Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
ENTO EXAM 2
front 1 What order do roaches and termites fall under? | back 1 Blattodea |
front 2 -Most common -2 stripes on pronotum -females produce 35,000 offspring in their lives --carry the egg case to where they think is best to glue them | back 2 German cockroach |
front 3 -yellow band across abdomen -found in homes, apartments -like starch, low water needs -like dry areas | back 3 Brown banded cockroach |
front 4 Insects depend on | back 4 external temperature to function and grow (if hot: develop fast; if cold: develop slow) |
front 5 -males have short wings and females have wings that cover 3/4 of body -seasonal development (winter=adults, spring=mate, outside for summer and inside in fall) -like decaying organic matter (drains) | back 5 Oriental cockroach |
front 6 What problems do cockroaches cause in homes? | back 6 -Contamination (fecal and salivatory contaminate food) -carry disease and allergens |
front 7 Cockroaches are_______ which means they prefer to live outside but like being inside for stability and food | back 7 Exophilic |
front 8 What are problems do cockroaches cause in homes? | back 8 -Contamination (fecal and salivatory contaminate food) -carry disease and allergens |
front 9 What is a ootheca? | back 9 is an egg case from german cockroach |
front 10 Termites colonize in groups in soil and wood. They cause more than___ | back 10 $2 billion of damage per year in the US |
front 11 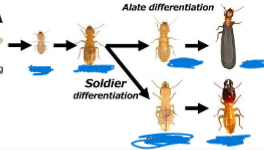 Termite stages: | back 11 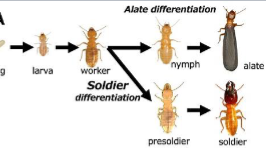 |
front 12  | back 12 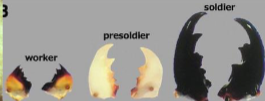 |
front 13  What is their role? | back 13 reproductives |
front 14 Subterranean termites like to build on the ground which causes | back 14 more home damage because their homes won't suffer any consequences |
front 15 What order and family to bed bugs fall in? | back 15 -Hemiptera -Cimicidae |
front 16 Where do bed bugs dwell? | back 16 where hosts live, like mattress/carpet |
front 17 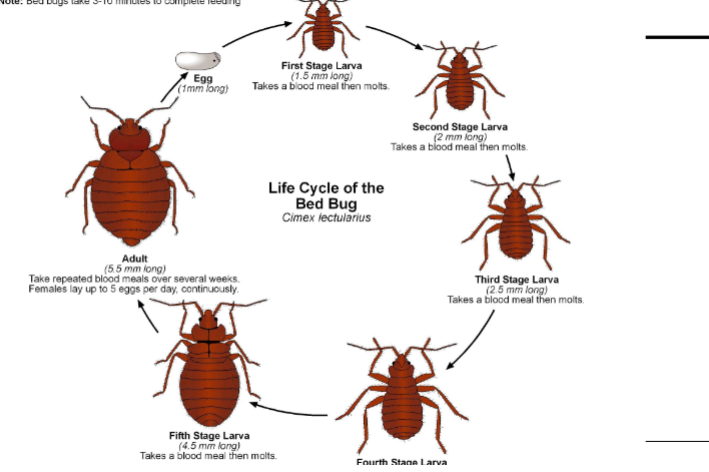 What is the difference between nymphs and adults? | back 17 -nymphs take blood meals then mult - Adults constant feeding on blood |
front 18 In order to get rid of bed bugs, one must | back 18 expose clothes to extremely hot temperatures and throw away mattress |
front 19 Assassin bugs/ kissing bugs causes Chages disease which causes | back 19 serious heart degeneration and other problems |
front 20 Chages disease can also be contracted from | back 20 blood donations |
front 21 How do you decide which case to take? | back 21 -look if it's within your expertise -consider how emotionally taxing the case will be to you |
front 22 What is the order name for fleas? | back 22 Silphonaptera |
front 23 What is the scientific name of flea? | back 23 Ctenocephalides felils |
front 24 What is the family and order name of kissing bugs? | back 24 - Hemiptera - Reduviidae |
front 25 What are tenurial adults? | back 25 Adults that just emerged from pupae |
front 26 Natural or unavoidable damage, foreign substance in foods for human use that isn't harmful to humans | back 26 Defect in food |
front 27 What is the point of having levels of defect in food? | back 27 because it is economically impractical to grow, harvest, or process raw products that are free of naturally occurring defects |
front 28 What is the common name of this insect: Order: Lepidoptera Family: Pyralidae | back 28 moths and butterflies |
front 29 What is the common name of this insect: Order: coleoptera Family: Ptinidae | back 29 Biscuit beetle |
front 30 What is the common name of this insect: Order: Coleoptera Family: dermestidae | back 30 Larder beetle |
front 31 What is the common name of this insect: Order: Coleoptera Family: Tenebrionidae | back 31 red flour beetle |
front 32 What is the common name of this insect: Order: Coleoptera Family: Silvanidae | back 32 Sawtoothed grain beetle |
front 33 What is the common name of this insect: Order: Diptera 1. Family: Drosophilidae 2. Family : Tephritidae | back 33 -Vinegar flies -True fruit flies |
front 34 -infest food -dried, stored products -make a silk film on food -flour, oats, cereal, energy bars, dried fruit, cat & dog food -Adults have bright copper sheen and fly in a zigzag pattern | back 34 Indian Meal moth (plodia interpunctella) |
front 35 -inhabits herbs, teas, drugs, foodstuffs, pasta -pearly white eggs -c-shaped grubs | back 35 Drugstore/biscuit beetle (stegobium paniceum) |
front 36 -inhabits cured meat, cheese, dried dog food, animal by-products, and even dead insects -eggs are yellowish -hairy larvae -bore into wood | back 36 Larder beetle (Dermestes lardarius) |
front 37 -Inhabits wheat flour, dried fruits, breakfast cereals, damaged grains -like moist environment -long and armored larvae -eggs are clear/white -larvae yellowish and change from yellow to brown | back 37 Red flour beetle (tribolium castaneum) |
front 38 - Inhabited milled grains (damaged), cereals, bread, popcorn, dried fruit, cake mix, crackers, and macaroni | back 38 Sawtoothed grain beetle (Oryzaephilus surinamensis) |
front 39 -attracted to moist organic matter -larvae feed on organic material(rotting) | back 39 "fruit" flies (vinegar flies) |
front 40 - use fruit as host -female lay eggs on fruit and larvae develop in fruit -major pests | back 40 True fruit fly (tephritidae) |
front 41 The best method to get rid of fruit flies and vinegar flies is by | back 41 throwing away contaminated product |
front 42 What method is best to control stored product infestations? | back 42 removal of infested product or food source |
front 43 D. Suzukii is unique because females have a______ that can lay eggs inside healthy fruits | back 43 Ovipositor |
front 44 the study of decomposing or decaying organisms over time, including the process leading to fossilized remains | back 44 Taphonomy |
front 45 Non-living physical and chemical elements in an ecosystem | back 45 Abiotic factors |
front 46 The study of the processes and phenomena of the atmosphere | back 46 meteorology |
front 47 The state of the atmosphere, mainly to its effects upon human activities. Short-term variability of the atmosphere (time scales of minutes to months) | back 47 Weather |
front 48 Long term statistical description of the atmospheric conditions, averaged over a specific period-usually decades | back 48 Climate |
front 49 What abiotic factors affect decomposition and insect behavior? | back 49 temperature, wind speed, moisture, wind direction, clouds, shade vs. sunlight |
front 50 When it comes to temperature, insects depend on | back 50 external temperature to function and grow (if hot: develop fast; if cold: develop slow) |
front 51 How does moisture affect insect development and behavior? | back 51 Larvae stay on body for entire lifespan, but if moisture is lost, larvae leave to find new food sources |
front 52 Fatty tissue breakdown in moist conditions | back 52 Adipocere |
front 53 How does wind speed affect adult insect development and behavior? | back 53 Flight and olfactory senses |
front 54 How does wind speed affect larvae insect development and behavior? | back 54 development and survival |
front 55 How does wind direction affect insect development and behavior? | back 55 movement, exposure, location-based |
front 56 How do clouds affect insect development and behavior? | back 56 -development - activtiy (within and across season) -Location |
front 57 T or F: Sunlight vs. shade affects insect development and behavior. | back 57 true |
front 58 What biotic factors affect decomposition? | back 58 -Scavengers -Necrophagous insects -Microbes -fungi bacteria -soil-dwelling microorganism |
front 59 -Coma and cerebral unresponsiveness -Dilated pupils -absent cephalic reflexes -Apnea | back 59 brain death |
front 60 Body cools to ambient temperature | back 60 Algor mortis |
front 61 -Fibers in muscles stiffen due to calcium build up -takes 12 hrs to appear fully, lasts 12 hrs, and takes 12 hrs to disappear -affected by exercise, convulsions, electrocution, heat -physical conditions where body is found | back 61 Rigor mortis |
front 62 -Purplish-blue discoloration due to settling of blood by gravitational forces -evident as early as 20 mins after death -fixed after 8-12 hrs | back 62 livor mortis |
front 63 a postmortem discoloration of the sclera, or white part of the eye, that appears as a brown or black stripe due to exposure and occurs from minutes to hours | back 63 tache noir |
front 64 -Can be localized due to trauma/ stress before death -occurs in deaths preceded by great excitement or tension | back 64 Cadaveric spasm |
front 65 -Self-dissolution by body enzymes/chemicals (fuels putrefaction) | back 65 Autolysis |
front 66 -Decomposition changes produced by action of bacteria and microorganisms - gases are produced | back 66 Putrefaction |
front 67 The ______ is an elected official that does not have expertise in medicine | back 67 coroner |
front 68 _____physician/forensic pathologist (autopsy) | back 68 Medical examiner |
front 69 Scientists that uses knowledge of body and body processes to gather information pertaining to death. | back 69 forensic pathologist |
front 70 What are the things to look for in an autopsy? | back 70 -Fatty liver -brain tumor -enlarged heart -lung cancer |
front 71 Bruises | back 71 contusions |
front 72 Scraping damage to skin | back 72 Abrasion |
front 73 Why might both a pathologist and an entomologist be needed? | back 73 - determine PMI using state of human remains - pre-existing wounds and trauma -burned remains -drug abuse |
front 74 What are methods of PMI estimation? | back 74 -PMI calculation based on temperature -ocular changes -Potassium levels -livor mortis -rigor mortis -Stomach contents |
front 75 What are the uses of insect evidence? | back 75 - ability to rapidly locate and colonize corpse -Predictable patterns for succession |
front 76 -time since death (range) -links suspects and victims -establish timeline of abuse or neglect -algor mortis, rigor mortis, blood coagulations | back 76 PMI |
front 77 -identification of flies and age of developmental stage - base temperature threshold for the species - temp data from remains recovery scene - temp data from nearby weather station - experimental development data at relevant temps for fly of interest | back 77 TOC |
front 78 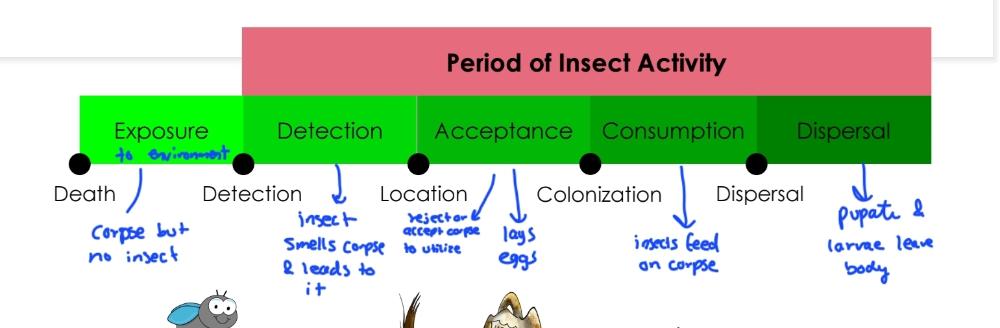 | back 78 Process of how bugs colonize |
front 79 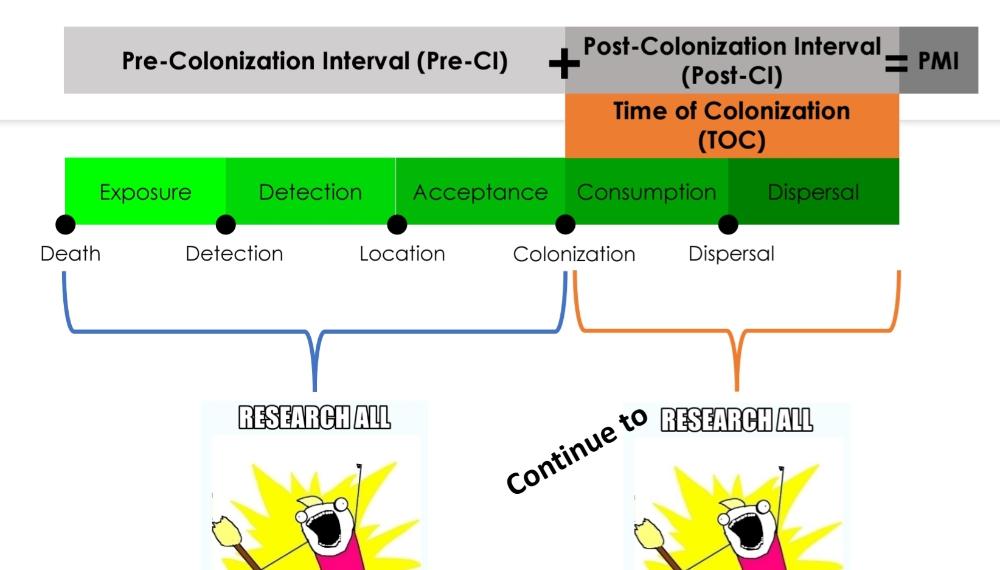 | back 79 How PMI and TOC can align |
front 80 ABFE ( American Board of Forensic Entomology) is a | back 80 certifying board for forensic entomologists in North America |
front 81 There are three tiers to the ABFE which are the | back 81 members, diplomats, and technicians |
front 82 Deliberate harm to someone or something | back 82 abuse |
front 83 Failure to meet basic life needs: -food -water -shelter | back 83 neglect |
front 84 What are the types of abuse? | back 84 -physical -sexual - Emotional -Trafficking |
front 85 What are the types of neglect? | back 85 neglectful supervision, medical neglect, physical neglect, abandonment and refusal to accept parental responsibility |
front 86 How can myiasis affect PMI? | back 86 because of the parasitic investation of a living animal -insect colonization before death |
front 87 Does myiasis always fall under cases of neglect or abuse? | back 87 NOOO, it can be due to bad hygiene |
front 88 What are forms of funeral home negligance? | back 88 -embalming errors -Improper treatment of remains -cemetery negligence |
front 89 What can insect evidence tell us? | back 89 -Duration -movement of remains -Location of crime -injury - Ante-mortem drug ingestion (from skin and gut of insect) - cause or manner of death |
front 90 What methods can be used to collect adults? | back 90 -Sweep net sampling -kill jar -sticky traps |
front 91 What methods can be used to collect immature? | back 91 -look at body orficies and body folds - soil, under body, maggot masses -representative samples of egg masses, largest and smallest larvae, larvae of diff. species |
front 92 -Alcohol filled jar - allow for pupate to emerge (send empty pupal casing) | back 92 Preservation of evidence |
front 93 Olfactory cues | back 93 Insects pick up on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) |
front 94 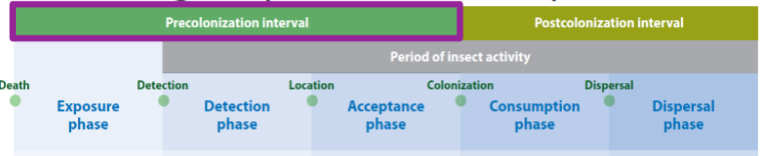 | back 94 Entomological phases of decomposition: |
front 95 In postcolonization interval, | back 95 lay eggs and move off the body |
front 96 In exposure, there are no | back 96 insects and have microbe activity |
front 97 Detection results in insects | back 97 smelling volatile compounds |
front 98 In the acceptance step, insects | back 98 interact with remains and accept or reject the resource |
front 99 Consumption step oviposition (laying eggs) occurs and | back 99 insects are actively feeding |
front 100 The dispersal step, | back 100 insects complete feeding and leave remains |
front 101 A repeatable sequence of community changes specific to particular environmental circumstances | back 101 seres |
front 102 What are factors of spatial variability? | back 102 urban, rural, forest, field, submerged, buried, europe, South America, Indoors, and outdoors |
front 103 What is temporal variability? | back 103 night, day, winter, and summer |
front 104 Does size affect the type of insects that colonize the body? | back 104 YES |
front 105 Does being burned or wrapped affect the insect activity? | back 105 YES |
front 106 Catalog of taxa present (kingdom, phylum, order, etc.) | back 106 structure |
front 107 Number of taxa in a given environment (# of taxa) | back 107 diversity/biodiversity |
front 108 Number of different species represented in a given community | back 108 Species richness |
front 109 What abiotic factors affect decomposition and insect behavior? | back 109 temperature, wind, moisture, clouds, shade vs. sunlight |
front 110 Catalog of "what" taxa are doing (roles of taxa) | back 110 Function |
front 111 Insects depend on external temperature to | back 111 function and grow (if hot: develop fast; if cold: develop slow) |
front 112 feed on others present on the carrion | back 112 Predator |
front 113 Live on others that feed on carrion | back 113 Parasite |
front 114 Do it all (wasps, ants) | back 114 Omnivorous |
front 115 How many maggots should be collected from each maggot mass? | back 115 2 maggots per maggot mass |
front 116 Use remains as extensions of environment (springtail) | back 116 Adventive |
front 117 Death is a major event not only for the person who dies but also for the microbes that inhabit their body. Which of the following statements best describes why? A. Microbial populations grow and spread to different areas of the body after the person dies. B. All the microbes that were living inside the person’s body die when the person dies. C. Microbes in the body have fewer resources after the person dies, which increases competition. | back 117 A. Microbial populations grow and spread to different areas of the body after the person dies. |
front 118 Microbes in the body have fewer resources after the person dies, which increases competition. Which of the following statements about cadavers (dead bodies) is most likely to be true? A. Microbial communities in and around a cadaver change over time. B. Samples taken from different cadavers always contain the same microbes. C. The microbial community found in a cadaver is very similar to the one found in a living body. | back 118 A. Microbial communities in and around a cadaver change over time. |
front 119 The microbial community found in a cadaver is very similar to the one found in a living body. After death, gases build up inside the body and cause the skin to rupture (break open). Rupture is a significant event because microbes from outside the body can now access the inside. Which of the following can be a source of the microbes that enter the body after it ruptures? Select all that apply. A. skin B. air C. soil D. insects | back 119 A,B, C, D |
front 120 In 3-4 complete sentences, describe in your own words (no quotes) how the scientists in the second video are using microbes to create a tool to estimate the time since death. | back 120 Scientists collect skin and soil swab samples of cadavers because it was proven that testing for microbes can almost accurately determine the time of death. They can find which microbes should be present based on a microbial clock created that can give a better visual of which microbes show up in different stages of decomposition. The DNA is then sequenced from the microbes on the swab. The results can then be compared to the microbial clock to determine the time of death. |
front 121 The law of conservation of energy states that the amount of energy in an isolated system stays constant. In other words, energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only change form. Explain in your own words, no quotes, how the decomposition of a cadaver demonstrates this law. | back 121 The decomposition of cadavers demonstrates the law of conservation because when an organism, human or animal, dies, the energy is then consumed by microbes to regenerate and grow. The energy can be transferred or recycled to start a new life for a different organism. |
front 122 a. Eventually, most of the cadaver’s mass is transferred into the ground or consumed by scavengers. Fungi flourish. Decomposition gradually slows as maggots and scavengers leave. Plants close to the cadaver may die from the overload of nutrients and other components coming from the cadaver. b. The heart stops beating, so there is less oxygen inside the body. Cells begin to die, and the body no longer maintains a stable temperature. With no immune system regulating microbes that live inside the body, their populations start to shift and grow. Flies lay eggs, which will develop into maggots, in the cadaver’s orifices (such as the mouth and nostrils). c. Only dried bones, cartilage, and skin remain. Surrounding plant life begins to surge due to the cadaver’s nutrients, which may influence the ecosystem for years to come. d. With less oxygen inside the cadaver, anaerobic bacteria flourish. These bacteria break down the body’s carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, producing byproducts such as the gases hydrogen sulfide, methane, and ammonia. The accumulation of these gases gives the cadaver a strong odor and causes it to bloat. Maggots start to feed on the cadaver’s tissues. e. The cadaver breaks open. Fluid spills out of the body’s openings, releasing an abundance of nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, into the soil. Breaks in the skin allow more microbes, insects, and scavengers to enter the body. Assign the letters of these descriptions to the stages in Figure 1. | back 122 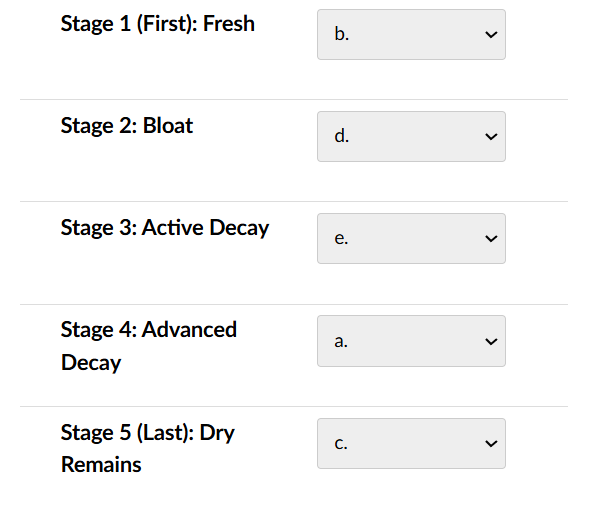 |
front 123 What abiotic factors might affect the kind of scavengers that contribute to a cadaver’s decomposition? | back 123 Factors could include temperature or season, as well as the location of the cadaver (above ground or underground, in water or on land, etc.). |
front 124 Other scavengers include beetles, wasps, dogs, crows, and crustaceans. Explain how these other scavengers could also affect decomposition. | back 124 The scavengers may consume the cadaver or spread their own microbes to the cadaver, influencing the microbial community present. Some scavengers, such as insects, may also attract larger scavengers that prey on both the smaller scavengers and the cadaver. |