Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
A&P II Lab Practical 1 Review
front 1 What are the 6 hormones associated with the Anterior Pituitary gland? | back 1 TSH, FSH, LH, ACTH, GH, PRL |
front 2 What are the 2 hormones associated with the Posterior Pituitary gland | back 2 Oxytocin, ADH |
front 3 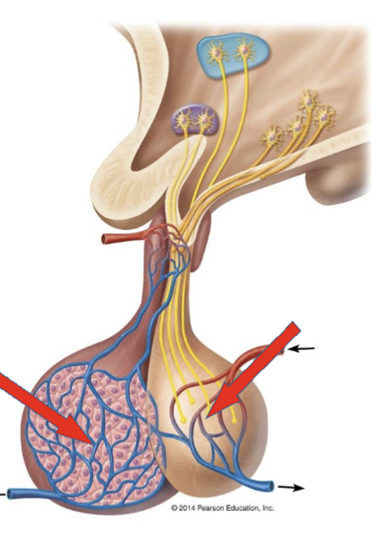 Name the 2 parts of this gland | back 3 Anterior and Posterior Pituitary gland |
front 4 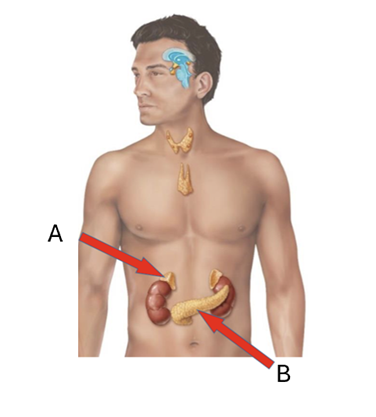 What is A? | back 4 Adrenal gland |
front 5  What hormones are secreted by A? | back 5 Mineralocorticoids, Glucocorticoids, Gonadocordicords |
front 6  What is B? | back 6 Pancreas |
front 7  List the hormones secreted by B | back 7 Insulin, Glucagon |
front 8 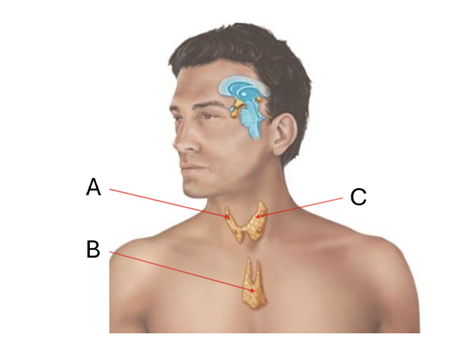 What is A? | back 8 Parathyroid gland |
front 9  What is B? | back 9 Thymus |
front 10  What is C? | back 10 Thyroid gland |
front 11  What hormones are secreted by A? | back 11 PTH |
front 12  What hormones are secreted by B? | back 12 thymulin, thymosin, thymopoietin |
front 13  What hormones are secreted by C? | back 13 TH, Calcitonin |
front 14 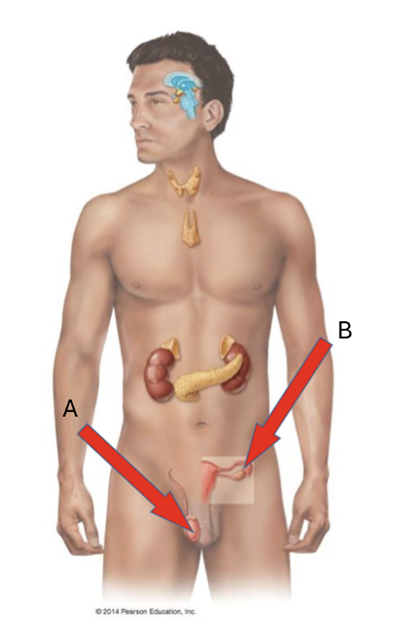 What is A? | back 14 Testis |
front 15  What is B? | back 15 Ovary |
front 16  List the hormones secreted by A | back 16 testosterone |
front 17  List the hormones secreted by B | back 17 estrogen, progesterone |
front 18 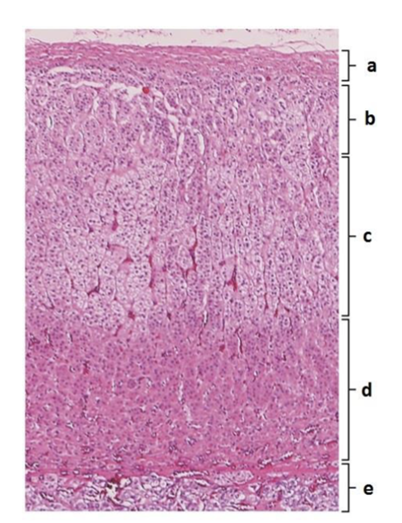 What gland is this? | back 18 Adrenal gland |
front 19  What is a? | back 19 Capsule |
front 20  What is e? | back 20 Adrenal medulla |
front 21  What hormones are secreted by e? | back 21 epinephrine, norepinephrine |
front 22  What is b? | back 22 zona glomerulosa |
front 23  What is c? | back 23 zona fasciculata |
front 24  What is d? | back 24 zona reticularis |
front 25  What hormones are released by b? | back 25 mineralocorticoids/aldosterone |
front 26  What hormones are released by c? | back 26 glucocorticoids/cortisol |
front 27  What hormones are released by d? | back 27 gonadocorticoids/estrogen/testosterone |
front 28 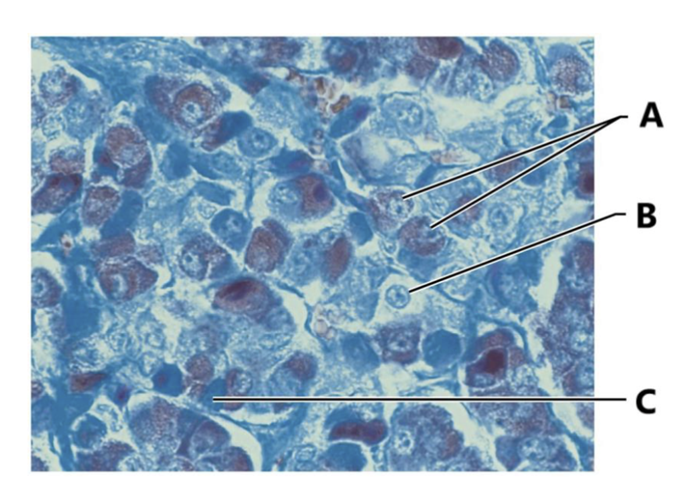 What gland is this? | back 28 Anterior pituitary gland |
front 29  What is A? | back 29 Acidophils |
front 30  What is C? | back 30 Basophil |
front 31  What hormones are made by A? | back 31 growth hormones and prolactin |
front 32  What hormones are made by B? | back 32 TSH, ACTH, FSH, LH |
front 33 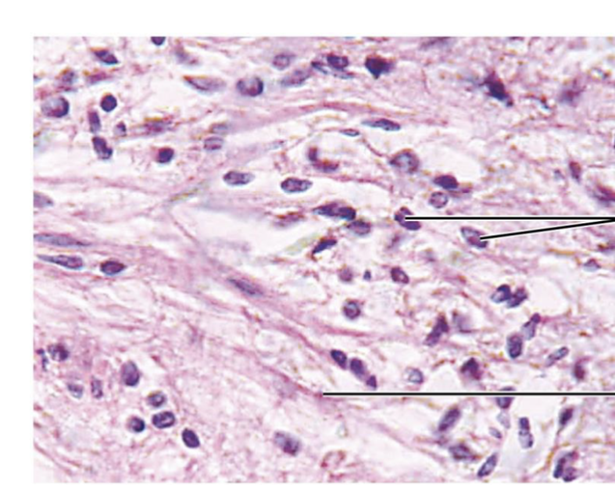 What gland is this? | back 33 Posterior pituitary gland |
front 34  What hormones are associated with this gland? | back 34 oxytocin and ADH |
front 35  What is made here? What is stored here? | back 35 Nothing is made here but oxytocin and ADH are stored here |
front 36 How is the release of ACTH stimulated? | back 36 another hormone |
front 37 How is the release of Calcitonin stimulated? | back 37 humoral factors |
front 38 How is the release of Estrogens stimulated? | back 38 another hormone |
front 39 How is the release of Insulin stimulated? | back 39 humoral factors |
front 40 How is the release of Norepinephrine stimulated? | back 40 the nervous system |
front 41 How is the release of Parathyroid hormone stimulated? | back 41 humoral factors |
front 42 How is the release of T4/T3 stimulated? | back 42 another hormone |
front 43 How is the release of Testosterone stimulated? | back 43 another hormone |
front 44 How is the release of TSH/FSH stimulated? | back 44 another hormone |
front 45 Define hormone | back 45 A chemical substance liberated into the extracellular fluid that enter blood for transport through the body |
front 46 Chemically hormones belong chiefly to two molecular groups, the ________ and the ______________ molecules | back 46 Steroids, Amino acid-based |
front 47 Define target cell | back 47 cell responding to a particular hormone in a specific way |
front 48 If hormones travel in the bloodstream, why don’t all tissues respond
to | back 48 The proper “hormone” receptors must be present on the |
front 49 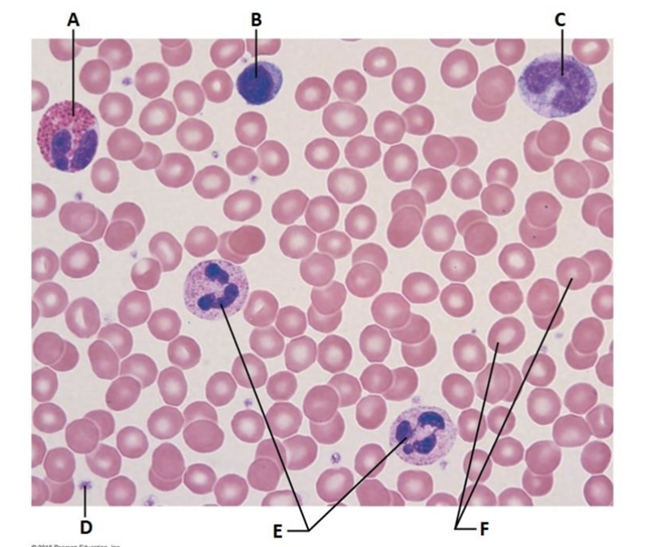 Label A, what is its main function | back 49 Eosinophil, kills parasitic worms |
front 50  Label B, what is its main function | back 50 Lymphocyte, immune response |
front 51  Label C, what is its main function | back 51 Monocyte, phagocytizes |
front 52  Label D, what is its main function | back 52 Platelet, vital to clotting |
front 53  Label E, what is its main function | back 53 Neutrophil, phagocytosis, MOST COMMON |
front 54  Label F, what is its main function | back 54 Erythrocyte, transport O2 and CO2 |
front 55 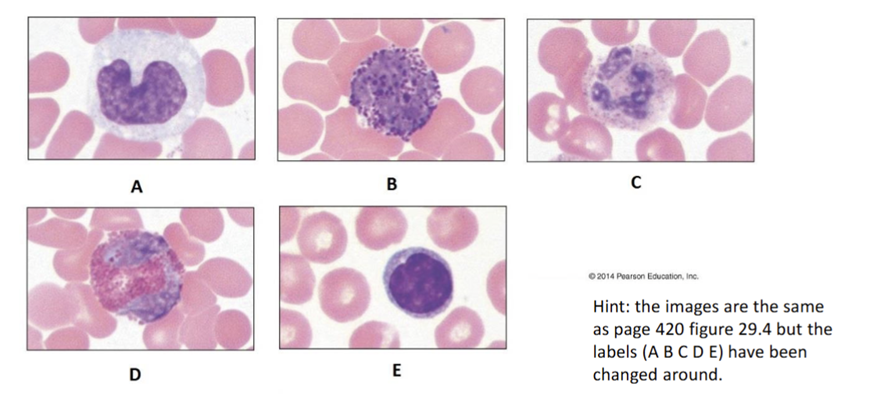 All 5 are categorized as what? | back 55 Leukocytes |
front 56  What is A? | back 56 Monocyte, Agranulocyte |
front 57  What is B? | back 57 Basophil, Granulocyte, LEAST COMMON |
front 58  What is C? | back 58 Neutrophil, Granulocyte, MOST COMMON |
front 59  What is D? | back 59 Eosinophil, Granulocyte |
front 60  What is E? | back 60 Lymphocyte, Agranulocyte |
front 61 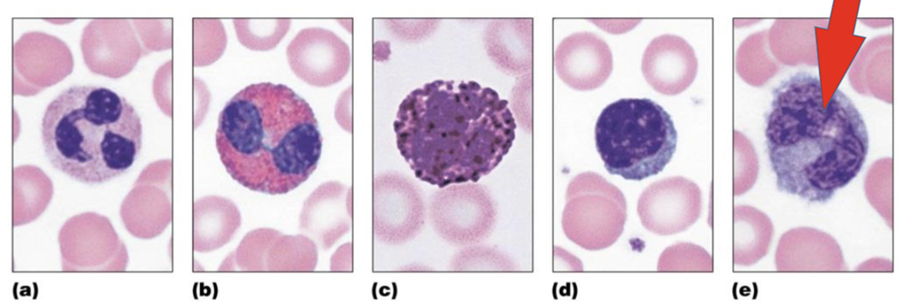 What is A? | back 61 Neutrophil, phagocytize, MOST COMMON |
front 62  What is B? | back 62 Eosinophil, kill parasitic worms |
front 63  What is C? | back 63 Basophil, release mediators of inflammation, LEAST COMMON |
front 64  What is D? | back 64 Lymphocyte, immune response |
front 65  What is E? | back 65 Monocyte, phagocytize |
front 66 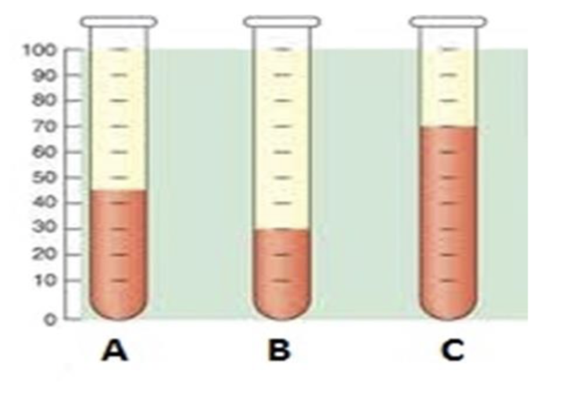 Which is a normal hematocrit level? | back 66 A. |
front 67  What is condition associated with sample B? | back 67 Anemia |
front 68  What is condition associated with sample C? | back 68 Polycythemia |
front 69 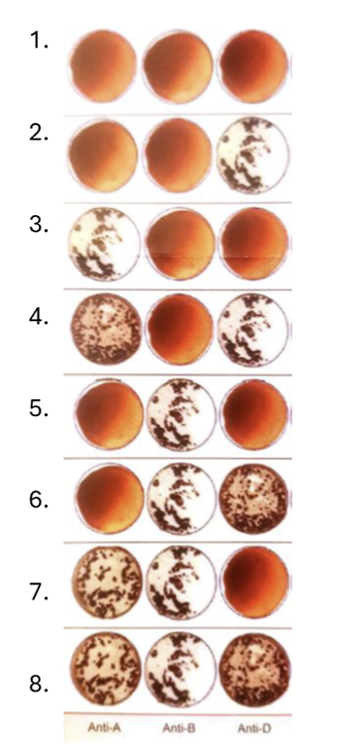 What blood type is sample 1? | back 69 O -, UNIVERSAL DONATER |
front 70  What blood type is sample 2? | back 70 O + |
front 71  What blood type is sample 3? | back 71 A - |
front 72  What blood type is sample 4? | back 72 A + |
front 73  What blood type is sample 5? | back 73 B - |
front 74  What blood type is sample 6? | back 74 B + |
front 75  What blood type is sample 7? | back 75 AB - |
front 76  What blood type is sample 8? | back 76 AB +, UNIVERSAL ACCEPTER |
front 77 Most numerous leukocyte | back 77 Neutrophil |
front 78 Precursor cell of platelets | back 78 megakaryocyte |
front 79 Destroys parasitic worms | back 79 Eosinophil |
front 80 Transports oxygen | back 80 Erythrocytes |
front 81 Exits a blood vessel to develop into a macrophage | back 81 Monocyte |
front 82 Produces antibodies | back 82 Lymphocytes |
front 83 What hormone acts as a stimulus for this process of RBC production? | back 83 erythropoietin (EPO) |
front 84 What name is given to the process of RBC production? | back 84 erythropoiesis |
front 85 What name is given to the production of blood cells in general? | back 85 hematopoiesis |
front 86 What is the average lifespan of a RBC? | back 86 120 days |
front 87 Why is a differential WBC count more informative than a total WBC count? | back 87 It helps in diagnosing illnesses, since any abnormality in percentages of WBC types may indicate a problem and the source of pathology |
front 88 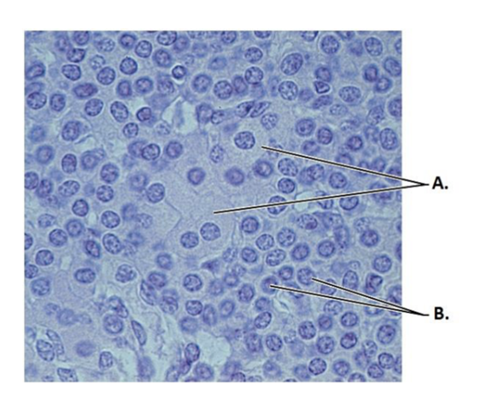 What gland is this? | back 88 Parathyroid gland |
front 89  What is A? | back 89 Oxyphil cells |
front 90  What is B? | back 90 Parathyroid cells |
front 91  What hormone is made by B? | back 91 PTH |
front 92 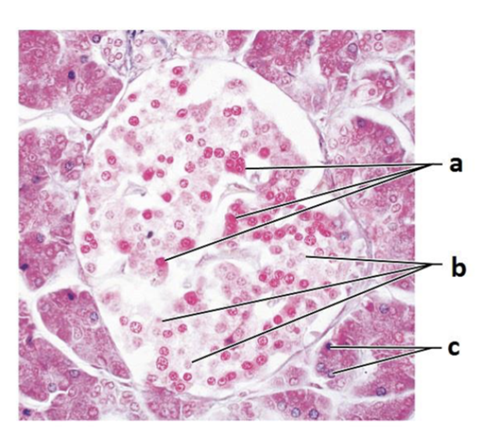 What gland is this from? | back 92 Pancreases |
front 93  What is the specific names are given to this "little island" within the organ? | back 93 Pancreatic islet |
front 94  Label A | back 94 alpha cells |
front 95  Label B | back 95 beta cells |
front 96  Label C | back 96 Pancreatic acinar cells |
front 97  What hormones are made by a? | back 97 glucagon |
front 98  What hormones are made by b? | back 98 insulin |
front 99  What is made by c? | back 99 produce exocrine secretion of digestive enzymes |
front 100  Is a, b, or c the exocrine cell? | back 100 c, the pancreatic acinar cells |
front 101 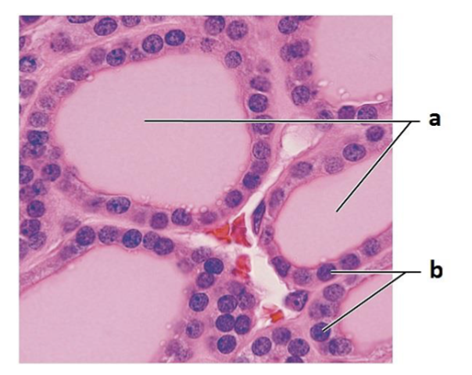 What gland is this? | back 101 Thyroid gland |
front 102  What is a? | back 102 Colloid-filled follicles |
front 103  What is b? | back 103 Follicular cells |
front 104  What is made by b? | back 104 T4, T3 |
front 105  what is made by a? | back 105 thyroglobulin |
front 106 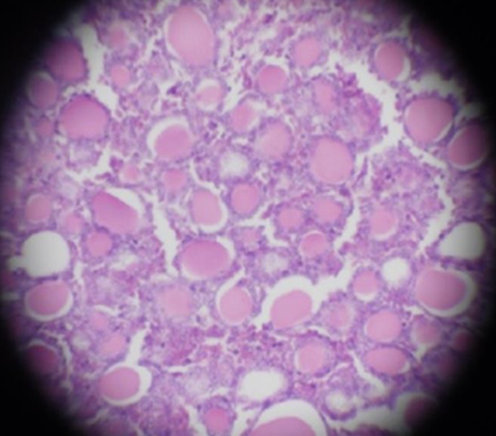 What gland is this? | back 106 Thyroid gland |
front 107  What hormones are produced in this gland? | back 107 T3, T4, Calcitonin |
front 108  What hormone stimulates this gland? | back 108 TSH |
front 109  What other gland releases a hormone that stimulates this gland? | back 109 Anterior Pituitary gland |
front 110 TSH | back 110 thyroid hormone, stimulates the thyroid gland |
front 111 LH | back 111 ovulation, estrogen/progesterone/testosterone |
front 112 ACTH | back 112 glucocorticoids, androgens release |
front 113 PRL | back 113 Milk production |
front 114 FSH | back 114 follicle maturation and estrogen/sperm production |
front 115 GH | back 115 stimulates body growth and protein synthesis |
front 116 Oxytocin | back 116 uterine contraction, milk ejection |
front 117 ADH | back 117 stimulates kidneys to reabsorb water |