Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 11: The Gastrointestinal System - Gastroenterology
front 1 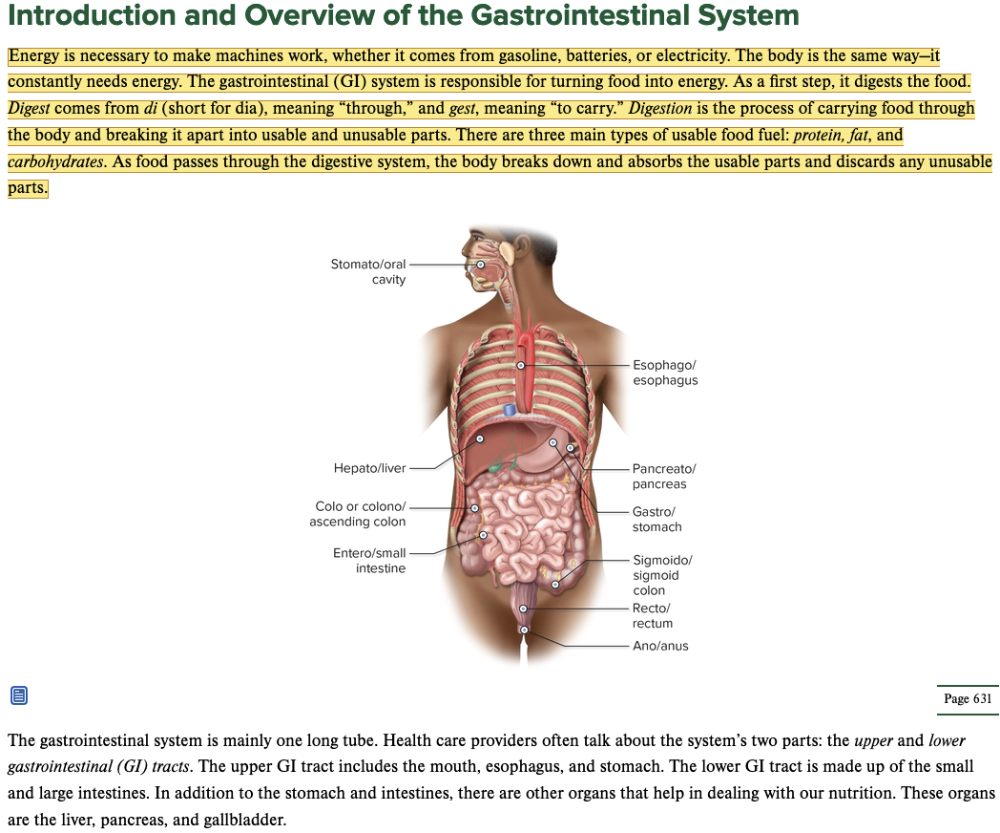 Chapter 11 Introduction and Overview of the Gastrointestinal System | back 1 no data |
front 2 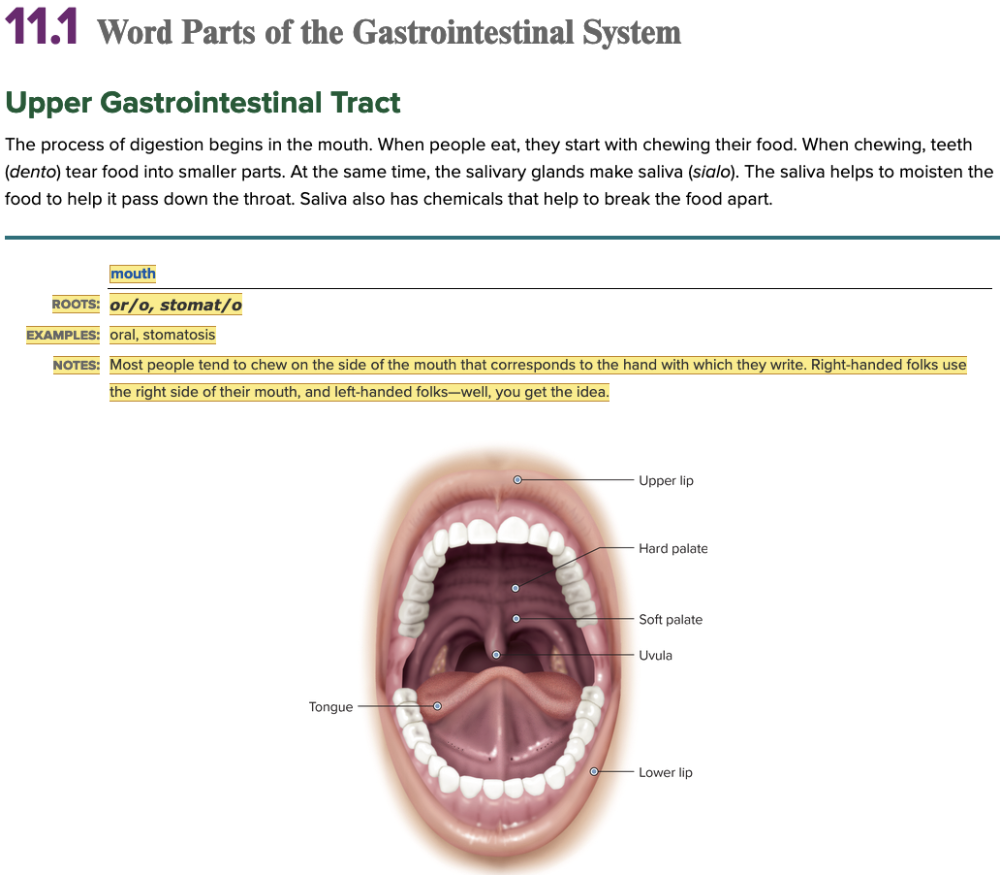 Chapter 11.1 Word Parts of the Gastrointestinal System Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
| back 2 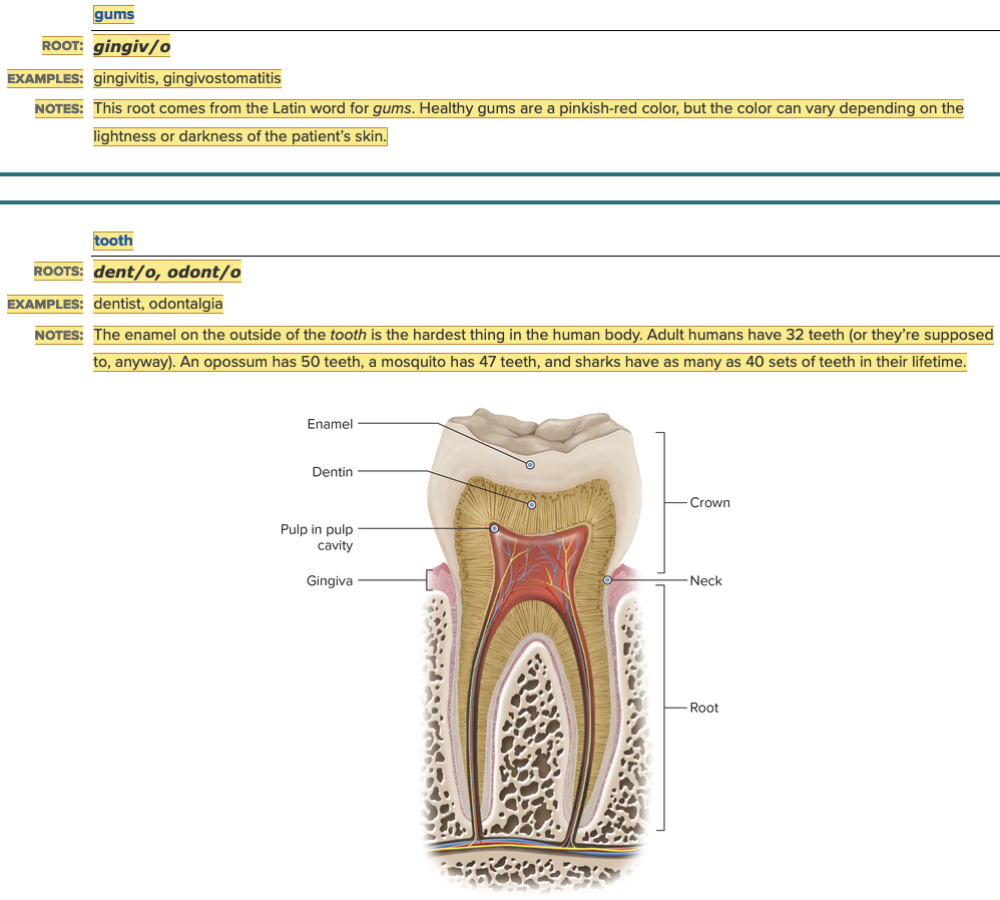 Chapter 11.1 Word Parts of the Gastrointestinal System Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
|
front 3  Chapter 11.1 Word Parts of the Gastrointestinal System Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
| back 3 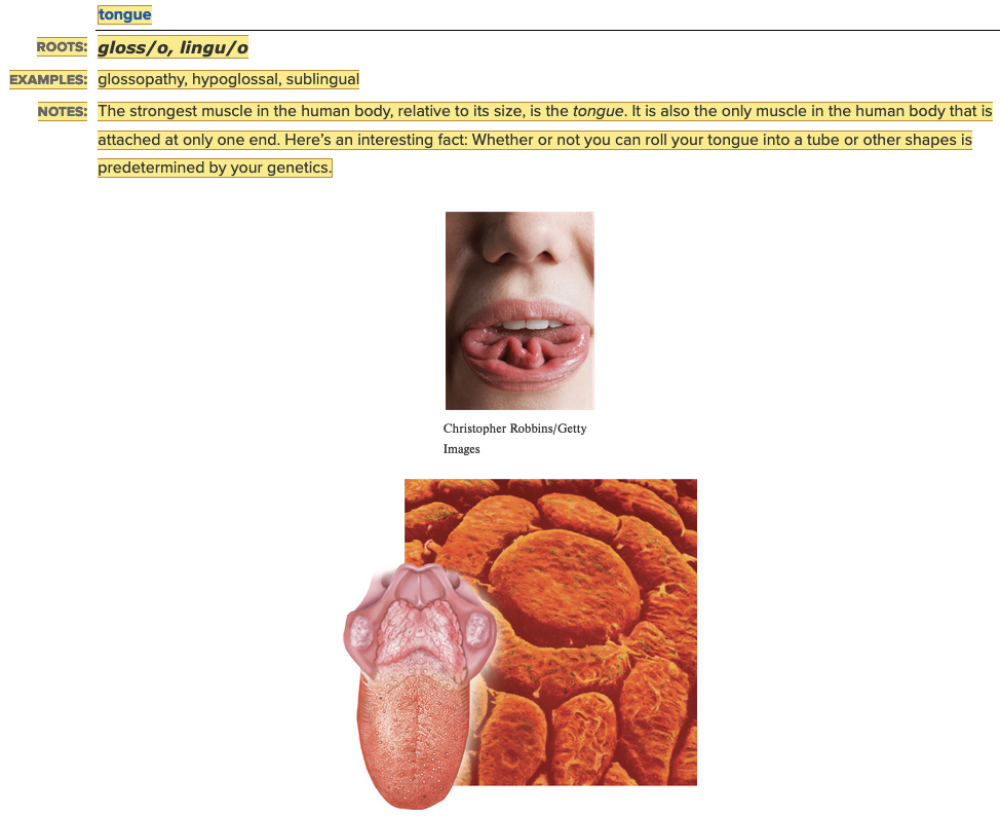 Chapter 11.1 Word Parts of the Gastrointestinal System Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
|
front 4 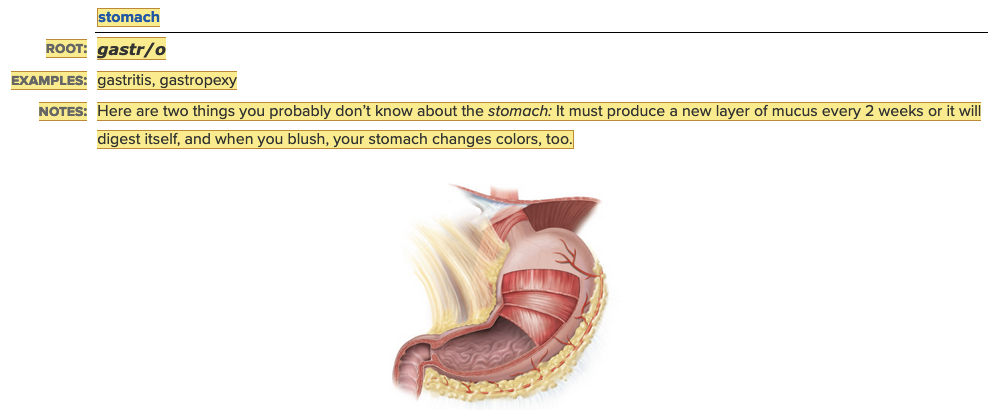 Chapter 11.1 Word Parts of the Gastrointestinal System Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
| back 4 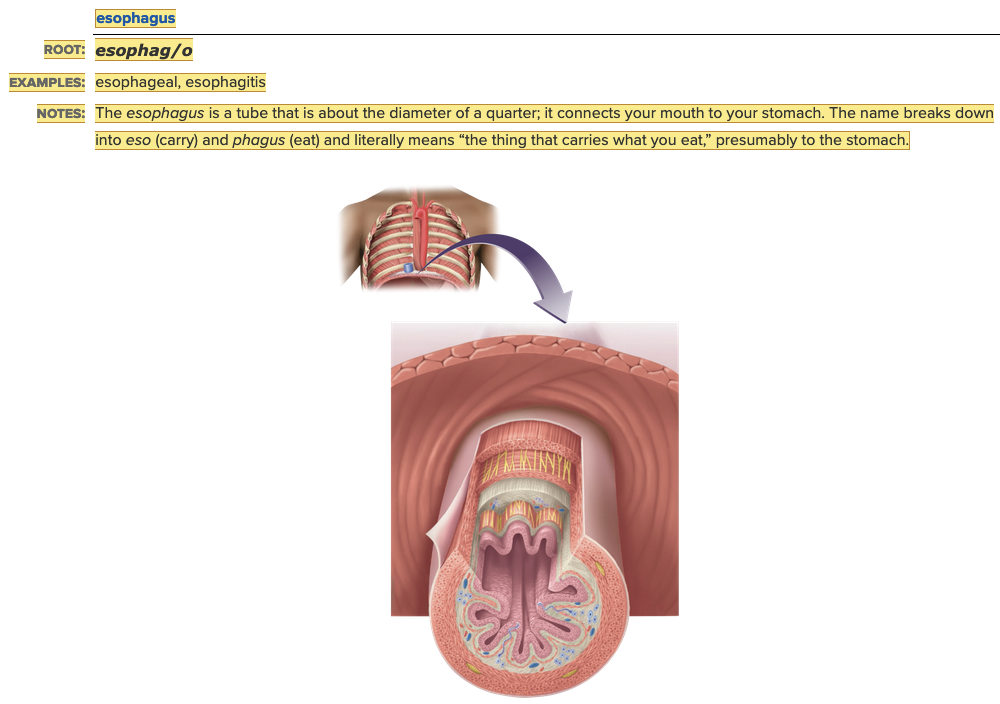 Chapter 11.1 Word Parts of the Gastrointestinal System Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
|
front 5  Chapter 11.1 Word Parts of the Gastrointestinal System Lower Gastrointestinal Tract | back 5 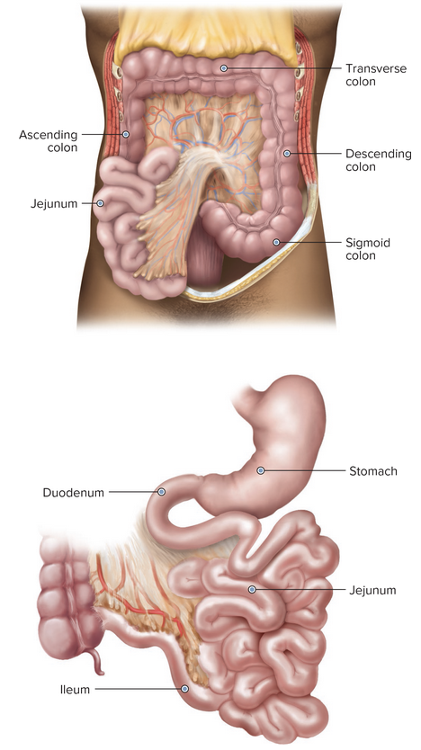 |
front 6 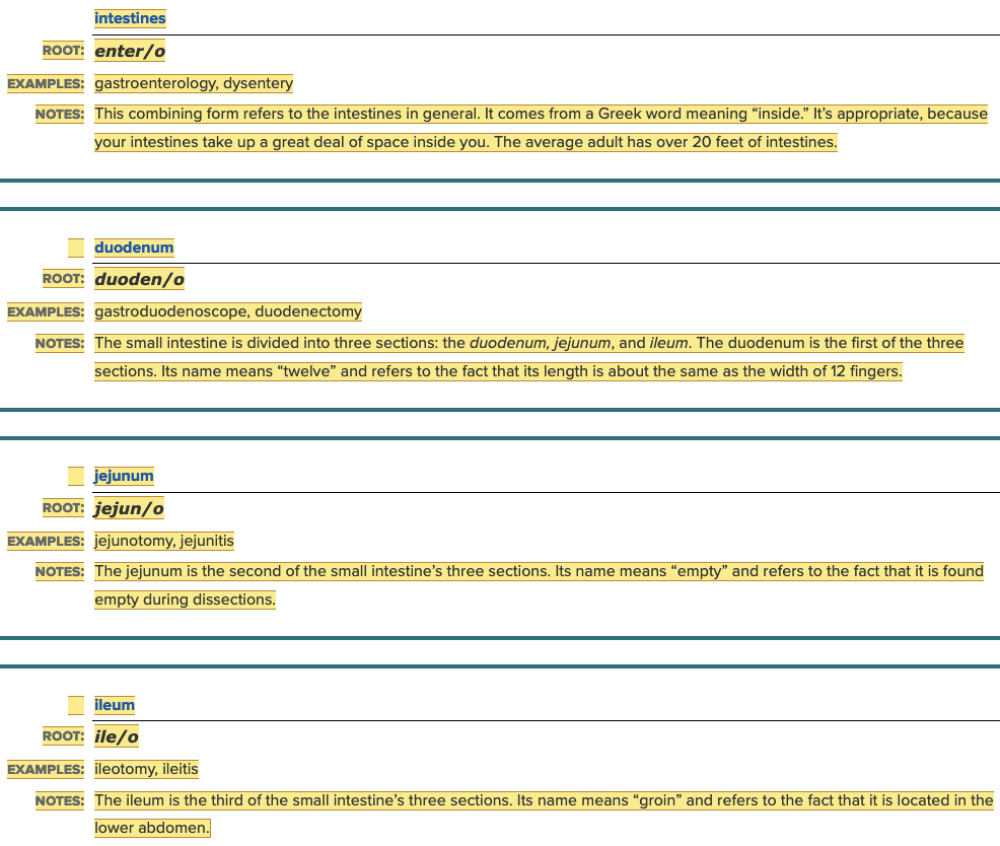 Chapter 11.1 Word Parts of the Gastrointestinal System Lower Gastrointestinal Tract
| back 6 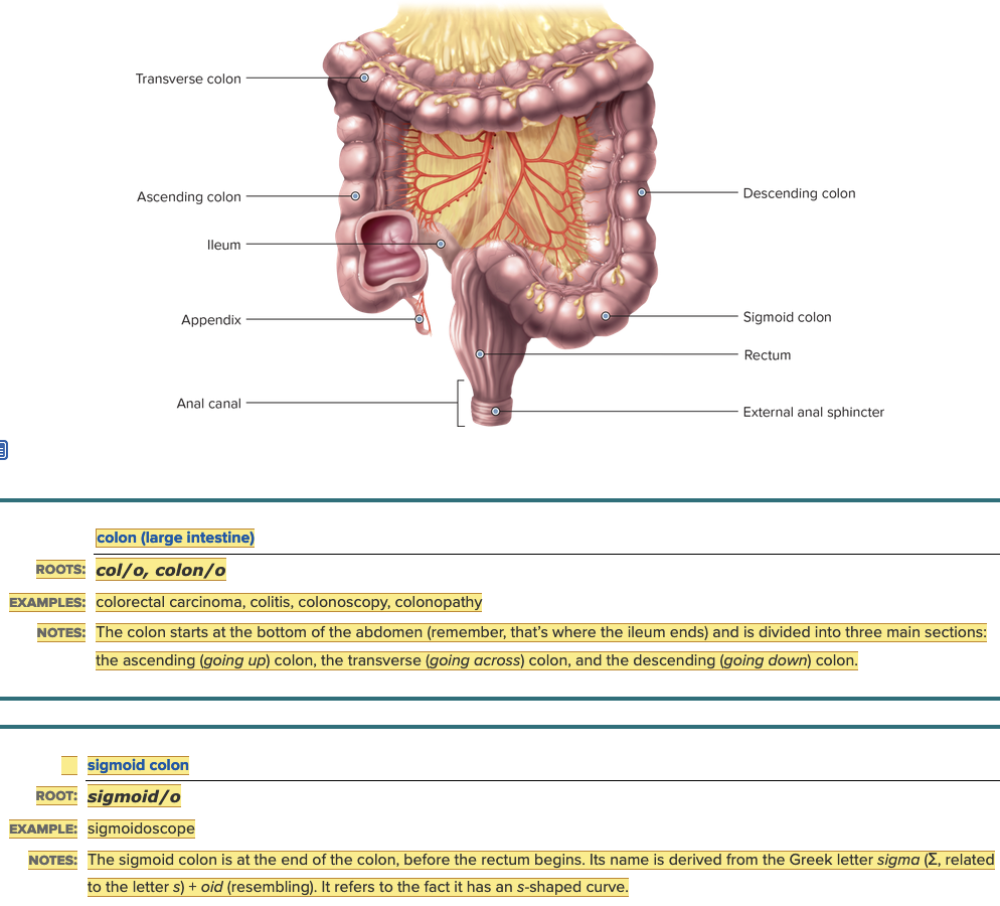 Chapter 11.1 Word Parts of the Gastrointestinal System Lower Gastrointestinal Tract
|
front 7  Chapter 11.1 Word Parts of the Gastrointestinal System Lower Gastrointestinal Tract
| back 7 no data |
front 8  Chapter 11.1 Word Parts of the Gastrointestinal System Supporting Structures/Digestive Organs | back 8 no data |
front 9 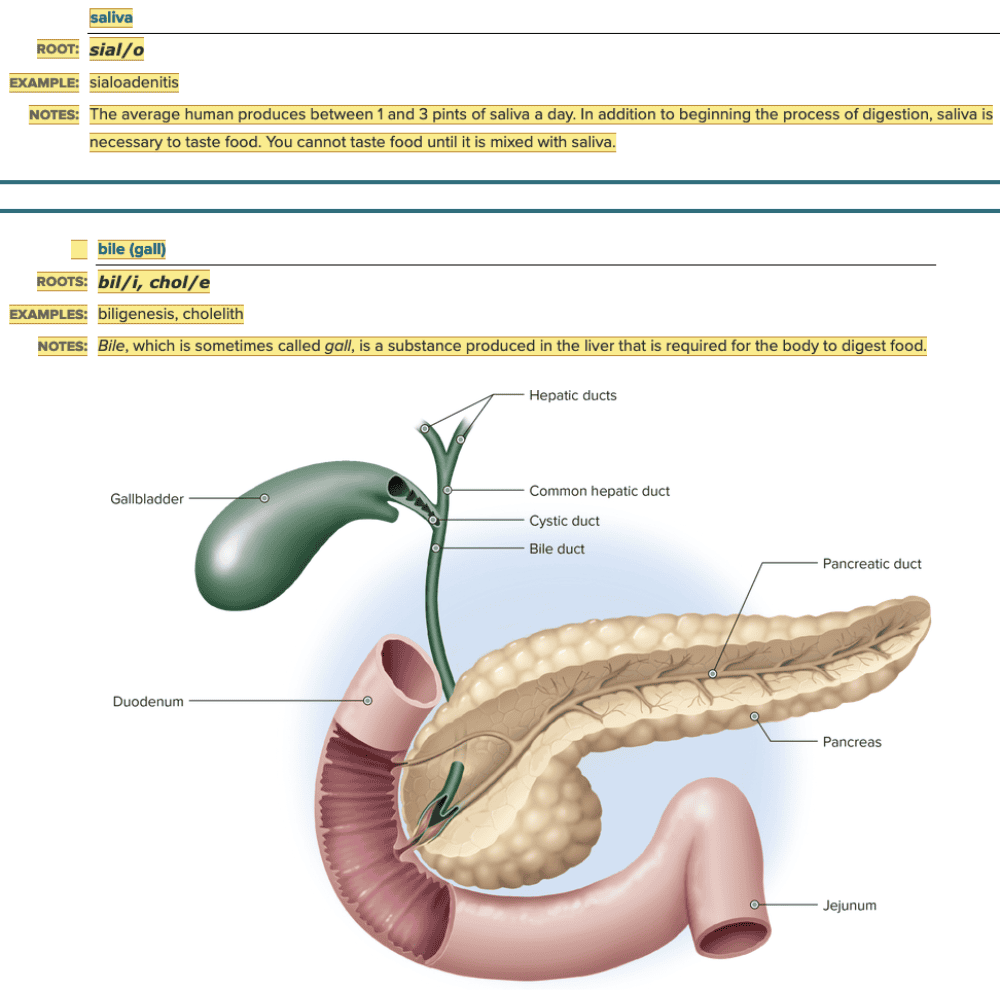 Chapter 11.1 Word Parts of the Gastrointestinal System Supporting Structures/Digestive Organs
| back 9  Chapter 11.1 Word Parts of the Gastrointestinal System Supporting Structures/Digestive Organs
|
front 10  Chapter 11.1 Word Parts of the Gastrointestinal System Supporting Structures/Digestive Organs
| back 10 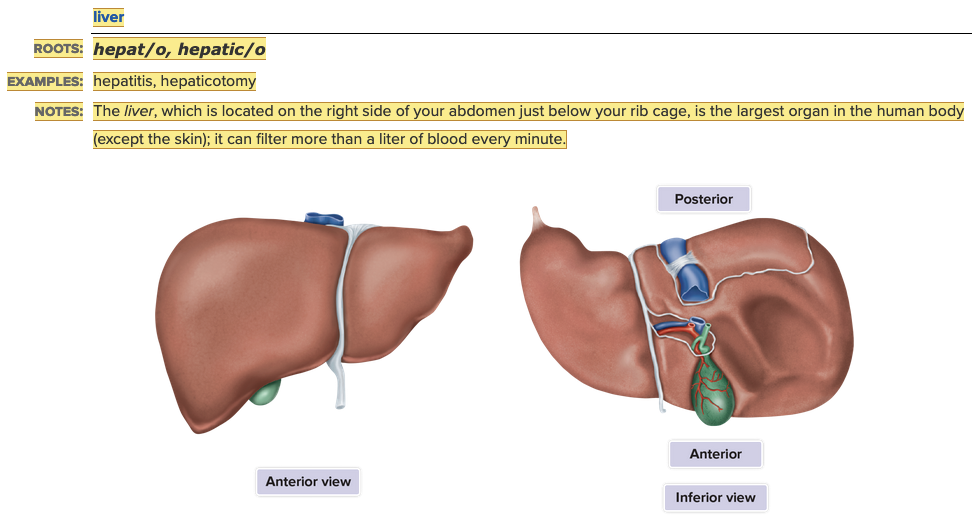 Chapter 11.1 Word Parts of the Gastrointestinal System Supporting Structures/Digestive Organs
|
front 11  Chapter 11.1 Word Parts of the Gastrointestinal System Supporting Structures/Digestive Organs
| back 11 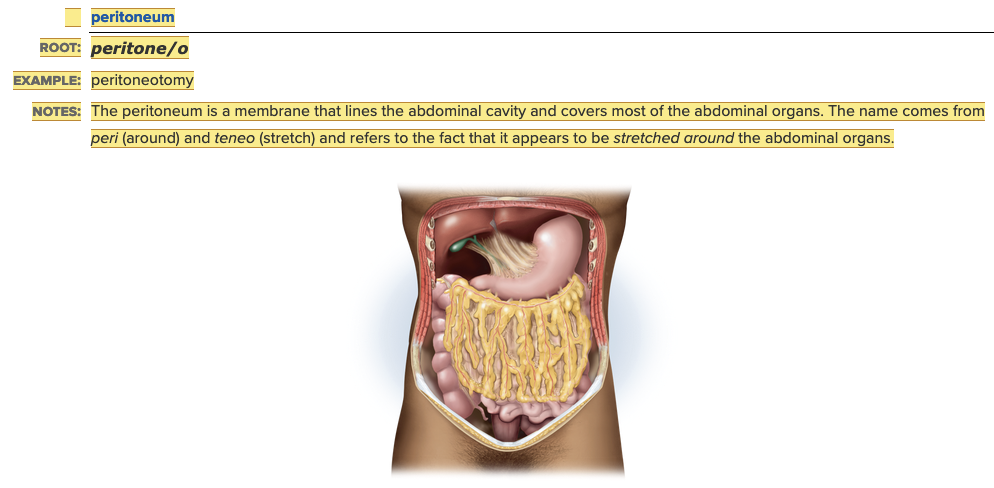 Chapter 11.1 Word Parts of the Gastrointestinal System Supporting Structures/Digestive Organs
|
front 12 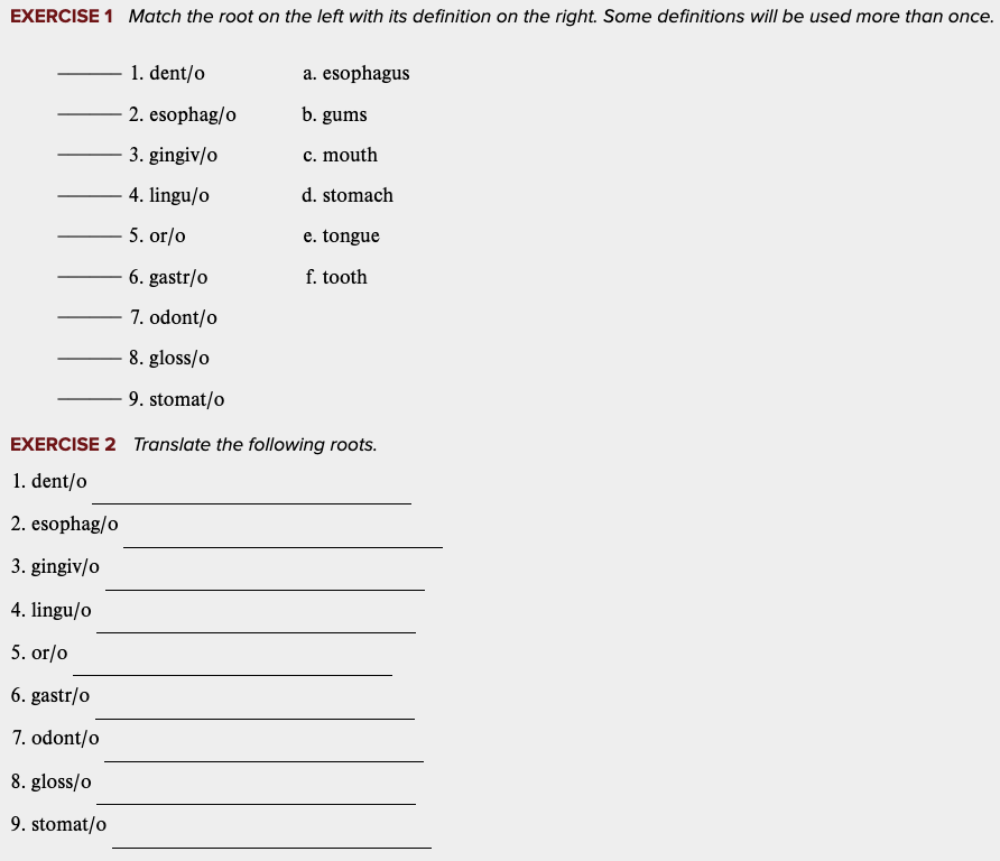 Learning Outcome 11.1 Exercises: Exercise 1, 2. | back 12 no data |
front 13  Learning Outcome 11.1 Exercises: Exercise 3, 4. | back 13 no data |
front 14  Learning Outcome 11.1 Exercises: Exercise 5, 6. | back 14 no data |
front 15  Learning Outcome 11.1 Exercises: Exercise 7, 8. | back 15 no data |
front 16  Learning Outcome 11.1 Exercises: Exercise 9, 10. | back 16  |
front 17 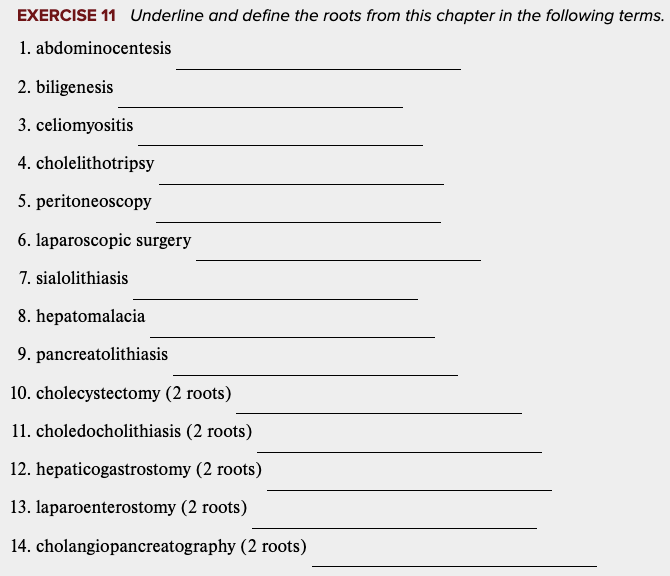 Learning Outcome 11.1 Exercises: Exercise 11, 12. | back 17 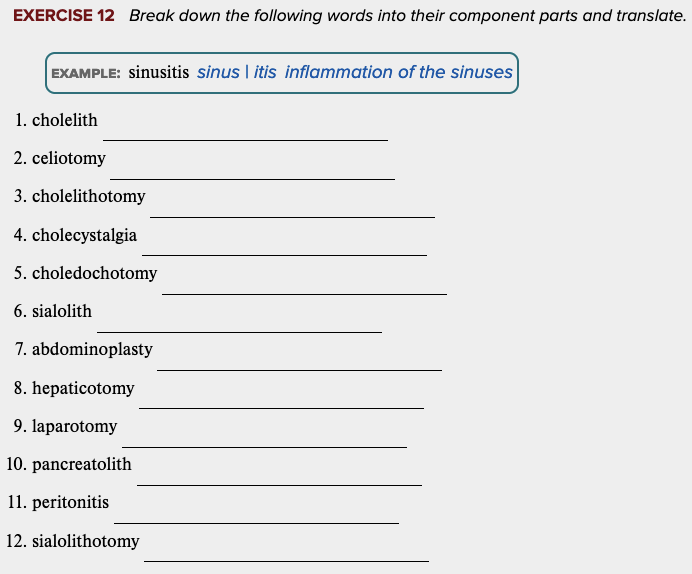 |
front 18  Learning Outcome 11.1 Exercises: Exercise 13, 14. | back 18 no data |
front 19 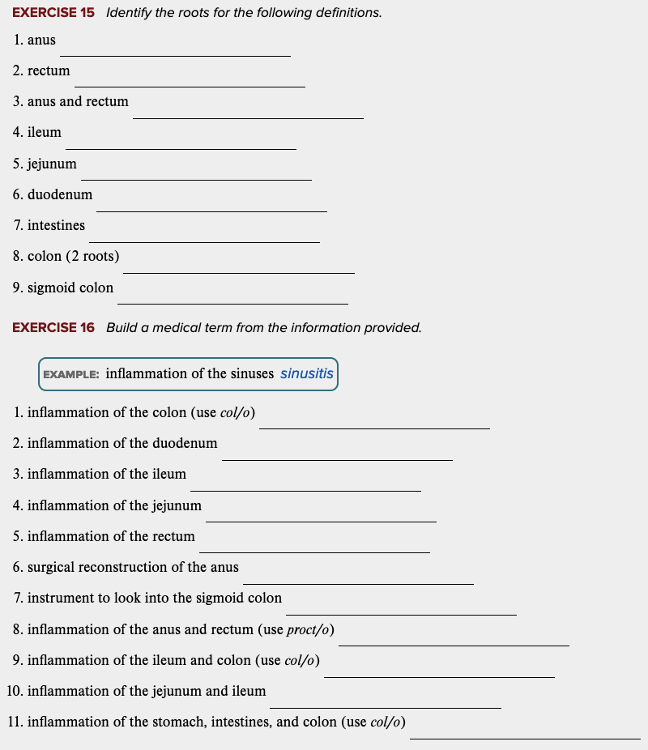 Learning Outcome 11.1 Exercises: Exercise 15, 16. | back 19 no data |
front 20  Learning Outcome 11.1 Exercises: Exercise 17, 18. | back 20 no data |
front 21  Learning Outcome 11.1 Exercises: Exercise 19. | back 21  |
front 22  Chapter 11.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
| back 22  Chapter 11.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
|
front 23 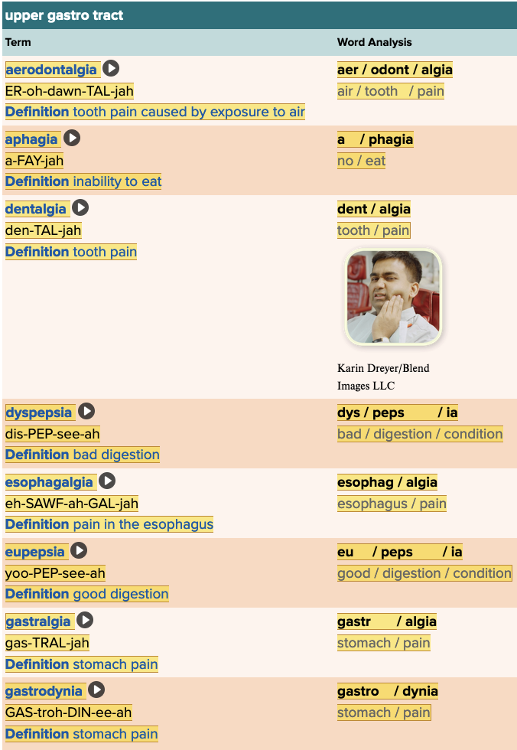 Chapter 11.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
| back 23 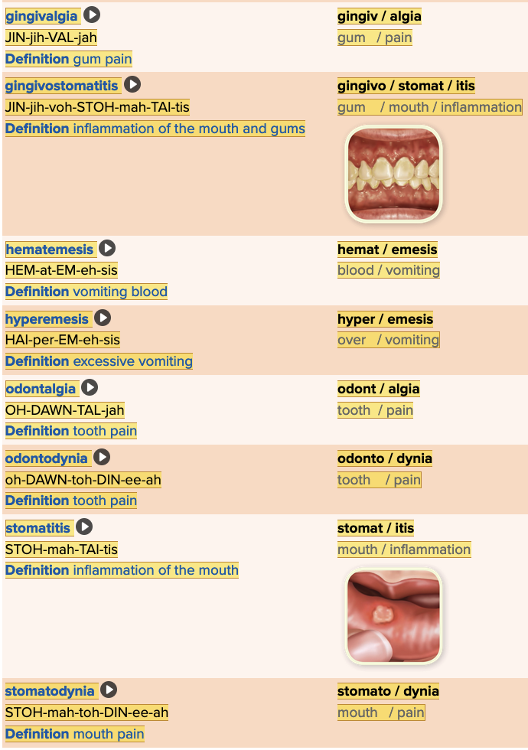 Chapter 11.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
|
front 24 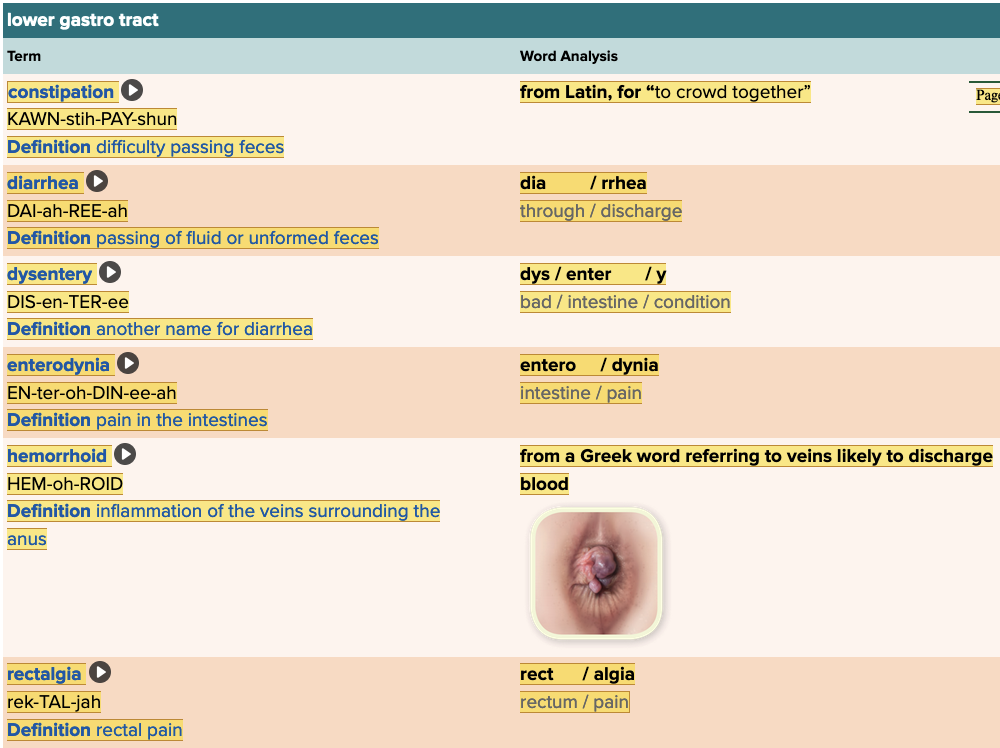 Chapter 11.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
| back 24 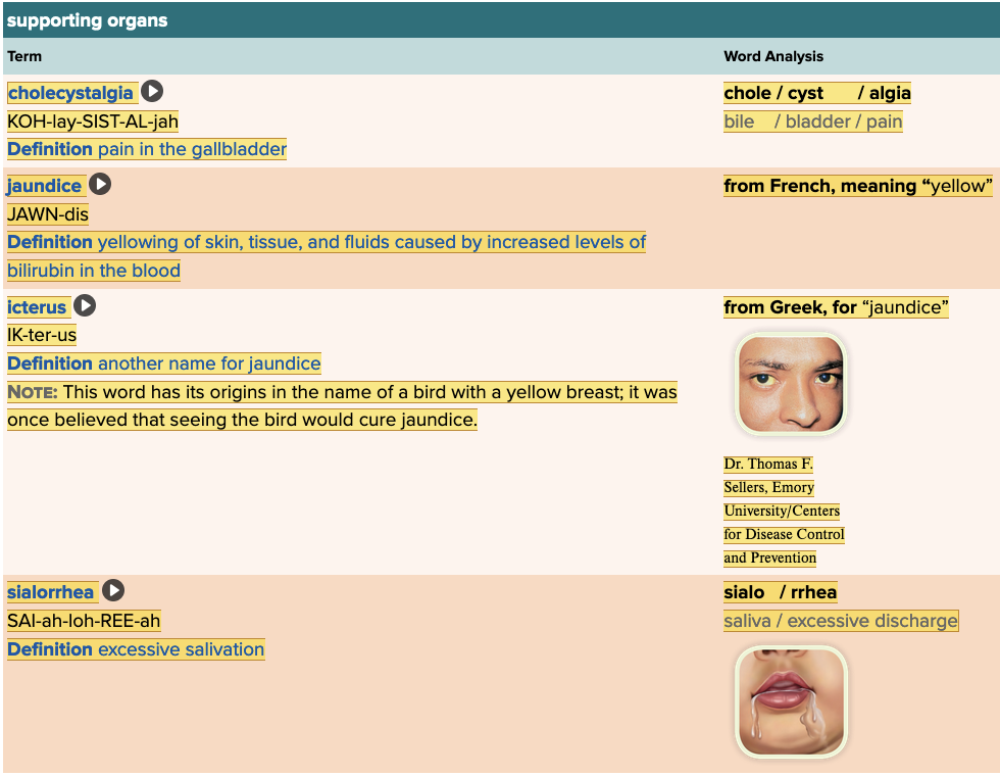 Chapter 11.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
|
front 25  Learning Outcome 11.2 Exercises: Exercise 1, 2. | back 25  |
front 26  Learning Outcome 11.2 Exercises: Exercise 3, 4. | back 26 no data |
front 27  Learning Outcome 11.2 Exercises: Exercise 5, 6, 7. | back 27  |
front 28  Learning Outcome 11.2 Exercises: Exercise 8. | back 28  |
front 29  Chapter 11.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 29  Chapter 11.3 Observation and Discovery
|
front 30 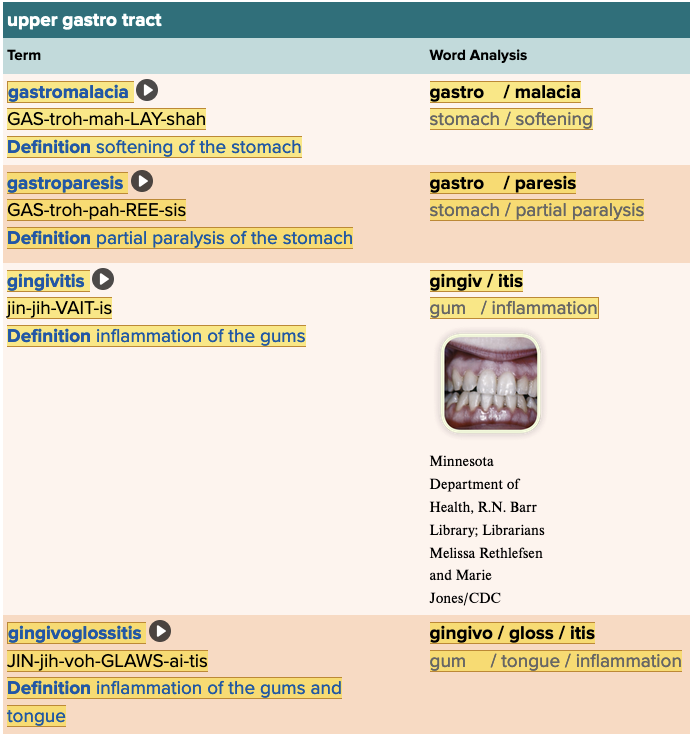 Chapter 11.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 30 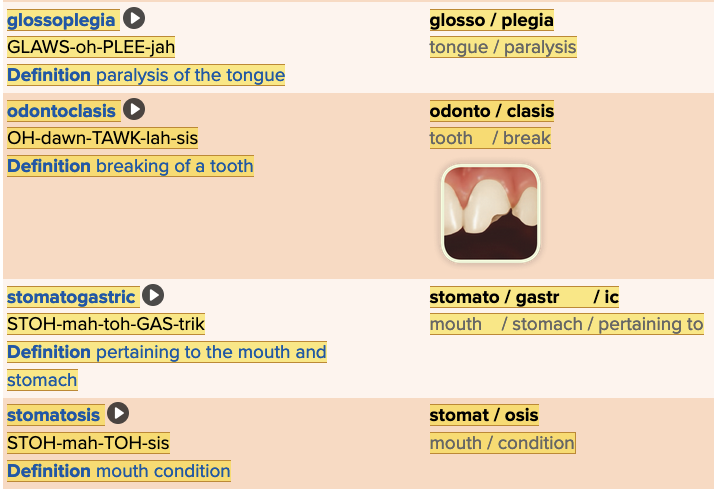 Chapter 11.3 Observation and Discovery
|
front 31  Chapter 11.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 31 no data |
front 32 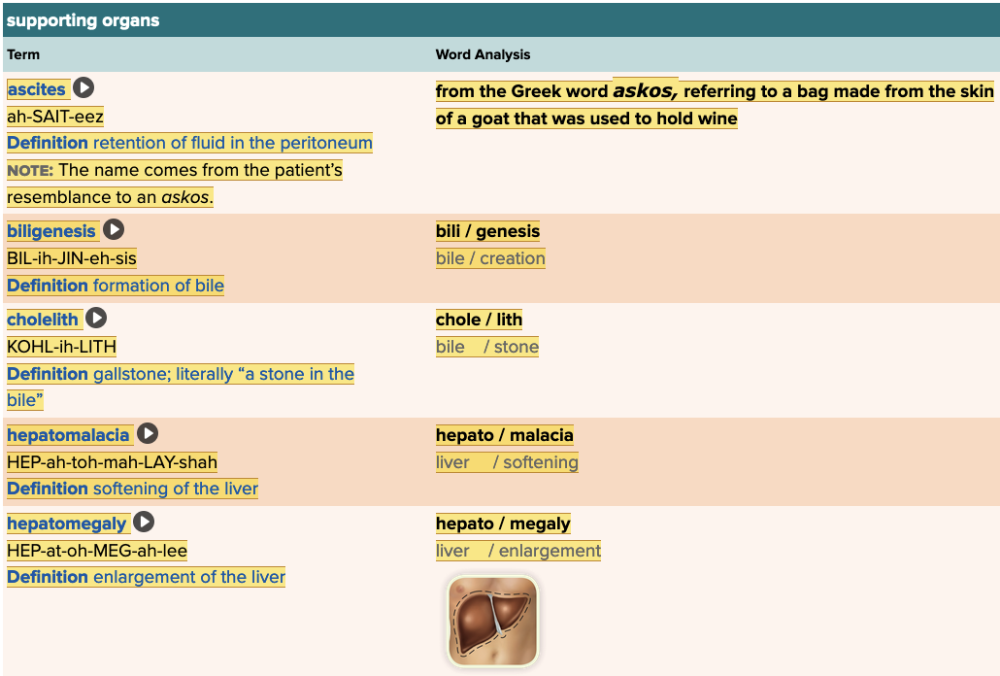 Chapter 11.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 32 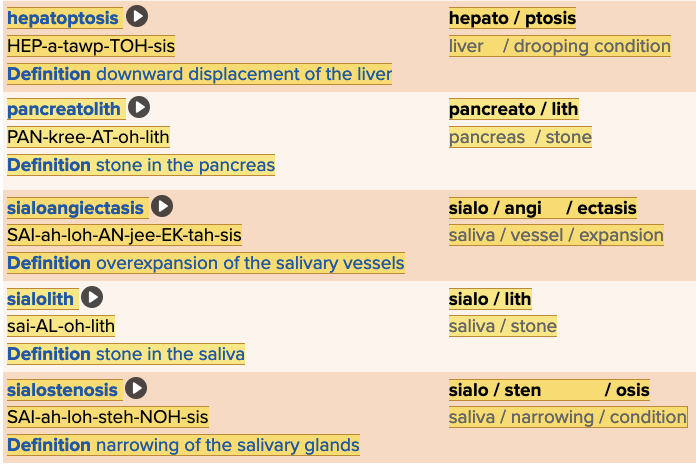 Chapter 11.3 Observation and Discovery
|
front 33  Chapter 11.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 33 no data |
front 34  Chapter 11.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 34  Chapter 11.3 Observation and Discovery
|
front 35  Chapter 11.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 35 no data |
front 36  Chapter 11.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 36 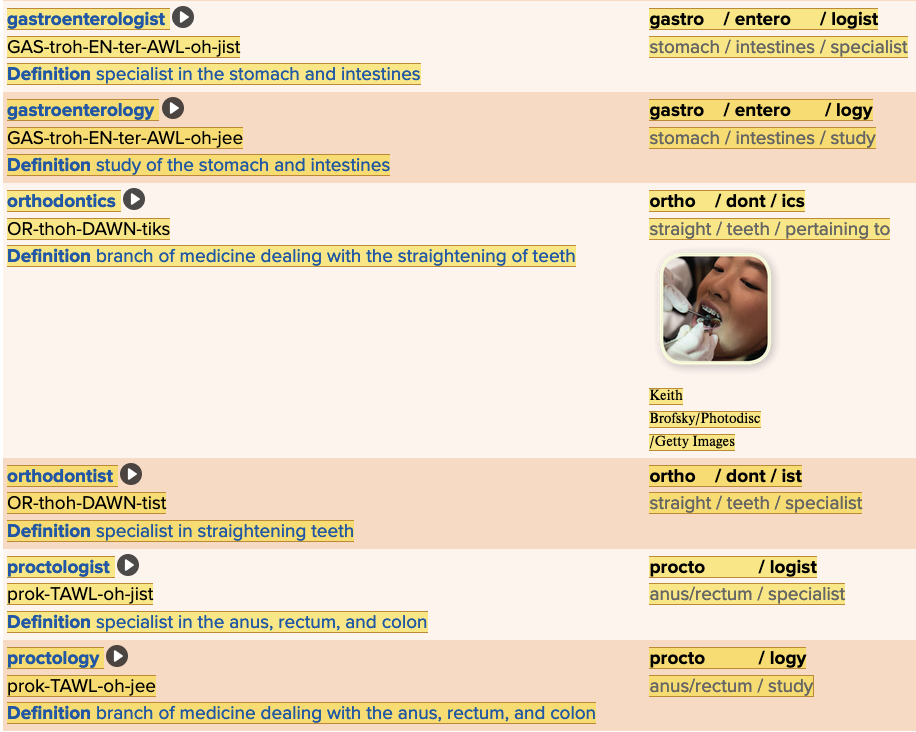 Chapter 11.3 Observation and Discovery
|
front 37 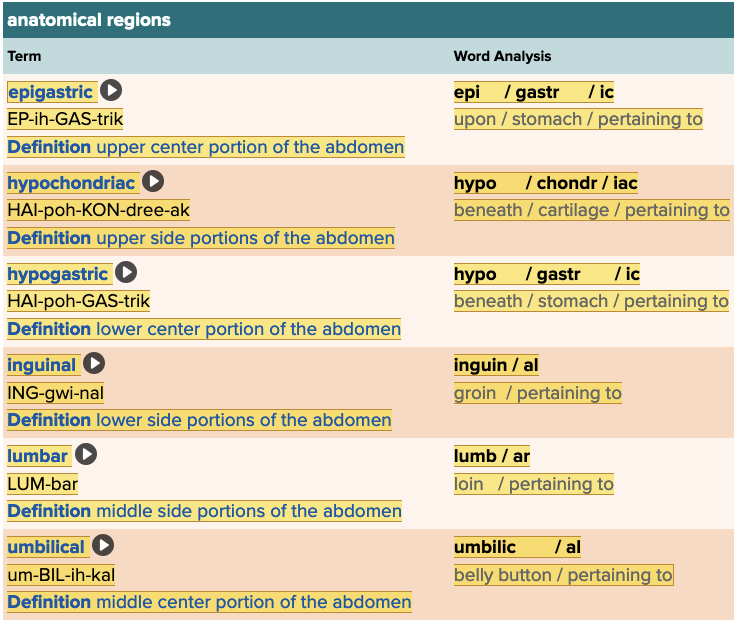 Chapter 11.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 37 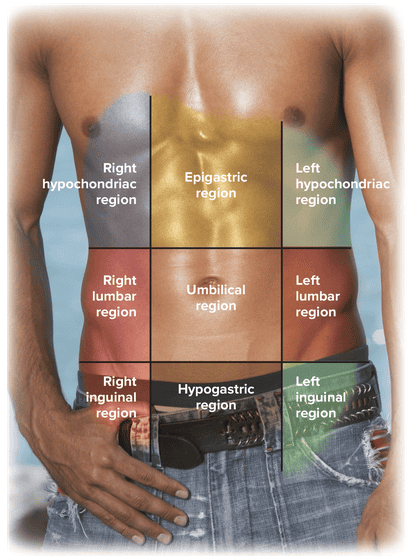 Chapter 11.3 Observation and Discovery
|
front 38  Learning Outcome 11.3 Exercises: Exercise 1. | back 38  |
front 39  Learning Outcome 11.3 Exercises: Exercise 2. | back 39  |
front 40  Learning Outcome 11.3 Exercises: Exercise 3. | back 40  |
front 41  Learning Outcome 11.3 Exercises: Exercise 4, 5. | back 41 no data |
front 42  Learning Outcome 11.3 Exercises: Exercise 6, 7. | back 42  |
front 43  Learning Outcome 11.3 Exercises: Exercise 8. | back 43  |
front 44  Learning Outcome 11.3 Exercises: Exercise 9. | back 44 no data |
front 45  Chapter 11.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 45 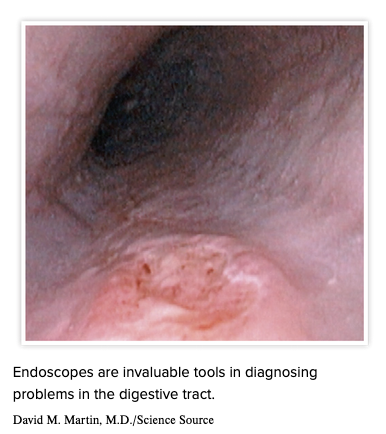 |
front 46 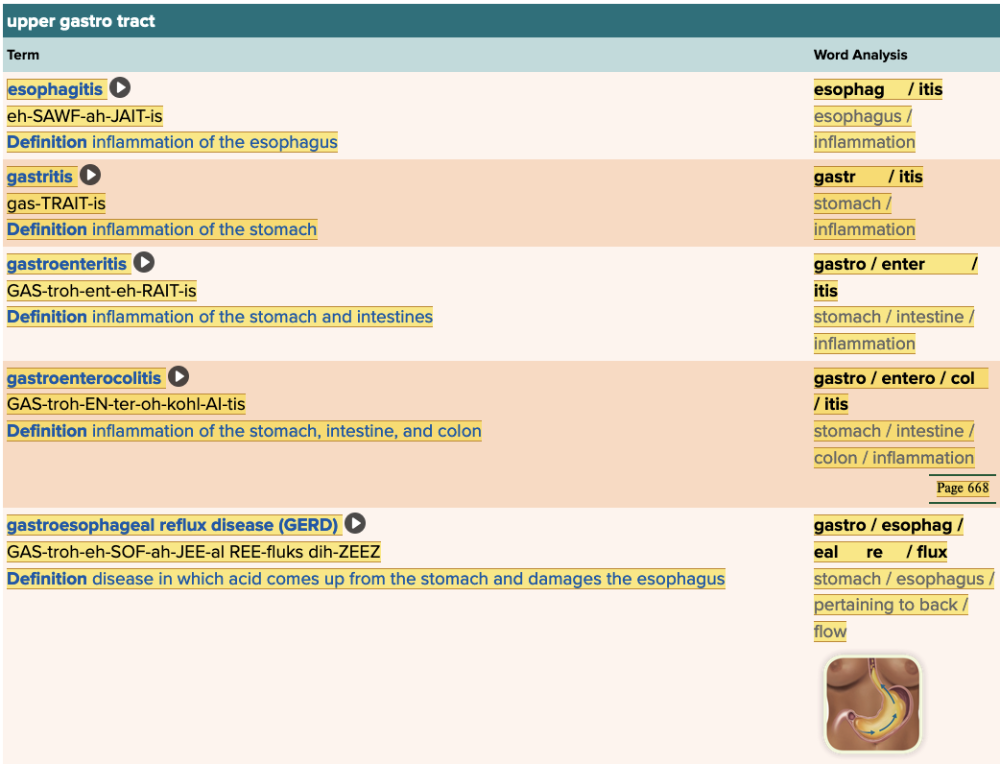 Chapter 11.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 46 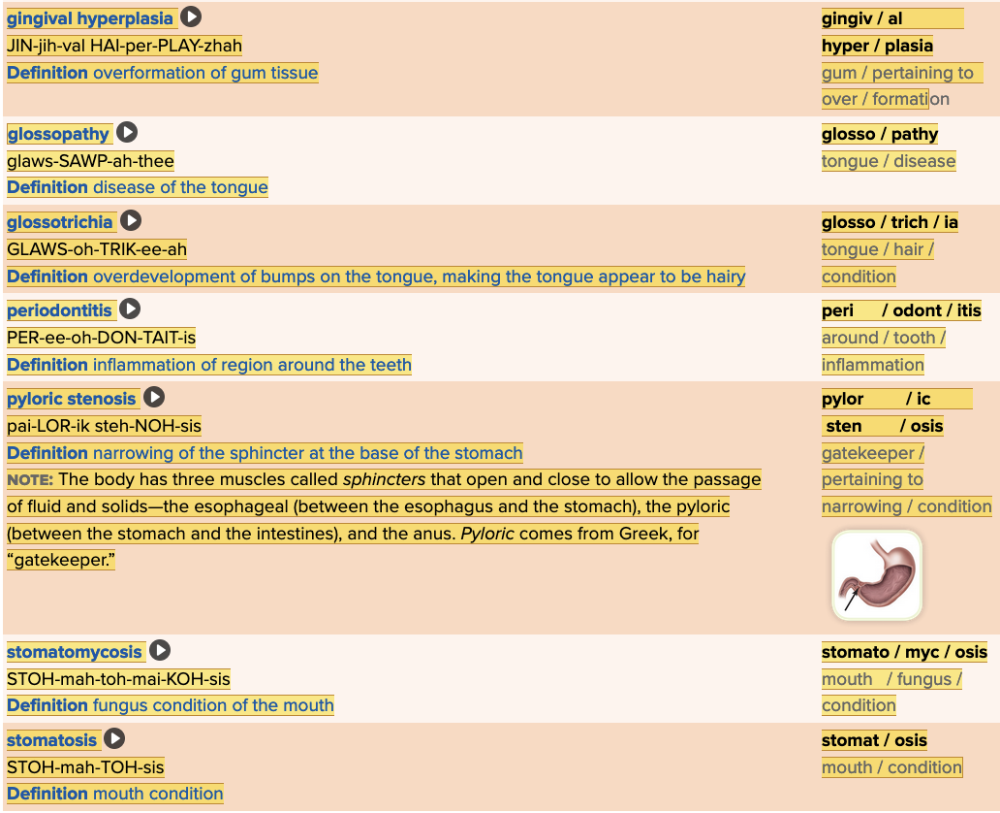 Chapter 11.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
|
front 47 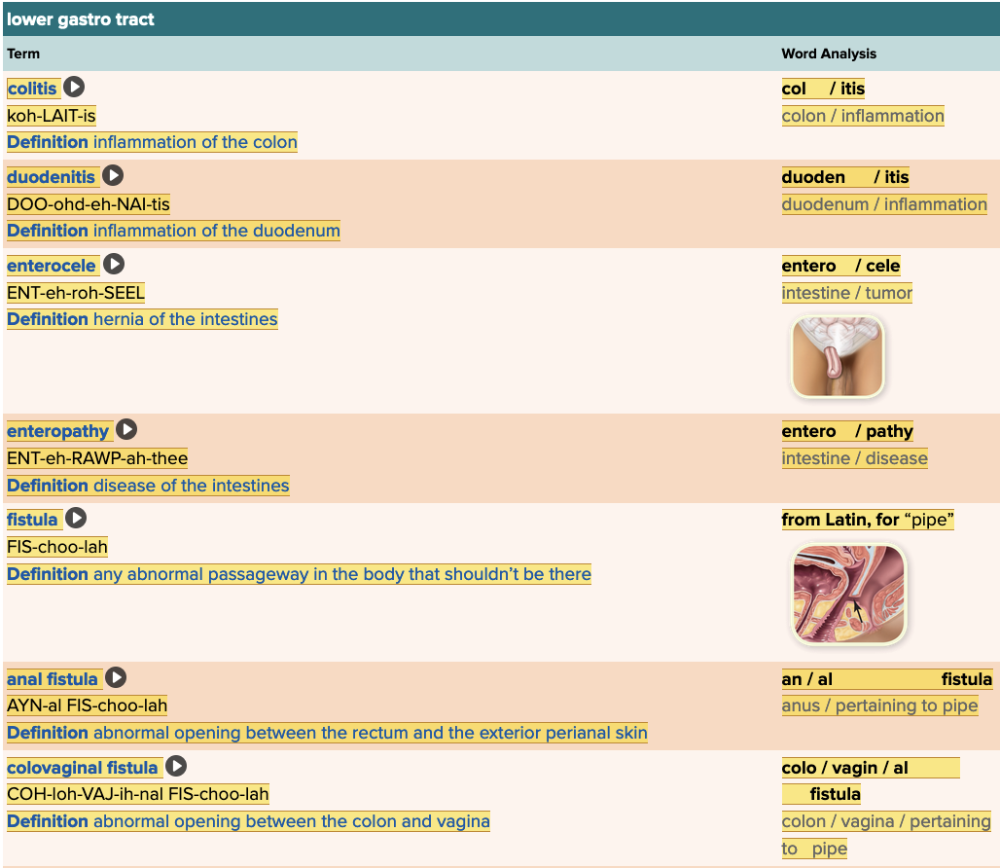 Chapter 11.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 47 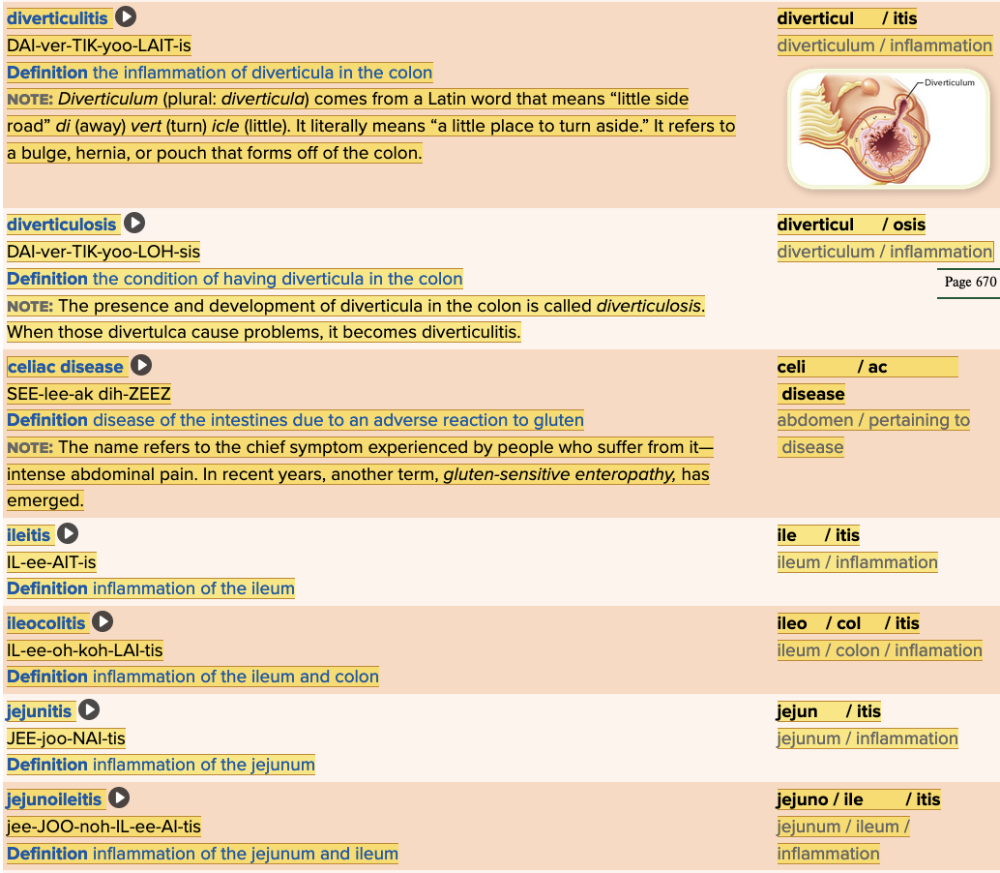 Chapter 11.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
|
front 48  Chapter 11.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 48 no data |
front 49 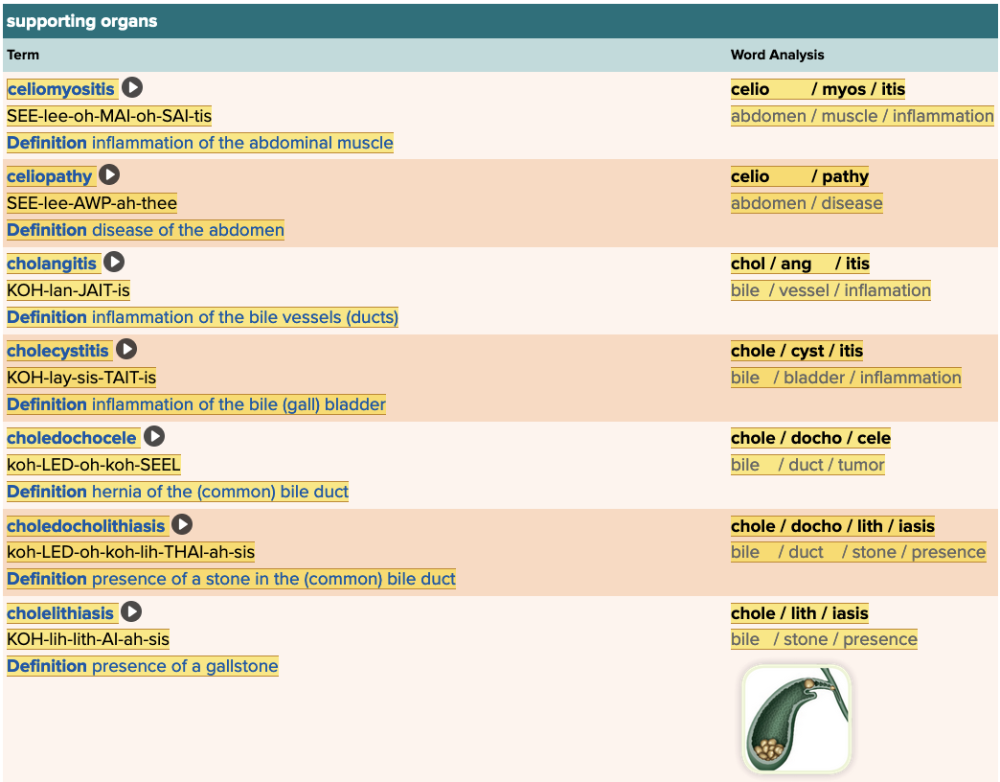 Chapter 11.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 49  Chapter 11.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
|
front 50  Chapter 11.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 50 no data |
front 51  Chapter 11.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 51 no data |
front 52  Learning Outcome 11.4 Exercises: Exercise 1, 2. | back 52  |
front 53  Learning Outcome 11.4 Exercises: Exercise 3. | back 53 no data |
front 54  Learning Outcome 11.4 Exercises: Exercise 4, 5, 6. | back 54 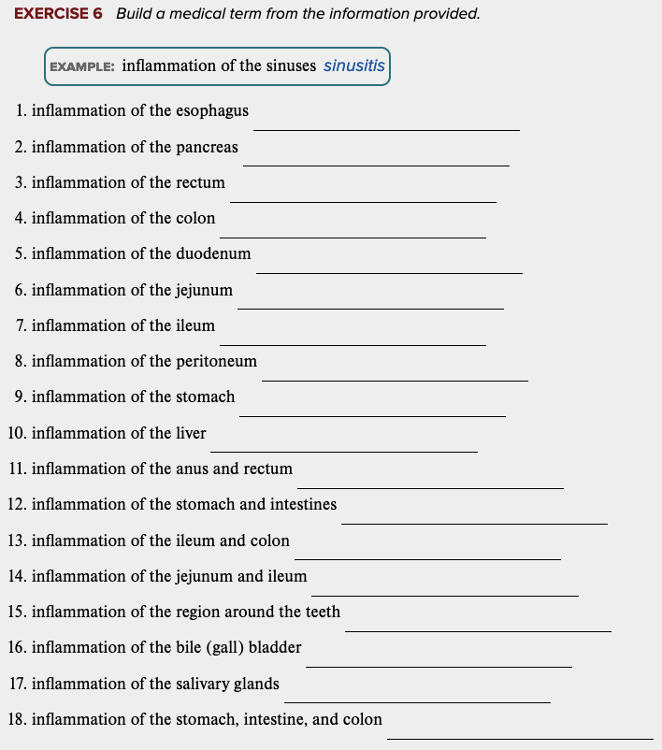 |
front 55  Learning Outcome 11.4 Exercises: Exercise 7, 8. | back 55  |
front 56  Chapter 11.5 Treatments and Therapies
| back 56 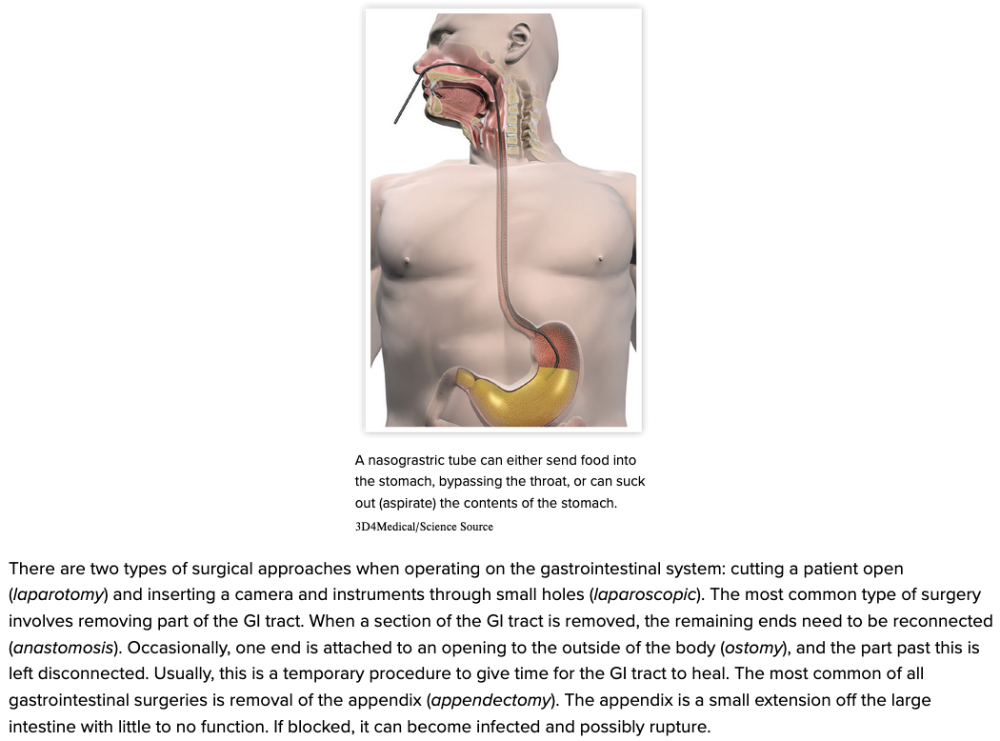 Chapter 11.5 Treatments and Therapies
|
front 57 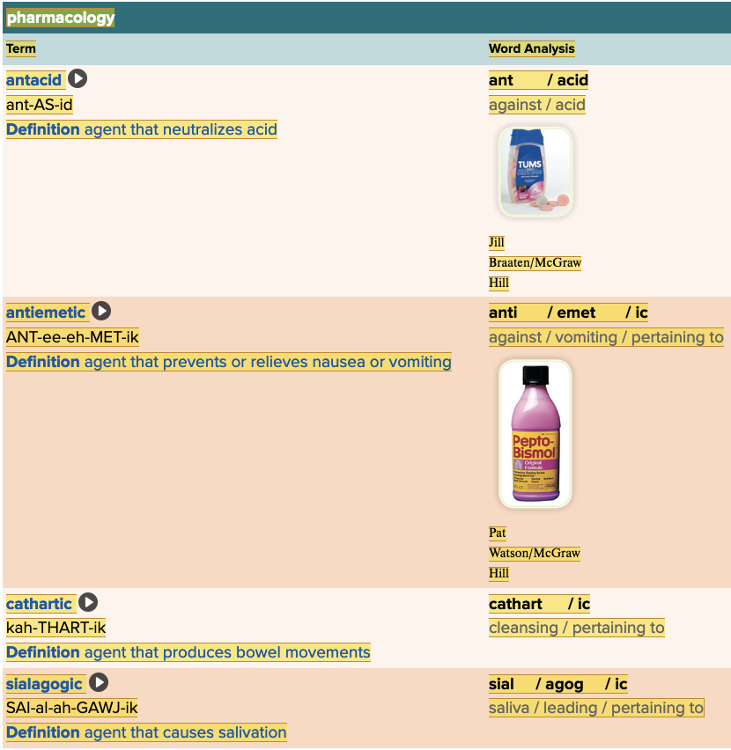 Chapter 11.5 Treatments and Therapies
| back 57 no data |
front 58 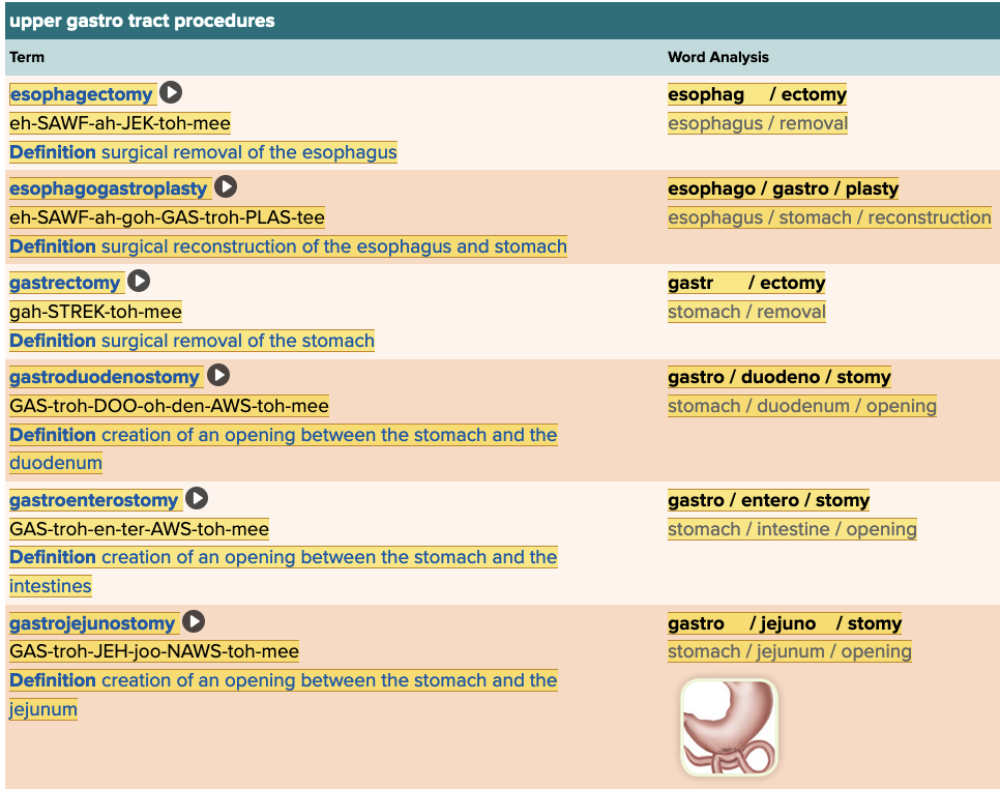 Chapter 11.5 Treatments and Therapies
| back 58 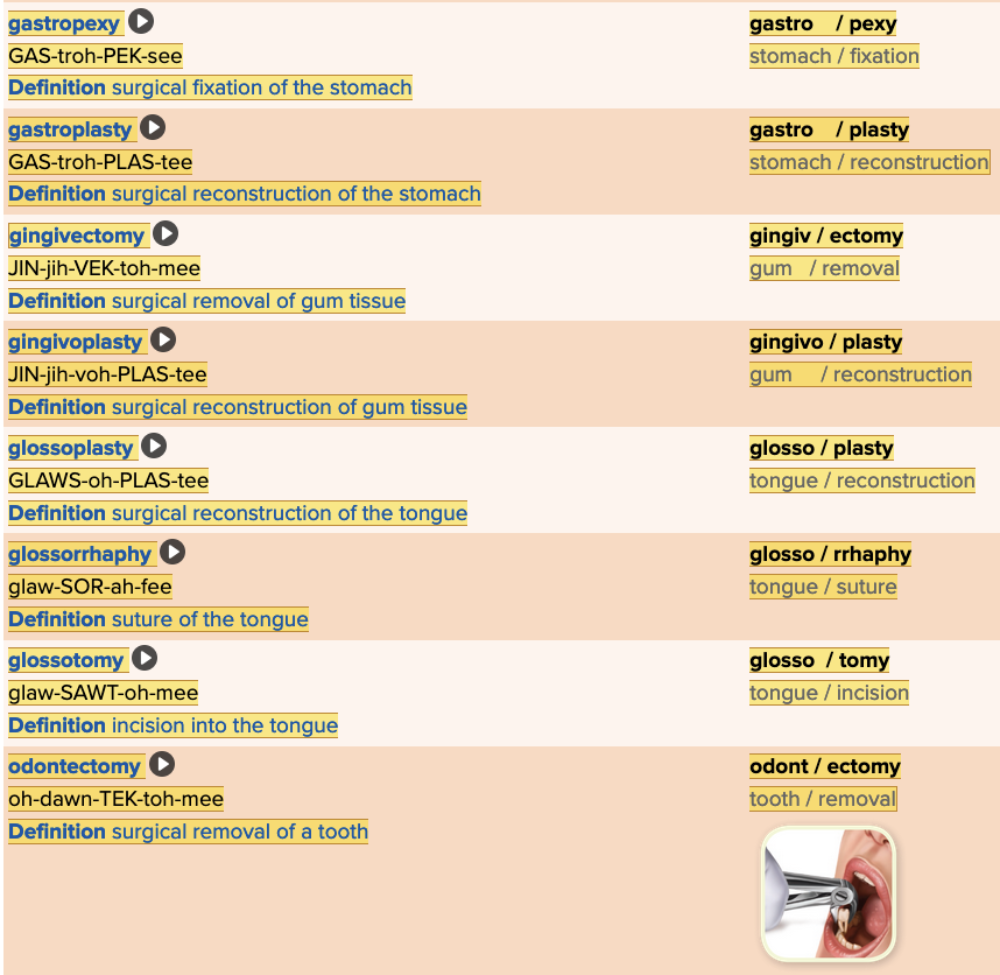 Chapter 11.5 Treatments and Therapies
|
front 59 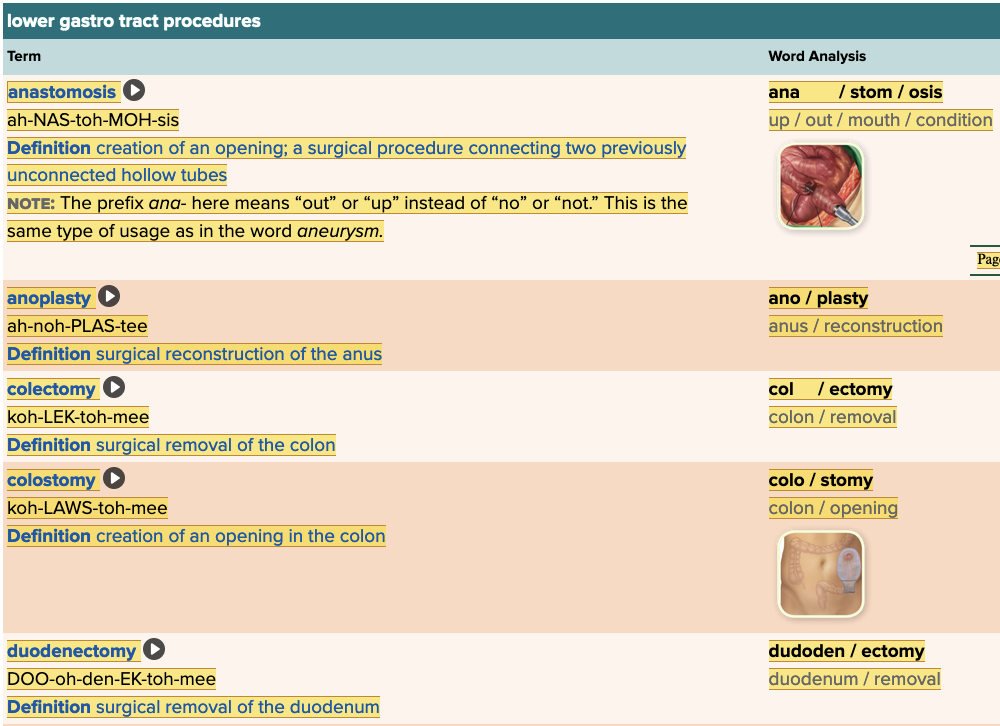 Chapter 11.5 Treatments and Therapies
| back 59 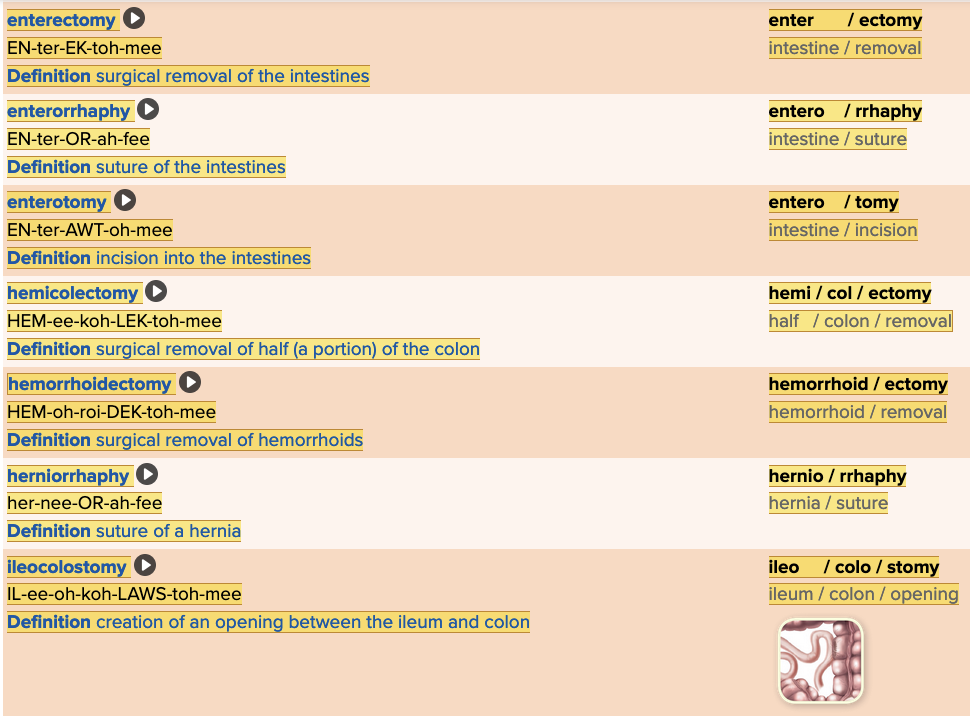 Chapter 11.5 Treatments and Therapies
|
front 60 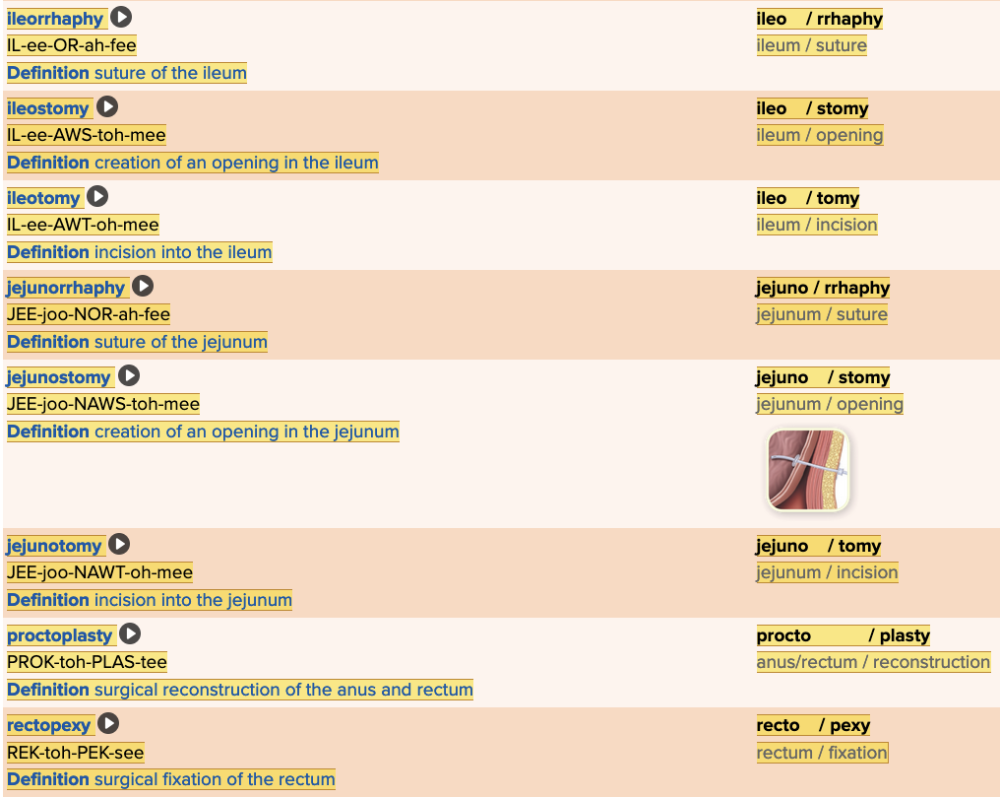 Chapter 11.5 Treatments and Therapies
| back 60 no data |
front 61  Chapter 11.5 Treatments and Therapies
| back 61  Chapter 11.5 Treatments and Therapies
|
front 62  Chapter 11.5 Treatments and Therapies
| back 62 no data |
front 63  Learning Outcome 11.5 Exercises: Exercise 1. | back 63 no data |
front 64  Learning Outcome 11.5 Exercises: Exercise 2. | back 64 no data |
front 65  Learning Outcome 11.5 Exercises: Exercise 3. | back 65  |
front 66  Learning Outcome 11.5 Exercises: Exercise 4, 5. | back 66 no data |
front 67  Learning Outcome 11.5 Exercises: Exercise 6, 7. | back 67  |
front 68  Learning Outcome 11.5 Exercises: Exercise 8. | back 68  |
front 69  Learning Outcome 11.5 Exercises: Exercise 9. | back 69 no data |
front 70  Chapter 11.6 Abbreviations | back 70 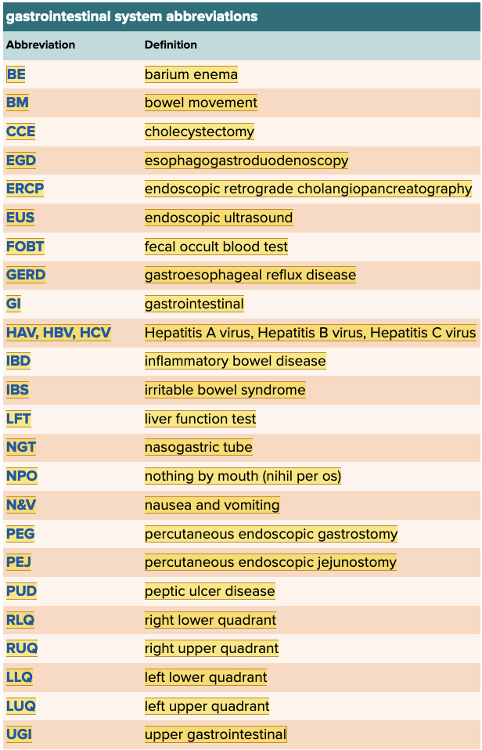 Chapter 11.6 Abbreviations
|
front 71  Learning Outcome 11.6 Exercises: Exercise 1, 2. | back 71 no data |
front 72  Learning Outcome 11.6 Exercises: Exercise 3, 4. | back 72 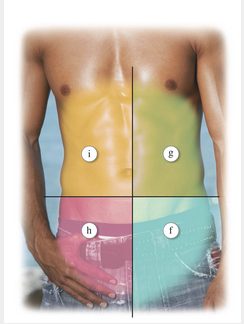 |
front 73  Chapter 11.7 Electronic Health Records Clinic Note | back 73 no data |
front 74  Learning Outcome 11.7 Exercises: Exercise 1, 2. | back 74 no data |
front 75  Learning Outcome 11.7 Exercises: Exercise 3, 4. | back 75 no data |
front 76  Chapter 11.7 Electronic Health Records GI Consult | back 76  |
front 77  Learning Outcome 11.7 Exercises: Exercise 5. | back 77 no data |
front 78  Learning Outcome 11.7 Exercises: Exercise 6, 7. | back 78 no data |
front 79  Learning Outcome 11.7 Exercises: Exercise 8. | back 79 no data |
front 80  Chapter 11.7 Electronic Health Records Discharge Summary | back 80  |
front 81  Learning Outcome 11.7 Exercises: Exercise 9, 10. | back 81 no data |
front 82  Learning Outcome 11.7 Exercises: Exercise 11, 12. | back 82 no data |
front 83 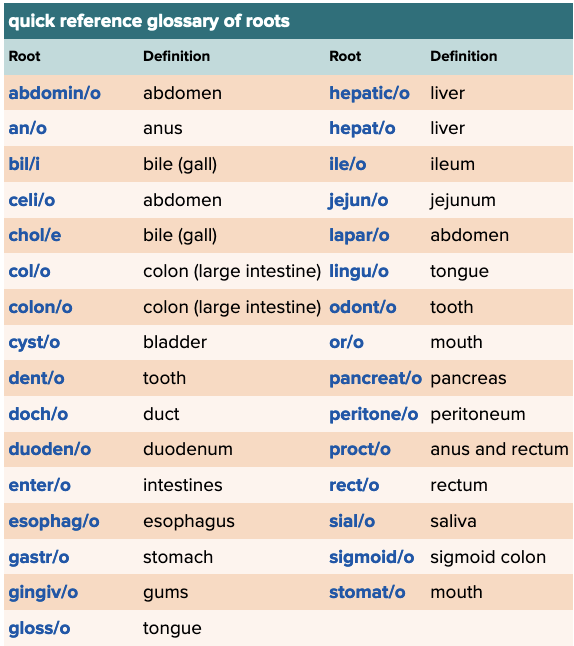 Chapter 11 Quick Reference
| back 83 no data |
front 84 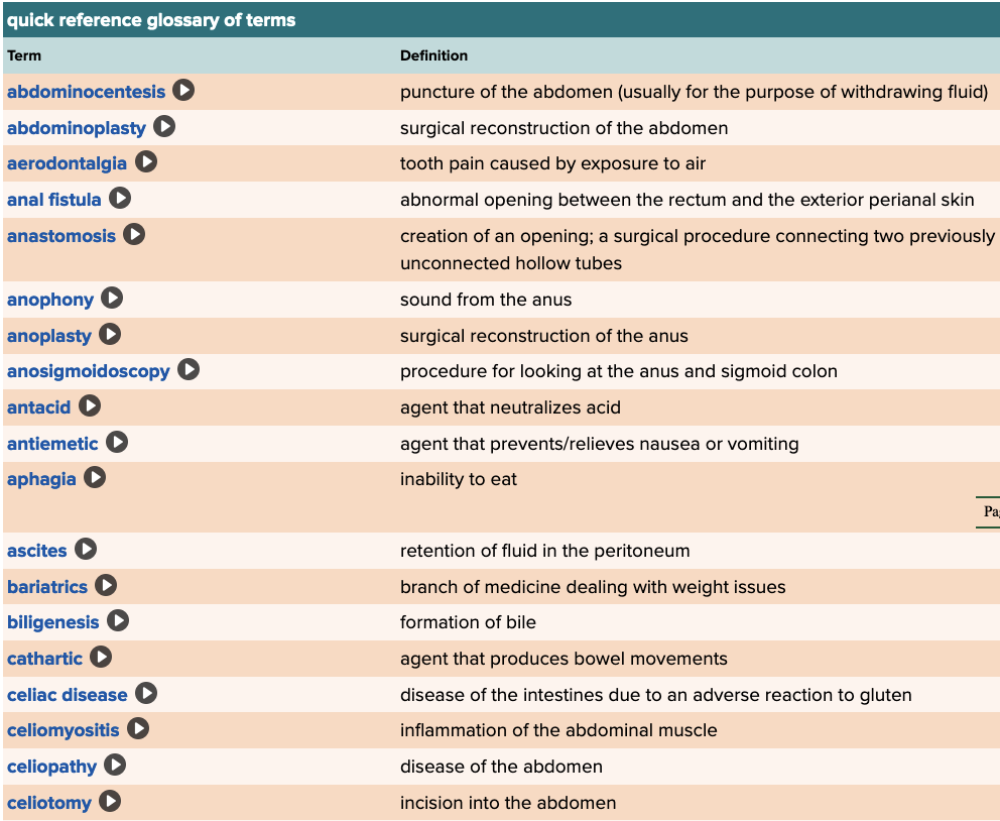 Chapter 11 Quick Reference
| back 84 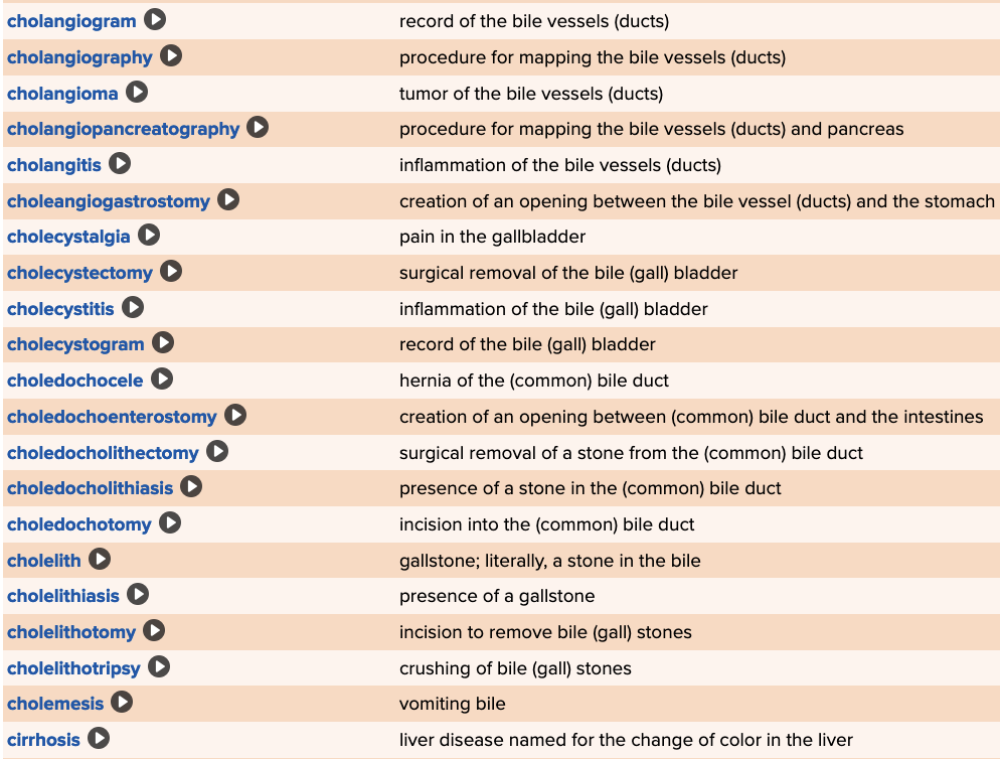 Chapter 11 Quick Reference
|
front 85 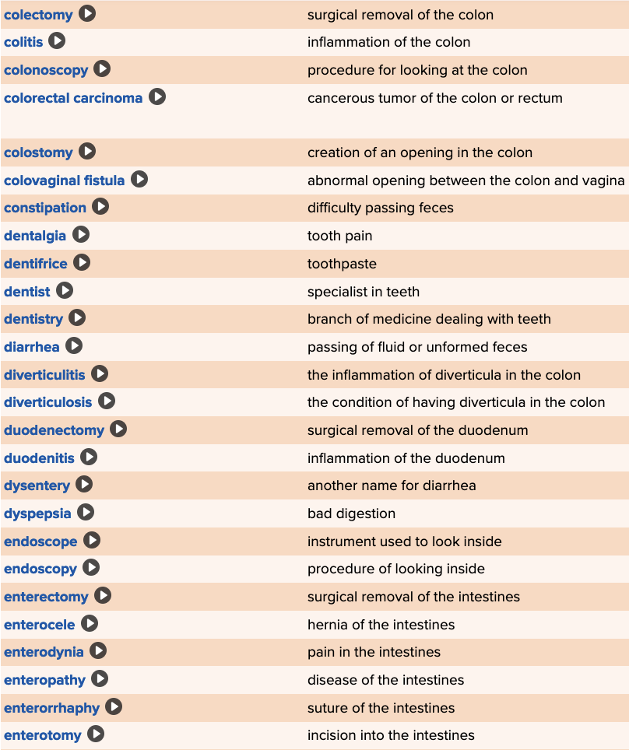 Chapter 11 Quick Reference
| back 85 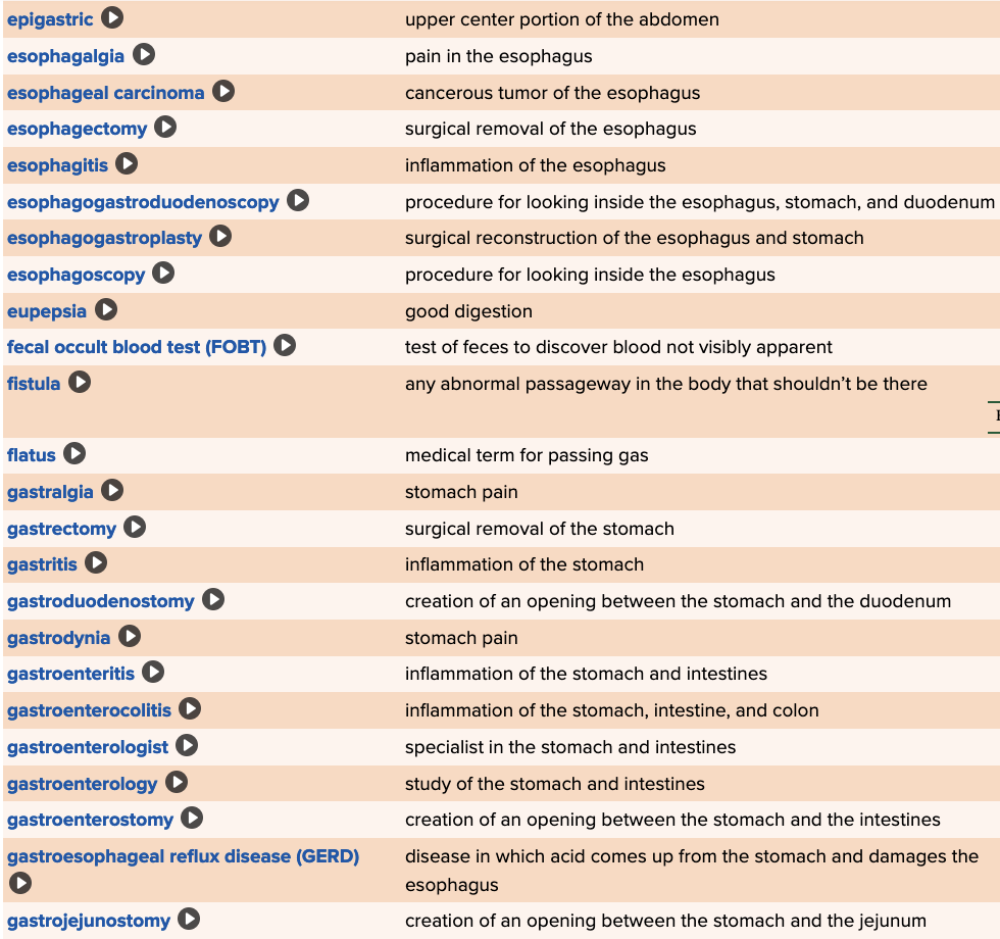 Chapter 11 Quick Reference
|
front 86 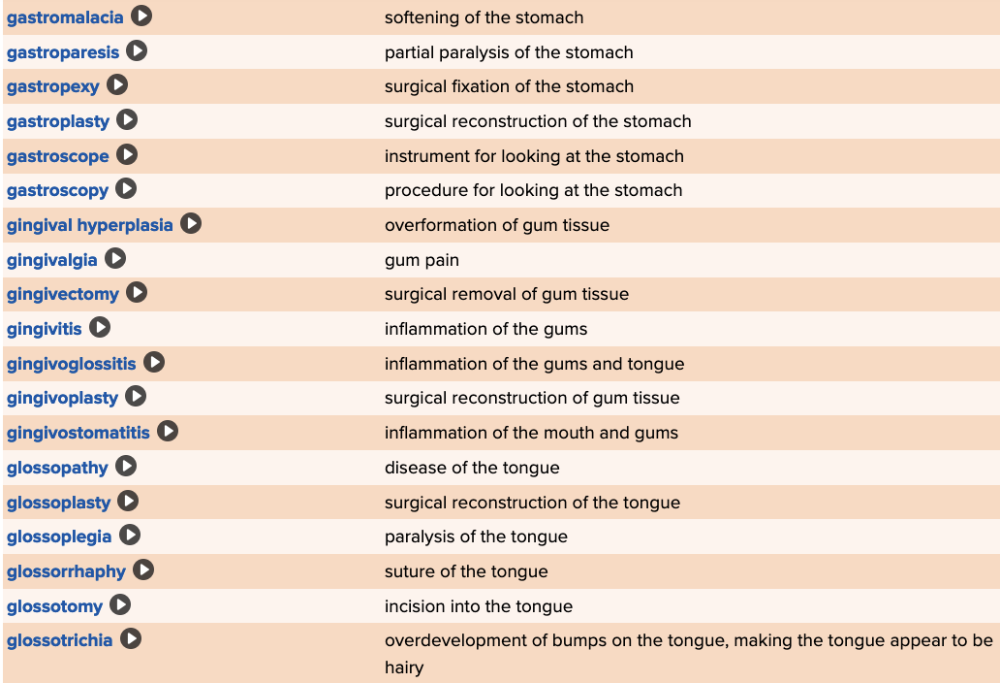 Chapter 11 Quick Reference
| back 86 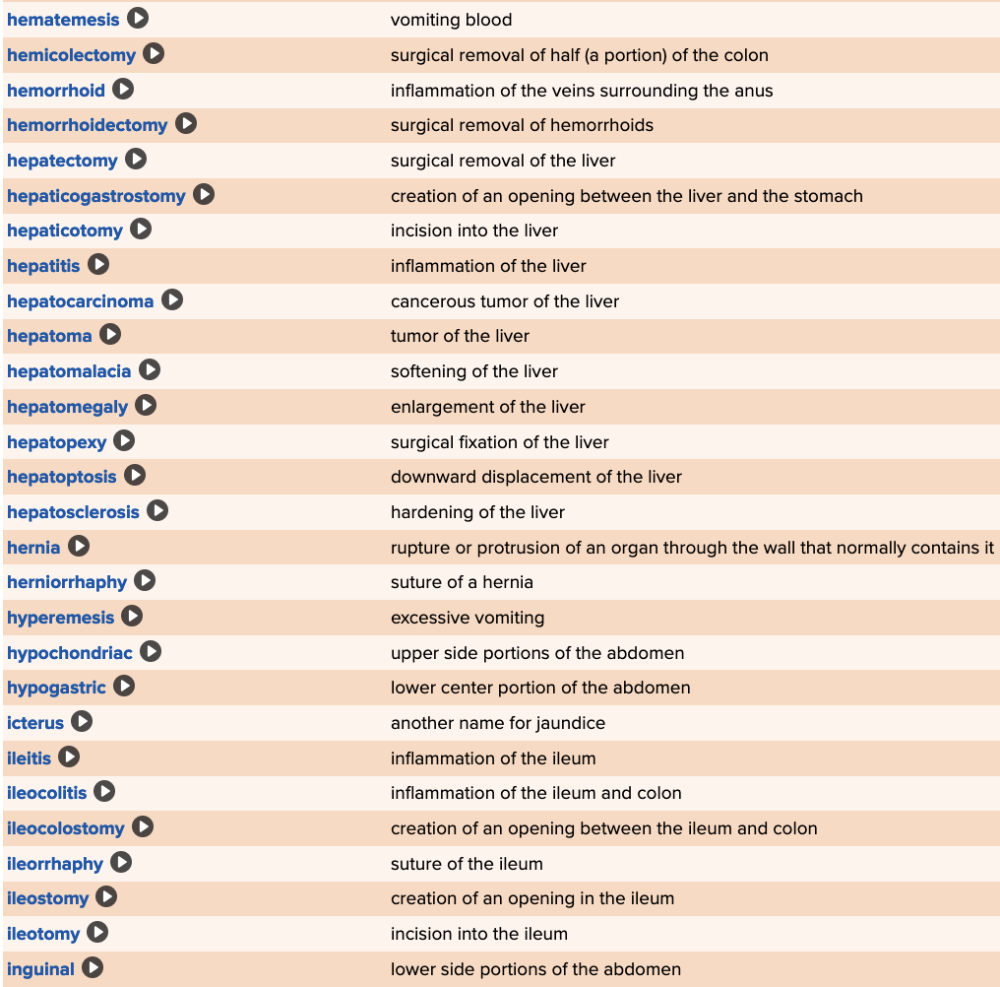 Chapter 11 Quick Reference
|
front 87 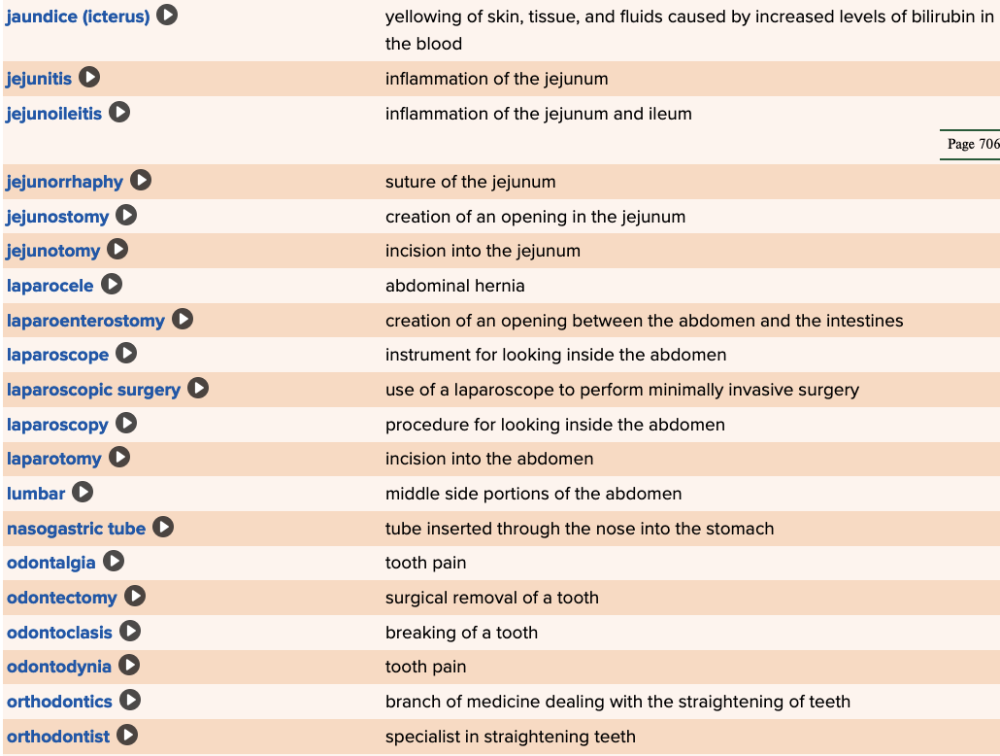 Chapter 11 Quick Reference
| back 87 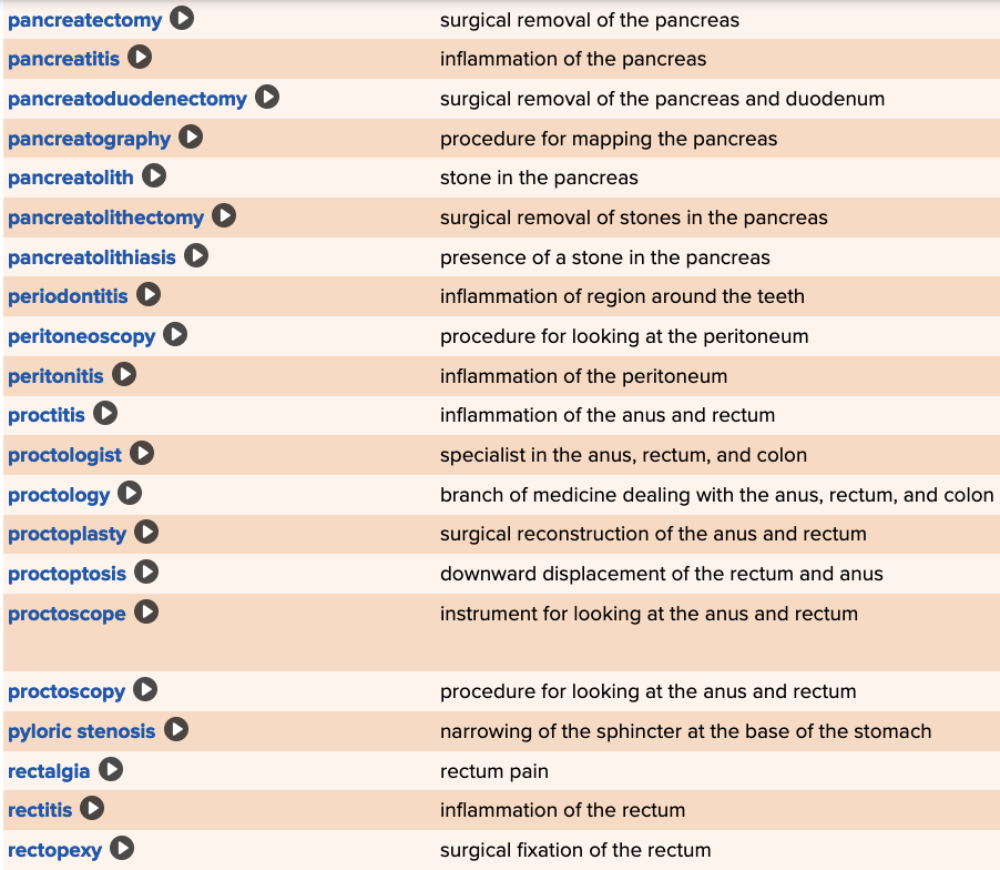 Chapter 11 Quick Reference
|
front 88 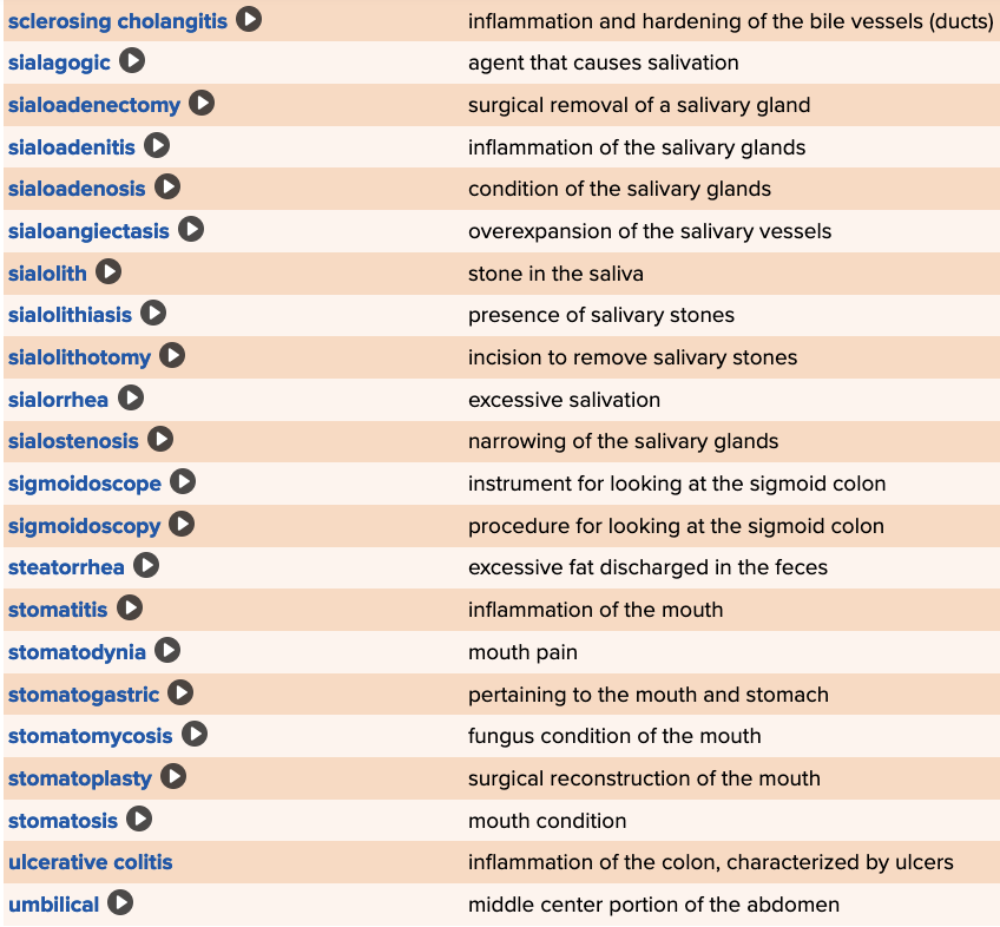 Chapter 11 Quick Reference
| back 88 no data |
front 89 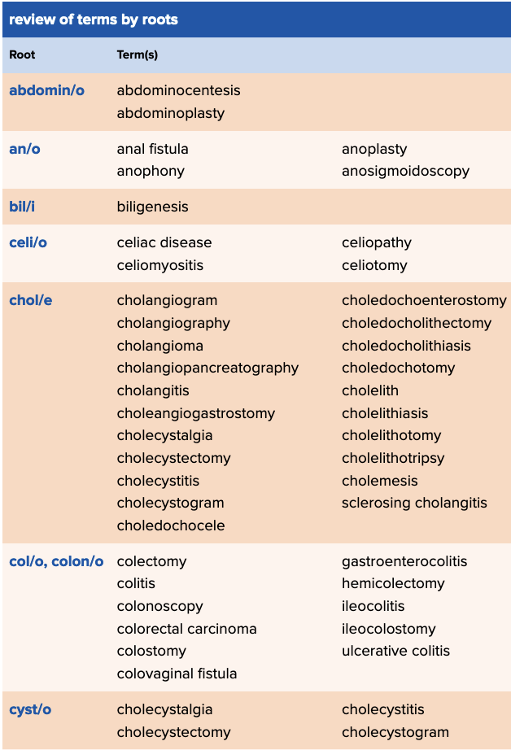 Chapter 11 Quick Reference
| back 89 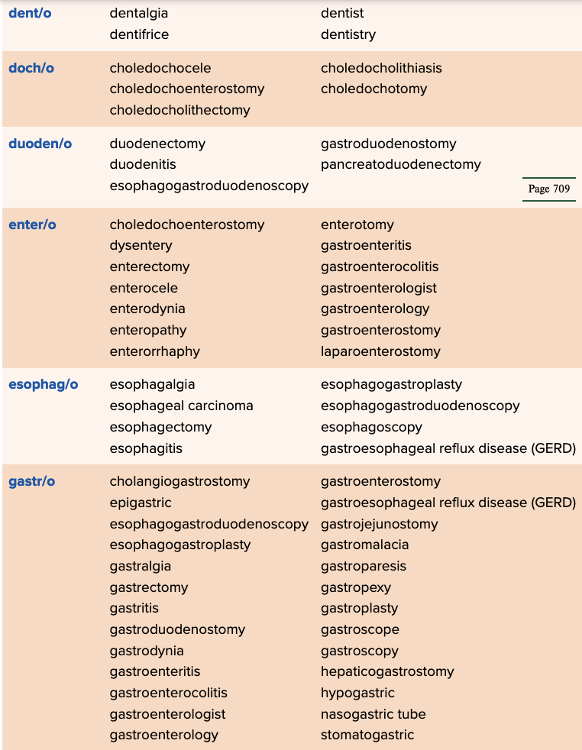 Chapter 11 Quick Reference
|
front 90 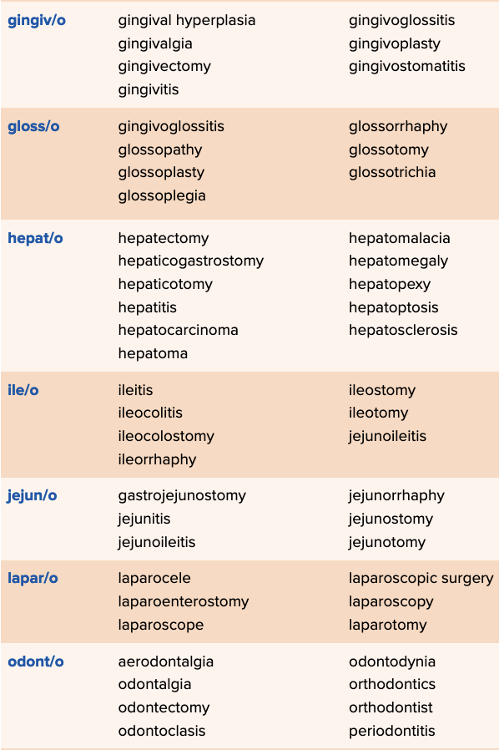 Chapter 11 Quick Reference
| back 90 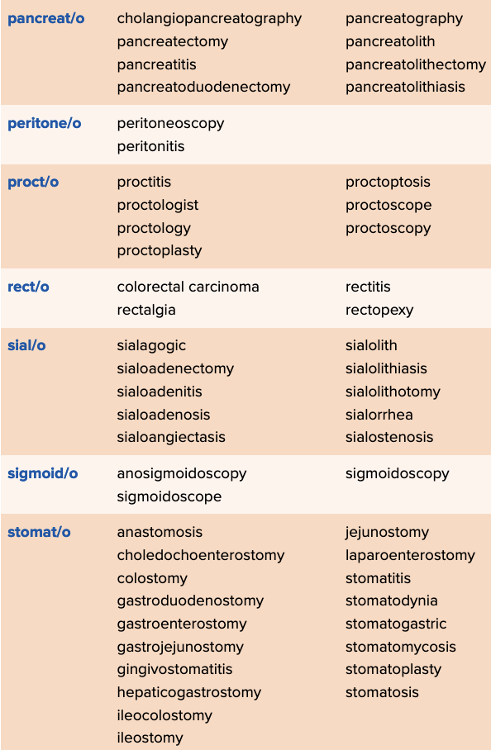 Chapter 11 Quick Reference
|
front 91 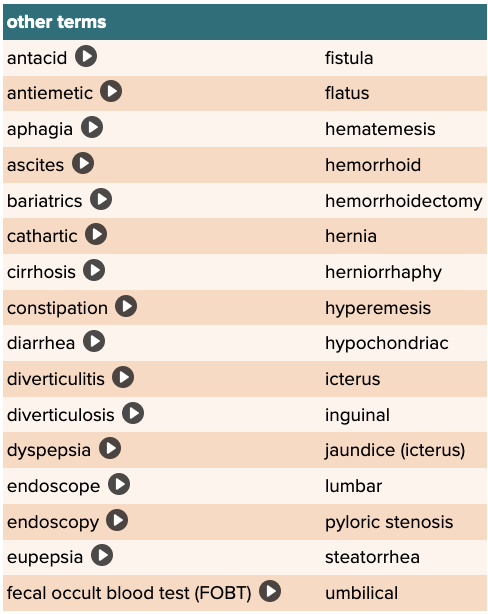 Chapter 11 Quick Reference
| back 91 no data |
front 92  Chapter 11 Review Exercises: Exercise 1, 2, 3. | back 92  |
front 93  Chapter 11 Review Exercises: Exercise 4, 5. | back 93 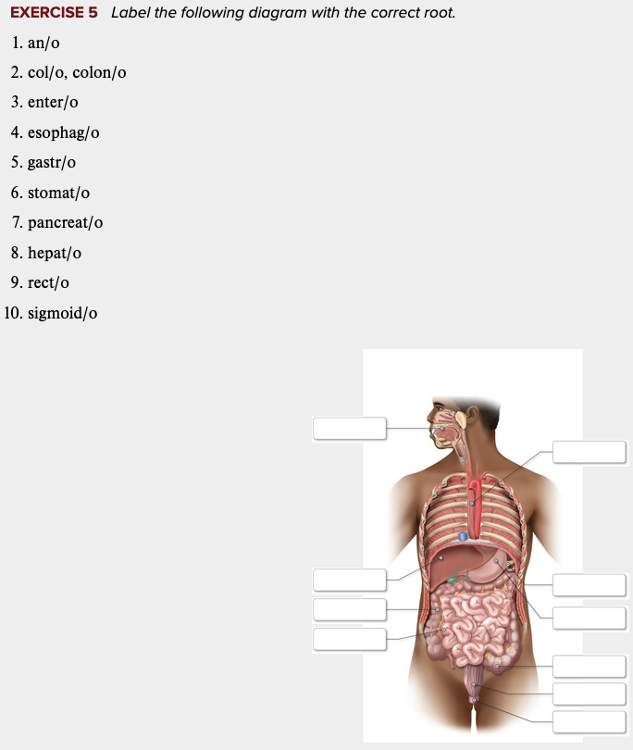 |
front 94  Chapter 11 Review Exercises: Exercise 6, 7, 8. | back 94 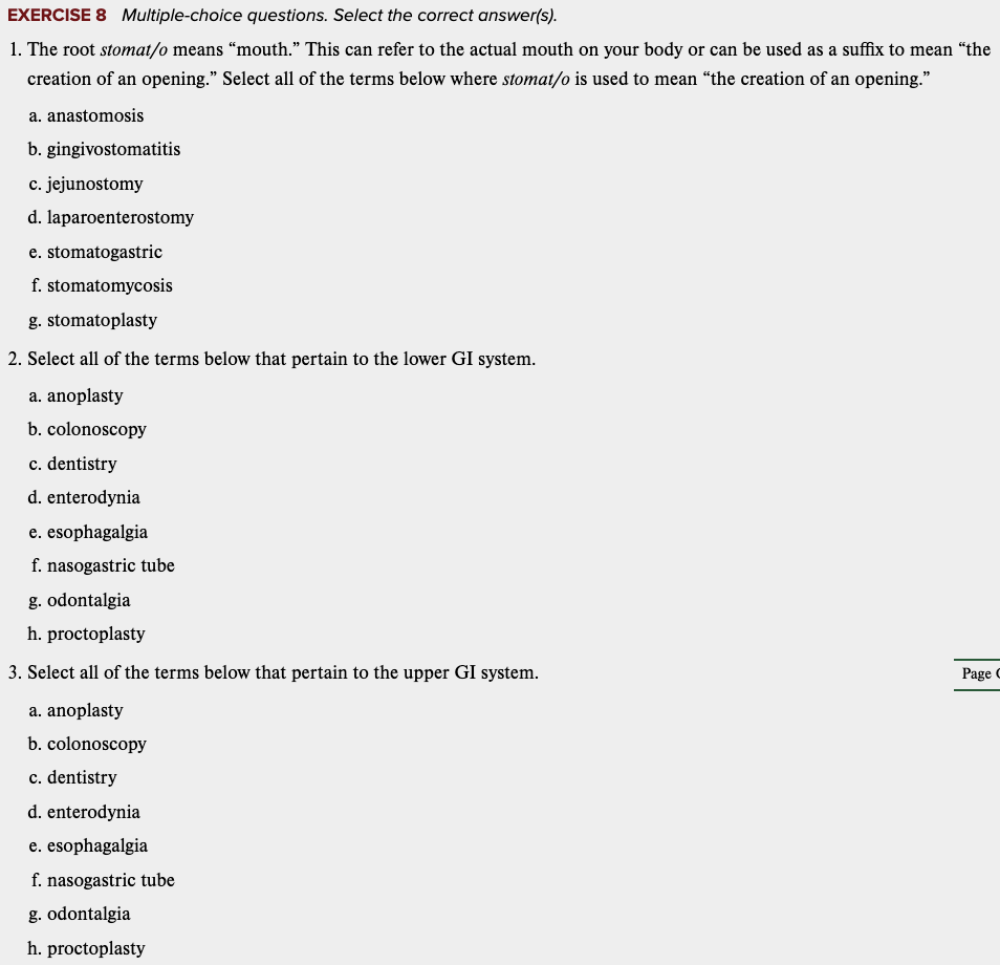 |
front 95 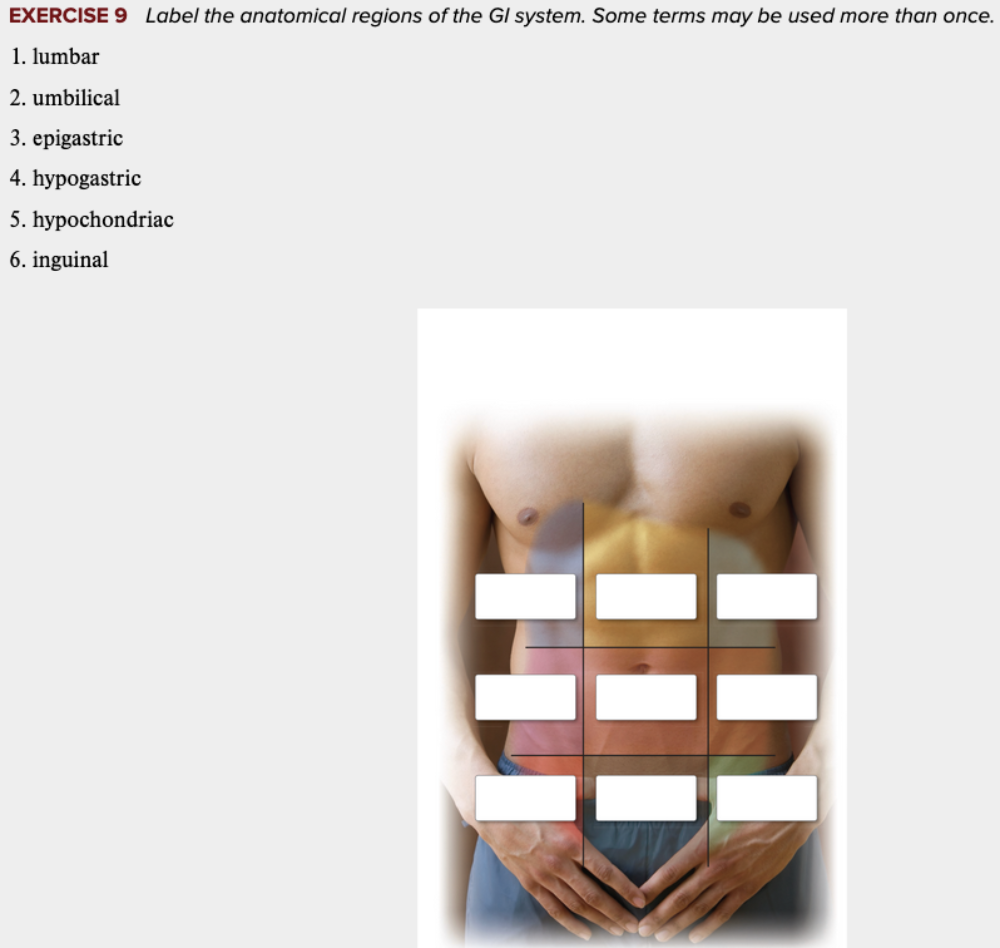 Chapter 11 Review Exercises: Exercise 9, 10. | back 95 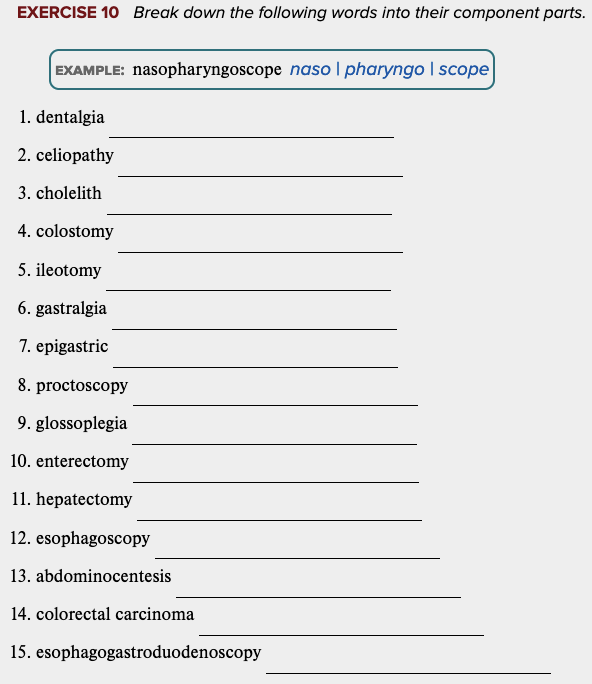 |
front 96  Chapter 11 Review Exercises: Exercise 11, 12. | back 96  |
front 97  Chapter 11 Review Exercises: Exercise 13, 14. | back 97  |
front 98  Chapter 11 Review Exercises: Exercise 15. | back 98  |
front 99  Chapter 11 Review Exercises: Exercise 16. | back 99  |
front 100  Chapter 11 Review Exercises: Exercise 17, 18. | back 100 no data |
front 101  Chapter 11 Review Exercises: Exercise 19, 20. | back 101 no data |
front 102 The ______ system is responsible for turning food into energy. | back 102 gastrointestinal, digestive, or GI |
front 103 The root term stomat-o is used to define what part of the gastrointestinal system? Multiple choice question.
| back 103 Mouth |
front 104 Which of the following is a root used to describe the gums? Multiple choice question.
| back 104 gingiv-o |
front 105 Click and drag on elements in order Rank the parts of a tooth in order from the outside (visible part) to the inside. | back 105  |
front 106 The pylorus is best defined as the ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 106 passageway from the stomach into the small intestine |
front 107 What is the process of carrying food through the body and breaking it apart? Multiple choice question.
| back 107 digestion |
front 108 Select all that apply Mark the roots that are used to describe the tongue. Multiple select question.
| back 108
|
front 109 Select all that apply Which of the following are roots used to describe the mouth? Multiple select question.
| back 109
|
front 110 ______ is the suffix for the term gastropexy. | back 110 Pexy |
front 111 What is the root for the term gingivitis? Multiple choice question.
| back 111 gingiv |
front 112 The ______ connects your mouth to your stomach. Multiple choice question.
| back 112 esophagus |
front 113 Click and drag on elements in order Rank the parts of a tooth in order from the uppermost (chewing surface) to the lowermost. | back 113 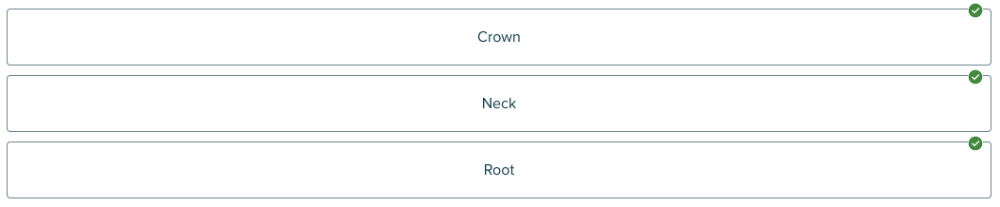 |
front 114 Select all that apply The lower GI tract is made up of ______. Multiple select question.
| back 114
|
front 115 Chyme is formed in the ______.
| back 115 stomach |
front 116 Select all that apply The small intestine divides into three sections. What are the names of those sections? Multiple select question.
| back 116
|
front 117 Which of the following is the strongest muscle in the body relative to its size? Multiple choice question.
| back 117 Tongue |
front 118 A fistula is a connection between two tubes that should not connect. For example, an opening between the anus and nearby skin is called a(n) ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 118 anal fistula |
front 119 The ______ must produce a new layer of mucus every two weeks or it will digest itself. Multiple choice question.
| back 119 stomach |
front 120 Which of the following is the root for the term esophagitis? Multiple choice question.
| back 120 esophag |
front 121 Select all that apply Bile is sent to the ______ ______ and the ______ in the digestive system. Multiple select question.
| back 121
|
front 122 Most of the chemical breakdown in the small intestine happens in the ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 122 duodenum |
front 123 The suffix -itis means inflammation. Inflammation of the salivary glands is called ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 123 sialoadenitis |
front 124 The suffix -itis means inflammation. Inflammation of the intestines is called ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 124 enteritis |
front 125 The peritoneum is the membrane that Multiple choice question.
| back 125 lines the abdominal cavity. |
front 126 The root that means both anus and rectum is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 126 proct/o |
front 127 Select all that apply Select the roots for abdomen. Multiple select question.
| back 127
|
front 128 Cyst/o is the root for ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 128 bladder |
front 129 The ______ makes chemicals known as enzymes that break down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. Multiple choice question.
| back 129 pancreas |
front 130 Lithos is a Greek word that means stone. A gallstone (stone in the gallbladder) is called a ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 130 cholelith |
front 131 The root for duct is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 131 doch/o |
front 132 The membrane that surrounds the gastrointestinal organs in the abdomen is called the ______. | back 132 peritoneum |
front 133 The suffix -itis means inflammation. Inflammation of the liver is termed ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 133 hepatitis |
front 134 In the term laparoscope, the root means ______. | back 134 abdomen or abdominal |
front 135 The suffix -itis means inflammation. Peritonitis means inflammation of the ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 135 membrane lining the abdominal cavity |
front 136 Bile is used to digest ______.
| back 136 fatty foods |
front 137 In the term stomatodynia, the suffix means ______. | back 137 pain |
front 138 The role of the ______ is to get rid of dangerous toxins, store energy, and break down fat. Multiple choice question.
| back 138 liver |
front 139 ______ is a yellow discoloration of the eyes and skin due to accumulation of bilirubin in the blood. | back 139 jaundice or icterus |
front 140 The Greek word for stone is lithos. A condition that involves a stone in the common bile duct is called ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 140 choledocholithiasis |
front 141 Tooth pain caused by exposure to air is termed ______. | back 141 aerodontalgia |
front 142 Select all that apply The root for liver is ______. Multiple select question.
| back 142
|
front 143 The prefix in the term dyspepsia means ______. | back 143 no data |