Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chemistry ch. 11-13 Exam Study
front 1 BEGINNING OF CH. 11 | back 1
BEGINNING OF CH. 11 (back of card)
|
front 2 Crystalline solids ________. | back 2 have ordered structures |
front 3 ________ liquid crystals are colored because the molecular layers are arranged in slightly twisted planes with respect to one another. | back 3 Cholesteric |
front 4 What are the common types of smectic liquid-crystalline phases? | back 4 A and C |
front 5 There are ________ types of smectic liquid-crystalline phases. | back 5 3 |
front 6 For a given substance that exhibits liquid-crystalline properties, the transition from solid to liquid-crystal state occurs ________. | back 6 at the melting point of the solid |
front 7 In liquids, the attractive intermolecular forces are ________. | back 7 strong enough to hold molecules relatively close together but not strong enough to keep molecules from moving past each other |
front 8 As a gaseous element condenses, the atoms become ________ and they have ________ attraction for one another. | back 8 closer together, more |
front 9 Together, liquids and solids constitute ________ phases of matter. | back 9 the condensed |
front 10 The strongest interparticle attractions exist between particles of a ________, and the weakest interparticle attractions exist between particles of a ________. | back 10 solid, gas |
front 11 ________ are particularly polarizable. | back 11 Large molecules, regardless of their polarity, |
front 12 The ease with which the charge distribution in a molecule can be distorted by an external electrical field is called the ________. | back 12 polarizability |
front 13 Elemental iodine (I2) is a solid at room temperature. What is the major attractive force that exists among different I2 molecules in the solid? | back 13 London dispersion forces |
front 14 Hydrogen bonding is a special case of ________. | back 14 dipole-dipole attractions |
front 15 ________ is the energy required to expand the surface area of a liquid by a unit amount of area. | back 15 Surface tension |
front 16 Which statements about viscosity are true? (i) Viscosity increases as temperature decreases. | back 16 All of the above. |
front 17 The shape of a liquid's meniscus is determined by ________. | back 17 the relative magnitudes of cohesive forces in the liquid and adhesive forces between the liquid and its container |
front 18 Viscosity is ________. | back 18 the resistance to flow |
front 19 The property responsible for the "beading up" of water is ________. | back 19 surface tension |
front 20 Heat of sublimation can be approximated by adding together ________ and ________. | back 20 heat of fusion, heat of vaporization |
front 21 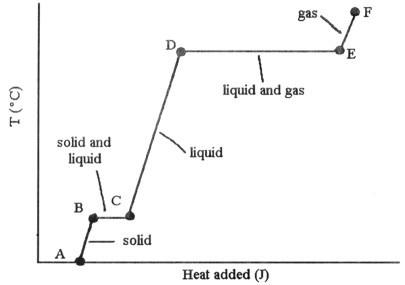 A-B solid The ________ (is)are associated with the heat energy being used up to increase distances between molecules. | back 21 phase changes B → C and D → E |
front 22 Large intermolecular forces in a substance are manifested by ________. | back 22 high heats of fusion and vaporization |
front 23 Of the following, ________ is an exothermic process. freezing | back 23 freezing |
front 24 A volatile liquid is one that ________. | back 24 readily evaporates |
front 25 In general, the vapor pressure of a substance increases as ________ increases. | back 25 temperature |
front 26 The vapor pressure of any substance at its normal boiling point is ________. | back 26 1 atm |
front 27 Volatility and vapor pressure are ________. | back 27 directly proportional to one another |
front 28 On a phase diagram, the critical pressure is ________. | back 28 the pressure required to liquefy a gas at its critical temperature |
front 29 On a phase diagram, the critical temperature is ________. | back 29 the temperature above which a gas cannot be liquefied |
front 30 On a phase diagram, the melting point is the same as ________. | back 30 the freezing point |
front 31 BEGINNING OF CH. 12 | back 31 BEGINNING OF CH. 12 (back of card) |
front 32 A solid has a very high melting point, great hardness, and poor electrical conduction. This is a(n) ________ solid. | back 32 covalent network |
front 33 Trends in melting points for metals can be explained with the ________. | back 33 electron-sea model |
front 34 The ________ for Ge shows it to be a semiconductor, because the gap between the filled lower and empty higher energy bands is relatively small. | back 34 molecular-orbital model |
front 35 All of the following are a type of solid except ________. metallic | back 35 supercritical |
front 36 Consider the following statements about crystalline solids: (i) Molecules or atoms in molecular solids are held together via
ionic bonds. Which of the statements is true? | back 36 (ii) |
front 37 The ________ of light waves upon passing through a narrow slit is called diffraction. | back 37 scattering |
front 38 What fraction of the volume of each corner atom is actually within the volume of a face-centered cubic unit cell? | back 38 1/8 |
front 39 What portion of the volume of each atom or ion on the face of a unit cell is actually within the unit cell? | back 39 1/2 |
front 40 ________ have properties that depend on the manner in which the solid is formed. | back 40 Heterogeneous alloys |
front 41 ________ are examples of homogeneous alloys. | back 41 Intermetallic compounds |
front 42 ________ generally differ from compounds in that the atomic ratios of the constituent elements in the former are ________ and may vary over a wide range. | back 42 Alloys, not fixed |
front 43 Of the following, ________ may be added to steel to modify its properties. | back 43 carbon and nickel |
front 44 How many valence electrons do inorganic compounds contain if they are considered semiconductors? | back 44 4 |
front 45 All of the following are natural polymers except ________. | back 45 nylon |
front 46 The empirical formula of an addition polymer ________. | back 46 is the same as that of the monomer from which it is formed |
front 47 What happens to a polymer as it becomes more crystalline? Its yield stress decreases. | back 47 None of the above is correct. |
front 48 Natural rubber is too soft and chemically reactive for practical applications. ________ of natural rubber entails crosslinking reactive polymer chains with sulfur atoms. | back 48 Vulcanization |
front 49 The formation of a ________ polymer generally involves the elimination of a small molecule. | back 49 condensation |
front 50 All of the following are classified as a nanomaterial except ________. buckminsterfullerene | back 50 All of the above are classified as nanomaterials. |
front 51 The properties of graphene include ________. high strength | back 51 All of the above. |
front 52 BEGINNING OF CH. 13 | back 52 BEGINNING OF CH. 13 (back of card) |
front 53 Hydration is a specific example of the phenomenon known generally as ________. | back 53 solvation |
front 54 Pressure has an appreciable effect on the solubility of ________ in liquids. | back 54 gases |
front 55 The phrase "like dissolves like" refers to the fact that ________. | back 55 polar solvents dissolve polar solutes and nonpolar solvents dissolve nonpolar solutes |
front 56 In a saturated solution of a salt in water, ________. | back 56 the rate of crystallization = the rate of dissolution |
front 57 An unsaturated solution is one that ________. | back 57 has a concentration lower than the solubility limit |
front 58 A solution with a concentration higher than the solubility allows is ________. | back 58 supersaturated |
front 59 Molality is defined as the ________. | back 59 moles solute/kg solvent |
front 60 Which one of the following concentration units varies with temperature? Molality. | back 60 Molarity. |
front 61 The magnitudes of Kf and of Kb depend on the identity of the ________. | back 61 solvent |
front 62 As the concentration of a solute in a solution increases, the freezing point of the solution ________ and the vapor pressure of the solution ________. | back 62 decreases, decreases |
front 63 The ratio of the actual value of a colligative property to the value calculated, assuming the substance to be a nonelectrolyte, is referred to as ________. | back 63 the van't Hoff factor |
front 64 Colligative properties of solutions include all of the following except ________. an increase in the osmotic pressure of a solution upon the addition of more solute the increase of reaction rates with increase in temperature elevation of the boiling point of a solution upon addition of a solute to a solvent depression of vapor pressure upon addition of a solute to a solvent depression of the freezing point of a solution upon addition of a solute to a solvent | back 64 the increase of reaction rates with increase in temperature |
front 65 The process of a substance sticking to the surface of another is called ________. | back 65 adsorption (not absorption) |
front 66 All of the following are considered to be colloids except ________. a foam | back 66 a homogeneous mixture |
front 67 Hydrophobic colloids ________. | back 67 can be stabilized by adsorption of ions |
front 68 END Good luck on the exam! | back 68 END (back of card) |