Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Biochemistry
front 1 monomers of nucleic acids | back 1 nucleotides |
front 2 elements found in carbohydrates | back 2 carbon, hydrogen , oxygen 1:2:1 ratio |
front 3 elements found in nucleic acids | back 3 carbon, hydrogen, oxygen , nitrogen and phosphorus |
front 4 elements found in proteins | back 4 carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, |
front 5 6 most common elements in living things | back 5 carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur |
front 6 elements found in lipids | back 6 carbon, hydrogen , oxygen |
front 7 lipids | back 7 made up of fatty acids store energy insulation form cell membrane (phospholipids) |
front 8 monomer | back 8 1 unit the building block of larger molecules (like a brick in a brick wall) |
front 9 carbohydrates | back 9 macromolecule made up of monosaccharides includes sugars and starches used for energy |
front 10 proteins | back 10 macromolecule made up of amino acids acts as enzymes, form hair, nails, skin, helps in movement of muscles (communication, identification, structure) |
front 11 nucleic acids | back 11 macromolecule made up of nucleotides carries genetic information DNA and RNS |
front 12 monomer of lipids | back 12 fatty acids |
front 13 monomer of carbohydrates | back 13 monosaccharides |
front 14 monomer of proteins | back 14 amino acids |
front 15 polymer | back 15 large molecule made up of many units brick wall would be the large molecule made up of smaller units of bricks |
front 16 enzyme | back 16 proteins that speed up chemical reactions in living orgranisms names end in -ase |
front 17 activation energy | back 17 the amount of energy needed to get a reaction started |
front 18 active site | back 18 the spot on an enzyme that binds the substrate |
front 19 substrate | back 19 the molecule an enzyme acts upon |
front 20 primary protein structure | back 20 the sequence of amino acids (chain) |
front 21 secondary structure of proteins | back 21 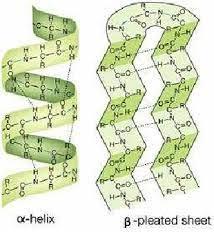 the bending or helical shape of protein strand |
front 22 tertiary structure of protein | back 22 the unique 3-D shape of a protein When it become functional Structure determines function |
front 23 quaternary structure of proteins | back 23 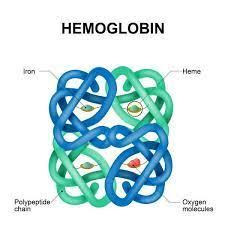 two or more polypeptide chains working together as a functional protein example: hemoglobin |
front 24 disaccharide | back 24 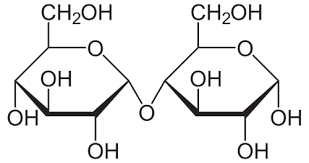 composed of two sugars (sucrose) |
front 25 polysaccharide | back 25 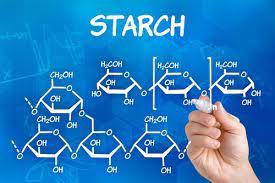 carbohydrate composed of many sugars starch and cellulose |
front 26 factors that affect enzymes | back 26 pH temperature co-enzymes inhibitors |