- Extrinsic motivation includes both
punishers and reinforcers.
- Social punishers and reinforcers
(as in external motivation) are included in extrinsic
motivation.
- Internal states are irrelevant to external
motivation as described in the passage.
|
front 49 Which statement best applies Rogers’s concept of incongruence to
SDT’s suggestion for how healthcare professionals can promote
autonomous motivation?
- A.By encouraging their patients’ initiative, healthcare
professionals motivate their patients to reduce the gap in their
need for self-actualization.
- B.By giving their patients
options, healthcare professionals make it possible for their
patients to reduce the gap between their actual behavior and their
expected behavior.
- C.By encouraging the patients’
initiative, healthcare professionals motivate their patients to
reduce the gap between their behaviors and their attitudes.
- D.By giving their patients options, healthcare professionals
offer their patients ways to reduce the gap between their ideal
selves and their actual selves.
| back 49
The solution is D.
- Incongruence does not refer to a person’s need for
self-actualization.
- Incongruence does not refer to a gap
between a person’s actual and expected behavior.
- Incongruence does not refer to the gap between a person’s
behavior and attitudes.
-
Incongruence refers to the gap between a person’s actual
self and ideal self.
|
front 50 What is Roger's concept of incongruence? | back 50 Roger's concept of incongruence refers to a mismatch
or conflict between a person's self-image (how they see themselves)
and their ideal self (how they would like to be). This gap can lead to
feelings of discomfort, anxiety, or frustration because the person
feels that their true self doesn't align with who they want to be.
Example in simple terms:
Imagine a person who sees themselves as someone who is confident and
social (self-image), but deep down they feel shy and insecure in
social situations (ideal self). This mismatch creates
incongruence. The person might struggle with feelings
of dissatisfaction because their actual behavior doesn't match their
ideal sense of who they are.
In summary, incongruence happens when there's a disconnect between
how we see ourselves and how we want to be, which can lead to
emotional distress. |
front 51 What is base rate fallacy? | back 51 - The base rate fallacy refers to the error people make when they
ignore the base rates (i.e., prior probabilities) when evaluating
the probabilities (or frequencies) of events.
|
front 52 What is public verifiabiltiy? | back 52 - the reason other scientists are attempting to replicate the
original findings.
|
front 53 What is the function of the lens? | back 53 - The cornea and iris can accommodate and focus the incoming
light rays. This is not a function of the retina.
-
The retina contains photoreceptors such as rods and cones,
which detect light and transduces light to energy. The energy
eventually becomes an action potential and the signal travels
through the optic nerve and travels to the primary visual
cortex.
- The retina does not function in providing
oxygen and nutrients for the vitreous humor. The vitreous humor is a
gel-like substance that is in the posterior segment of the eye.
- The lens can focus the incoming light rays on the
photoreceptors. This is not a function of the retina.
|
front 54 What is the glass escalator concept? | back 54 The sociological concept of the “glass escalator” suggests that men
who pursue occupations that have high proportions of women (such as
teaching or nursing) will quickly ascend the career ladder with promotions. |
front 55 Which concern about the study reflects problems as a result of the
response rate?
- A.Participants provided four responses to four hypothetical
scenarios.
- B.The participants may differ from the employees
who did not respond to the survey.
- C.The manager and
assistant participants may have interpreted the scenarios
differently.
- D.Participants were aware of the status of the
target employee.
| back 55
The solution is B.
- Any threats to the internal validity of the study created by
the repeated measures approach (which are usually addressed through
counter-balancing or similar techniques) would also be present with
a 100% response rate.
-
A low response rate to a survey raises the question of
whether the survey respondents differ from the nonrespondents on
some important characteristics, such as personality traits or
other factors.
- Differences between how manager
and assistant participants may have interpreted the scenarios are
expected, based on the experimental design for testing
in-group/out-group differences.
- It is true that
participants were aware of whether the target employee was a manager
or an assistant; this is how the researchers manipulated in-group
and out-group bias. This manipulation was independent of response
rate.
|
front 56 How would the pattern of attributions found in the study most likely
be predicted to change during times of intense group conflict between
managers and assistants?
- A.Recognizing the need to reduce conflict, situational
attributions would be the most common.
- B.The conflict would
increase the effects of the in-group and out-group bias.
- C.In-group bias fighting within the organization would reverse
the pattern of attributions found in the study.
- D.The
increase in self-reliance during conflict would reduce the in-group
and out-group bias effects.
| back 56
The solution is B.
- Although situational attributions would likely prevent a
conflict to spiral out of control, people are less likely to make
situational attributions when emotions rise during conflict.
-
Intense group conflict increases the effects of the in-group
and out-group bias and would most likely have the same effects on
the attributions made by the different groups. For example, a
delay in responding by management caused by some computer
malfunction would be much more likely to be attributed to an
internal factor (“they are not trustworthy”) compared to a
situational factor (“computer malfunction”).
- Conflict between groups (management versus assistants) tends to
reduce in-group bias fighting and unify the group against the
out-group.
- Increased group cohesion is more common than
increased self-reliance during times of conflict.
|
front 57 People have a self-serving bias, wherein ________________________________ | back 57 people tend to attribute their own successes to internal factors and
attribute their own failures to external factors. |
front 58 A consultant is hired by an organization to break down barriers
between managers and assistants by conducting a series of
team-building activities over a period of time. If the team-building
activities are successful, how would they most likely influence the
attributions made by the organization’s employees?
- A.Managers would attribute positive outcomes by other managers
to situational factors.
- B.Managers and assistants would
attribute positive outcomes by managers to dispositional
factors.
- C.Assistants would attribute negative outcomes by
other assistants to dispositional factors.
- D.Managers and
assistants would attribute negative outcomes by managers to
dispositional factors.
| back 58
The solution is B.
- If team-building has been successful, then the managers will
attribute all positive outcomes to dispositional factors.
-
If the team building activities are fully effective, then
the managers and assistants would all see themselves as part of
one group. There would be an in-group bias for all employees. They
would all make dispositional attributions for their coworkers’
successes and situational attributions for their coworkers’
failures.
- If team-building has been successful, then
the assistants will attribute all negative outcomes to situational
factors.
- If the team building activities are fully effective,
then both managers and assistants will attribute all negative
outcomes to situational factors, regardless of whether a manager or
an assistant performed the behavior that led to a negative
outcome.
|
front 59 Labeling theory is closely associated to _______ | |
front 60 A researcher applying the sociological perspective of labeling theory
to the passage is likely to suggest that social skills training will
have the greatest impact on:
- A.social stigma applied to some students.
- B.social
capital represented by the school.
- C.cultural capital
associated with the school.
- D.cultural diversity reflected
in the students.
| back 60
The solution is A.
-
Labeling theory suggests that people are often placed into
social categories, one of which could be a stigmatized category.
Thus, labeling theory is most closely associated with social
stigma. As related to the passage, labeling theory would suggest
that social skills training could potentially prevent or
counteract the stigmatization of some students in
schools.
- Social capital focuses on the value of
social networks and is not closely connected to labeling
theory.
- Cultural capital (social status derived from
knowledge, preferences, or skills connected to the school) is not
specifically relevant to labeling theory.
- The cultural
diversity of the students is not directly relevant to labeling
theory.`
|
front 61 Attraction and commitment to a group is likely to be greatest when
group members:
- A.promote their social networks.
- B.express diverse
cultural values.
- C.share equivalent cultural capital.
- D.present their back-stage selves.
| back 61
The solution is C.
- Promoting group members’ distinct social networks has the
potential for illustrating differences. It would not provide a
common characteristic that strengthens group bonds.
- Although diverse cultural values can be a source of strength for
a group, it can also provide disconnection and possible
disagreement. Thus, the impact is likely to be uneven.
-
Group affiliation (attraction and commitment) is likely to
be greatest when the members or participants in the group share
similar outlooks, knowledge, preferences, skills, and other
aspects of cultural capital. Among the options, similarity in
cultural capital would be most likely to solidify group bonds in a
way that increases commitment to the group.
- The
back-stage self is presented when an individual does not feel the
need to conform to certain expectations. In most social interactions
within groups, individuals will be presenting their front-stage self
(acting according to group norms and expectations).
|
front 62 When asked whether a person who is afraid of spiders would be
diagnosed as having a psychological disorder, a psychologist replies,
“It depends on whether or not this fear interferes with the person’s
life.” The psychologist appears to rely most heavily on which
criterion of abnormality?
- A.Distress
- B.Maladaptiveness
- C.Statistical
deviancy
- D.Violation of social norms
| back 62
The solution is B.
- The distress criterion takes into account whether the behavior
demonstrates unusual or prolonged levels of stress.
-
The maladaptiveness criterion takes into account whether the
behavior negatively impacts the person’s life or poses a threat to
others.
- The statistical deviancy criterion takes
into account whether the behavior is statistically rare.
- The violation of social norms criterion takes into account
whether the behavior violates social norms.
|
front 63 In an evaluation study for a diabetes intervention program, the
subjects in the sample had a median age of 45 and a mean age of 55.
Which statement accounts for the difference between the median age and
the mean age?
- A.The sample had more subjects under the age of 45 than over
the age of 45.
- B.The sample had more subjects over the age
of 45 than under the age of 45.
- C.The sample included
subject(s) who were much older than the age of 45.
- D.The
sample included subject(s) who were much younger than the age of
45.
| back 63
The solution is C.
- This option states that there are more subjects under age 45
than over age 45. However, the median splits the distribution with
an equal number of subjects above and below it.
- This option
states that there are more subject over age 45 than under age 45.
However, there are an equal number of subjects above and below the
median of distribution.
-
A mean age (of 55) that is higher than the median age (of
45) suggests that the sample had a skew toward older ages. One way
to represent this is to say that the sample included subject(s)
who were much older than the average age.
- If
the sample included subject(s) who were much younger than 45, then
the mean would most likely skew younger than the median age.
|
front 64 Which research design would allow a researcher to determine whether
the study’s finding about heterosexual marriage and alcohol
consumption also holds for same-sex marriage?
- A.Ask a random sample of respondents whether individuals in
same-sex marriages consume alcohol in different patterns than
married heterosexuals.
- B.Conduct a study of gender role
attitudes that consists of respondents currently living with a
partner, including those in same-sex marriages.
- C.Survey
alcohol consumption patterns of a random sample of American adults
across demographic characteristics, including sexual
orientation.
- D.Compare rates of alcohol consumption among a
random sample of single, homosexual respondents and those married to
a same-sex partner.
| back 64
The solution is D.
- This design calls for measuring opinions or beliefs about
consumption patterns rather than behavior. It would not provide data
on differences in behavior based on marital status.
- This
design does not explicitly measure one of the variables (alcohol
consumption). Instead, this study would measure variation in gender
role attitudes among cohabiting couples.
- This design does
not explicitly measure the role of same-sex partnerships. It would
allow comparison across sexual orientation (and other demographic
characteristics) but would not be able to determine the relationship
between alcohol consumption and marital status.
-
To assess the relationship between variables, both variables
must be measured and exhibit variation. The key describes an
appropriate design because both variables (alcohol consumption and
same-sex partnerships) are measured for a relevant population. It
would thus provide data that could provide for a comparison with
the findings of the study in the passage.
|
front 65
When participants respond to questions about their childhood
health history, they are retrieving autobiographical information,
which is an important type of ____ | |
front 66 The findings of Study 1 suggest that the assessment of alcohol use
involved which indicator?
- A.Presence of aggressive behaviors
- B.Presence of
withdrawal symptoms
- C.Difficulty with memory function
- D.Difficulty with impulse control
| back 66
The solution is B.
- Although aggressive behaviors can be associated with alcohol
use, the presence of such behaviors can be the result of several
other factors besides alcohol dependence.
-
Alcohol dependence is most strongly indicated by withdrawal
symptoms.
- Although memory problems can be associated
with alcohol use, the presence of such problems can be the result of
several other factors besides alcohol dependence.
- Although
impulse control can be associated with alcohol use, its presence can
be the result of several other factors besides alcohol
dependence.
|
front 67 Text: In addition, childhood psychological disorders predicted
marital instability and were associated with the Big Five personality
traits during adulthood.
Based on the findings of Study 2, which characteristic in adulthood
is LEAST likely associated with childhood psychological disorders?
- A.Conscientiousness
- B.Agreeableness
- C.Neuroticism
- D.Impulsivity
| back 67
The solution is D.
- Conscientiousness is one of the personality traits identified
in Cattell’s Five Factor (BIG Five) theory.
- Agreeableness
is one of the personality traits identified in Cattell’s Five Factor
(BIG Five) theory.
- Neuroticism is one of the personality
traits identified in Cattell’s Five Factor (BIG Five) theory.
-
The passage states that Study 2 found childhood
psychological disorders were associated with the Big Five
personality traits during adulthood. Impulsivity is not among the
factors identified in Cattell’s Five Factor (the BIG Five)
theory.
|
front 68 Text: Statistical analyses revealed that retrospective reports of
depressive symptoms or alcohol dependence were associated with lower
income during adulthood.
Based on the results of Study 1, which symptom in childhood is most
likely to be a risk factor for lower SES in adulthood?
- A.Repetitive behaviors
- B.Unwanted cognitions
- C.Delusions of grandeur
- D.Feelings of
worthlessness
| back 68
The solution is D.
- Repetitive behaviors are symptoms of obsessive-compulsive
disorder, not substance abuse or depression.
- Unwanted
cognitions are symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder, not
substance abuse or depression.
- Delusions of grandeur is a
symptom of schizophrenia not substance abuse or depression.
-
Study 1 found an association between childhood depression
and substance use and lower SES in adulthood. Feelings of
worthlessness is among the symptoms of depression.
|
front 69 What is the naming explosing? | back 69 Refers to a rapid increase in a young child's vocabulary, typically
occurring between 18 and 24 months of age. During this period,
toddlers begin to learn and use a large number of words very quickly,
often labeling objects, people, and actions in their environment.
Before the naming explosion, toddlers may have a smaller vocabulary,
usually consisting of a few words or sounds. But once the naming
explosion begins, they may start picking up new words every day, and
their vocabulary can grow from a handful to several hundred words in a
relatively short time. |
| back 70
“Overextension” is the term for applying a term for one class
of objects to other objects that bear only a superficial resemblance
(for example, “doggie” for a cow). |
front 71 What is categorical perception? | back 71 Categorical perception refers to the way we perceive stimuli (such as
sounds, colors, or objects) as belonging to distinct categories, even
when there might be subtle differences between them. Essentially, we
tend to group things into "categories" rather than noticing
the small differences between them. |
| back 72 Refers to the initial stage(s) of grammatical (i.e., syntactic) development. |
front 73 What is elaborative encoding? | back 73
Elaborative encoding is a memory technique where new
information is linked to existing knowledge in a meaningful way. By
making these connections, the information becomes more memorable and
easier to recall. It’s a process that helps transform simple, shallow
information into deeper, more meaningful memories.
For example, you could think of the famous character
"Alice" from Alice in Wonderland. You might also
picture her with a curious look on her face, like the character, which
creates a vivid image and a meaningful link to the name. |
front 74 What is systematic desensitization? | back 74
Systematic desensitization is a type of behavioral
therapy used to help people reduce or eliminate their fear or anxiety
toward a specific object or situation. It involves gradually exposing
the person to the feared stimulus in a controlled and gradual way,
while helping them remain relaxed. The goal is to replace the fear
response with a relaxation response.
If someone has a fear of flying:
-
Relaxation training: They learn relaxation
techniques.
-
Fear hierarchy: The list might start with looking
at pictures of airplanes, then watching videos of flights, imagining
being on a plane, sitting in a stationary plane, and finally flying
on an airplane.
-
Gradual exposure: The person begins with looking at
pictures and progresses through each step, practicing relaxation
techniques until they no longer feel anxious.
|
front 75 Which statement does NOT describe a monocular depth cue?
- A.Objects that are higher up in the visual field are perceived
as being farther away than the objects that are lower in the visual
field.
- B.Objects that are occluded by other objects are
perceived as being farther away than the objects that occlude
them.
- C.Objects that have more detailed textures are
perceived as being closer than objects that have less detailed
textures.
- D.Objects that are to the front of the point of
focus are perceived as being closer than objects that are behind the
point of focus.
| back 75
The solution is D.
- This statement describes retinal height, which is a monocular
depth cue.
- This statement describes occlusion, which is a
monocular depth cue.
- This statement describes texture
gradient, which is a monocular depth cue.
-
Using the distance from the object of focus as a depth cue
is associated with retinal disparity, which is a binocular depth
cue.
|
front 76 Globalization is more likely to increase awareness of each disorder, ___________ | back 76 due to the spread of knowledge and treatment modalities across the world. |
front 77 Efforts to raise public awareness about dementia in LMICs are most
likely to take the form of which community-based program?
- A.Inform people that dementia is an abnormal condition rather
than a normal part of aging.
- B.Educate people about all the
disorders that can lead to dementia if they are left untreated.
- C.Help people to distinguish between fluid intelligence and
crystallized intelligence.
- D.Explain to people that memory
interference occurs more often than memory decay.
| back 77
The solution is A.
-
Dementia is an abnormal condition, and not an inevitable
result of normal aging. Making people aware of this fact may help
alleviate the problem of underreporting of dementia in LMICs,
mentioned in the passage.
- Listing all the
disorders involving dementia would not be helpful, because
Alzheimer’s Disease is the cause of most dementia cases. In
addition, such a program may lead to increased levels of
stigmatization of persons with dementia, which could, in turn, bring
about increased underreporting of dementia in LMICs.
- Informing people about the distinction between fluid and
crystallized intelligence is unlikely to raise public awareness of
dementia. Declines in fluid intelligence can be expected to occur as
a normal result of aging, rather than an abnormal condition.
- Informing people about the distinction between decay and
interference is unlikely to raise public awareness of dementia,
because that distinction is not clearly relevant to dementia.
|
front 78 The focus on structural factors, such as poverty or race/ethnicity,
is most consistent with ________, which focuses on the social
determinants of health and disease. | |
front 79 Text: However, excessive alcohol use is also associated with
preventable injuries, which are more likely to result from binge
drinking than alcohol dependence.
The distinction between binge drinking and alcohol dependence in the
passage is best described as attributing preventable injuries to which
effect of alcohol use?
- A.Tolerance
- B.Disinhibition
- C.Negative
reinforcement
- D.Positive reinforcement
| back 79
The solution is B.
Disinhibition refers to the reduction or removal of a person's
usual inhibitions or self-control, leading to behavior that is more
impulsive, uninhibited, or socially inappropriate. It can occur in
various contexts, such as in social behavior, emotions, or even in
cognitive functions.
- Tolerance, which refers to a need to increase dosage to obtain
the desired previous effect, is not directly relevant to the risky
behavior that can result in preventable injuries.
-
The passage states that excessive alcohol use is associated
with preventable injuries, which are more often due to binge
drinking than to alcohol dependence. Disinhibition is associated
with binge drinking and often leads to risk taking, which can lead
to preventable injuries.
- Negative reinforcement
refers to the strengthening of a behavior after the response has
been followed by the removal of an aversive stimulus. It is not
mentioned in the passage as relevant to the risky behavior (more
often due to binge drinking than to alcohol dependence) that can
result in preventable injuries.
- Positive reinforcement
refers to the strengthening of a behavior after the response has
been followed by the delivery of an appetitive stimulus. It is not
mentioned in the passage as relevant to the risky behavior (more
often due to binge drinking than to alcohol dependence) that can
result in preventable injuries.
|
front 80 The passage suggests that family caregivers of patients with dementia
are likely to experience:
- A.role strain.
- B.relative deprivation.
- C.role conflict.
- D.relative poverty.
| back 80
The solution is C.
- Role strain involves tensions in the demands from a single
social role. Because the passage describes multiple social roles,
role strain is incorrect.
- Relative deprivation is when
expectations surpass the material resources that a group or
individual has. This concept does not address the passage reference
from the question.
-
The end of the dementia section states that support for
family caregivers of dementia patients is also essential to help
caregivers balance the demands of caregiving with their other
social responsibilities. Balancing the demands of one role
(caregiving) with other roles (other social responsibilities)
defines role conflict (tensions stemming from multiple social
roles).
- Relative poverty refers to having fewer
resources in relation to the more affluent in one’s society. This
concept does not address the passage reference used in the
question.
|
front 81 A researcher proposes an alternative to the hypothesis in the passage
that mammography rates are partly due to social capital. An
alternative hypothesis that draws on the concept of institutional
discrimination is most likely to make which prediction?
- A.Patients whose healthcare provider is from the same
racial/ethnic group will have above average rates of
mammography.
- B.Mammography rates will be affected by
healthcare providers who interact with patients differently
according to racial/ethnic group.
- C.Metropolitan areas that
are highly segregated across different racial/ethnic groups will
have below average rates of mammography.
- D.Mammography
rates will be affected by healthcare policies that have a
disproportionate impact on racial/ethnic minority groups.
| back 81
The solution is D.
- This option suggests racial concordance in healthcare
interactions.
- This option suggests individual discrimination
during interactions.
- This option is more directly related
to residential segregation by race/ethnicity. Although
discrimination and segregation are commonly discussed together, from
a sociological perspective they can be distinguished from one
another. Segregation refers to separation in physical space, whereas
discrimination describes unfair treatment.
-
The passage refers to research suggesting that the breast
cancer mortality disparity may be partly related to differences in
cancer screening with mammography. The question introduces another
researcher’s alternative hypothesis, proposing that the correct
answer must apply the concept of institutional discrimination.
Institutional discrimination calls attention to policies at the
organizational or institutional level in health care. Rather than
being directly exclusionary, these policies tend to have a
disproportionate impact on certain groups.
|
front 82 A researcher applying the concept of assimilation to immigrant health
would propose which hypothesis?
An immigrant group’s life expectancy will:
- A.surpass the majority group’s life expectancy over time.
- B.approximate the majority group’s life expectancy over
time.
- C.fall behind the majority group’s life expectancy over
time.
- D.maintain the same disparity with the majority group’s
life expectancy over time.
| back 82
The solution is B.
- The assimilation perspective suggests that immigrant groups
will become more like the rest of society, rather than surpassing
the outcomes of other groups.
-
The concept of assimilation proposes that an immigrant group
will eventually adopt the customs (norms, values, etc.) of the
majority group in a society. Because of taking on such norms over
time, the immigrant group’s health outcomes (including life
expectancy) would be likely to approximate the majority group’s
health outcomes (including life expectancy).
- The
assimilation perspective suggests that immigrant groups will become
more like the rest of society, rather than falling behind the
outcomes of other groups.
- The concept of assimilation is
not about stasis. Instead, the assimilation process predicts that
the immigrant group would become, over time, very similar to the
rest of society.
|
front 83
_____________ posits that individuals develop a sense of self,
or identity, through the interactions and relationships that they
have with others. The theory suggests that social relationships are
fundamental for individuals to develop a sense of who they are. | |
front 84 Proprioceptors are a type of sensor that helps an individual to
__________ and/or its position. These receptors are found within the ______________ | back 84 determine the location of a body part
vestibular system, muscles, and/or tendons. |
front 85 Chemoreceptors are found in the ______________ | back 85 carotid bodies and the aortic arch. |
front 86 Osmoreceptors are usually located in the_______________ | back 86 hypothalamus and they usually detect the change in osmotic pressures |