front 1 Nitrogen in the benzene ring would have a lone pair that could accept
a _______________, thus increasing the solubility of the compound. | |
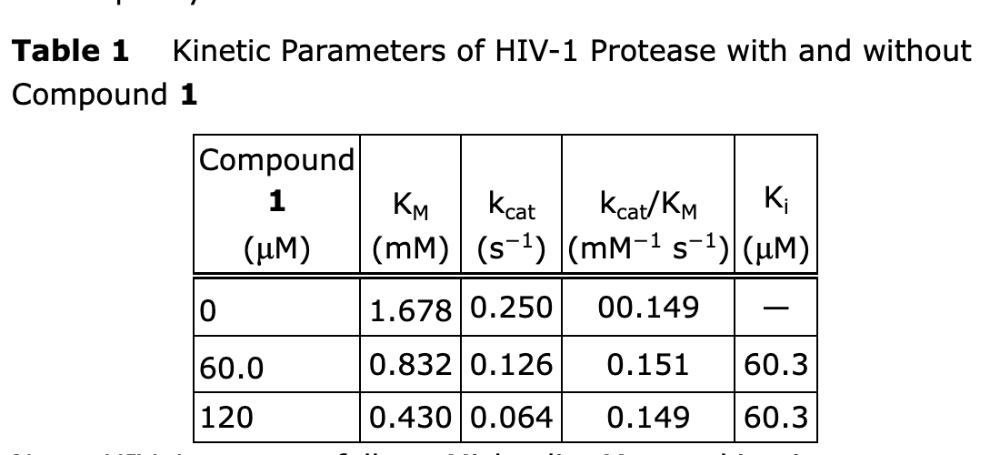
front 2 In μM•s–1 and μM, what should the approximate values of k
cat/KM and K
i be, respectively, when [I] = 180 μM?
- A.33.5 and 15.7
- B.75 and 30.1
- C.150 and
60.3
- D.300 and 120.
| back 2
Solution: The correct answer is C.
No, substrate concentration does not directly change the Ki
(inhibition constant). Ki is a constant
that reflects the affinity between the enzyme and the inhibitor, and
it is independent of the concentration of the substrate.
- These values are one-fourth of both the actual
kcat/KM and the K
i. The latter is impossible as K
i , being an equilibrium constant, is unaffected by [I],
and the former does not match the trend in Table 1.
- These
values are half of both the actual kcat/KM and
the K
i. The latter is impossible as K
i, being an equilibrium constant, is unaffected by [I],
and the former does not match the trend in Table 1.
-
Based on the data in Table 1, increasing [I] has no effect
on kcat/KM, so it should remain at 150
M–1•s–1. Also, K
i is an equilibrium constant, so it will not be
affected by a change in [I].
- These values are
double both the actual kcat/KM and the K
i. The latter is impossible as K
i , being an equilibrium constant, is unaffected by [I],
and the former does not match the trend in Table 1.
|
front 3 What functional group transformation occurs in the product of the
reaction catalyzed by Na+-NQR?
- A.RC(=O)R → RCH(OH)R
- B.ROPO3
2- → ROH + Pi
- C.RC(=O)NHR'→ RCOOH +
R'NH2
- D.RC(=O)OR'→ RCOOH + R'OH
| back 3
Solution: The correct answer is A.
The reaction catalyzed by Na+-NQR (Sodium-quinone
reductase) is involved in the reduction of quinones
in biological systems, often with the production of reduced
intermediates like hydroquinones. Na+-NQR primarily functions as part
of the electron transport chain, where it helps reduce quinone
molecules in certain organisms.
-
This is two-electron reduction of a ketone to an alcohol,
which is the reaction catalyzed by
Na+-NQR.
- This is the reaction catalyzed
by a phosphatase.
- This is the reaction catalyzed by a
protease or amidase.
- This is the reaction catalyzed by an
esterase.
In simple terms, a reduction reaction is when a
molecule gains electrons or hydrogen atoms.
For the transformation from a carbonyl group (C=O)
to a hydroxyl group (C-OH), here's why it is
considered reduction:
- A carbonyl group (C=O) is made up of a carbon
atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom.
- In
reduction, the carbonyl group gains
electrons or hydrogens.
- The double bond between the carbon and oxygen
breaks, and the carbon gains a hydrogen atom,
turning the oxygen into a hydroxyl group (-OH).
|
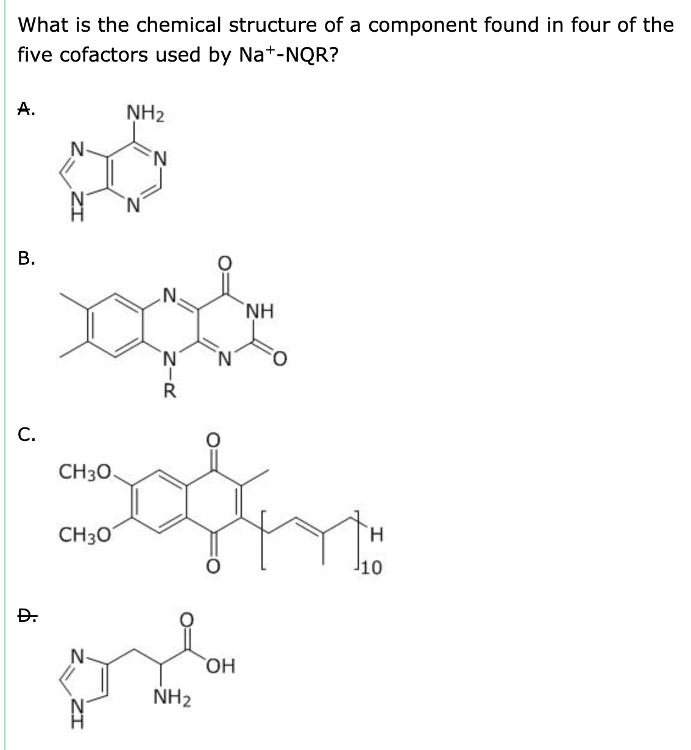
front 4 What is the chemical structure of a component found in four of the
five cofactors used by Na+-NQR? | back 4
Solution: The correct answer is B.
- This is the structure of adenine. It is only found in
FAD.
-
This is the structure of flavin, found in four of the five
cofactors used by Na+-NQR.
- This is
the structure of ubiquinone. It is a substrate, but not a
cofactor.
- This is the structure of histidine. It is an amino
acid, not a cofactor.
|
front 5 Text: Na+-NQR was diluted to a final concentration of 0.75
mM in 0.150 M LiCl, NaCl, KCl, RbCl, or NH4Cl (each
solution also contained redox active mediators) and placed in a glass
instrument cell with CaF2 windows.
What is the ratio of cation to enzyme in the spectroelectrochemical
experiments described in the passage?
- A.1:2
- B.2:1
- C.20:1
- D.200:1
| back 5
Solution: The correct answer is D.
- If the ratio of cation to enzyme was 1:2, the cation
concentration needed to be 0.375 mM. Alternatively, the
concentration of enzyme could have been 0.300 mM.
- If the
ratio of cation to enzyme was 2:1, the cation concentration needed
to be 1.50 mM. Alternatively, the concentration of enzyme could have
been 0.075 mM.
- If the ratio of cation to enzyme was 20:1,
the cation concentration needed to be 15 mM. Alternatively, the
concentration of enzyme could have been 7.5 µM (0.0075 mM).
-
The ratio can be found by noting that the enzyme
concentration was 0.75 mM, while the concentration of cations was
0.150 M = 150 mM. The ratio is therefore 200:1.
|
front 6 The reaction between NADH and ubiquinone is exergonic, but the
reaction, when catalyzed by Na+-NQR, does not generate much
heat in vivo. What factor accounts for this difference?
The reaction catalyzed by Na+-NQR in vivo:
- A.is more exothermic as a result of the lower activation
energy.
- B.occurs sequentially in several small steps.
- C.maintains a large separation between the reacting
centers.
- D.is coupled to the movement of a charged particle
against a concentration gradient.
| back 6 - This is impossible. Even if it were true, this would make the
heat generation larger, not smaller, for the catalyzed reaction.
Catalysis does not change thermodynamics.
- By Hess's Law,
the heat of reaction will sum and be the same. The fact that the
reaction can be broken down into steps will not change the overall
thermodynamics.
- This is also impossible. The reactants
ultimately must be close together to react.
-
The movement of a charged particle against its concentration
gradient is energetically costly. Coupling the two processes: the
redox reaction between NADH and ubiquinone and the movement of
Na+ up a concentration gradient makes the overall
process less exothermic.
- Na+-NQR (sodium-translocating NADH:quinone oxidoreductase)
is involved in a process that couples the oxidation of NADH to the
translocation of sodium ions (Na+) across a membrane, contributing
to the generation of an electrochemical gradient. This is an example
of active transport, where the energy from the reaction is used to
move sodium ions against their concentration gradient, helping
create the gradient that can be used for various cellular processes. |
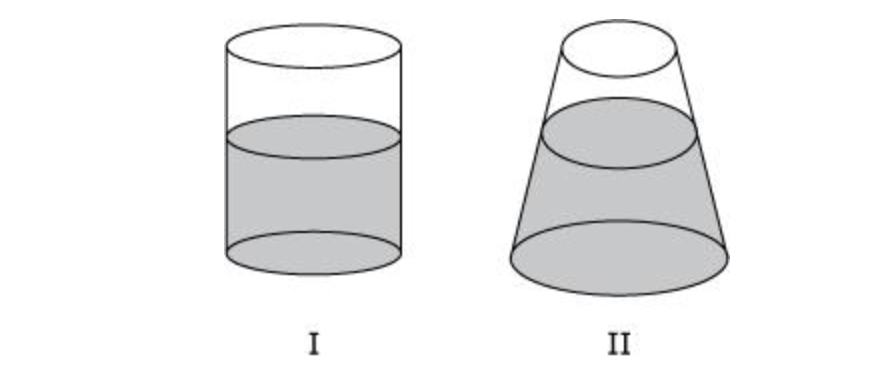
front 7 Two open flasks I and II contain different volumes of the same
liquid. Suppose that the pressure is measured at a point 10 cm below
the surface of the liquid in each container. How will the pressures compare?
- A.The pressures will be equal.
- B.Pressure in flask I
will be less.
- C.Pressure in flask II will be less.
- D.The pressures cannot be compared from the information
given.
| back 7
Solution: The correct answer is A.
-
The pressure at a point 10 cm below the surface of the
liquid is the same in both flasks because the pressure is equal to
the liquid density multiplied by the gravitational acceleration
multiplied by 10 cm.
- The pressure at a point 10
cm below the surface of the liquid in flask I is the same as the
pressure in flask II at 10 cm below the surface because the pressure
is equal to the liquid density multiplied by the gravitational
acceleration multiplied by 10 cm.
- The pressure at a point
10 cm below the surface of the liquid in flask II is the same as the
pressure in flask I at 10 cm below the surface because the pressure
is equal to the liquid density multiplied by the gravitational
acceleration multiplied by 10 cm.
- The pressures can be
compared because both pressures are calculated according to the
hydrostatic pressure formula p = ρgd, where ρ is the liquid
density, g is the gravitational acceleration, and
d is the depth where pressure is measured.
When you have a liquid, the pressure at any point in that liquid
depends on how deep you are below the surface. The deeper you go, the
more liquid is above you, and the heavier the liquid becomes pressing
down on you, so the pressure increases.
Now, when we're talking about the pressure 10 cm below the
surface in both flasks, the formula that shows how pressure
changes with depth is:
Pressure=Weight of liquid above you\text{Pressure} = \text{Weight of
liquid above you}Pressure=Weight of liquid above you
This weight is directly related to the height of the
liquid above the point where you're measuring, and
not the total amount of liquid in the container.
So, even though the two flasks have different amounts of liquid, the
pressure at 10 cm below the surface is only affected by how high the
liquid is above that point (which is 10 cm in both cases).
That's why the pressure at that depth will be the same in both
flasks. The volume of liquid in each flask doesn’t change the pressure
at that specific 10 cm depth, since the formula focuses only on the
height of the liquid above that depth.
Key points:
-
Pressure depends on the height of the liquid above
the point you're measuring.
-
Not the total volume or how much liquid is in the
flask overall.
- Since both flasks have 10 cm of liquid above
the measuring point, the pressure will be the same in both.
|
front 8 What is the molecular formula of the heterocyclic aromatic compound pyrrole?
- A.C2H3N
- B.C4H5N
- C.C6H7N
- D.C8H9N
| back 8
Solution: The correct answer is B.
- This is the molecular formula of the non-aromatic heterocycle
2H-azirine.
-
This is the molecular formula of pyrrole, a five-membered
aromatic heterocycle containing one nitrogen atom.
- This is the molecular formula of various forms of azepine, a
seven-membered heterocycle, none of which are aromatic.
- There is a cyclohexene-fused pyrrole with this molecular
formula, but not pyrrole itself.
|
front 9 Text: They used the fluorescence spectrometer depicted in Figure 2,
which employs a 86Kr+ laser that simultaneously emits radiations of
wavelengths 407 nm and 605 nm. Inside the laser, the noble gas is
contained in a 11^cm3 tube.
Approximately how many moles of Kr+ are contained in the
laser tube at 0°C and 1 atm?
- A.3 x 10-
7
- B.2 x 10-
6
- C.4 x 10-
5
- D.5 x 10-4
| back 9 - 1 cm³ (cubic centimeter) = 1 milliliter (mL)
- 1 mL =
0.001 L (since there are 1000 milliliters in a liter)
Solution: The correct answer is D.
- This number of moles of gas occupies only 0.00672 mL at
STP.
- This number of moles of gas occupies only 0.0448 mL at
STP.
- This number of moles of gas only occupies 0.90 mL at
STP.
-
There is 1 mole of gas in a volume of 22.4 L = 2.24 x
104 cm3 at STP; there are approximately 5 x
10-4 moles in 11 cm3.
|
front 10 The radiation of wavelength 605 nm CANNOT be used to produce the
fluorescence radiations depicted in Figure 3 because:
- A.the energy of the absorbed radiation must be larger than the
energy of the fluorescence radiation.
- B.the energy of the
absorbed radiation must be smaller than the energy of the
fluorescence radiation.
- C.the 605-nm radiation has more
energy than the 407-nm radiation.
- D.the 605-nm radiation is
not visible.
| back 10
Solution: The correct answer is A.
-
Fluorescence can occur when the absorbed radiation has a
photon energy larger than the photon energy of the radiation
emitted through fluorescence. The photon energy is inversely
proportional to the radiation wavelength, thus the 605-nm
wavelength radiation cannot produce the entire fluorescence
radiation spectrum shown in Figure 3 as its photon energy is below
that of the fluorescence radiation of wavelength 604
nm.
- The photon energy of the absorbed radiation must
exceed the photon energy of the fluorescence radiation because the
energy difference cannot be created from nothing, per the energy
conservation principles.
- The photon energy is inversely
proportional to the radiation wavelength according to the formula
Energy = Planck's constant multiplied by the speed of light divided
by the wavelength, thus the 605-nm wavelength radiation has less
photon energy than the 407 nm wavelength radiation.
- The 605
nm wavelength radiation is visible, but this feature is unrelated to
fluorescence.
|
front 11 In a protein, each amino acid residue, except Gly, has a chiral __________ | |
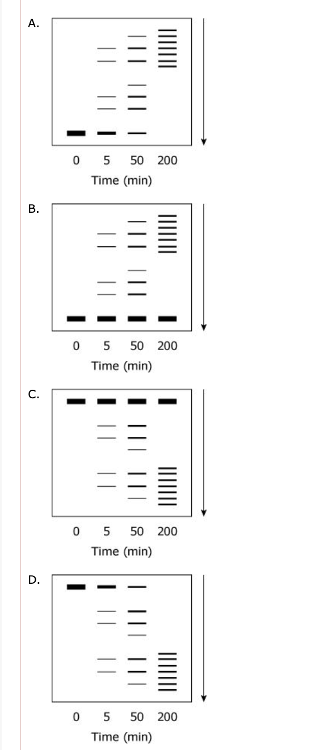
front 12 Samples from various time points of the proteolysis of TPMTwt were
subjected to SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. Which figure best
depicts the expected appearance of the gel?
(Note: The arrow indicates the movement of the protein through the gel.) | back 12
Solution: The correct answer is D.
- This gel depicts protein aggregation, not proteolysis, over
time. The molecular weights of the bands are increasing rather than
decreasing.
- This gel shows protein aggregation, instead of
proteolysis, and does not even decrease the amount of starting
protein.
- Although the increase in the number of lower
molecular weight bands with time fits proteolysis, the original
protein band at the highest molecular weight should diminish over
time.
-
As befits proteolysis, the number of lower molecular weight
bands with time increases and the original protein band at the
highest molecular weight diminishes with time.
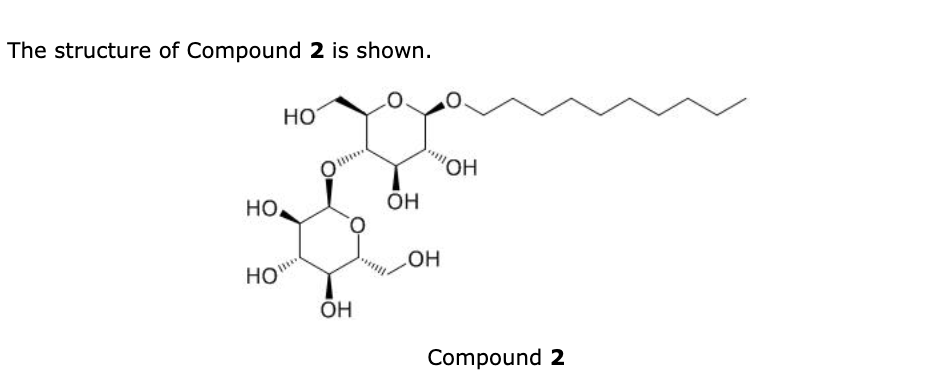
|
front 13 What structural feature(s) is(are) most important to the functioning
of this compound as described in the passage?
- A.Specific configuration of numerous chirality centers
- B.Multiple hydrolysable linkages
- C.Combination of large
hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
- D.Presence of a
reducing sugar
| back 13
Solution: The correct answer is C.
- Chirality is important for specific binding to other
compounds. This is not a requirement of a detergent.
- Multiple hydrolysable linkages would facilitate metabolism.
Compound 2 was a detergent used to help isolate membrane
proteins.
-
Compound 2 was used as a detergent. It liberated a protein
from a membrane so that it might be isolated. The combination of
large hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions allows Compound 2 to
function in this capacity.
- The presence of a
reducing sugar makes the compound susceptible to oxidation and
imparts aqueous compatibility. It does not provide all the necessary
components of a functioning detergent
It’s specifically stating extraction from a membrane in the
passage, meaning you should think amphipathic molecule. Remember
detergents: polar and non polar regions break down a membrane and form pores. |
front 14 Enantiomers can exhibit a difference in which chemical or physical property?
- A.Density
- B.Boiling point
- C.Smell
- D.IR spectrum
| back 14
Solution: The correct answer is C.
- Enantiomers will not display different densities.
- The
boiling points of enantiomers are identical, and they cannot be
separated by distillation.
-
Enantiomers have the same physical and chemical properties.
They differ only in their three dimensional arrangement of atoms
and their interactions with other chiral molecules. They can
differ in their smell due to interacting differently with chiral
odorant receptors.
- The IR spectra of enantiomers
are identical when a normal light source is used. Circularly
polarized light will potentially illustrate differences.
|
front 15 Blood flows with a speed of 30 cm/s along a horizontal tube with a
cross-section diameter of 1.6 cm. What is the blood flow speed in the
part of the same tube that has a diameter of 0.8 cm?
- A.7.5 cm/s
- B.15 cm/s
- C.60 cm/s
- D.120 cm/s
| back 15
Solution: The correct answer is D.
Continuity equation: A1v1=A2v2
A=pi (d/2)^squared
- A flow speed of 7.5 cm/s corresponds to a diameter of 3.2 cm,
not 0.8 cm.
- A flow speed of 15 cm/s corresponds to a
diameter of 2.25 cm, not 0.8 cm.
- A flow speed of 60 cm/s
corresponds to a diameter of 1.125 cm, not 0.8 cm.
-
The flow is characterized by the continuity equation because
no amount of blood is lost between the two locations. The
continuity equation is 30 cm/s × π × ((1.6 cm)/2)2 =
v × π × ((0.8 cm)/2)2. Solving for v
yields v = 4 × 30 cm/s = 120 cm/s.
|
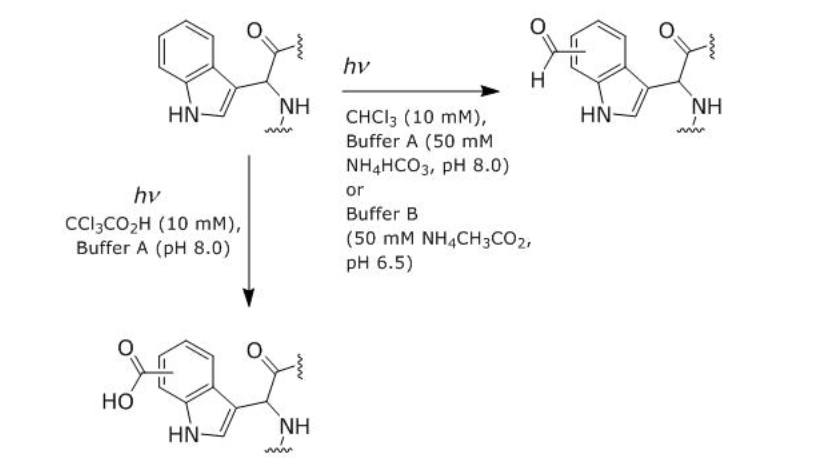
front 16 Which classification of amino acids applies to the Trp residues after
photochemical modification by CCl3CO2H?
- A.Acidic
- B.Basic
- C.Hydrophobic
- D.Polar neutral
| back 16
Solution: The correct answer is A.
-
The Trp residues after being photochemically modified by
CCl3CO2H have a carboxylic acid group
attached to the benzene ring.
- The group attached
to the Trp residues is acidic, not basic.
- The group
attached to the Trp residues is polar and hydrophilic.
- At
pH 7, the group attached to the Trp residues would ionize and
develop a negative charge.
|
front 17 Which chromatographic technique would most likely separate a mixture
of native carbonic anhydrase from carbonic anhydrase photochemically
modified by CCl3CO2H?
- A.Anion-exchange chromatography
- B.Cation-exchange
chromatography
- C.Gas-liquid chromatography
- D.Size-exclusion chromatography
| back 17
Solution: The correct answer is A.
-
Because the passage states that native carbonic anhydrase
has a net charge of -2.9 and the modified enzyme would have
greater negative charge, anion-exchange chromatography can
separate them as this technique separates proteins with different
negative charges.
- The native and modified
Enzymes both have net negative charge. In cation-exchange
chromatography, both Enzymes would elute together in the void
volume.
- Proteins degrade before they would vaporize.
- The molecular weights of the native and modified proteins are
too close (< 1 kDa difference) to allow separation by
size-exclusion chromatography.
Chromatographic Techniques:
- Anion-exchange chromatography:
- This technique uses a
positively charged stationary phase (e.g., a resin with
positively charged groups) to attract negatively charged
molecules (anions).
- Since modified carbonic
anhydrase is likely more negatively charged than the
native form, it would interact more strongly with the positively
charged stationary phase and elute later.
- Cation-exchange chromatography:
- This technique uses a
negatively charged stationary phase (e.g., a resin with
negatively charged groups) to attract positively charged
molecules (cations).
- In this case, since both forms of
carbonic anhydrase are likely to be negatively
charged (with the modified version being more
negatively charged), this technique wouldn't be ideal for
separating them.
Likely Separation:
- The key difference between the native and
modified forms of carbonic anhydrase is likely the
charge difference. The modified
enzyme will be more negatively charged due to the
introduction of the carboxyl group from CCl₃CO₂H, and the
native enzyme will have a less negative
charge.
-
Anion-exchange chromatography would likely separate
them because the more negatively charged modified enzyme would bind
more strongly to the positively charged stationary phase than the
native enzyme.
|
front 18
Text: MCS oligomers can be obtained from plants via a
lipophilic MCS precursor. This MCS precursor was isolated from plant
roots through an extraction that involved mixing an aqueous emulsion
with tert-butyl methyl ether ((CH3)3COCH3).
In which phase(s) will the MCS precursor be predominantly found
after the extraction step?
The MCS precursor will:
- A.be found in the aqueous layer.
- B.be found in the
tert-butyl methyl ether layer.
- C.be distributed
equally between the aqueous layer and the tert-butyl methyl
ether layer.
- D.form a precipitate between the aqueous and
tert-butyl methyl ether layers.
| back 18
Solution: The correct answer is B.
Explanation:
- The organic layer typically consists of organic solvents
(e.g., ether, chloroform, hexane), which are generally hydrophobic.
This means that the solvent does not mix well with water and tends
to dissolve non-polar or hydrophobic compounds.
- The aqueous
layer, on the other hand, consists of water or aqueous solutions,
which are hydrophilic and typically dissolve polar or charged
compounds.
- According to the passage, the MCS precursor is lipophilic, so
it is not water soluble.
-
The passage described the MCS precursor as being lipophilic,
which means that it would not dissolve as readily in the aqueous
layer. Therefore, it should be found in the tert-butyl
methyl ether layer, which is hydrophobic.
- According to the passage, the MCS precursor is lipophilic, so it
prefers to dissolve in organic solvents.
- The MCS precursor
should dissolve in the organic layer.
|
front 19 - The salt bridge refers to an electrostatic
interaction between_______________. In this case, the
phosphate group on PLP, which is
negatively charged, can form a salt bridge with
positively charged amino acids.
- The
π-stacking interaction occurs______________(like
the one found in tyrosine or other aromatic amino
acids) and the aromatic ring of PLP.
| back 19 oppositely charged residues
between an aromatic ring |
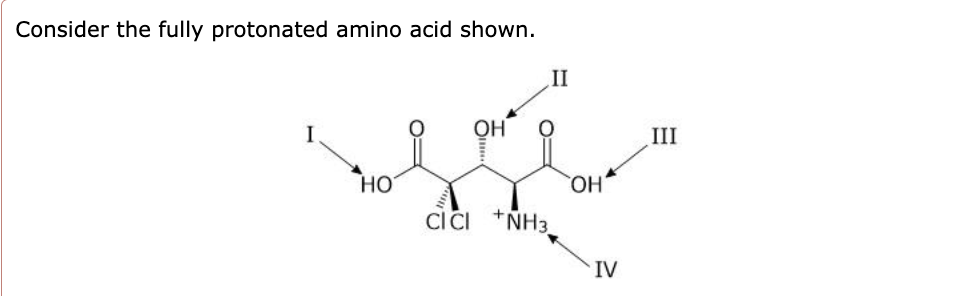
front 20 As the pH of a solution of this amino acid is raised, which group
deprotonates first?
| back 20
Solution: The correct answer is A.
-
As the pH is raised, the most acidic group deprotonates
first. Of the choices, two are carboxylic acids, one is a hydroxyl
group, and one is a protonated amine. The hydroxyl group is least
acidic, while the protonated amine is less acidic (pK
a ~ 10) than a carboxylic acid group (pK
a ~ 5). Of the two carboxylic acid groups, the one next
to the chlorine atoms will be more acidic since its conjugate base
(an anion) will be stabilized by an inductive effect which
dissipates negative charge building up.
- A proton
on alcohol is much less acidic than one in a carboxylic acid because
the negative charge cannot be delocalized to several electronegative
atoms.
- This carboxylic acid proton is less acidic than the
one on the left because it is not near two electronegative chlorine
atoms.
- Protonated amines are less acidic than carboxylic
acids (pK
a of 10 versus 5).
-
Electronegative atoms: If the conjugate base has a
highly electronegative atom (like oxygen or nitrogen) that can
better stabilize the negative charge after the proton dissociates,
the proton will be more acidic.
- For example, acids
with oxygen (like carboxylic acids, H–COOH) are more
acidic than those without oxygen (like methane, CH₄) because the
conjugate base (carboxylate anion) can be stabilized by
resonance and the electronegativity of oxygen.
-
Resonance: If the negative charge on the conjugate
base can be delocalized (spread out), this further stabilizes it and
makes the proton more acidic.
- For example, in
carboxylic acids (R-COOH), the conjugate base
(carboxylate anion, R-COO⁻) is stabilized by
resonance between the two oxygen atoms.
|
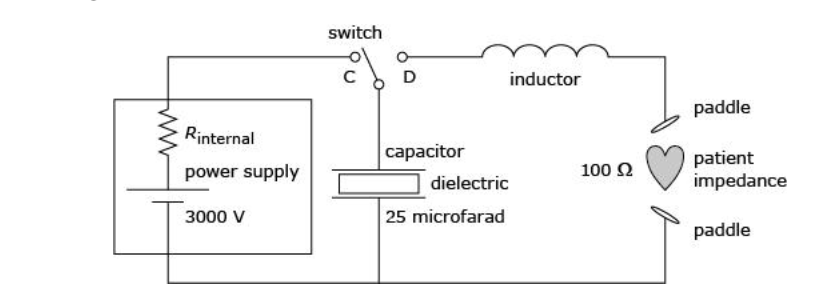
front 21 If the defibrillator described in the passage were fully charged and
the entire charge were discharged through a patient in 10 ms, which of
the following is closest to the average electrical current that would
flow through the paddles?
- A.7.5 A
- B.15 A
- C.22.5 A
- D.30 A
| back 21 -
The full charge of the capacitor is 25 μF × 3000 V = 75 mC.
The average discharge current is (75 mC)/(10 ms) = 7.5
A.
- If the average discharge current is 15 A, it
implies the full charge of the capacitor should have been 10 ms × 15
A = 150 mC. In fact, the full charge of the capacitor is 25 μF ×
3000 V = 75 mC.
- If the average discharge current is 22.5 A,
it implies the full charge of the capacitor should have been 10 ms ×
22.5 A = 225 mC. In fact, the full charge of the capacitor is 25 μF
× 3000 V = 75 mC.
- If the average discharge current is 30 A,
it implies the full charge of the capacitor should have been 10 ms ×
30 A = 300 mC. In fact, the full charge of the capacitor is 25 μF ×
3000 V = 75 mC.
|
front 22 If both the capacitor and the power supply in Figure 1 are
adjustable, which of the following changes would result in an increase
in the charge on the capacitor?
- A.Decreasing the area of the parallel plates
- B.Decreasing the separation between the parallel plates
- C.Removing the dielectric from the capacitor
- D.Decreasing the voltage of the power supply
| back 22
Solution: The correct answer is B.
- Because the capacitance is directly proportional to the area
of the parallel plates, a decrease in the area corresponds to a
decrease in the capacitance. Given that the charge on the capacitor
is directly proportional to the capacitance, a decreased capacitance
results in a decrease in the charge as long as the power supply
voltage is constant.
-
Capacitance C is inversely proportional to the
separation d between the parallel plates according to the formula
C =(ϵ0 ϵr A)/d. A
decrease in the separation corresponds to an increase in the
capacitance. Given that the charge on the capacitor is directly
proportional to the capacitance, an increased capacitance results
in an increase in the charge as long as the power supply voltage
is constant.
- Capacitance C is directly
proportional to the permittivity ϵr > 1 of the
dielectric between the parallel plates according to the formula
C =(ϵ0 ϵr A)/d.
Removing the dielectric essentially means decreasing the
permittivity ϵr to 1, which corresponds to a decrease in
the capacitance. Given that the charge on the capacitor is directly
proportional to the capacitance, a decreased capacitance results in
a decrease in the charge as long as the power supply voltage is
constant.
- The charge on the capacitor is directly
proportional to the capacitance multiplied by the voltage of the
power supply. Decreasing the voltage results in a decrease in the
charge unless the capacitance is increased independently.
|
front 23 If the 25 μF capacitor in the defibrillator in Figure 1 is replaced
with a 30 μF capacitor, what new power supply setting would produce
the same amount of charge?
- A.3600 V
- B.3500 V
- C.3000 V
- D.2500
V
| back 23
Solution: The correct answer is D.
- A power supply setting of 3600 V would produce a charge of 108
mC, not 75 mC.
- A power supply setting of 3500 V would
produce a charge of 105 mC, not 75 mC.
- A power supply
setting of 3000 V would produce a charge of 90 mC, not 75 mC.
-
On the 25 μF capacitor, the power supply stores a charge of
25 μF × 3000 V = 75 mC. On the 30 μF capacitor, the same charge is
stored by a power supply that has a voltage of 75 mC/30 μF = 2500
V.
|
front 24 If the energy of a photon is doubled, which of the following
properties of the photon will also double?
- A.Amplitude
- B.Wavelength
- C.Frequency
- D.Intensity
| back 24
Solution: The correct answer is C.
- Amplitude is a characteristic of waves, whereas photons
constitute the particle description of light. Therefore, photons
cannot be characterized by the property of amplitude.
- The
energy of a photon is given by the relationship E =
hc/l. If E is doubled, then wavelength l is halved not
doubled.
-
The energy of a photon is given by the relationship
E = hf. If E is doubled, then frequency
f is doubled, too, as Planck's constant h does
not change.
- Intensity is a characteristic of
waves, whereas photons constitute the particle description of light.
Therefore, photons cannot be characterized by the property of
intensity unless as the number of photons of a certain energy that
pass through a surface per unit time.
|
front 25 If the red line in the Balmer series has a wavelength of 656 nm,
which of the following is closest to its frequency?
- A.4.6 × 1014 Hz
- B.4.6 × 10−14
Hz
- C.2.1 × 1015 Hz
- D.2.1 ×
10−15 Hz
| back 25
Solution: The correct answer is A.
-
For light that travels in vacuum, wavelength and frequency
are related according to wavelength × frequency = 3.0 ×
108 m/s. Solving for frequency yields (3.0 ×
108 m/s)/(656 × 10-9 m) = 4.6 ×
1014 Hz.
- A frequency of 4.6 ×
10-14 Hz corresponds to a wavelength of 6.56 ×
1021 m , not 656 × 10-9 m.
- A
frequency of 2.1 × 1015 Hz corresponds to a wavelength of
143 nm, not 656 nm.
- A frequency of 2.1 × 10-15
Hz corresponds to a wavelength of 1.43 × 1023 m, not 656
× 10-9 m.
|
front 26 Which of the following is closest to the wavelength of a photon whose
energy is 2 eV?
- A.740 nm
- B.620 nm
- C.450 nm
- D.310
nm
| back 26
Solution: The correct answer is B.
- A wavelength of 740 nm corresponds most closely to a photon
with energy E = 1.66 eV, not 2 eV.
-
Using hc = 4.1 × 10–15 eV•s × 3 ×
108 m/s = 1230 eV•nm, and λ = hc/E,
then E = 2 eV corresponds to λ = (1230 eV•nm)/(2 eV) =
615 nm, which is closest to 620 nm.
- A wavelength
of 450 nm corresponds most closely to a photon with energy
E = 2.75 eV, not 2 eV.
- A wavelength of 310 nm
corresponds most closely to a photon with energy E = 4 eV,
not 2 eV.
|
front 27 What is the value of K
b for the conjugate base of a weak organic acid that has a pK
a of 5?
- A.10−2.5
- B.10−5
- C.10−9
- D.10−10
| back 27
Solution: The correct answer is C.
- This is the K
b for the conjugate base of an acid with a pK
a of 11.5.
- This is the K
b for the conjugate base of an acid with a pK
a of 9.
-
Because pK
b = 14 - pK
a, this is the K
b for the conjugate base of an acid with a pK
a of 5.
- This is the K
b for the conjugate base of an acid with a pK
a of 4.
|
front 28 An ester is prepared by the method of direct esterification using an
esterase enzyme as a catalyst. Which of the following modifications
will NOT appreciably increase the final yield of ester?
- A. Using 2 times as much enzyme
- B.Using 2 moles of
RCOOH instead of 1 mole
- C.Using 2 moles of
RCH2OH instead of 1 mole
- D.Removing
RCOOCH2R from the reaction mixture as it is formed
| back 28
Solution: The correct answer is A.
-
This modification will increase the rate of formation, not
the final yield of ester.
- Doubling the
concentration of RCOOH will increase the yield of ester by Le
Châtelier's principle.
- Doubling the concentration of
RCH2OH will increase the yield of ester by Le Châtelier's
principle.
- By Le Châtelier's principle, removing the ester
product as it forms will drive the reaction to form more ester.
|
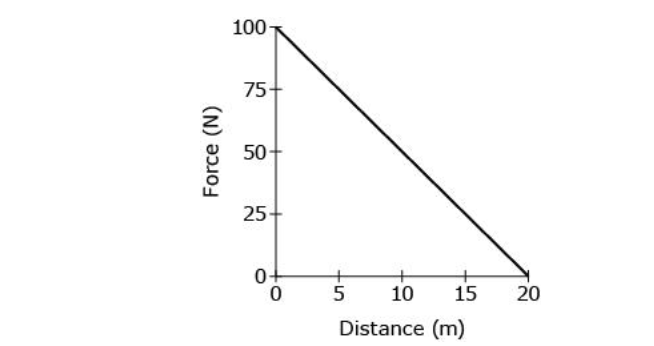
front 29 A person pushes on a rolling cart with a force that diminishes with
time because the person must walk faster to keep up with the
accelerating cart. How much work does the person generate while
pushing on the cart?
- A.500 J
- B.1000 J
- C.2000 J
- D.4000
J
| back 29
Solution: The correct answer is B.
- This quantity corresponds to a calculation error of the area
under the force-distance line as (100 N/2) × (20 m/2) = 500 J.
-
The work generated by the person while pushing the cart is
equal to the area under the force-distance line, according to the
definition of work. The area is equal to 1/2 × (100 N - 0 N) × (20
m - 0 m) = (100 N × 20 m)/2 = 1000 J.
- This
quantity corresponds to a calculation error of the area under the
force-distance line as (100 N × 20 m) = 2000 J.
- This
quantity corresponds to a calculation error of the area under the
force-distance line as (100 N × 20 m) × 2 = 4000 J.
|
front 30 -
Adaptive immunity: Involves__________ both of which
are regulated by various miRNAs to control immune responses.
-
Innate immunity: Involves the ___________ to
pathogens or transplanted tissues, which also involves miRNAs that
regulate inflammatory pathways and the activation of immune cells
like macrophages and dendritic cells.
| back 30 T cells (cell-mediated immunity) and B cells (humoral immunity),
initial response |
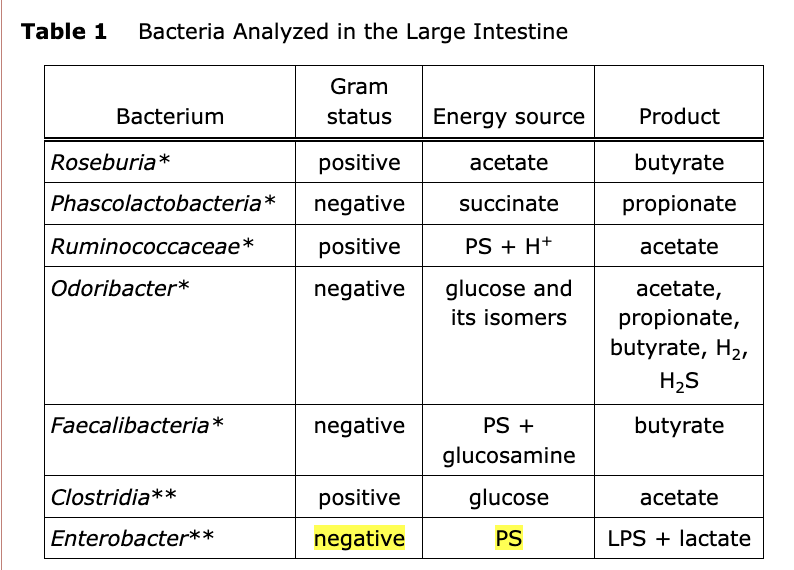
front 31 Text:
GI tract bacteria digest dietary fibers and convert them into
butyrate, propionate, and acetate. These three molecules modulate the
innate immune system response by attenuating the inflammatory response
to GI tract commensal bacteria. Furthermore, butyrate is a major
source of energy for colonocytes.
The GI tract microbiome of healthy individuals exhibits a
predominance of gram-positive bacteria Firmicutes and
Bacteroidetes and a reduced amount of Proteobacteria
and Actinobacteria.
From Table 1, in which metabolic process are GI tract bacteria
directly involved?
- A.Conversion of PS into short chain fatty acids
- B.Absorption of amino acids
- C.Fermentation of dietary
fibers into peptides
- D.Absorption of monosaccharides
| back 31
Solution: The correct answer is A.
-
GI tract bacteria convert monosaccharides and
polysaccharides into acetate, propionate, and butyrate, which are
short chain fatty acids.
- The table does not
indicate a direct role for amino acids in metabolic functioning of
GI tract bacteria, but rather that such bacteria convert
polysaccharides into short chain fatty acids.
- Based on the
table, dietary fibers are not converted into peptides, but short
chain fatty acids (acetate, propionate, and butyrate).
- Table 1 indicates that GI tract bacteria use monosaccharides as
an energy source, but does not indicate whether these bacteria
function in monosaccharide absorption.
|
front 32 Based on the passage, the microbiome of CD-affected individuals will
result in which physiological change?
- A.Increased polypeptide digestion
- B.Slower dietary
fiber absorption
- C.Increased amount of propionate
- D.Decreased immune tolerance
| back 32
Solution: The correct answer is D.
- There is no information indicating that any of the bacteria
listed in Table 1 impact polypeptide digestion.
- Dietary
fibers are not absorbed by the human intestine.
- Based on
Table 1, the two bacteria that produce propionate,
Phascolactobacteria and Odoribacter, are decreased
in CD-affected individuals. Thus, the levels of propionate are most
likely decreased, rather than increased, in CD-affected
individuals.
-
As explained in the passage, molecules such as butyrate,
acetate, and propionate inhibit the inflammatory response against
commensal bacteria of the GI tract. CD is an inflammatory
condition, in which Table 1 indicates that many bacteria producing
these anti-inflammatory molecules are reduced during CD. This is
consistent with the interpretation that inflammation observed
during CD is caused by decreased production of propionate,
butyrate, and acetate, which decreases immune tolerance of
commensal bacteria.
|
front 33 - Leucine contains a ___________, not a beta-branched chain.
-
Isoleucine contains a_____________
| back 33 gamma-branched side chain
beta-branched side chain. |
front 34 Which membrane transporter is electrogenic and translocates a net
charge across the membrane?
- A.Na+− H+ exchanger
- B.Na+−Cl- cotransporter
- C.Na+−glucose cotransporter
- D.GLUT2
facilitative glucose transporter
| back 34
Solution: The correct answer is C.
- The Na+–H+ exchanger is an antiporter in
which the transport of one Na+ is coupled with the
transport of one H+ in the opposite direction. This
results in no net translocation of charge.
- The
Na+–Cl– cotransporter transports one Na+
and one Cl– in the same direction. Therefore, there
is no net movement of charge and this is an electroneutral
process.
-
The Na+–glucose cotransporter transports
Na+ cations and glucose into the cell. This process is
electrogenic, as it results in the net movement of positively
charged molecules into the cell.
- As glucose is
not a charged molecule, GLUT2 activity will not be associated with
the net movement of charged molecules. Consequently, GLUT2 activity
represents an electroneutral transport process.
|
front 35 Interested in developing ways to treat human strokes, researchers are
attempting to develop forms of EPO that act on CNS neurons without
affecting erythrocyte production in the bone marrow. One benefit of
such a form of EPO in stroke treatment would be to:
- A.promote apoptosis of damaged CNS neurons without affecting
blood oxygen levels.
- B.limit neuronal cell death without
causing an immediate decrease in the oxygen-carrying capacity of the
blood.
- C.prevent apoptosis in the CNS without causing a
harmful increase in blood viscosity.
- D.promote healing in
the CNS without increasing the risk of developing tumors.
| back 35
Solution: The correct answer is C.
- Apoptosis in the CNS is associated with neuron death, in which
this would not be of benefit during stroke treatment.
- Based
on the passage, EPO is a molecule that will increase, not decrease,
the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.
-
Preventing apoptosis is the first step to treating the
adverse conditions of stroke. However, EPO-dependent stimulation
of erythrocyte production results in an increase in blood
viscosity. For this reason, a drug that can prevent apoptosis
without increasing blood viscosity will be ideal to treat the
consequences of stroke.
- Based on the passage,
circulating EPO is produced by tumor cells, it does not increase the
risk of developing tumors.
Erythropoietin (EPO) is a hormone that your body makes when there’s
not enough oxygen in the blood. It tells your bone marrow to make more
red blood cells (erythrocytes), which help carry
oxygen throughout your body.
When the number of red blood cells increases, the blood
becomes thicker because there are more cells in the same
amount of fluid. This makes the blood more viscous
(or "stickier"). This can be a problem because thicker blood
can be harder to pump, which could put extra strain on your heart. |
front 36 - Many __________ and secreted by bacteria. Production of
eukaryotic proteins in bacteria is a process often used by
researchers to better understand the function of a protein or to
produce the protein in high levels.
- Viruses do
_____________. Bacteria do, as well.
| back 36 eukaryotic proteins are produced
not exclusively contain all cellular machinery necessary to express
recombinant proteins |
front 37 Based on information presented in Table 1, which relationship between
pH and charged functional groups is accurate?
- A.At pH 8.50, the ratio of the cationic to anionic functional
groups in the NqrD subunit is equal to 1.
- B.At pH 7.00,
half of the functional groups in the NqrE subunit are
protonated.
- C.At pH 6.30, the net charge of the cationic and
anionic functional groups in the NqrA subunit is equal to 1.
- D.At pH 6.00, the majority of the functional groups in the NqrF
subunit are protonated.
| back 37
Solution: The correct answer is A.
-
Table 1 shows that the isoelectric point of NqrD is 8.50.
The ratio of the cationic (+) to anionic (–) functional groups in
a protein at its pI is always equal to one.
- Table 1 shows that the isoelectric point of the NqrE subunit is
equal 5.35. At a higher pH, like at pH 7.0, the majority of
functional groups in the NqrE subunit will lose their protons and
will be deprotonated.
- Table 1 shows that the isoelectric
point of NqrA is 6.30. The net charge of functional groups in a
protein at its pI is equal to zero, not 1.
- Table 1 shows
that the isoelectric point of NqrF is 5.25. At any pH higher than
5.25, the majority of the functional groups in the NqrF subunit will
be deprotonated, not protonated.
|
front 38 How does molecules react in conditions where pH is above or below the pI? | back 38 -
Above pI (in basic conditions): The molecule is
negatively charged because acidic groups
deprotonate (lose protons).
-
Below pI (in acidic conditions): The molecule is
positively charged because basic groups
protonate (gain protons).
|
front 39 What is the most likely effect of adding a sodium ionophore to a
culture of V. cholerae?
- A.Decreased activity of Na+-NQR
- B.Decreased production of ATP
- C.Decreased pH of the
periplasm
- D.Decreased consumption of O2
| back 39
Solution: The correct answer is B.
- A sodium ionophore does not interfere with the function of
Na+-NQR, but it degrades the sodium gradient (sodium
motive force) that is established by the action of
Na+-NQR.
-
Ionophores are compounds that bind to ions and facilitate
their movements across membranes. A sodium ionophore would
collapse the sodium gradient (sodium motive force) that is
established by the action of Na+-NQR, resulting in
decreased production of ATP.
-
V. cholerae uses an electrochemical gradient of
Na+, not of protons, to generate ATP. Therefore the pH of
the periplasm is not affected.
- Since sodium ionophores
degrade the electrochemical gradient required for ATP synthesis,
they cause a decrease in ATP levels. To compensate for this event,
V. cholerae is likely to increase the flux of electrons
to the respiratory chain, which results in increased, not decreased,
oxygen consumption.
|
front 40 Which type of reaction has a K
eq > 1 and is kinetically fast?
- A.Endergonic with high activation energy level
- B.Endergonic with low activation energy level
- C.Exergonic with high activation energy level
- D.Exergonic with low activation energy level
| back 40
Solution: The correct answer is D.
- A reaction that has a K
eq > 1 is exergonic, not endergonic. Additionally, a
high activation energy results in a kinetically slow, and not a fast
reaction.
- A reaction that has a K
eq > 1 is exergonic, not endergonic.
- A high
activation energy results in slow, not fast, reaction kinetics.
-
A reaction that has a K
eq > 1 is exergonic and a low activation energy
results in fast reaction kinetics.
|
front 41 If the small bumps seen when half of the membrane is peeled away were
chemically shown to consist of the lipid cholesterol, how would the
Fluid Mosaic Model have to be modified?
- A.The proteins would have to be embedded less than halfway
through the membrane.
- B.There could be no proteins in the
membrane.
- C.The lipids would have to be embedded in the
proteins.
- D.It would not necessarily have to be altered, but
there would be less evidence supporting it.
| back 41
Solution: The correct answer is D.
- Not necessarily, as transmembrane proteins could remain
embedded within the membrane leaflet that was removed.
- Even
if the small bumps were identified as cholesterol, proteins could
still be positioned within the membrane leaflet that was
removed.
- Because the middle of the bilayer is hydrophobic,
the lipids do not need to be embedded in the proteins.
-
The Fluid Mosaic Model indicates that the hydrophilic
regions of proteins are found on the membrane surfaces, while the
hydrophobic regions are buried among phospholipid tails. This
arrangement allows proteins to span the membrane. Consistently,
the passage mentions that, upon peeling back the top membrane
layer, small bumps are observed. This is consistent with the idea
that proteins span the membrane. If these bumps were identified as
cholesterol, this does not necessarily disprove the model.
Instead, it is possible that membrane-spanning proteins remain
adhered to the leaflet that has been peeled back.
|
front 42 The information in the passage best supports which hypothesis?
- A.Exercise prevents glucose uptake.
- B.Exercise
promotes less effective cellular respiration.
- C.Exocrine
secretions of skeletal muscle act on adipose tissue.
- D.Endocrine secretions of adipose tissue act on skeletal
muscle.
| back 42
Solution: The correct answer is B.
- The information in the passage indicates that exercise
correlates with increased FNDC5 expression. Additionally, mice
overexpressing FNDC5 exhibit lower nonfasting glucose levels, most
likely because of higher, not lower, cellular glucose uptake.
-
According to the pathway suggested by the information in the
passage, exercise ultimately increases UCP1 levels which in turn
degrades the proton gradient that drives oxidative
phosphorylation. More energy is dissipated as heat and less is
used to synthesize ATP.
- The passage notes that
irisin is secreted into blood and therefore it would be an
endocrine, not an exocrine, secretion of skeletal muscle.
- The passage notes that irisin is a protein formed by cleaving
the extracellular domain of FNDC5 which is expressed in skeletal
muscles, not adipose tissues.
|
front 43 The viruses that encode either FNDC5 or control protein transfer
genetic material via:
- A.transformation.
- B.transduction.
- C.contamination.
- D.conjugation.
| back 43
Solution: The correct answer is B.
- Transformation is the process that transfers genetic material
from the environment into bacteria.
-
Transduction is the process by which nucleic acids are
transferred from viruses to cells.
- Contamination
is the act of making a solution or sample impure.
- Conjugation is the exchange of nucleic acids between
bacteria.
|
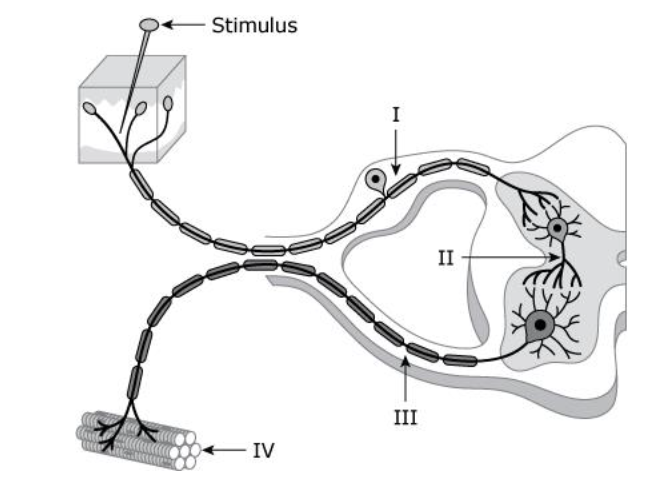
front 44 Which Roman numeral represents the CNS integration for a pain reflex arc?
| back 44
Solution: The correct answer is B.
- Roman numeral I represents the dorsal root ganglion.
-
Roman numeral II represents an interneuron, which serves as
an intercommunication point for the afferent and efferent neurons
within the CNS.
- Roman numeral III represents the
ventral root.
- Roman numeral IV represents the effector
muscle.
|
front 45 In an enzyme-catalyzed reaction where enzyme concentration is held
constant and substrate concentration is relatively low, which kinetic
parameter will increase with the addition of more substrate?
(Note: Other than substrate concentration, assume no other changes
to reaction conditions.)
- A.K
M
- B.k
cat
- C.V
max
- D.V
0
| back 45
Solution: The correct answer is D.
-
K
M, the rate constant of a reaction, does not change with
changes in substrate concentration.
-
K
cat is the reaction turnover number and does not change
with changes in substrate concentration.
-
V
max is the maximum velocity of a reaction and is a
constant property which does not change with the addition of more
substrate.
-
V
0 is the initial velocity of an enzymatic reaction. At
low concentrations of substrate and constant enzyme concentration,
adding more substrate will increase V
0 until the maximal velocity is reached.
|
front 46 Text: Lactose intolerance, also known as lactase deficiency, is a
condition that results from insufficient synthesis of the enzyme
lactase, which converts lactose into glucose and galactose. Although
all healthy newborns produce sufficient levels of lactase, two
distinct phenotypes exist in adults: lactase persistence (LP)
(includes heterozygotes) and lactase non-persistence (LNP). LP adults
continue to produce lactase into adulthood, whereas LNP individuals do
not. It has been suggested that the LP phenotype is the result of a
mutation event that coincided with the domestication of dairy animals
thousands of years ago in areas such as northwestern Europe and within
some Afro-Arabian nomadic populations. In Northwestern Europeans, sets
of alleles located closely together on the same chromosome
(haplotypes) associated with the LP phenotype contain several single
nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). However, only one appears to be
directly responsible for this phenotype; the others are silent. By
comparison, several different SNPs appear to be directly responsible
for the LP phenotype in Afro-Arabian LP-associated haplotypes.
Based on the information in the passage, the mutation that causes
the LP phenotype is most likely located in:
- A.an intron within the lactase gene.
- B.the coding
sequence of the lactase gene.
- C.an enhancer sequence of the
lactase gene.
- D.the stop codon at the end of the lactase
gene.
| back 46
Solution: The correct answer is C.
- Although introns might have regulatory functions, mutations to
promoter and enhancer regions most specifically alter gene
expression.
- A mutation in the coding region is most likely
associated with a mutated enzyme, which is not the case with the LP.
Instead, lactase expression is altered during LP.
-
The enhancer is a DNA region that is able to bind
transcriptional activators in order to increase the expression of
a particular gene. Since LP is caused by continuous lactase
synthesis, this is the region most likely targeted by the
mutation. Specifically, the mutation makes it easier for
transcriptional activators to bind an enhancer
sequence.
- A mutation affecting the STOP codon would
result in a mutated enzyme, which is not the case in LP.
|
front 47 Which cells express lactase?
- A.Enterocytes of the duodenal villi
- B.Epithelial
cells of the colon lining
- C.Parietal cells of the stomach
lining
- D.Bile-producing hepatocytes of the liver
| back 47
Solution: The correct answer is A.
-
Enterocytes are the intestinal cells that produce Enzymes
that digest disaccharides. This includes lactase.
- Colonocytes do not produce digestive enzymes. Lactose digestion
by the body does not occur in the colon, though bacteria in the
colon may break unusual sugars (oligosaccharides) down.
- Parietal cells of the stomach produce HCl, they do not produce
digestive enzymes.
- Hepatocytes do not produce digestive
enzymes.
|
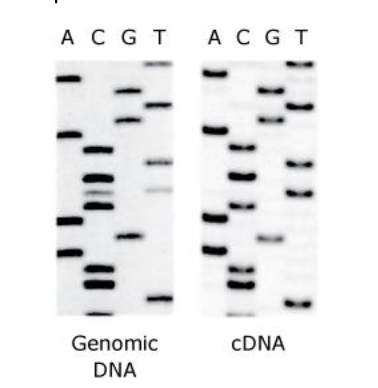
front 48 The SNP resulted from what type of mutation?
- A.Purine to purine
- B.Purine to pyrimidine
- C.Pyrimidine to purine
- D.Pyrimidine to pyrimidine
| back 48
Solution: The correct answer is D.
- The genomic radiograph indicates an SNP containing both
cytosine and thymine. These nucleobases are pyrimidines, not
purines.
- The radiograph shows an SNP containing cytosine and
thymine at the same position. Both of these are pyrimidines.
- Based on the radiograph, cytosine and thymine are the two
nucleobases that occupy the same position within the SNP. These
nucleobases are pyrimidines.
-
The radiograph indicates an SNP containing both a cytosine
and thymine nucleotide, instead of just thymine. Since both
nucleobases are pyrimidines, this indicates that the SNP resulted
from the mutation of a pyrimidine to another
pyrimidine.
|
front 49 What is the differences between cDNA and genomic DNA? | back 49 The key differences between cDNA (complementary DNA)
and genomic DNA are as follows:
1. Source:
-
cDNA: Is synthesized from mRNA (messenger RNA)
through a process called reverse transcription. It
represents only the expressed genes in the cell (i.e., the genes
that are actively being transcribed).
-
Genomic DNA: Refers to the entire DNA in an
organism, including both coding (exons) and non-coding regions
(introns, regulatory sequences, etc.). It is found in the nucleus
(in eukaryotic cells) and contains the full genetic blueprint of an
organism.
2. Structure:
-
cDNA: Only contains the exons
(coding regions) of the gene because it is derived from processed
mRNA. It lacks introns (non-coding regions).
-
Genomic DNA: Contains both exons
and introns, along with all regulatory sequences,
promoters, and non-coding regions.
3. Purpose and Use:
-
cDNA: Often used in gene expression studies,
cloning, and in cases where researchers are interested in studying
the expressed part of the genome (i.e., the parts of the genome that
get transcribed into RNA and then translated into proteins). It
helps in studying gene function and protein
synthesis.
-
Genomic DNA: Represents the entire genetic
information of an organism and is typically used in genome mapping,
genetic analysis, sequencing, and inheritance studies.
4. Presence of Introns:
-
cDNA: Does not contain introns
because it is synthesized from mature mRNA that has already
undergone splicing to remove the introns.
-
Genomic DNA: Contains both exons and introns.
Introns are non-coding regions that are transcribed into RNA but are
later removed during RNA splicing.
5. Length and Size:
-
cDNA: Typically shorter than
genomic DNA because it only represents the parts of the genome that
are transcribed into mRNA (i.e., the coding sequence).
-
Genomic DNA: Longer and contains
the entire genetic code of the organism, including both coding and
non-coding regions.
6. Production:
-
cDNA: Produced from mRNA by
reverse transcription, which involves the enzyme reverse
transcriptase to convert RNA into DNA.
-
Genomic DNA: Extracted directly from the organism’s
cells or tissues and represents the full DNA content.
|
front 50 Consider an experiment that consists of two ionic solutions separated
by a membrane that contains a ligand-gated potassium channel. The lack
of current generation in response to addition of ligand is explained by:
- lack of potassium in either solution.
- the presence of
potassium in only one solution.
- equal concentrations of
potassium in the two solutions.
- A.I only
- B.I and II only
- C.I and III
only
- D.II and III only
| back 50
Solution: The correct answer is C.
- If there are equal concentrations of potassium in the two
ionic solutions, it follows that there is no net movement of ions
across the channel and thus no current generation.
- The
presence of potassium in only one solution results in its movement
to the other side, thus generating a current.
-
Lack of current means no net movement of ions, which only
happens when the concentration of ions is the same on both sides
of the membrane or there are no ions present that the channel is
specific for (K
+).
- If only one of the
solutions contains potassium, the ion will move to the other
solution to create a concentration equilibrium, thus generating a
current.
|
front 51 A particular diploid organism is heterozygous in each of 3 unlinked
genes. Considering only these 3 genes, how many different types of
gametes can this organism produce?
| back 51
Solution: The correct answer is D.
- Gametes are haploid and will contain a combination of the
unlinked three genes. Since the organism contains two different
alleles within each gene, the number of distinct gametes that could
be produced is 8, not 3.
- There would be four distinct
gametes that could be produced if there were two, not three,
unlinked genes with a heterozygous genotype.
- There are 8,
not 6, possible gametes that can be formed from a diploid organism
that is heterozygous at three unlinked genes.
-
There are 8 distinct gametes that can be formed from an
diploid organism that is heterozygous at three unlinked genes.
Each gene (A, B, and C) will have two alleles (1 and 2) which can
be termed: A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, and C2. The resulting gamete
combinations will be: A1, B1, C1; A1, B2, C1; A1, B2, C2; A1, B1,
C2; A2, B1, C1; A2, B2, C1; A2, B2, C2; A2, B1, C2.
|
front 52 Which brain region will be LEAST activated when participants are
completing the tasks in the study?
- A.Parietal lobe
- B.Hippocampus
- C.Prefrontal
cortex
- D.Amygdala
| back 52
Solution: The correct answer is A.
-
The primary function of the parietal lobe is the integration
of sensory information. This brain region is less likely to be
involved in the task as compared to others.
- The
hippocampus is involved in memory encoding, which is necessary for
the recall of the critical incident. Therefore, this structure is
likely to be involved in the task.
- The prefrontal cortex is
involved in executive functioning and decision making, which is
likely to be involved in answering the assessments in the tasks, and
is thus incorrect.
- The amygdala is involved in emotional
encoding, which is likely to be involved in recalling the critical
incident.
|
front 53 Which statement is NOT a plausible application of psychodynamic
theory to explain psychological responses to upward comparison?
- A.The superego demands that the individual should either match
or surpass the partner on the dimension of comparison.
- B.The ego fails to satisfy the demands of the superego, and the
individual experiences anxiety.
- C.The id attempts to use
the pleasure principle to resolve the subconscious conflict caused
by the superego.
- D.The ego uses rationalization by
suggesting that the dimension of comparison is unimportant.
| back 53
Solution: The correct answer is C.
- According to psychodynamic theory, the superego is the
structure of personality which houses an individual's conscience,
developed via the internalization of parental and societal
expectations and values. The superego demands that one perform to
their highest possible standard, which makes this statement a
plausible application of psychodynamic theory to explain
psychological responses to upward comparison.
- According to
psychodynamic theory, the ego is the structure of personality
responsible for balancing the conflicting demands of the id and the
superego. When these demands are not met, anxiety is experienced.
This statement is a plausible application of psychodynamic theory to
explain psychological responses to upward comparison.
-
While the id does operate according to the pleasure
principle, according to psychodynamic theory, it is the
responsibility of the ego and not the id to resolve subconscious
conflict caused by the superego. Thus, this statement is not a
plausible application of psychodynamic theory to explain
psychological responses to upward comparison.
- Rationalization is a defense mechanism, and according to
psychodynamic theory, defense mechanisms are used to reduce anxiety
stemming from unconscious conflicts. This statement is a plausible
application of psychodynamic theory to explain psychological
responses to upward comparison.
|
front 54 Weber's characteristics of an ideal bureaucracy suggest that most
formal organizations will:
- A.train employees to conduct a variety of tasks.
- B.select employees based on technical qualifications.
- C.require employees to seek consensus in decisions.
- D.evaluate employees based on individualized criteria.
| back 54
Solution: The correct answer is B.
- According to Weber's conceptualization of ideal bureaucracy, a
formal organization requires specialization in a limited number of
tasks, rather than completing a variety of tasks.
-
Employment in a formal organization is based on technical
qualifications; therefore, this option is consistent with the
characteristics of an ideal bureaucracy.
- Decisions in ideal bureaucracies are based on an organizational
hierarchy instead of consensus among employees.
- Evaluation
of performance and skills in ideal bureaucracies are not based on
individualized criteria, but on standardized rules and
procedures.
|
front 55 Which statement best describes the sociological conceptualization of
race and ethnicity?
Racial and ethnic identities are:
- A.consistent across time periods and geography
- B.composed of mutually exclusive categories.
- C.based
primarily on physical characteristics.
- D.institutionalized
in major social structures.
| back 55
Solution: The correct answer is D.
- Race and ethnicity are concepts that change over time and
location.
- An individual might have multiple overlapping
racial and ethnic backgrounds that are not mutually exclusive.
- Both race and ethnicity encompass cultural and social categories
that change over time and location; therefore, they are not stable
categories primarily based on physical characteristics.
-
Race and ethnicity are institutionalized in social
structures. Neither race nor ethnicity is simply an individual
characteristic. Instead, they are tied to social structures beyond
an individual's control and become
institutionalized.
|
front 56 Which conclusion demonstrates a fundamental attribution error when
interpreting the results of the study?
- A.Dispositional attributions of others' behavior are weaker
when attitude ratings are influenced by the presence of others than
when alone.
- B.Dispositional attributions of others'
behavior are stronger when attitude ratings are influenced by the
presence of others than when alone.
- C.Situational
attributions of others' behavior are weaker when attitude ratings
are influenced when alone than when in the presence of others.
- D.Situational attributions of others' behavior are stronger when
attitude ratings are influenced by the presence of others than when
alone.
| back 56
Solution: The correct answer is B.
- Fundamental attribution error refers to the tendency to
attribute people's behavior to internal, dispositional traits,
rather than situational factors. Weak dispositional attributions, as
described in this option, are not representative of the fundamental
attribution error.
-
Fundamental attribution error refers to the tendency to
attribute people's behavior to dispositional traits, even when
situational explanations are available. A strong tendency for
making dispositional attributions in one of the study conditions
demonstrates the fundamental attribution error.
- Situational attributions are not representative of the
fundamental attribution error. Therefore, this option does not
provide definitive information regarding the fundamental attribution
error.
- When participants make situational attributions
regarding others' behavior, this suggests that they are not
influenced by the fundamental attribution error.
|
front 57 What is the difference between cultural transmission vs. diffusion? | back 57 Summary of Differences:
-
Cultural Transmission is the passing down of
culture within a society or group, ensuring
continuity of cultural practices and traditions.
-
Cultural Diffusion involves the spread and mixing
of cultural elements between different societies or
groups, leading to cultural exchange and change.
|
front 58 What is fundamental attribution error? | back 58 An example of fundamental attribution error is when
you see someone cut in line at the grocery store, and you immediately
think, "That person is rude or selfish." In
this case, you're attributing their behavior to their character
(internal traits) rather than considering external factors that could
explain their actions, such as being in a hurry because of an
emergency or not noticing the line.
The fundamental attribution error refers to the
tendency to overestimate the influence of someone's personality or
character on their behavior, while underestimating the role of
situational factors that might be influencing their actions.
Another Example:
If someone fails to return your call or message, you might think,
"They're ignoring me, they don't care,"
assuming it's their personality (e.g., they're inconsiderate).
However, you might not consider that they could be busy, dealing with
personal issues, or simply forgot (external factors).
This bias leads to making judgments about others' behaviors based on
internal traits, instead of considering the larger context that could
be influencing their actions. |
front 59 What is social facilitation? | back 59 Social facilitation occurs when the presence of an audience improves performance.
Social inhibition occurs when the presence of an audience hinders performance. |
front 60 Based on the elaboration likelihood model, which type of processing
was most likely induced by the administrator when interacting with the participants?
- A.High elaboration processing
- B.Central route
processing
- C.Careful processing
- D.Peripheral route
processing
| back 60
Solution: The correct answer is D.
- The elaboration likelihood model focuses on the role of
central and peripheral characteristics of a communication in
changing individuals' attitudes. High elaboration processing is
likely to involve processing through the central characteristics of
a message, which refer to its informational content and the quality
of its arguments. These are not the cues presented by the
administrator that shape participants' attitudes toward them.
- Central route processing occurs when the central characteristics
of a message, such as its informational content and the quality of
its arguments, are used to form an attitude. The attitude formation
in the passage is based on the behavioral cues presented by the
administrator, which are peripheral characteristics.
- Careful processing of information is more likely to attune
participants to the central characteristics in a communication. The
attitude formation in the passage is most likely determined by the
peripheral characteristics.
-
Peripheral characteristics of a communication refer to the
message characteristics that are not central to the information
and arguments presented in the message, such as the emotional
appeals made to the audience or characteristics of the individual
presenting the message. Peripheral route processing occurs when
peripheral characteristics drive an individual's processing and
attitude formation in a given social setting. In the passage
example, the administrator uses peripheral cues (their behavior)
to affect participants' attitudes toward them.
|
front 61 What is the elaboration likelihood model? | back 61 In summary, the Elaboration Likelihood Model
suggests that people process persuasive messages in two ways: through
careful, thoughtful analysis (central route) or through more
automatic, surface-level cues (peripheral route). The route people
take depends on their motivation and ability to process the information. |
front 62 What is locus of control? What are the two types? | back 62 - Locus of control refers to the types of attributions
individuals make to explain their outcomes. Individuals with an
external locus of control believe that forces outside of their
control primarily contribute to their outcomes. This is most
relevant to the student attributing their success to luck (an
external force).
|
front 63 A woman loses her job, finds that she is unable to pay her bills, and
accumulates debt. She must sell her home and move into an apartment.
This woman has experienced which type of social mobility?
- A.Horizontal mobility
- B.Vertical mobility
- C.Intergenerational mobility
- D.Structural mobility
| back 63
Solution: The correct answer is B.
- Horizontal mobility would represent an individual's change of
role within the same social class. Because the individual described
in the prompt experiences a decline in socioeconomic status, the
example does not represent horizontal mobility.
-
Vertical mobility indicates a change in someone's
socioeconomic status. This option is the correct answer because
the individual experiences vertical mobility, by moving into a
lower socioeconomic status.
- Intergenerational
mobility refers to generational change in socioeconomic status
across different generations. This is not discussed in the
prompt.
- Structural mobility refers to social mobility as a
result of macro-social changes, generally impacting a significant
part of the population. The individual described in the prompt
experiences mobility at the individual level and not at the
structural level.
|
front 64 What is the difference between horizontal and vertical mobility? | back 64 Summary of Differences:
-
Horizontal Mobility: Movement within the same
social class or status. No change in position on the social
hierarchy.
- Example: A person switching jobs within the same
field at the same level.
-
Vertical Mobility: Movement between different
social levels or statuses. This can be upward (improving social
status) or downward (declining in social status).
- Example:
A person moving from a lower-income job to a high-income
position (upward) or a person experiencing job loss and economic
hardship (downward).
|
front 65 Medicalization refers to the recategorization of a condition as a
medical problem that requires diagnosis and treatment by medical
experts. Alcoholism provides a classic case of medicalization, as
alcohol abuse has transitioned from what was once ________________ | back 65 considered a problem of individual moral character to being
considered a treatable medical condition today. |
front 66 ______________ refers to an individual basing their sense of self on
how they think others perceive them. This tendency is associated with
one's self-concept, rather than attraction to potential romantic partners. | |
front 67 ______________ refers to the preference for familiar stimuli over
novel stimuli. When individuals develop a romantic attraction to
people they see frequently, this may be due to the mere exposure effect. | |
front 68 _________ describes how people react to social constraints to
achieving goals. | back 68
Strain theory
It explains how individuals or groups may experience
strain or frustration when they are
unable to achieve culturally approved goals through legitimate means.
According to strain theory, the pressure or "strain" that
results from these blocked opportunities can lead to deviance, as
people adapt to their situation in different ways.
-
-
Conformity: Individuals continue to pursue
socially approved goals using accepted means, even when they
face barriers.
-
Innovation: Individuals accept the goals of
society (e.g., wealth or success) but use illegitimate
means (like crime or fraud) to achieve them.
-
Ritualism: Individuals abandon the goals of
success but continue to strictly adhere to the accepted means,
even if they are no longer achieving the original goals. This
can be seen in people who follow rules and routines without hope
of success.
-
Retreatism: Individuals reject both societal
goals and means. They "drop out" of society’s
expectations entirely, often engaging in substance abuse or
other escapist behaviors.
-
Rebellion: Individuals reject both societal
goals and means, and seek to replace them with alternative
systems of values and goals. Rebels may challenge the existing
social order through protest or activism
Imagine a young person from a low-income neighborhood who is taught
that success and happiness are achieved through a good job and wealth.
However, due to limited access to quality education and employment
opportunities, they cannot achieve these goals through traditional
means. The strain created by this gap between societal expectations
and their reality might lead them to resort to
innovation, such as engaging in illegal activities
(e.g., selling drugs) to gain financial success. |
front 69 ________ specifically focuses on how deviant behaviors in the past
have long-term stigmatizing impacts on individuals. | back 69 Labeling theory
Labeling theory suggests that when society labels
someone as deviant, it can influence their behavior and identity.
People may start to see themselves as the label they’ve been given,
leading to more deviant actions. For example, if a teenager is labeled
a "troublemaker" after being caught shoplifting, they might
begin to act out more, fulfilling the label. This process can turn an
initial minor act of deviance into a long-term pattern of behavior,
driven by society’s response to the individual.
- Primary Deviance: A high school student skips class a few
times or gets caught smoking a cigarette behind the school. This
might be a one-time or isolated incident that doesn't lead to a
permanent label or major consequences.
- Secondary Deviance:
If that same student is labeled a "troublemaker" by
teachers and peers, they might begin to act out more frequently,
internalizing the label of "bad kid." As a result, they
might get into further trouble, like skipping school regularly or
engaging in more disruptive behaviors, and the deviant identity
becomes a self-fulfilling prophecy.
|
front 70 In subsequent research, the study is expanded to examine how high-SES
African American adolescents adapt to predominantly white
neighborhoods. Which concept would be LEAST applicable to this
follow-up study?
- A.Front stage self
- B.Intersectionality
- C.Social role conflict
- D.Demographic transition
| back 70
Solution: The correct answer is D.
- Front stage self refers to an individual's impression
management that is consistent with the expectations of a particular
social role. This concept would be applicable to how an individual
adapts to their social environment when they interact with others in
that environment.
- Intersectionality (Intersectional
approach) indicates that the different aspects of someone’s social
background (e.g., race, ethnicity, age, gender, and class) might
concomitantly bestow privileges or disadvantages on an individual.
The question describes the intersection of racial and class
backgrounds; therefore, intersectionality would apply to the
study.
- Social role conflict indicates the conflicting demands
of two different social roles an individual carries. Role conflict
would be applicable to the study if the study found that an
individual experienced a role conflict between their social role
associated with their family background and their role as a member
of the community.
-
Demographic transition refers to the association between the
level of socioeconomic development and the balance between
fertility and mortality rates in a society. Because this approach
focuses on the changes at the societal level, it would be least
applicable to the follow-up study which requires a micro-level
approach. Demographic transition refers to the shift in a
country's population structure as it develops economically and
socially. It describes the change from high birth and death rates
to low birth and death rates over time, typically following a
pattern that happens in stages. This transition is closely tied to
changes in a society’s economic development, healthcare,
education, and overall standard of living.
|
front 71 The researchers who conducted Study 1 were interested in the
individual differences between the participants in terms of how they
update their beliefs. The participants' scores on which variable would
be most likely to predict how they update their beliefs?
- A.Optimism
- B.Self-esteem
- C.Impression
management
- D.Self-efficacy
| back 71
Solution: The correct answer is A.
-
Findings from Study 1 demonstrate that participants are more
likely to update their beliefs when the information is positive,
which indicates an optimistic bias. Individuals higher in trait
optimism may be more likely to show this tendency.
- Self-esteem is a person's global evaluation of self-worth. This
is not relevant to making evaluations about the likelihood of
negative events occurring.
- Impression management is the
process by which an individual attempts to manage how they are
perceived by others. This is not relevant to making evaluations
about the likelihood of negative events occurring.
- Self-efficacy is one’s belief about one’s personal ability to
perform behaviors that should lead to expected outcomes. This is not
relevant to making evaluations about the likelihood of negative
events occurring.
|
front 72 ______________ is a tendency to think of things based on their usual
functions. It is a barrier to problem solving rather than an approach
to it. | |
front 73 In operant conditioning, partial reinforcement, rather than
continuous reinforcement, leads to a response that is:
- A.slower to acquire and more resistant to extinction.
- B.faster to acquire and less resistant to extinction.
- C.faster to acquire and more resistant to extinction.
- D.slower to acquire and less resistant to extinction.
| back 73
Solution: The correct answer is A.
-
Continuous reinforcement refers to reinforcing every
response emitted by an individual. Partial reinforcement occurs
when only some of the responses emitted by an individual are
reinforced. Continuous reinforcement is associated with a fast
rate of acquisition, but quicker extinction. Partial
reinforcement, on the other hand, is associated with slower
acquisition and slower extinction.
- Compared to
continuous reinforcement, partial reinforcement results in slower
acquisition and greater resistance to extinction.
- Compared
to continuous reinforcement, partial reinforcement results in slower
acquisition.
- Compared to continuous reinforcement, partial
reinforcement results in greater resistance to extinction
|
front 74 Which structural feature does NOT characterize modern economic systems?
- A.Division of labor
- B.Craft apprenticeship
- C.Occupational specialization
- D.Structural
interdependence
| back 74
Solution: The correct answer is B.
- Division of labor refers to how different socioeconomic
classes complete different economic tasks that are interdependent.
Division of labor is one of the major characteristics of modern
economic systems.
-
Craft apprenticeship indicates a lengthy training under an
individual who is considered to have mastered the knowledge and
the skills in a specific craft. In this relationship, the
apprentice learns everything related to the craft from the
experienced craftsperson. Therefore, craft apprenticeship requires
a highly individualized relationship between the experienced
craftsperson and the apprentice. In modern economic systems, some
occupations, such as artisanal and small-scale products and
services, still have vestiges of a craft apprenticeship; however,
this stage is no longer a characteristic of modern economic
systems which require formal education and training for
employment.
- In modern economic systems, professions
require specialization where employees are trained to accomplish
certain tasks in a complex economic system.
- Modern economic
systems are structurally interdependent to each other because the
complexity of economic activities in these systems cannot be
sustained only with the social and material resources in a single
economy.
|
front 75 The categorization aspect of the cognitive functioning assessment
involves which type of memory?
- A.Sensory memory
- B.Short-term memory
- C.Episodic memory
- D.Semantic memory
| back 75 - The passage states that, "To assess cognitive functioning,
[participants] were presented with a list of fifteen items
categorizable as animals, clothing, and furniture. After
participating in a 2-minute distraction task, they were asked to
recall as many of the items as possible and categorize them."
Sensory memory is the system of memory which preserves information
in its original sensory form, typically only for a fraction of a
second. This is not the type of memory involved in recalling
previously learned information.
- Information is only
maintained in short-term memory for approximately 20 seconds, unless
it is actively rehearsed. Given the study included a 2-minute
distraction task, the information being recalled would not be in
short-term memory.
- Episodic memory is long-term memory for
personally experienced events. This is not the memory system used to
recall and categorize a list of items.
-
Semantic memory is memory for facts and knowledge. This is
the memory system used for a categorization task which requires
participants to use pre-existing knowledge to sort the
items.
|
front 76 Based on the passage, participation in which study is most likely to
be associated with a decrease in hippocampal volume in rats?
A study on:
- A.the extinction of conditioned responses
- B.learned
helplessness and avoidance learning
- C.the effectiveness of
stimulants as reinforcers
- D.instinctive drift and classical
conditioning
| back 76
Solution: The correct answer is B.
- The passage states that, "Studies on animals have shown
that chronic increases in stress-related hormones are associated
with reduced dendritic spines, decreased long-term potentiation, and
reduced neurogenesis in the hippocampus. Studies on humans show that
people who have experienced posttraumatic stress disorder have
reduced hippocampal volume." Extinction of conditioned
responses does not require exposure to a stressor and thus is not
relevant to the passage discussion of changes to hippocampal
volume.
-
Avoidance learning occurs when the individual responds to
prevent the presentation of an aversive stimulus, while learned
helplessness is a behavioral and physiological state that occurs
as a result of exposure to uncontrollable aversive consequences.
The inescapable aversive stimulus is a chronic stressor which
would be predicted to be associated with decreased hippocampal
volume.
- Stimulants are psychoactive substances which
increase central nervous system activity. As they are not stressors,
passage information does not support them being associated with a
decrease in hippocampal volume.
- Instinctive drift refers to
the interference of innate, species-specific behaviors with
continued performance of a learned response. As this is not a
stressor, it is not relevant to the passage discussion of decreased
hippocampal volume.
|
front 77 What is the difference between informative vs normative social influence? | back 77 - Informational social influence occurs when individuals conform
to others' behavior because they are in an ambiguous situation for
which they do not have a script. This is not relevant to seeking
social acceptance from a peer group.
-
Normative social influence refers to individuals acting in
ways that comply with the norms of their social groups. This is
most relevant to the description of novice users who view drug use
as a means of gaining social acceptance from a peer
group.
|
front 78 Participants' responses to the self-statements on the inventory
described in the passage could be affected by each of the following
confounds EXCEPT:
- A.Hawthorne effect.
- B.demand characteristics.
- C.self-serving bias.
- D.confirmation bias.
| back 78
Solution: The correct answer is D.
- The Hawthorne effect refers to the change in the participants’
behavior when they know their behavior is being observed, including
via self-report. This may affect participants' responses to the
self-statements on the inventory.
- Demand characteristics
occur if the research design provides cues to the participants
regarding the study hypothesis and causes them to respond in a
specific manner. This may affect participants' responses to the
self-statements on the inventory.
- Self-serving bias refers
to the tendency to attribute one’s successes to internal, stable
traits, and failures to situational factors. This may affect
participants' responses to the self-statements on the
inventory.
-
Confirmation bias refers to the tendency to put more weight
on information that confirms one’s preexisting attitudes. This
would not affect participants' responses to the self-statements on
the inventory.
|