Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
MSE 280 Exam 2
front 1 True or false. A flaw in the materials lowers the fatigue life. | back 1 True |
front 2 True or false. Failure by fatigue requires an applied stress greater than the yield stress/ | back 2 False |
front 3 True or false. Fatigue failure occurs earlier with a higher positive (tensile) mean stress. | back 3 True |
front 4 True or false. The stress concentration is lower around a crack than around a hole. | back 4 False |
front 5 True or false. The stress concentration is higher around a large hole than a small hole. | back 5 True |
front 6 True or false. The stress concentrated more near an internal flaw than with near a surface flaw. | back 6 False |
front 7 What polymer/condition would have the highest ductility? | back 7 Thermoplastic at T>Tg |
front 8 What polymer/condition that would have the highest ductility? | back 8 Thermoplastic slowly loaded |
front 9 True or false. The strength of a metal increases with increased temperature | back 9 False |
front 10 True or false. A Rockwell hardness of 100 is the same as a Brinell hardness of 100 | back 10 False |
front 11 What is the metal with the highest stiffness? | back 11 Steel |
front 12 What is the metal with the highest melting point? | back 12 Steel |
front 13 What is the metal witht he highest yield strength? | back 13 Steel |
front 14 What is the metal with highest ultimate tensile strength? | back 14 Steel |
front 15 What is the metal with the highest ductility? | back 15 Aluminum |
front 16 What happens to the creep rate at increased temperatures? | back 16 It increases exponetially |
front 17 What happens to the creep rate at increased loads? | back 17 It increases |
front 18 Typically as the strength of a metal increases what happens to the ductility? | back 18 Decreases |
front 19 An 650 lb tensile force is applied to an 0.12 inch diameter nickel wire having a yield strength of 45,000 psi and a tensile strength of 55,000 psi. Will the wire plastically deform? | back 19 Yes |
front 20 An 750 lb tensile force is applied to an 0.14 inch diameter nickel wire having a yield strength of 45,000 psi and a tensile strength of 50,000 psi. Will the wire experience necking? | back 20 No |
front 21 Possible mechanical properties obtained from a bend test include (more than one answer is possible) | back 21 The modulus of rupture and the modulus of elasticity in bending (flexural modulus) |
front 22 At room temperature, if you want to increase the strain in a steel, what has to happen to the applied stress? | back 22 it mus be increased |
front 23 The following graph shows tensile test results for three metal alloys. The metal with the highest yield strength is | back 23 steel |
front 24 Will a thermoplastic polymer be more brittle or more ductile above the glass transition temperature (versus below the glass transition temperature)? | back 24 it will be more ductile |
front 25 The metallic crystal structure with a ductile to brittle transition temperature is | back 25 BCC |
front 26 true or false. In most materials when strength is increased, ductility also increases. | back 26 false |
front 27 Which material has the higher ductility | back 27 metal |
front 28 The two most common impact test types are | back 28 charpy and izod |
front 29 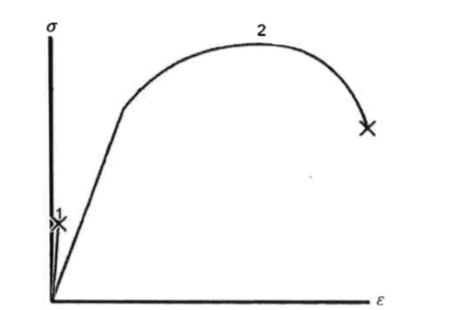 Which of the following curves is a typical tension test result for a ceramic? | back 29 curve 1 |
front 30 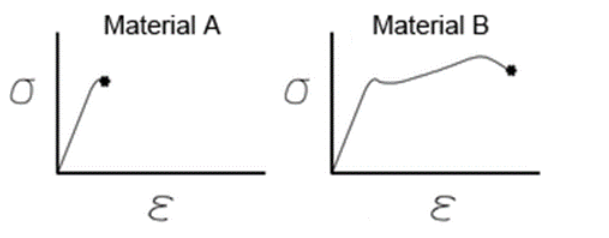 The tensile curve from the material with the lowest ductility is | back 30 curve A |
front 31 What happens to the strengths of a metal when the temperature increases significantly? | back 31 decreases |
front 32 How does the strain change with time for a viscoelastic material that is held at a constant applied stress? | back 32 increases |
front 33 true or false. There is a distinct change in density when a liquid transforms to an amorphous solid. | back 33 false |
front 34 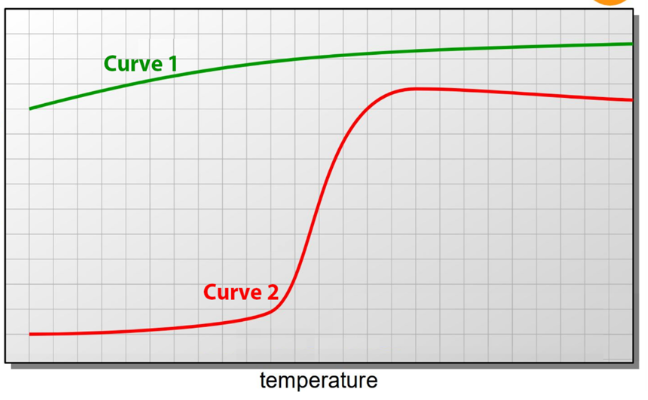 Match the curve in the following graph to the metal crystal structure. | back 34 1- FCC 2- BCC |
front 35 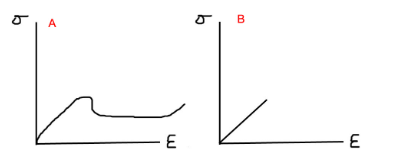 The tensile test for a slowly loaded thermoplastic and a rapidly loaded thermoplastic are shown below. Match the curve with the load rate. | back 35 A- slowly loaded B- rapidly loaded |
front 36  The tensile curves for a slowly loaded thermoplastic above the glass transition temperature and a slowly loaded thermoplastic below the glass transition temperature are shown below. Match the curve with the temperature of testing | back 36 A- above the glass B- below the glass |
front 37 Match the following hardness tests with their load range. 1. Brinell 2. Rockwell 3. microhardness | back 37 1. highest 2. medium 3. smallest |
front 38 Elastic deformation is permanent deformation. | back 38 false |
front 39 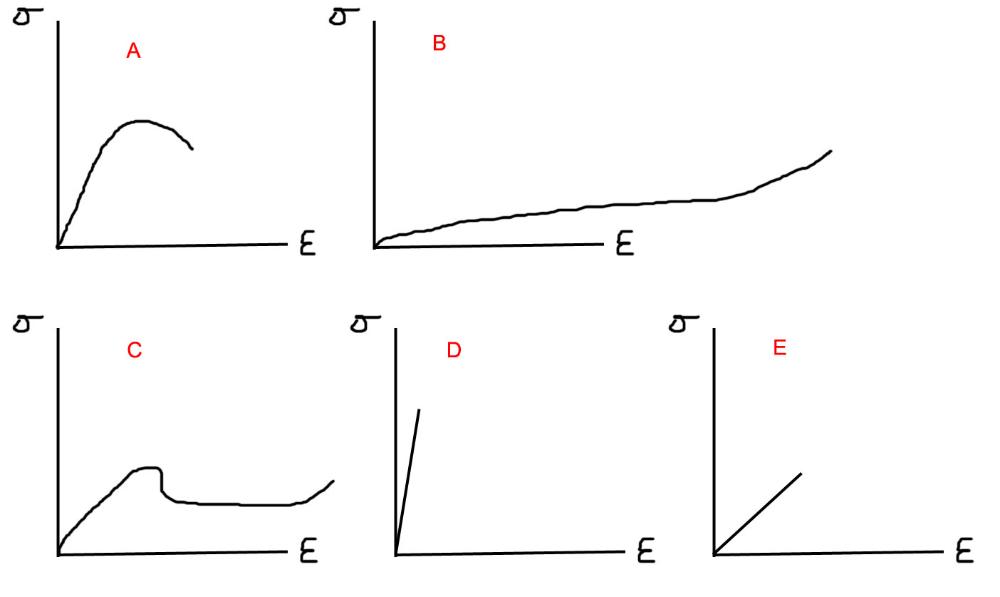 Match the curves | back 39 no data |
front 40 A Rockwell C hardness of 50 is the same as a Brinell hardness of 50. | back 40 false |
front 41 A brinell hardness value of 100 BHN is the same as a Rockwell hardness value of 100 RB. | back 41 false |
front 42 The boundary between plastic and elastic deformation on a tensile test is called | back 42 yield strength |
front 43 Does a more ductile or a more brittle steel have a higher ductile to brittle transition temperature? | back 43 more brittle |
front 44 Which material has a highest modulus? | back 44 cermaic |
front 45 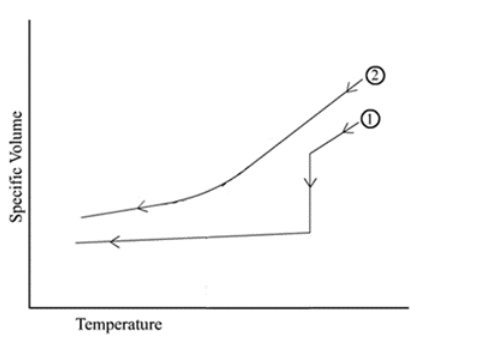 Which of the following curves represents the change in specific volume (1/density) of an amorphous material with temperature? | back 45 curve 2 |
front 46 A steel is to be used in Alaska where the temperature in winter can become extremely cold. The material will experience some impact loading. Would an fcc steel or a bcc steel be preferable? Why? | back 46 FCC |
front 47 Which material has the higher ductility and yield point? | back 47 metal |
front 48 The following shows two part, that are the same except for the size of the crack in the part. Which part would you expect would fail at a lower stress? | back 48 the one with the larger crack |
front 49 What is "fracture toughness" a measure of? | back 49 The resistance to fracture with a pre-existing flaw |
front 50 The following shows two parts that are the same except for the shape of the flaw in the part. The flaw is the same length in the two parts. Which part would you expect would fail at a lower stress? | back 50 The part with the sharper crack |
front 51 The critical surface crack length for a magnesium part is 0.2 inches. The nondestructive evaluation (NDE) technique used to evaluate the part has a resolution of 0.1 inches. The technique will resolve the critical flaws for this application. | back 51 true |
front 52 Would you expect a part that has been carefully machined to a smooth finish to fail before or after a similar part with a rough machined surface? | back 52 after |
front 53 Circle all of the following that will give failure at a lower applied stress. | back 53 a bigger flaw vs a smaller flaw |
front 54 The most common cause of failure is | back 54 fatigue |
front 55 The following shows two possible options for a highly stressed corner in a part you are designing. Which would you expect to last longer? | back 55 The design with the rounded corner |
front 56 Which would you expect to be more sensitive to a flaw on it's surface | back 56 cermaic |
front 57 Which of the following WOULD NOT have a longer fatigue life? | back 57 An aircraft with windows with square corners |
front 58 The following shows two parts that are the same except for the location of the crack in the part. The crack is the same size in the two parts. Which part would you expect would fail at a lower stress? | back 58 The part with the crack on the surface |
front 59 Which of the following can cause failure at applied stresses below the yield stress? | back 59 Stress corrosion cracking, a defect in a part, creep, and fatigue |
front 60 Which of the following is NOT a good description of a ductile failure. | back 60 it requires little energy |
front 61 At room temperature, if stress applied to a steel is constant, will the strain change over time? | back 61 no |
front 62 Which of the following is true for stress corrosion cracking. | back 62 Associated with a corrosive environment. |