Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
GIS test one, part 2
front 1 What did Ian McHarg do to become known as the Grandfather of GIS? | back 1 Pioneered the concept of ecological planning and was fundamental in forming the basic concepts used in GIS |
front 2 What is sieve mapping? | back 2 Process of adding transparent layers to a map such as roads, land use, boundaries, water, elevation, etc... (think High River flood map) |
front 3 What did Roger Tomlinson do to become known as the Father of GIS? | back 3 Created the Canadian Geographic System which used a layered approach to mapping. Considered the first operational GIS, it stored geospatial data for the Canada Land Inventory |
front 4 In 1964 SYMAP, one of the first computer mapping softwares was made by who? | back 4 Howard Fisher |
front 5 In 1969, Jack and Laura Dangermond founded which institute that went on to found the first commercial GIS product. | back 5 ESRI |
front 6 What was the first commercial GIS product? | back 6 ARC |
front 7 How is volunteered geographic information acquired? | back 7 Phones, surveys, georeferenced images or tags, etc... If it knows where you are or where you're going it's VGI, can be intentional or unintentional |
front 8 What are the five steps to the geographic approach | back 8 ask, acquire, examine, analyze, act |
front 9 What is metadata | back 9 descriptive info about a data file |
front 10 What is a geodatabase | back 10 a single folder that can hold numerous files with almost unlimited space |
front 11 What is a feature class | back 11 A single data layer (point, line or polygon) |
front 12 What is a feature dataset? | back 12 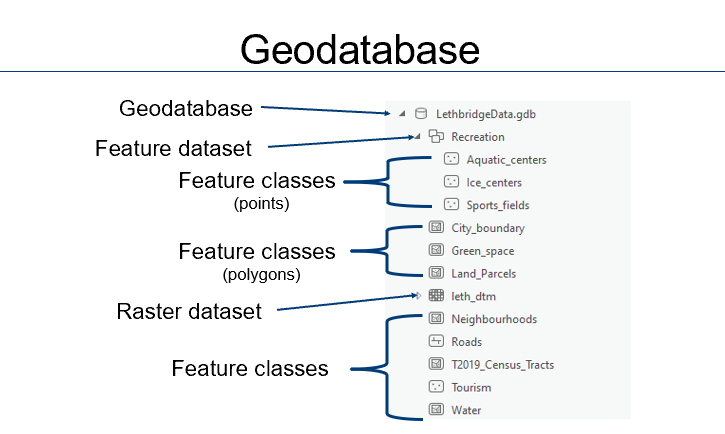 A grouping of multiple feature classes as a more effective way of storing and sharing data |
front 13 When sharing packages from ArcGIS Pro you have three options. What are the differences between sharing a layer, map or project package? | back 13 Layer: one layer, includes layer's properties and data Map: Shares map including properties and data for its layers Project: entire project including properties, data toolboxes, styles, models and more |
front 14 When sharing web content from ArcGIS Pro you can do it as a web layer or a web map. What is the positive of sharing data as web content as opposed to packages? | back 14 The data can be used in other apps (StoryMaps, Dashboards, Survey123...) |
front 15 What does discrete object view use to represent the world? | back 15 Points, lines and polygons |
front 16 How does continuous field view differ from discrete object view? | back 16 There are no hard boundaries (think temp, elevation...) thus continuous or along a continuum. |
front 17 How does a raster data model represent the world? | back 17 With equally sized cells arranged in rows and columns |
front 18 Between vector data and raster data which... - is more prone to generalization? - is effective for continous data? - is more asthetically pleasing? - can have blocky images? - is more ideal for mathematical modelling? - has accurate geographic locations without generalization? | back 18 - Rasters - Rasters - Vectors - Rasters - Rasters - Vectors |
front 19 In ArcGIS tables without spatial associations are called what? | back 19 Attribute tables |
front 20 To join attribute tables what must they have in common? | back 20 A common field |
front 21 How is a relate similar to a join? How is it different? | back 21 It requires a common field between tables but does not attach or move data |
front 22 When are spatial joins used? | back 22 when layers do not have a common attribute field |
front 23 In ArcGIS Pro what is an attribute? | back 23 Non-spatial data associated with a spatial location |
front 24 Database queries use a specific syntax called...? | back 24 Structured Query Language (SQL) |
front 25 What is a compound query? | back 25 A query used to make selections based on multiple |
front 26 What are the 4 logical operators used to make compound queries? | back 26 and, or, not, xor |
front 27 If you want to select for attributes that meet both criteria A and B which logical operator would you use? | back 27 and |
front 28 If you want to select for attributes that meet criteria A, B or both which logical operator would you use? | back 28 Or |
front 29 If you have selected attributes with either A or B but not both you have used which logical operator? | back 29 XOR |
front 30 If you have selected all attributes that do not meet criteria B which logical operator have you used? | back 30 Not |
front 31 When making a spatial query (select by location) what is the difference between "within" and "contains" | back 31 Within=is (at least) partially inside of the defined search area Contains=surrounds or holds (at least partially) the specified feature ex. Alberta is within Canada therefor Canada contains Alberta ex. Lethbridge is contained by Alberta therefor Lethbridge is within Alberta |
front 32 According to spatial relationships Alberta is not considered completely within Canada. Why? | back 32 Its border touches The States. |
front 33 Does the United States completely contain Kansas? Does it contain or completely contain Texas? | back 33 Completely contains Kansas, contains Texas (not completely contains) because it borders Mexico. |
front 34 What is digitizing? | back 34 Process of creating points, lines, or polygons which represent features from a map or image. |
front 35 What is the 0.5 mm rule of digitization? | back 35 For every additional 50,000 in the scale ratio there can only be maximum 0.5 mm or error. ex. 0.5 mm on a 1:50,000 map is ± 25 m, 1 mm 1:50,000 map is ± 50 m... |
front 36 What are the two types of digitization? Which is mostly obsolete now? | back 36 Heads down and heads up, heads down is mostly obsolete |
front 37 Heads _________ digitizing needed a Digitizing tablet and a Hardcopy map while heads ___________ digitizing needs a computer and Satellite images, air photos, or scanned maps | back 37 Down, up |
front 38 What is a sliver polygon? | back 38 Unwanted small polygons created when there is a gap or overlay between digitized polygons |
front 39 How can you avoid creating sliver polygons? | back 39 By using the snapping tool |
front 40 What is georeferencing? | back 40 The process of aligning an unreferenced dataset to one that has a spatial reference system. |
front 41 What are the locations that are identifiable and have known
| back 41 Control points |
front 42 Which two are good control points: Road intersections, boulders, tops of buildings, trees, shorelines? | back 42 Road intersections and boulders |
front 43 Why are shorelines bad control points? | back 43 They erode and shift with time |
front 44 There are three transformations that can happen depending on the amount of ground control points used: first, second and third order affines. How many ground control points (GCPs) do they each require minimum? | back 44 first-order affine=3 second-order affine=6 third-order affine=10 |
front 45 What does each transformation do? (hint first order does 3) | back 45 First-order= shift, scale, rotate Second-order= bend Third-order= twist |
front 46 When a transformation is applied the residual error is calculated. What is this an assessment of? | back 46 The transformation accuracy |
front 47 What is Root Mean Squared Error? | back 47 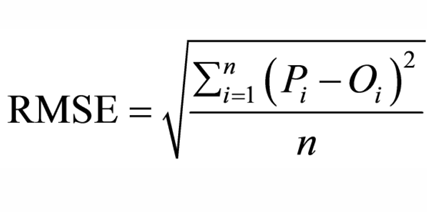 the square root of the mean value of all the squared errors (residuals). |
front 48 How many GCPs are needed to calculate the RMSE? | back 48 4 |
front 49 Do you want your RMSE to be high or low? | back 49 Low |
front 50 How does a Forward residual show error compared to a Inverse residual | back 50 Shows the error in the same units as the data frame vs measuring the
overall accuracy by |
front 51 What is resampling? | back 51 When each cell is goven a new value based on its location following a transformation |
front 52 What are the three common methods of resampling? | back 52 Nearest neighbor, Bilinear interpolation, Cubic convolution |
front 53 Nearest neighbour corrects images based on what? | back 53 The nearest pixel |
front 54 Bilinear interpolation corrects images based on what? | back 54 a weighted average of four pixels in the original grid nearest the new pixel |
front 55 Cubic convolution corrects images based on what? | back 55 A weighted average of 16 pixels from the original grid that surrounds the new output pixel. |
front 56 Of the three resampling methods which one produces a blocky appearance? | back 56 Nearest neighbour |
front 57 What does spatial analysis describe? | back 57 How features are spatially related to one another |
front 58 Thiessen polygons are a representation of proximity in spatial analysis. What do they show? | back 58 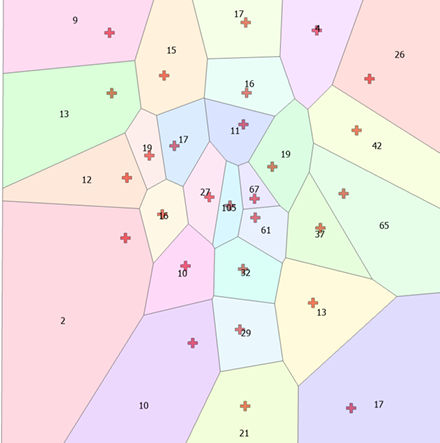 Area is divided into closest proximities to selected points |
front 59 What is a buffer? | back 59  A spatial proximity around a point, line or polygon |
front 60 Do buffers use Manhattan or Euclidean distance? | back 60 Euclidean |
front 61 Spatial analysis using Manhattan distance is called what? | back 61 Network Analysis |
front 62 When using Near features nothing is changed visually but the data is still stored where? | back 62 As a new field in the attribute table |
front 63 Kernel Density (KDE) calculates what? | back 63 The density of point features around each output raster cell |
front 64 What do you move across the data using KDE and what does it count? | back 64 a window, it counts the points within the window to calculate density |
front 65 Each cell within a raster can represent how many points? | back 65 Just one |
front 66 What is a vertical datum? What is it determined by? | back 66 A baseline used for measuring elevation determined by mean sea level curtesy of the geoid |
front 67 What is elevation represented by on topographic maps? | back 67 Contour lines |
front 68 What is LiDAR? (Light detection and Ranging) | back 68 A modelling method where laser pulses are shot to the ground and their return time is measured |
front 69 What are digital elevation models (DEMs)? | back 69 Representations of the surface of the Earth |
front 70 What are triangulated Irregular Networks (TINs)? | back 70 A vector based approach to creating Digital Elevation models where points are connected with non-overlapping triangles |
front 71 Are DEMs or TINs better at...
| back 71
|
front 72 Are DEMs or TINs worse at...
| back 72
|
front 73 What are digital surface models (DSMs) ? What do they look like? | back 73 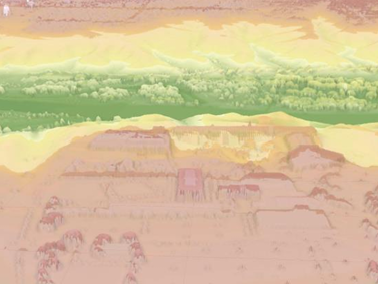 A measurement of ground elevation heights as well as the objects on the ground. Look like a thin sheet draped over the surface |
front 74 What is a surface drape? | back 74 An image overlayed (or draped) onto a DEM |
front 75 What makes rasters ideal for math? | back 75 Each cell has only one value |
front 76 What are predictive surfaces? | back 76 Models where known measurements of locations are used to predict values in location that were not measured |
front 77 Are predictive surfaces used for discrete or continuous data? | back 77 Continuous |
front 78 Predictive surfaces can be used to interpolate. What is interpolation? | back 78 Interpolation is the process of predicting values between known points |
front 79 Some predictive surfaces can be used to extrapolate. What is extrapolation? | back 79 Extrapolation is predicting values outside of known sample points |
front 80 Exact interpolation creates a surface that _________
____________ | back 80 passes through |
front 81 Approximate interpolation creates a surface that may _______ from known values | back 81 vary |
front 82 (Local/Global) methods use all the data in the study area while (Local/Global) methods use spatially defined data subsets. | back 82 Global, local |
front 83 Name the four predictive surfaces we covered in class | back 83 Inverse Distance Weighting (IDW), Natural Neighbor, Spline, Trend |
front 84 What is Tobler's first law of geography? | back 84 “Everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things.” Waldo R. Tobler (1969) |
front 85 Which predictive surface will use the nearest input samples to the grid cell (location on a raster) you've chosen and weights them based on proportionate areas (Thiessen polygons) overlapping the grid cell area? | back 85 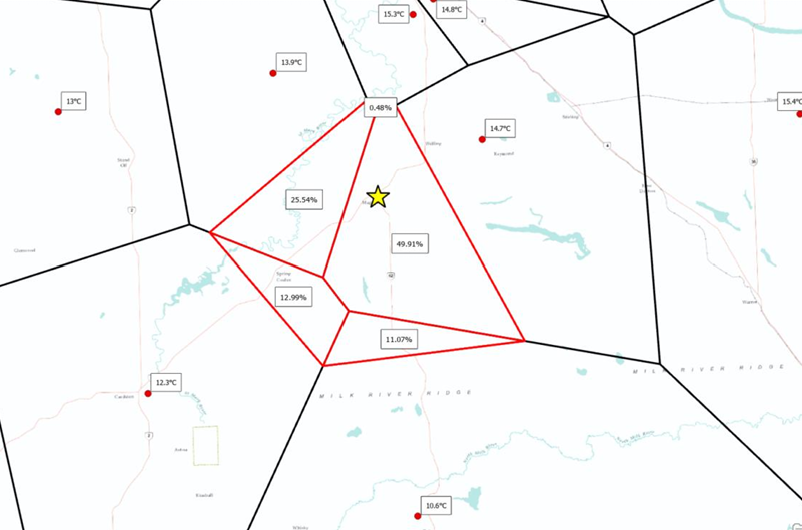 Natural Neighbor |
front 86 Which predictive surface uses a weighted combination of sample points with power controls that change their significance based on their distances from other points? | back 86 Inverse Distance Weighting |
front 87 Which predictive surface minimizes curvature to create a smooth surface and that exceeds the minimum and maximum values when used for exact interpolation? | back 87 Spline |
front 88 What are the two types of spline, which has a smoother surface? | back 88 Regularized and Tension, Regularized has a smoother surface |
front 89 Both spline methods exceed the min/max values but which is exact and which is approximate? | back 89 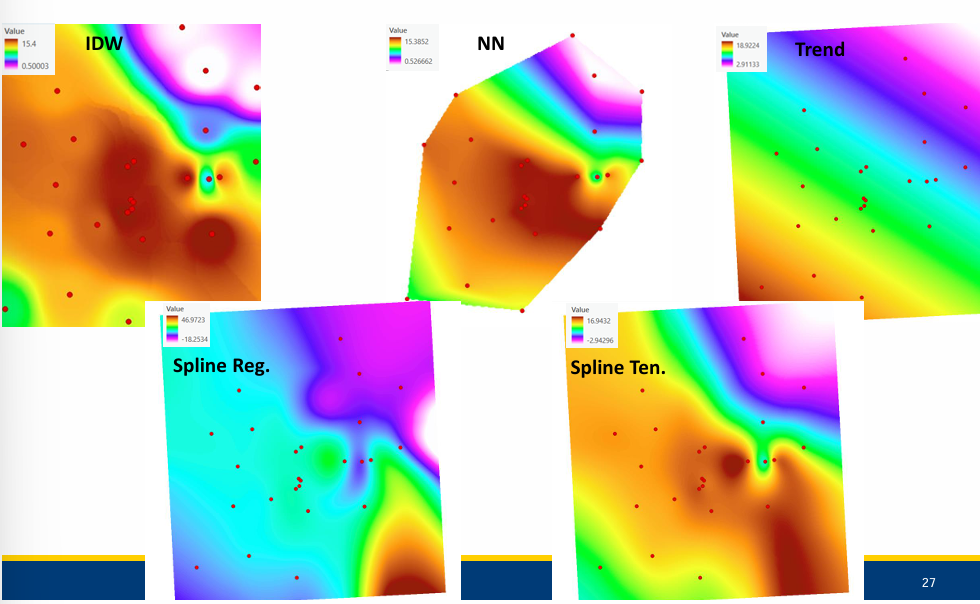 Regularized is exact, tension is approximate |
front 90 Trend is a global polynomial interpolation method used to capture coarse-scale patterns. Using first-order polynomials gives you a linear surface. How many bends will appear if you use a second-order polynomial? A Third-order polynomial? | back 90 one, two, pattern continues.... |
front 91  Which predictive surfaces do not extrapolate? | back 91 IDW and Natural neighbour |
front 92 Which predictive surfaces are approximate? | back 92 Tension spline and trend |