Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Molecular Evolution- Final
front 1 Which of the following is the least correct statement regarding the DNA molecule? | back 1 The deoxyribose portion of the molecule encodes the genetic variation we see between different species. |
front 2 How many possible reading frames do we need to evaluate when looking for genes in a DNA molecule? | back 2 6 |
front 3 Which of the following mutations is most likely to have the biggest phenotypic impact on an organism? | back 3 A in/del point mutation in a protein coding region. |
front 4 Which of the following would be considered part of a gene? | back 4 - Introns - Exons - Start codon |
front 5 What is the best estimate for the genetic distance between two sequences of DNA that have been allowed to mutate in an unrestrained manner while they have reached saturation? | back 5 0.75 |
front 6 Homologous sequences from two different species that fit the description in the question above would be a good source of data for phylogenetic analysis. | back 6 False |
front 7 The simplest model of evolution we reviewed was the Jukes and Cantor (JC). Select the statement below that is false when considering this model of evolution. | back 7 This model should be used for all nuclear DNA data sets, while more complex models should be used for mitochondrial data sets. |
front 8 What happens when a mutation results in a single amino acid substitution? | back 8 It can vary from a large impact (either good or bad) to no impact at all. |
front 9 Protein domains ___. | back 9 often correspond to specific functional parts of the protein, like a transmembrane domain. |
front 10 ___ is the most common mechanism for the origin of new genes. | back 10 Gene duplication |
front 11 Why was the original classification for Reptilia paraphyletic? | back 11 - Birds evolved a lot and now look very different from the ancestor of all reptiles (Sauria). - Many of the lineages most closely related to the birds are now extinct. |
front 12 Which of the following types of phylogenies shows both relationships among organisms and estimates rates of evolution along the branches? | back 12 Phylogram |
front 13 Neighbor-joining is a method of phylogenetic inference that uses ___ data and ___. | back 13 Distance, clustering algorithm |
front 14 Xenology is most common among ___. | back 14 Prokaryotes |
front 15 Using the genetic matrix below and the principle of parsimony, which of the trees is the best hypothesis for relationships among the species? | back 15 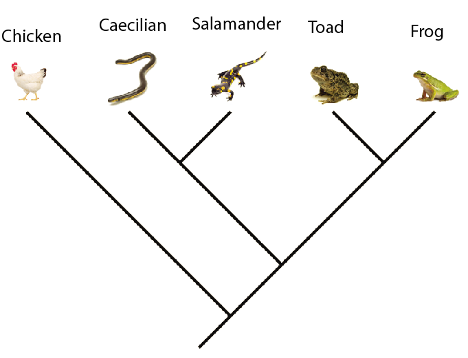 |
front 16 On the best phylogeny above, what is the closest relative of the Caecilian? | back 16 Salamander |
front 17 Which of the characters above provides no evidence for relationships among the various species? | back 17 Character 8 |
front 18 Classifying the caecilian, toad, frog, and salamander together would be a valid group based on the best phylogeny above. | back 18 True |
front 19 Are the lysozymes that aid in cellulose digestion in the cow and the langur monkey homologous? | back 19 Yes, as are the corresponding lysozymes in humans, however we know based on relationships of these organisms that the ability to digest cellulose was gained independently in these organisms. |
front 20 What information about protein coding genes might help when we try to align them? | back 20 Due to the degeneracy of the genetic code they are more conserved at the amino acid level. |
front 21 Parsimony | back 21 This method treats all mutations equally and uses an optimality criterion of the phylogeny that minimizes the number of overall mutations. |
front 22 Maximum likelihood | back 22 A method that used discrete data, an optimality criterion, and models of evoluation. |
front 23 Minimum evolution | back 23 A distance method that has an optimization criterion but is not frequently used anymore. |
front 24 Which of the following is an advantage of maximum likelihood over parsimony? | back 24 It allows you to perform statistical test to see if one phylogeny is significantly better than another. |
front 25 Optimality methods of phylogenetic inference are NP-Complete, this means ___. | back 25 there is no algorithm to find the optimal solution for relatively small data sets (50 species) and we can't evaluate every possible solution. |
front 26 What is a gene? | back 26 A section of DNA that is transcribed into RNA and has a phenotypic impact. |
front 27 What is the difference between a purine and a pyrimidine? | back 27 Purines (adenine and guanine) have two carbon rings, pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine) have one. |
front 28 What is the disadvantage of choosing more complex model of evolution? | back 28 More complexity means a loss of precision due to the estimation of many different parameters. |
front 29 Why does denaturation have such a profound effect on protein function? | back 29 A denatured protein has lost its 3D shape, since shape is critical for function this means denatured proteins cannot perform their function. |
front 30 The diagram below is a data set similar to the one you worked on for project 1. What does a row and a column in this data set represent? | back 30 - Row: DNA sequence from a representative species - Column: homology statement (aligned so each position in all genes match up) |
front 31 What are the two things that can be represented by a polytomy? | back 31 1. Uncertainty about relationships. 2. Simultaneous divergence of three or more descendant lineages. |
front 32 What is the best way to determine of two similar characteristics in different species are homologous? | back 32 Map the origin of that trait onto a phylogeny. |
front 33 What are two sources of homoplasy in a phylogenetic analysis? | back 33 1. Convergence 2. Symplesiomorphy |
front 34 List the main advantage and one disadvantage of neighbor joining. | back 34 - They are very efficient (fast, little computational time). - Disadvantage: distance data instead of discrete, no optimization criterion, often not as accurate as more inefficient methods. |
front 35 What does it mean when we say Maximum Likelihood analyses are circular? | back 35 They require a model of evolution but to pick the model and to estimate the parameters for this model we need a phylogeny. |
front 36 Define paralogy and describe a specific example. | back 36 Paralogy is when two homologous genes can trace their ancestral gene to a gene duplication event. Any two members of a gene family could serve as a specific example, like the hoatzin and mammal lysozymes we talked about in class, alpha and beta hemoglobin proteins, and many others. |
front 37 We can never be 100% certain that we've found the true phylogeny for a group of organisms, but what are two approaches that might give us confidence that our methods finding the best phylogenies are actually valid? | back 37 1. Testing our method on known phylogenies or simulated data sets for which we know the relationships. 2. Congruence of methods: if more than one methodology yields identical (or very similar) phylogenies we have more confidence that our phylogenies represent the actual species history. |
front 38 I complete a phylogeny of reptiles and want to be 100% sure it's completely accurate. Which of the following statements is most correct about my process of ensuring 100% accuracy? | back 38 Although congruence among methods might increase by confidence that mu results are accurate, because I am trying to reconstruct historical relationships, I can never know with 100% certainty that my results are accurate. |
front 39 If I accurately reconstruct the history of genes, I will always also reconstruct the history of the species to which those genes belong. | back 39 False |
front 40 What do the numbers above nodes represent in Bayesian analysis? | back 40 These are posterior probability scores estimated via a majority rule consensus tree of all phylogenies generated after the "burn-in" period. |
front 41 The Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) method allows for a rapid search of nearby phylogenetic tree space during a Bayesian analysis allowing for eventual optimization of a model of evolution and its parameters. | back 41 True |
front 42 What is meany by the term "congruence" when referring to phylogenetic trees? | back 42 That the patterns of relationships in the final phylogenies are completely or largely the same. |
front 43 Bootstrap support | back 43 Requires the creation of new data sets by sampling the original data matrix with character replacement. |
front 44 Jackknife support | back 44 Helps to determine how sensitive a data set is to taxon sampling. |
front 45 Posterior probability | back 45 Is created by making a consensus tree from all the phylogenies stored during the post "burn-in" phase of a Bayesian analysis. |
front 46 Although bootstrap support values are widely used there is good evidence that they tend to overestimate levels of confidence in relationships. | back 46 True |
front 47 Which of the following is not a valid criticism of supertree methods? | back 47 Models of evolution cannot be incorporated in any of the components of a supertree analysis. |
front 48 Which of the following best describes why researchers first began to use a supertree approach? | back 48 They were originally created as a way to combine results from separate analyses where the underlying data was not congruent enough to assemble into a single data set. |
front 49 Which of the following supertree methods is the most efficient? | back 49 Informal |
front 50 Both symplesiomorphy and convergence represent a type of homoplasy and therefore represent a less parsimonious pattern of evolution than synapomorphies. | back 50 True |
front 51 This supertree method uses an initial phylogeny (ex: a phylogeny generated via neighbor-joining) and then defines several parts of the overall tree with shared taxa between parts. Data sets for each of these parts are then generated and individual analyses of the parts are combined using an optimization method. | back 51 Disk covering method |
front 52 Select all of the answers below that accurately describes a pattern of characters mapped onto the phylogeny below. | back 52 - Character Z is a symplesiomorphy for the group consisting of species D, E, F, and G - Character Y provides no evidence for relationships between these species - Character X is best categorized as convergence |
front 53 When two distantly related lineages gain a similar feature it is called ___. | back 53 convergence |
front 54 Fitch optimization is a method that allows for a most parsimonious mapping of complex character patterns onto any given phylogeny. | back 54 True |
front 55 Which of the following is not a method that would be useful in testing alternative phylogenetic hypotheses? | back 55 Posterior branch support |
front 56 Which of the following is the most accurate statement regarding the mapping of characters onto a phylogeny? | back 56 It allows for the estimation of ancient ancestral character states, even if we have no fossil evidence for that ancestor. |
front 57 Which of the following best describes the mapping of character states on to ancestral nodes in a maximum likelihood analysis? | back 57 Character states are represented by probabilities at each node, these probabilities are calculated using the model of evolution and the relative branch lengths. |
front 58 The likelihood ratio test (LRT) is a very flexible statistical test and can be used to determine if there is a significant difference between many different types of molecular analyses. Which of the following is not an application of the LRT? | back 58 Test the difference between different competing equally parsimonious fitch optimization character mappings. |
front 59 Anagenesis corresponds with which of the following? | back 59 Length of internal branches |
front 60 Cladogenesis corresponds with which of the following? | back 60 Speciation events |
front 61 If I was doing a phylogeny of species using genes that were all part of a large gene family which of the following would give me the best chance of accurately reconstructing the species history? | back 61 Identify orthologous gene copies and represent each orthologous set of genes as a separate component of the overall matrix. |
front 62 Which of the following is the most widely used species concept? | back 62 Morphological |
front 63 What does it mean when we say a phylogenetic hypothesis is precise? | back 63 How many other answers are just as good, or similar enough so that they are not statistically different than the best answer. |
front 64 How is a Bremer support value calculated? | back 64 The difference between the score of most parsimonious tree and the score of the best tree that doesn’t contain a particular node. |
front 65 What is the effect of poor taxon sampling on a phylogeny? | back 65 This creates large gaps (longer branch lengths) and can compromise the accuracy of results. |
front 66 What is an informal supertree? | back 66 A tree made from the result of other analyses using a “copy and paste” method with no formal analysis. |
front 67 What is the biological process that creates xenology? | back 67 Horizontal gene transfer |
front 68 What is Dollo parsimony and what type of characters is it best applied to? | back 68 A form of weighted parsimony, a trait may be lost multiple times, but never re-evolves. This applies best to complex morphological characters. |
front 69 How does one select the best model of evolution to use for a Maximum Likelihood analysis? | back 69 A likelihood score can be generated for each model and then the best fit model can be determined using the Likelihood Ratio Test. |
front 70 What is a majority rule consensus tree? | back 70 A tree that summarizes relationships of two or more phylogenies, numbers above nodes represent the frequency of those nodes in the constituent trees. |
front 71 What is different about reconstructing the phylogenetic history of bacteria compared to eukaryotic species? | back 71 Because of horizontal gene transfer relationships among bacteria are more like a network than a tree. |
front 72 Why is there no single definition for a species? | back 72 Because speciation is a process and different factors can influence both how and how fast a species breaks into descendant lineages. |
front 73 What was the main impetus for the development of Bayesian approaches to phylogenetics and how is it different than Maximum Likelihood approaches? | back 73 Researchers wanted to be able to use models of evolution and statistical approaches to estimate phylogenetic relations, but Maximum Likelihood methods were very slow. Bayesian estimations calculate the likelihood score differently and generate support values (posterior probabilities) as a part of the initial analysis. |
front 74 Define lineage sorting and list two evolutionary factors that make it more likely. | back 74 When allelic diversity is maintained for long periods of time and subsequent fixation of alleles in descendant lineages creates a gene history that doesn’t match the species history. Rapid speciation events and long coalescent times increase its likelihood. |
front 75 Which of the following would be the best approach to estimate the Heterozygosity of a population? | back 75 Genotype a randomly selected sample of the population for a number of different loci. |
front 76 Why does a small population size create a population that is not at HW equilibrium? | back 76
|
front 77 You survey a population of wild cheetahs and find the following distribution of genotypes: AA: 360 Aa: 480 aa: 160 What are the allele frequencies for this population and are there evolutionary forces acting on this gene? | back 77 p = 0.6 q = 0.4, no sign of evolutionary forces |
front 78 You sample a gene in a chimpanzee population with the following results: AA: 300 Aa: 600 aa: 100 Which of the following statements about this gene is the most accurate? | back 78 There is an evolutionary force acting on this gene, if it is natural selection it is most likely overdominance |
front 79 Ka/Ks > 1 | back 79 A venom gene that has evolved to specifically target different prey items of the different sampled species |
front 80 Ka/Ks < 1 | back 80 NADH2 a gene critical for metabolism with identical function in all sampled species |
front 81 Ka/Ks = 1 | back 81 A pigmentation gene that is expressed in the dermis, but has no impact at all on the fitness of any of the sampled species |
front 82 Much of the diversity present within a population arose due to mutations that change only one base pair. What is this type of diversity called? | back 82 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) |
front 83 One of the fastest evolving types of genetic makers are made up of tandem repeat of DNA that mutate to have different numbers of repeats. What is this type of diversity called? | back 83 Microsatellite |
front 84 Most genes in wild populations | back 84 are polymorphic |
front 85 Which of the following genes in humans is least likely to be subject to recombination? | back 85 NADH2, found on the mitochondrion |
front 86 What two values would I need to estimate theta (Q)? | back 86 - Population size - Mutation rate |
front 87 The vast majority of genetic diversity in the human population shows no correlation with geography. | back 87 True |
front 88 Fst is a measure of genetic structure within a population. Which of the following describes how this value is determined? | back 88 It is estimated by looking for differences in heterozygosity in subpopulations when compared to the total population. |
front 89 When formulating his theory of natural selection Darwin was evaluating ________, however the majority of genetic diversity _________. | back 89 diversity that changed phenotype, is neutral |
front 90 If natural selection works to remove deleterious mutations, why do we still see them in populations? | back 90 A number of factors including genetics, environmental instability and varying strengths of selection means that the removal of some deleterious mutations is very slow. |
front 91 What accounts for the majority of the C-value paradox? | back 91 The differing amounts of non-coding DNA in eukaryotic genomes |
front 92 Which of the following is the best way to calibrate the molecular clock? | back 92 Use fossil data (when available) to get an independent estimate of coalescent times. |
front 93 What is the primary reason to perform a relative rate test? | back 93 To determine whether a molecular clock can be assumed for the data set being analyzed. |
front 94 These proteins can all be classified as part of a single protein family. | back 94 Opsins |
front 95 Co-option of a suitable subset of genes that perform a useful physiological function is the major force explaining their diversity. | back 95 Venom |
front 96 These proteins are found primarily on the mitochondrial genome. | back 96 None of the above |
front 97 Which of the following is the most accurate statement regarding genomes and transcriptomes. | back 97 Mapping a complete transcriptome onto a genome is the best way of determining the loci of all genes in the genome. |
front 98 Which of the main types of RNA are we targeting when doing transcriptome sequencing? | back 98 mRNA |
front 99 “Microevolution” and “macroevolution” are caused by different evolutionary forces. | back 99 False |
front 100 What is effective population size (Ne)? How is this different than census population size (N)? | back 100 Census population is an estimate of all individuals in a population, however effective population size is an estimate of the number of individuals that will contribute to the next generation. |
front 101 List two things that distinguish the mitochondrial genome from the nuclear genome. | back 101
|
front 102 What is the relative rate test? | back 102 An estimate of the genetic distance between two separate pairs of species that all share the same common ancestor. This can help us to know if the data can be used to estimate divergence time for these species. |
front 103 What effect does natural selection have on neutral mutations? | back 103 By definition, natural selection has no effect on neutral mutations (only beneficial and detrimental mutations). |
front 104 What happens to brand new mutations that are beneficial? List two factors that might influence this. | back 104 These mutations will spread through the population generation after generation. The rate of this spread can be influenced by genetics, strength of the benefit of the new mutation, stability of the environment that determines its advantage and the life stage at which the mutation provides a benefit. |
front 105 Why are dN/dS (Ka/Ks) values often elevated after a recent zoonotic transmission event? | back 105 This reflects the selective pressure on populations due to the changed environment of the new host/parasite interaction. |
front 106 What are GC content bias patterns like in prokaryotes? | back 106 They can vary widely between species ( ~25% - ~85%) but tend to be much across the genome of a single species. |
front 107 What three metazoan groups have evolved complex eyes and vision? | back 107 1. Arthropods 2. Vertebrates 3. Mollusks |
front 108 What is pleiotropy and how does this relate to proteins that act as venoms? | back 108 Pleiotropy is when one gene has more than one phenotypic impact. After recruitment many proteins used as venoms maintain their original function, this means there’s a higher amount of evolutionary constraint due to the two separate jobs for this protein. |
front 109 What is the G-value paradox and what are the three explanations for this paradox? | back 109
|
front 110 List four reasons why most mutations can be considered as neutral. | back 110
|
front 111 Outline how a Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL analysis) is performed. | back 111 An analysis is performed to look for linkage disequilibrium for any genetic condition and one or more of the tens of thousands of genetic markers in the human population. High levels of linkage disequilbrium in different parts of the genome don’t indicate a specific cause for the condition, but indicate that there is something in that area of the genome that contributes to the condition. |