Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 5: The Nervous System - Neurology and Psychiatry
front 1  Chapter 5 Introduction and Overview of the Nervous System | back 1  |
front 2  Chapter 5.1 Word Parts of the Nervous System Word Parts Associated with the Structure of the Nervous System | back 2 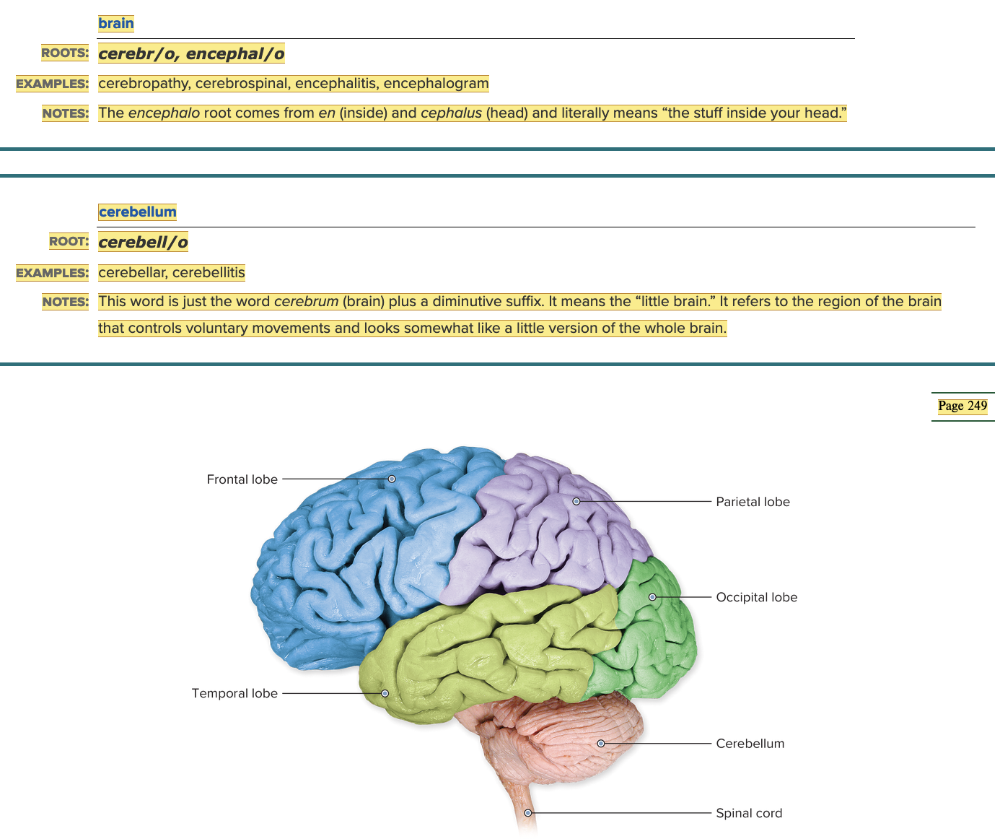 Chapter 5.1 Word Parts of the Nervous System Word Parts Associated with the Structure of the Nervous System
|
front 3  Chapter 5.1 Word Parts of the Nervous System Word Parts Associated with the Structure of the Nervous System
| back 3 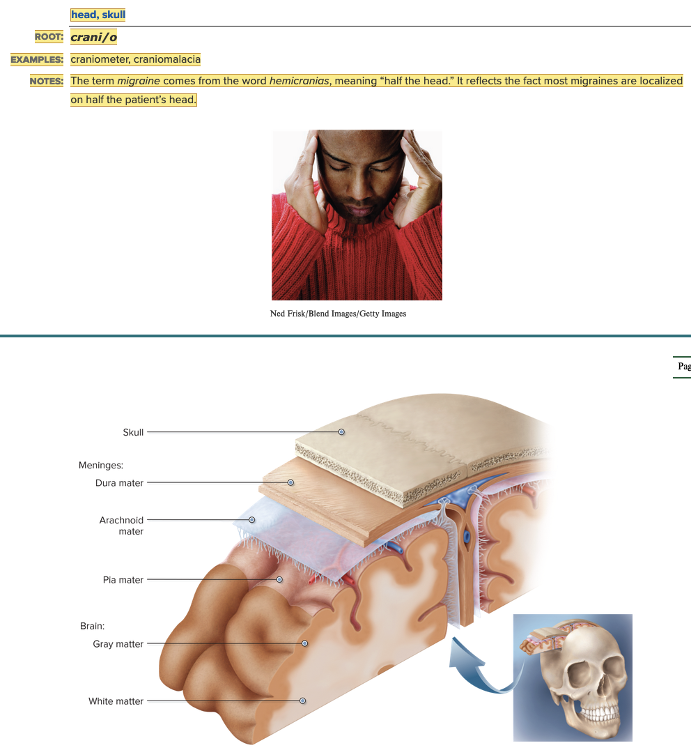 Chapter 5.1 Word Parts of the Nervous System Word Parts Associated with the Structure of the Nervous System
|
front 4  Chapter 5.1 Word Parts of the Nervous System Word Parts Associated with the Structure of the Nervous System
| back 4 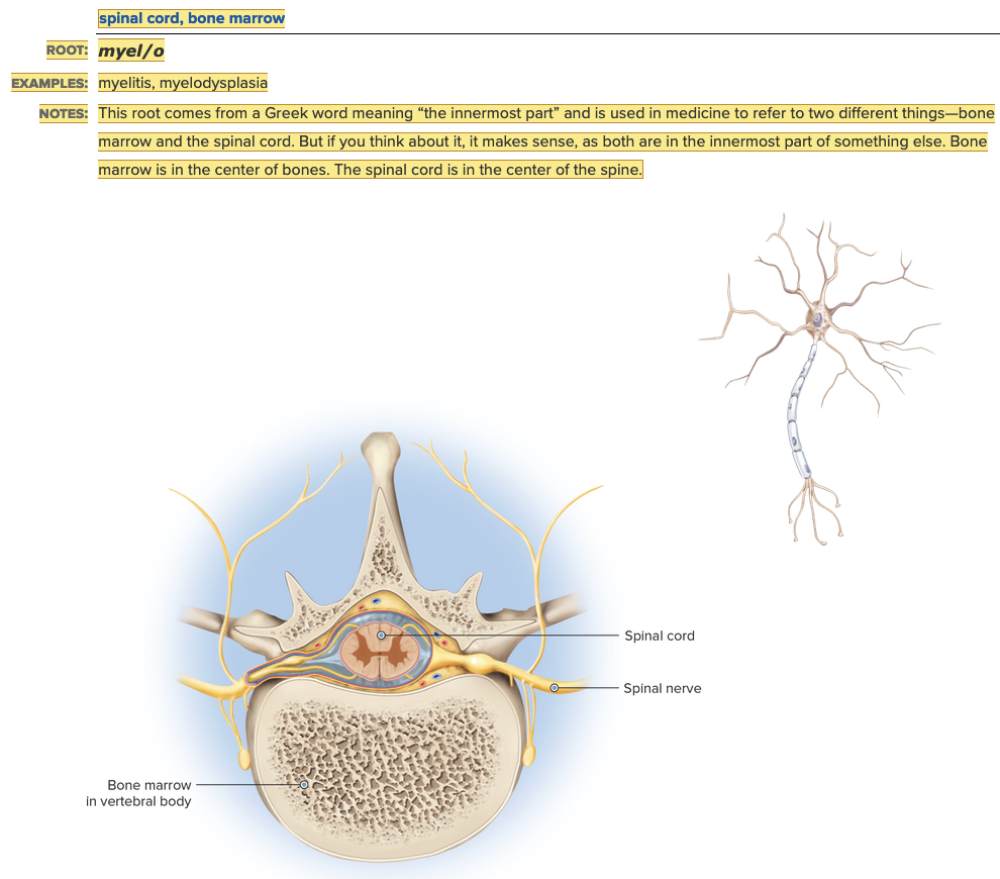 Chapter 5.1 Word Parts of the Nervous System Word Parts Associated with the Structure of the Nervous System
|
front 5  Chapter 5.1 Word Parts of the Nervous System Word Parts Associated with the Function of the Nervous System | back 5 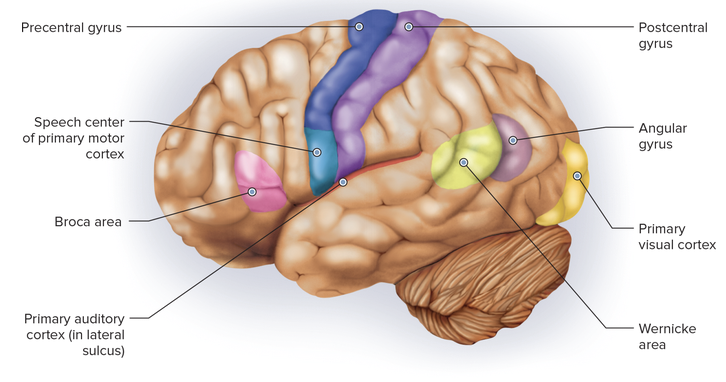 Chapter 5.1 Word Parts of the Nervous System Word Parts Associated with the Function of the Nervous System |
front 6 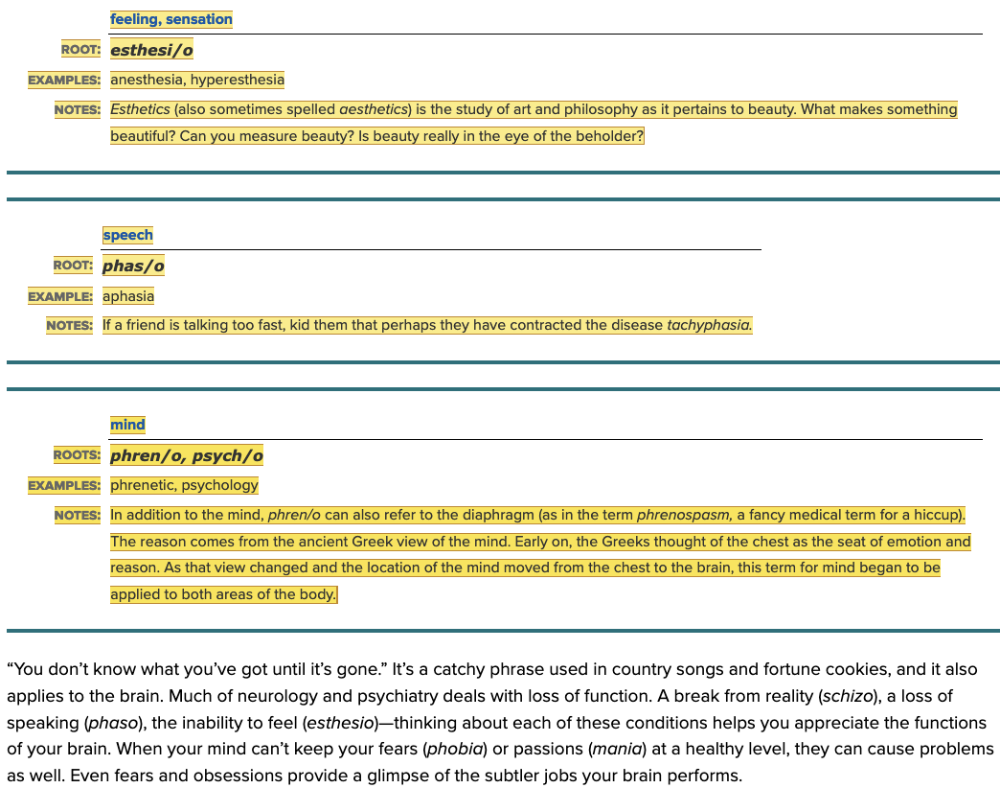 Chapter 5.1 Word Parts of the Nervous System Word Parts Associated with the Function of the Nervous System
| back 6 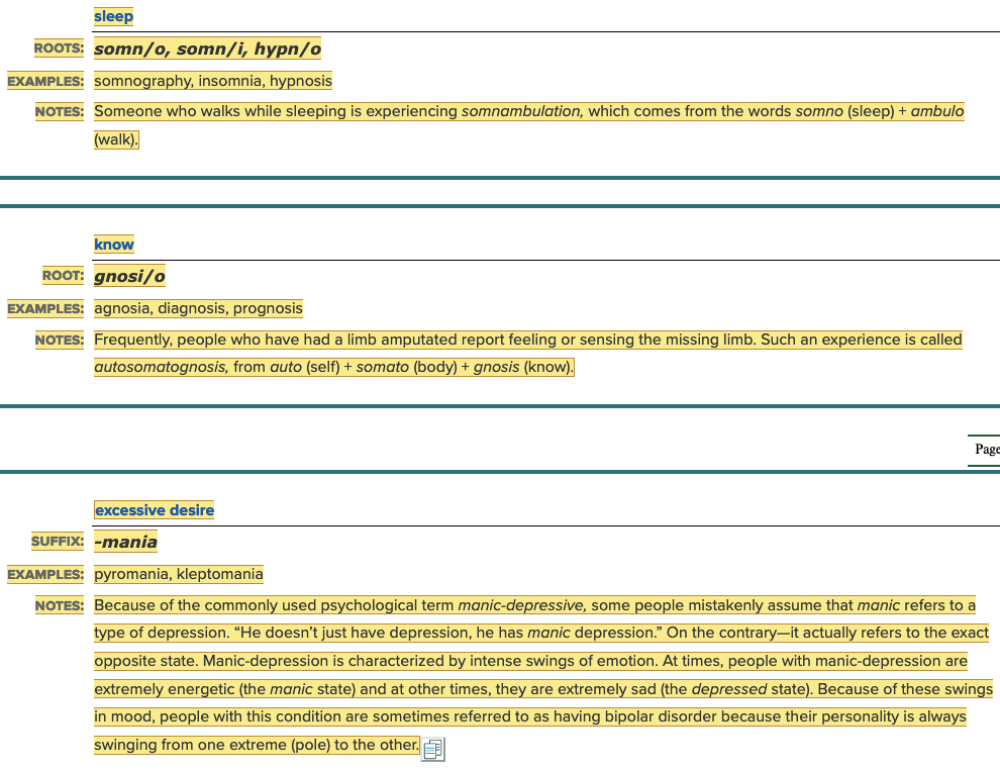 Chapter 5.1 Word Parts of the Nervous System Word Parts Associated with the Function of the Nervous System
|
front 7  Chapter 5.1 Word Parts of the Nervous System Word Parts Associated with the Function of the Nervous System
| back 7  Chapter 5.1 Word Parts of the Nervous System Word Parts Associated with the Function of the Nervous System
|
front 8 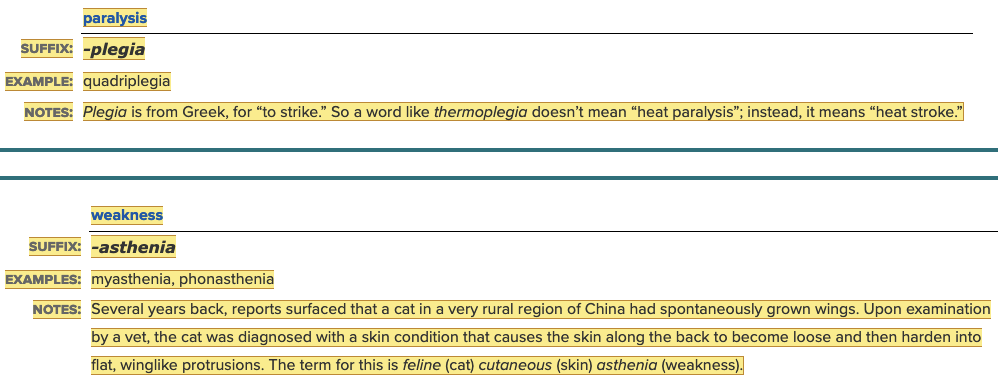 Chapter 5.1 Word Parts of the Nervous System Word Parts Associated with the Function of the Nervous System
| back 8 no data |
front 9  Learning Outcome 5.1 Exercises: Exercise 1, 2. | back 9 no data |
front 10 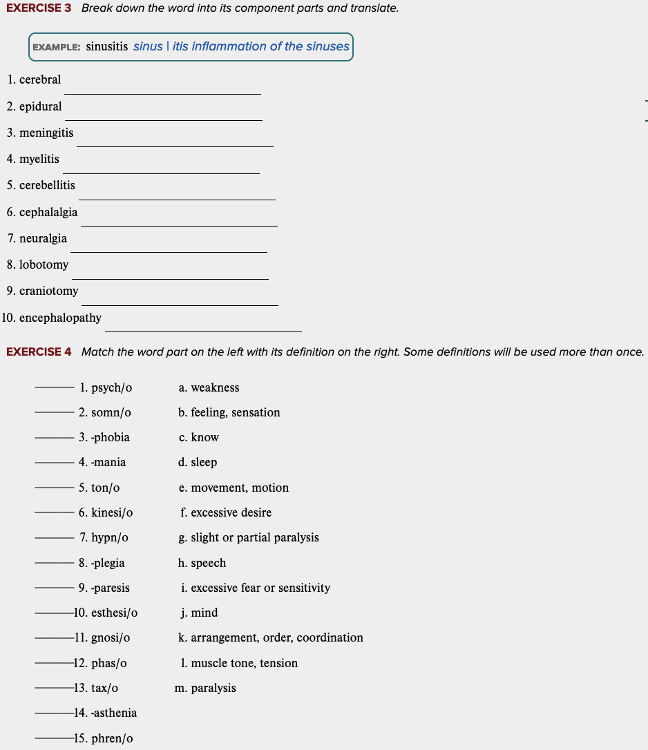 Learning Outcome 5.1 Exercises: Exercise 3, 4. | back 10 no data |
front 11  Learning Outcome 5.1 Exercises: Exercise 5, 6. | back 11 no data |
front 12  Learning Outcome 5.1 Exercises: Exercise 7, 8. | back 12 no data |
front 13  Learning Outcome 5.1 Exercises: Exercise 9, 10. | back 13 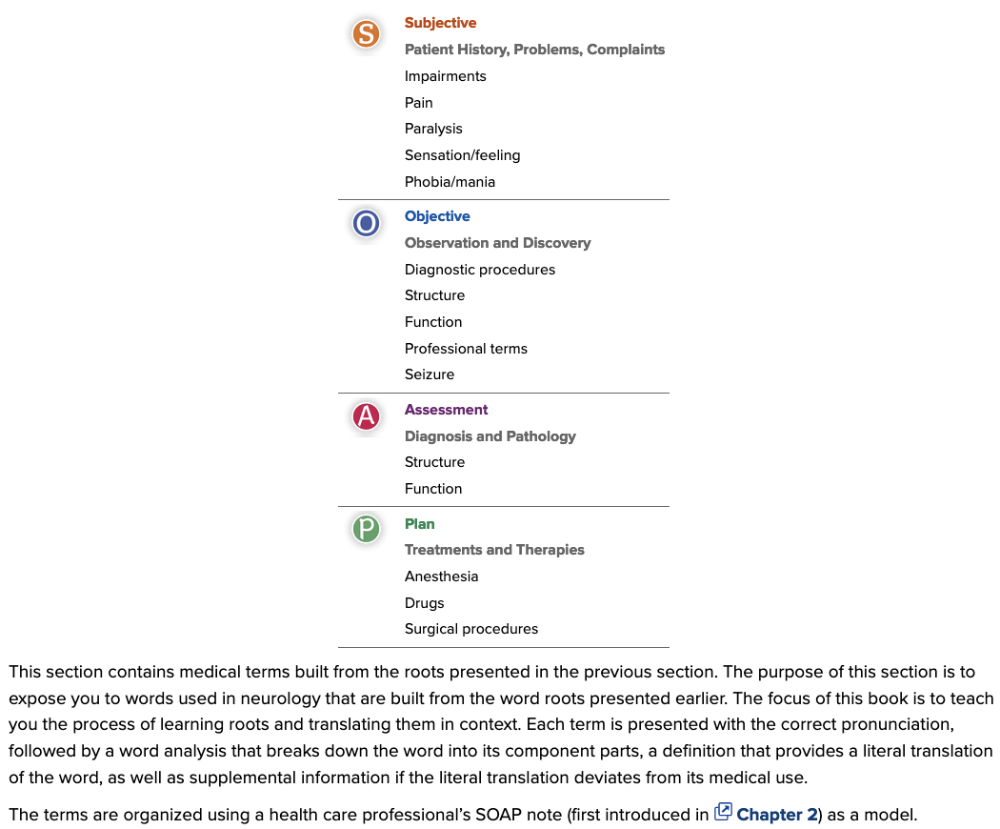 |
front 14  Chapter 5.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
| back 14 no data |
front 15  Chapter 5.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
| back 15  Chapter 5.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
|
front 16 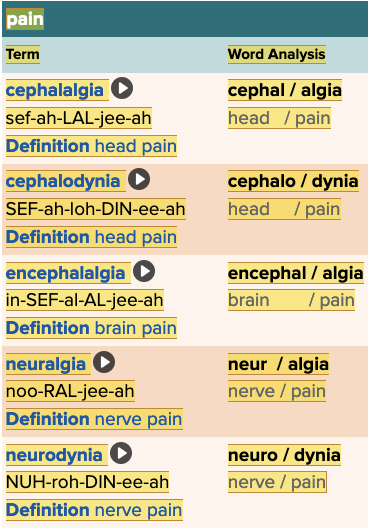 Chapter 5.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
| back 16 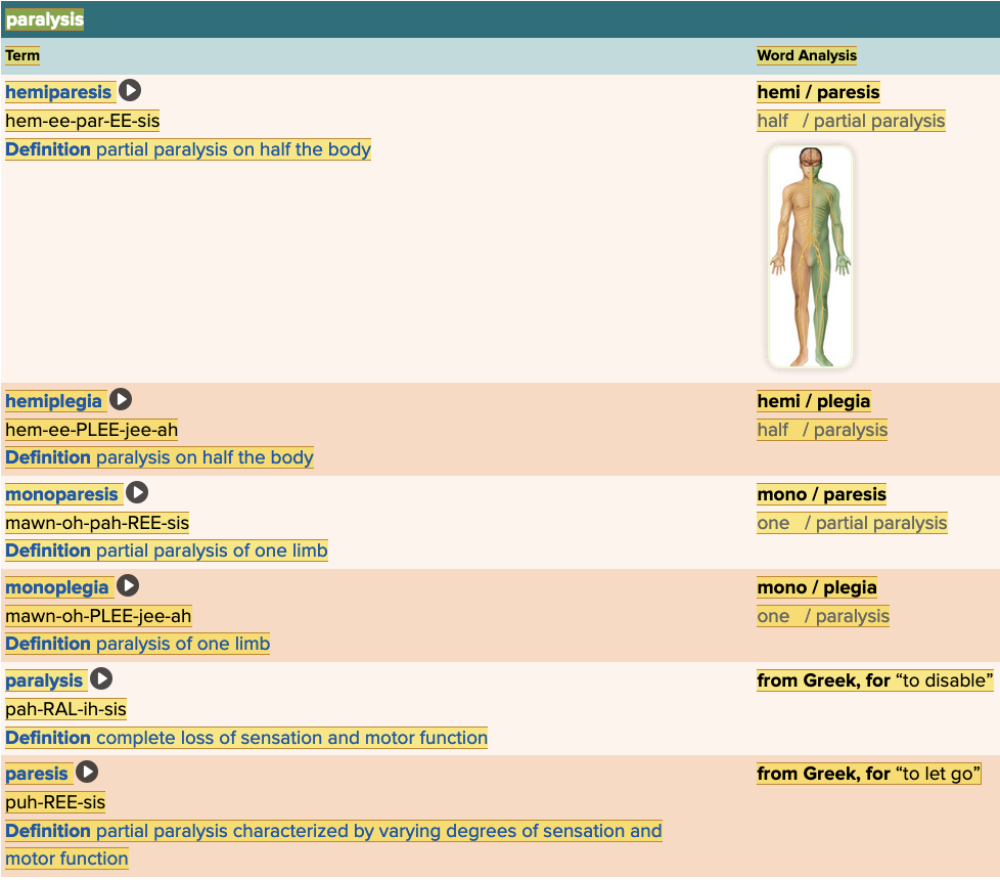 Chapter 5.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
|
front 17 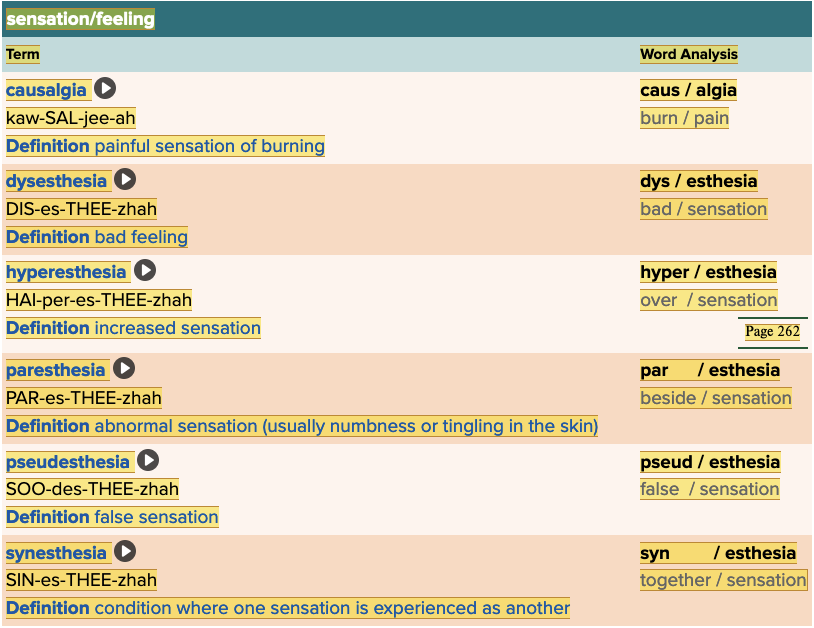 Chapter 5.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
| back 17 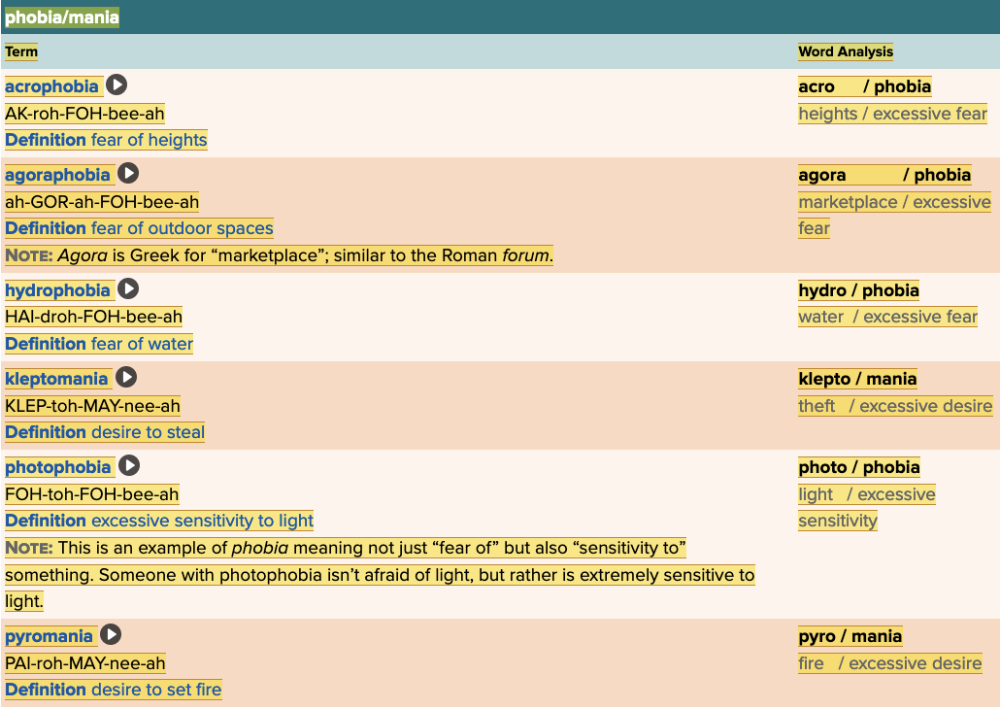 Chapter 5.2 Patient History, Problems, Complaints
|
front 18  Learning Outcome 5.2 Exercises: Exercise 1. | back 18 no data |
front 19  Learning Outcome 5.2 Exercises: Exercise 2. | back 19 no data |
front 20  Learning Outcome 5.2 Exercises: Exercise 3. | back 20 no data |
front 21  Learning Outcome 5.2 Exercises: Exercise 4. | back 21 no data |
front 22  Learning Outcome 5.2 Exercises: Exercise 5. | back 22 no data |
front 23  Learning Outcome 5.2 Exercises: Exercise 6. | back 23 no data |
front 24  Learning Outcome 5.2 Exercises: Exercise 7. | back 24 no data |
front 25  Learning Outcome 5.2 Exercises: Exercise 8, 9. | back 25  |
front 26  Chapter 5.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 26  Chapter 5.3 Observation and Discovery
|
front 27  Chapter 5.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 27 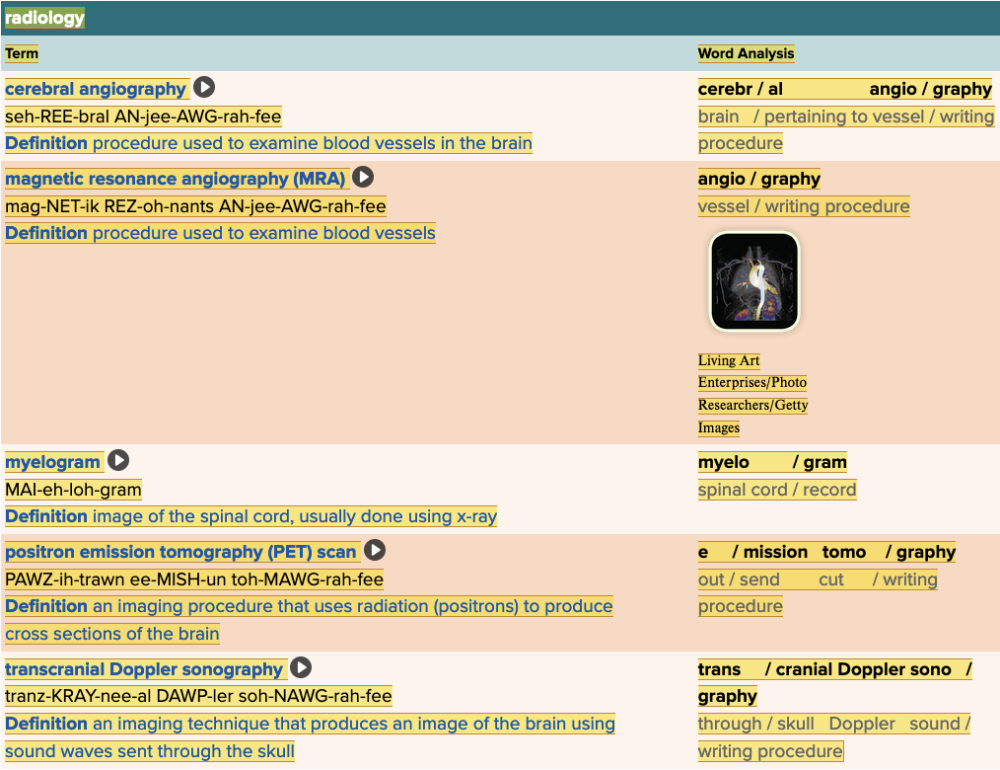 Chapter 5.3 Observation and Discovery
|
front 28  Chapter 5.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 28  Chapter 5.3 Observation and Discovery
|
front 29  Chapter 5.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 29 no data |
front 30  Chapter 5.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 30  Chapter 5.3 Observation and Discovery
|
front 31  Chapter 5.3 Observation and Discovery
| back 31  Chapter 5.3 Observation and Discovery
|
front 32  Learning Outcome 5.3 Exercises: Exercise 1. | back 32 no data |
front 33  Learning Outcome 5.3 Exercises: Exercise 2. | back 33 no data |
front 34  Learning Outcome 5.3 Exercises: Exercise 3. | back 34 no data |
front 35  Learning Outcome 5.3 Exercises: Exercise 4. | back 35 no data |
front 36  Learning Outcome 5.3 Exercises: Exercise 5. | back 36 no data |
front 37  Learning Outcome 5.3 Exercises: Exercise 6. | back 37 no data |
front 38  Learning Outcome 5.3 Exercises: Exercise 7. | back 38  |
front 39 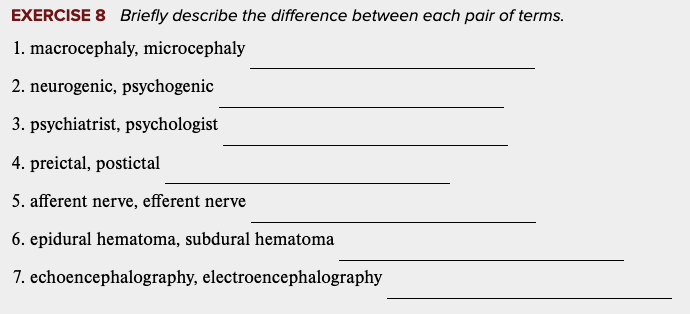 Learning Outcome 5.3 Exercises: Exercise 8. | back 39 no data |
front 40  Chapter 5.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 40  Chapter 5.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
|
front 41 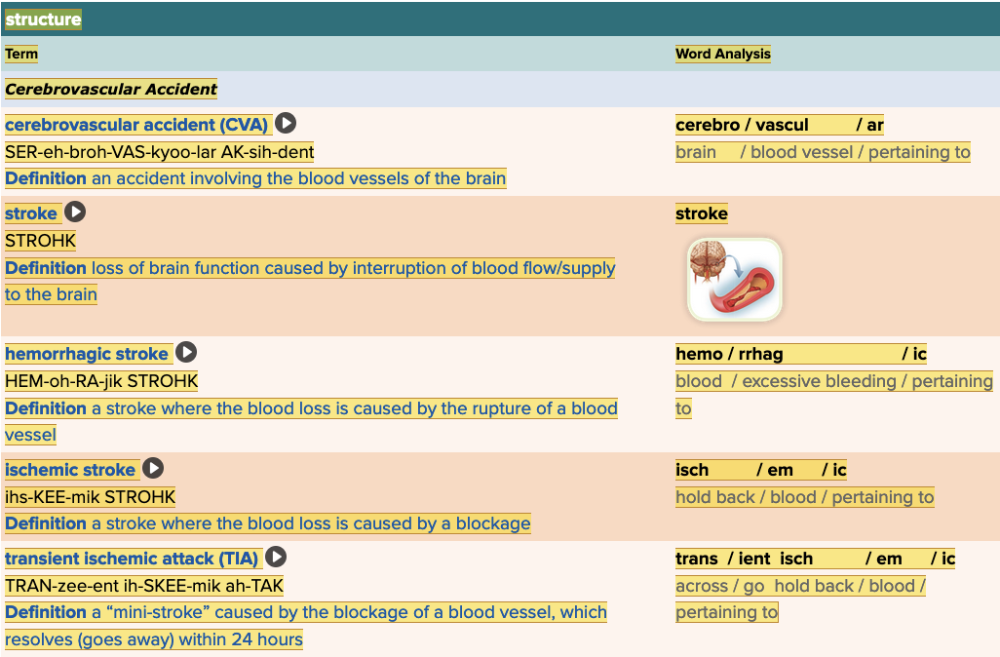 Chapter 5.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 41 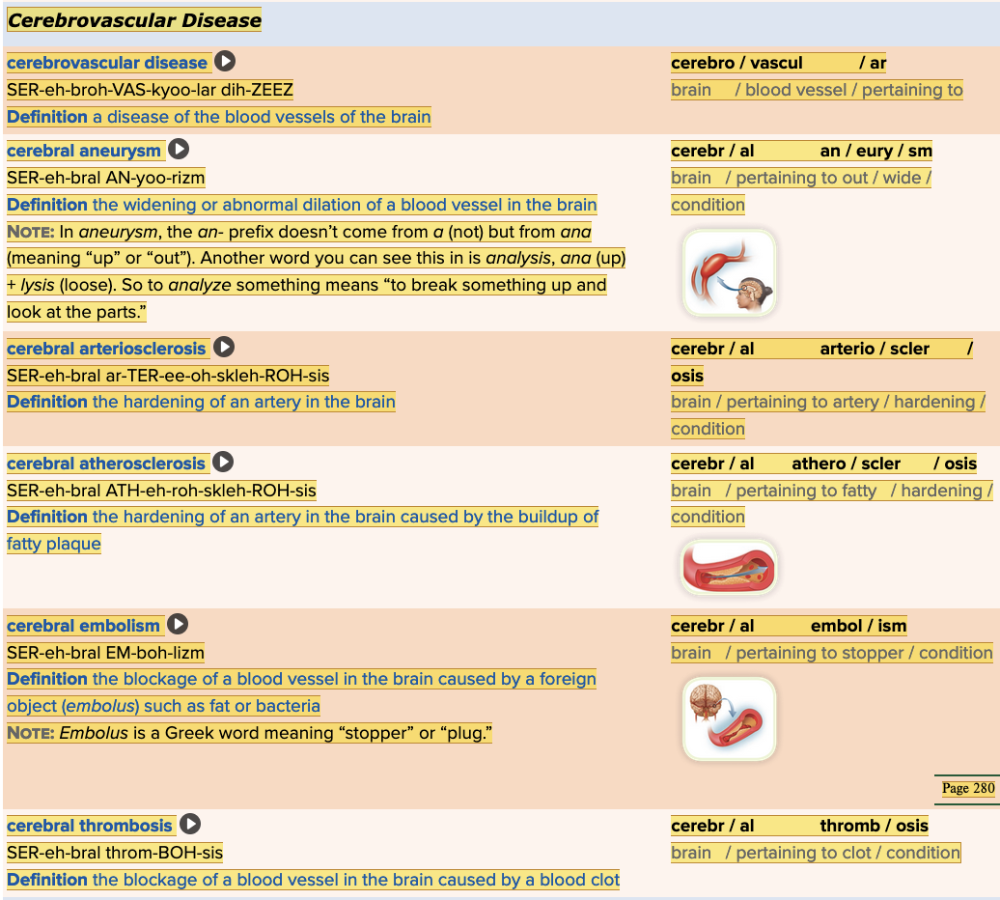 Chapter 5.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
|
front 42 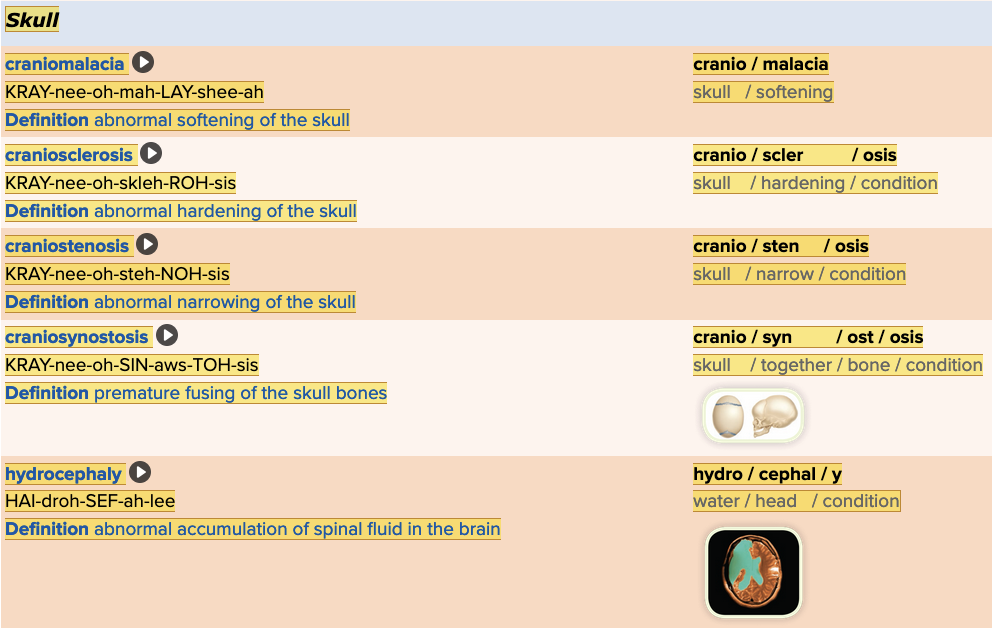 Chapter 5.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 42 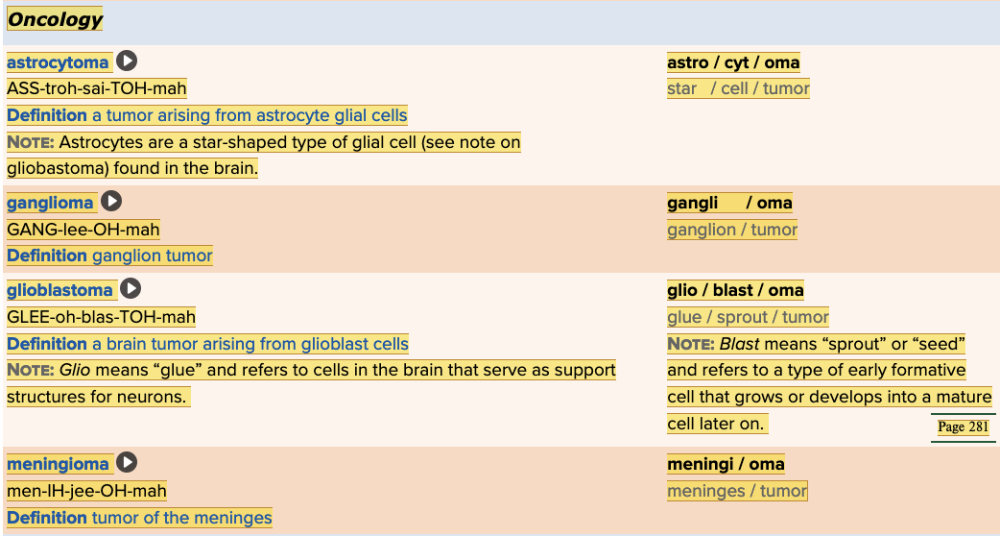 Chapter 5.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
|
front 43  Chapter 5.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 43  Chapter 5.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
|
front 44  Chapter 5.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 44 no data |
front 45  Chapter 5.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 45 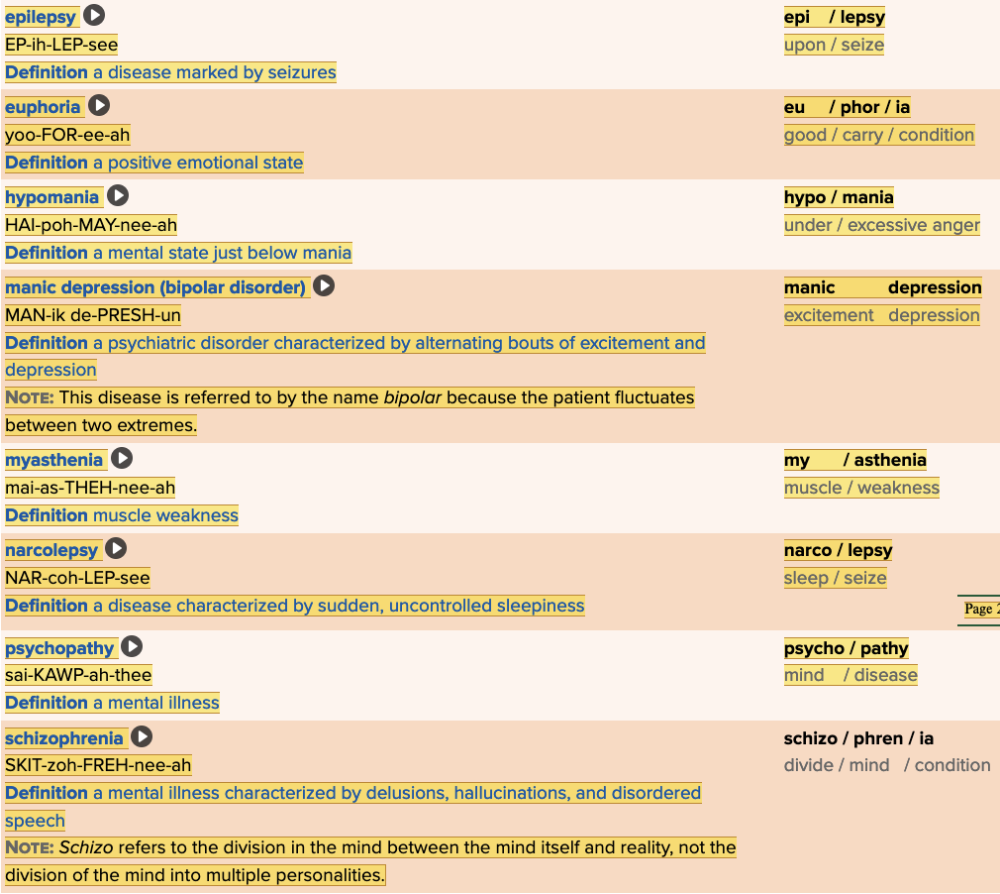 Chapter 5.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
|
front 46 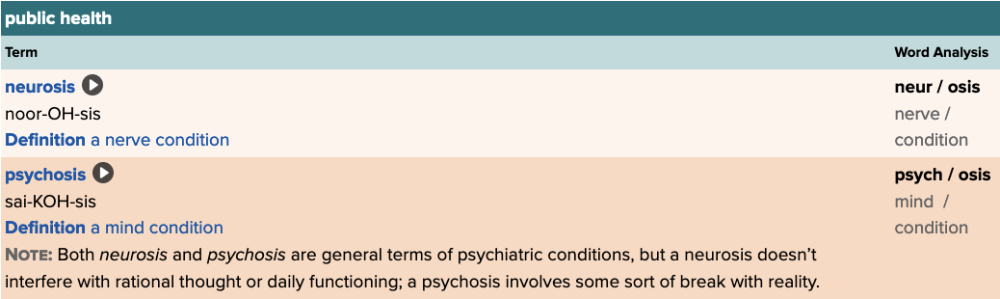 Chapter 5.4 Diagnosis and Pathology
| back 46 no data |
front 47 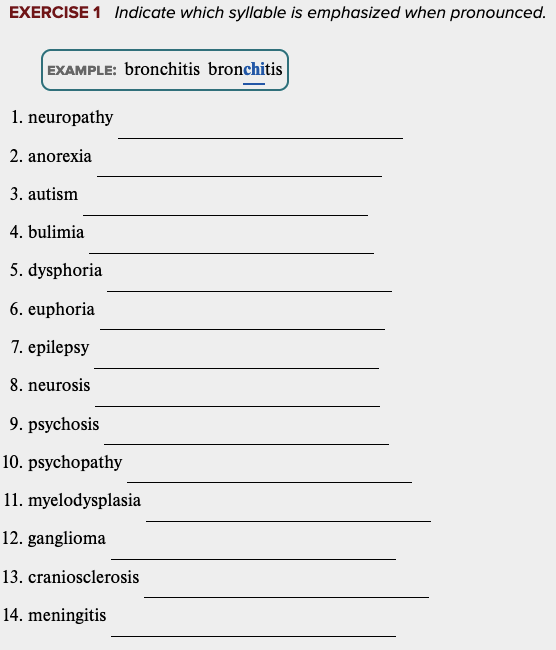 Learning Outcome 5.4 Exercises: Exercise 1. | back 47 no data |
front 48  Learning Outcome 5.4 Exercises: Exercise 2. | back 48 no data |
front 49  Learning Outcome 5.4 Exercises: Exercise 3. | back 49 no data |
front 50  Learning Outcome 5.4 Exercises: Exercise 4. | back 50 no data |
front 51  Learning Outcome 5.4 Exercises: Exercise 5. | back 51 no data |
front 52  Learning Outcome 5.4 Exercises: Exercise 6. | back 52 no data |
front 53  Learning Outcome 5.4 Exercises: Exercise 7. | back 53  |
front 54 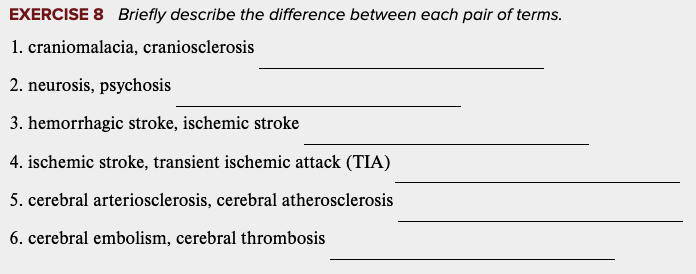 Learning Outcome 5.4 Exercises: Exercise 8. | back 54 no data |
front 55  Chapter 5.5 Treatments and Therapies
| back 55 no data |
front 56 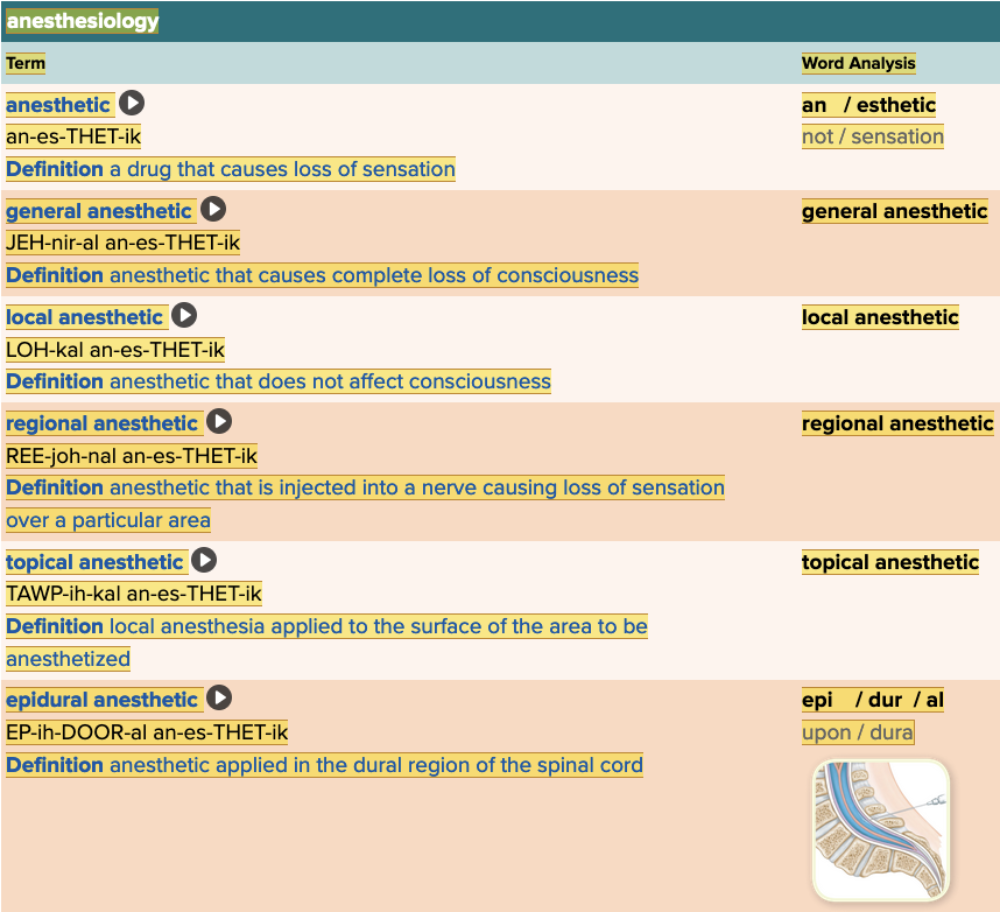 Chapter 5.5 Treatments and Therapies
| back 56 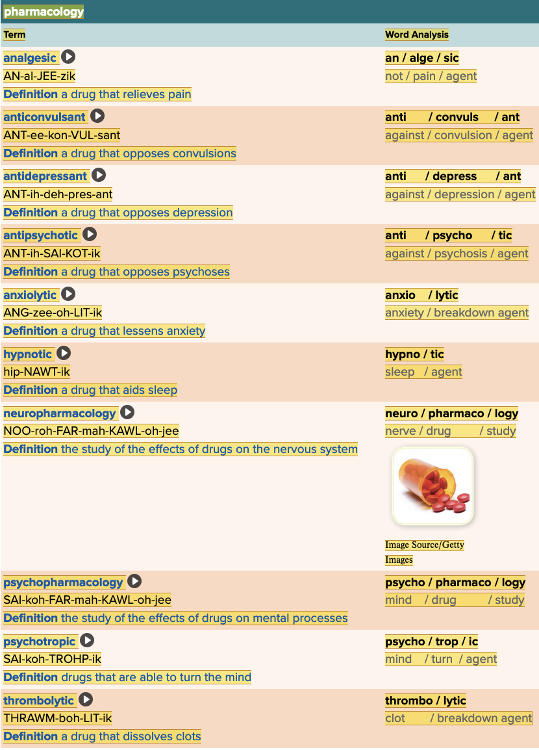 Chapter 5.5 Treatments and Therapies
|
front 57 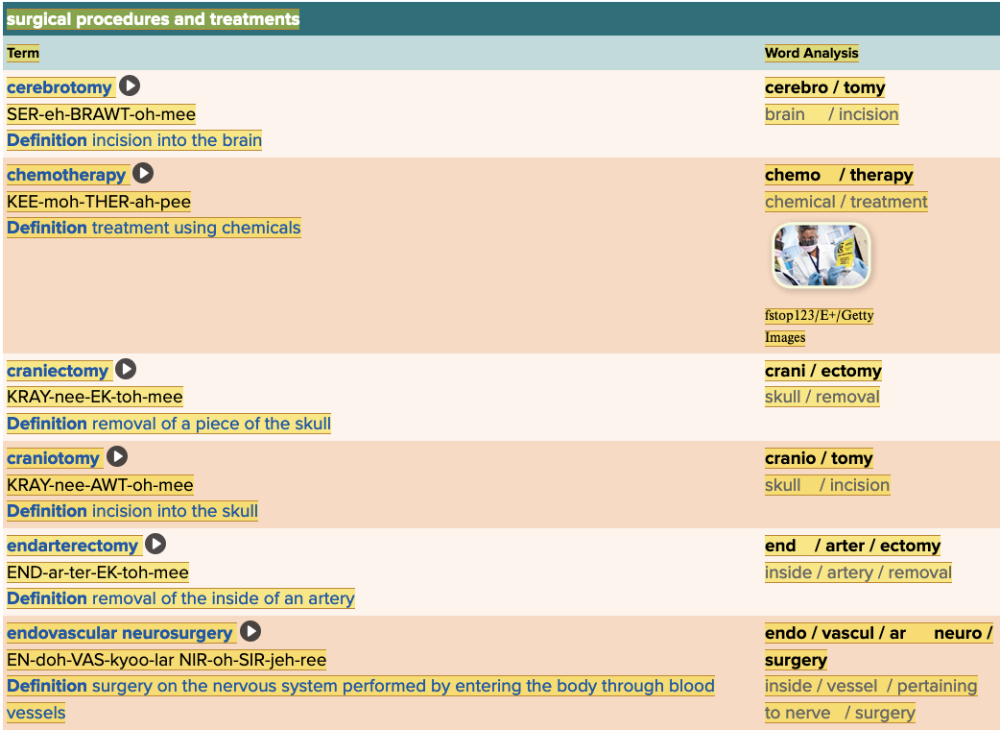 Chapter 5.5 Treatments and Therapies
| back 57 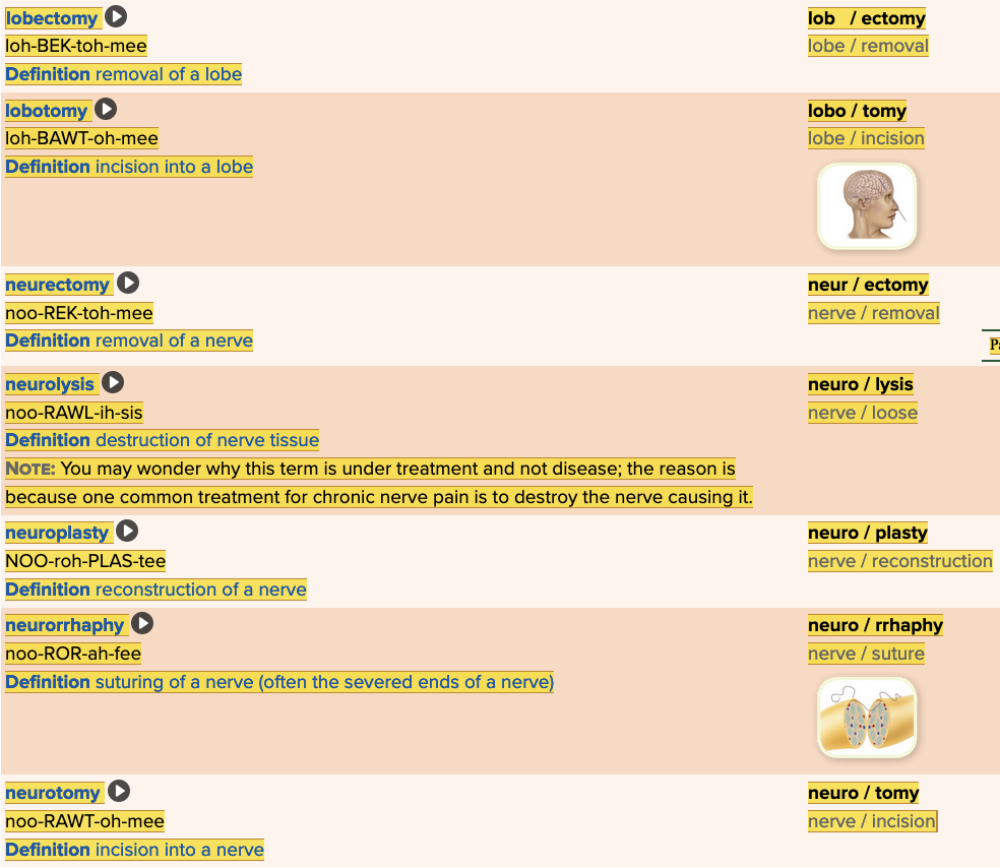 Chapter 5.5 Treatments and Therapies
|
front 58  Learning Outcome 5.5 Exercises: Exercise 1. | back 58 no data |
front 59  Learning Outcome 5.5 Exercises: Exercise 2, 3. | back 59 no data |
front 60 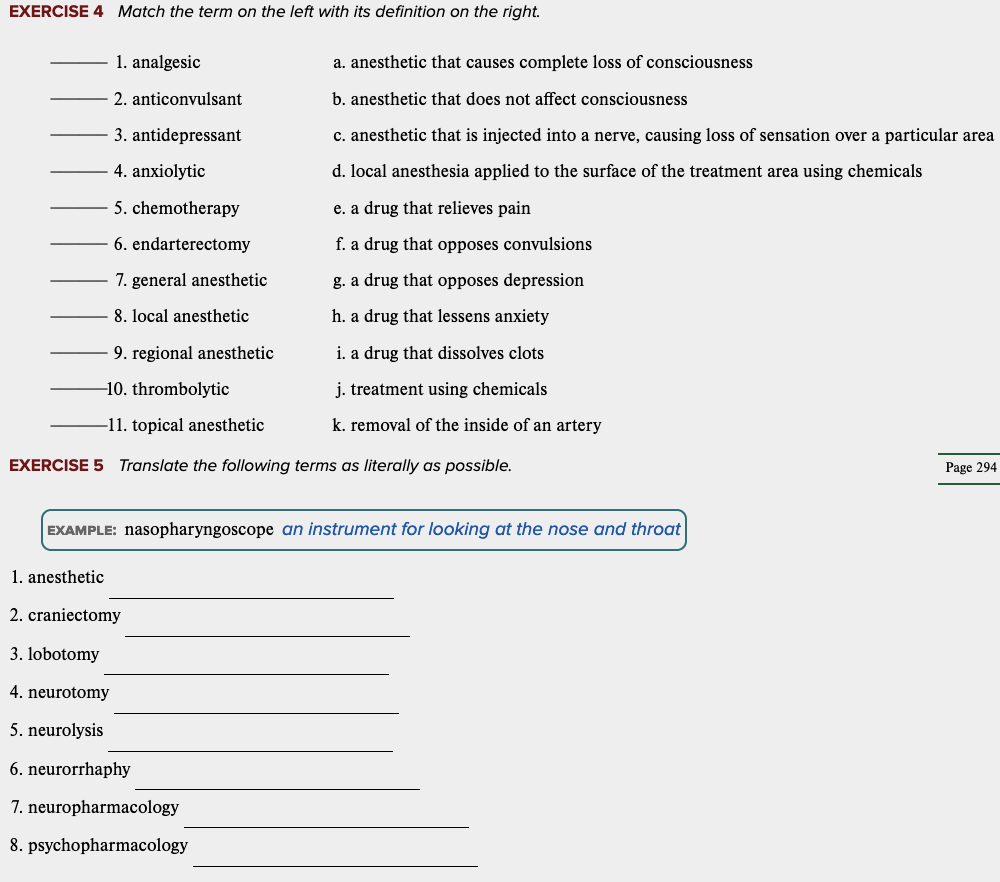 Learning Outcome 5.5 Exercises: Exercise 4, 5. | back 60 no data |
front 61 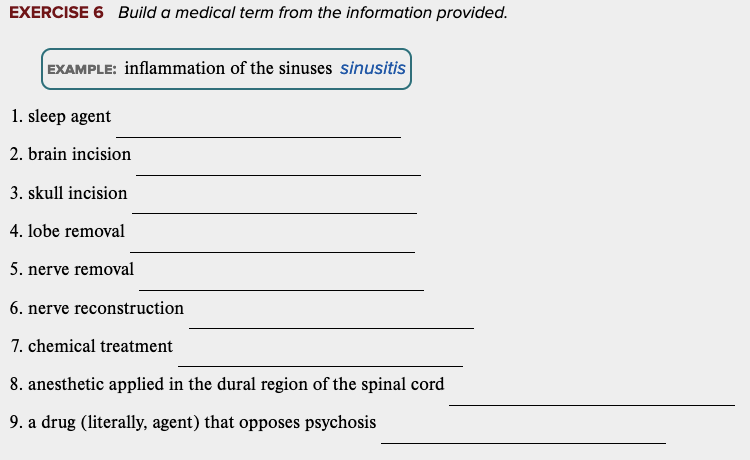 Learning Outcome 5.5 Exercises: Exercise 6. | back 61 no data |
front 62  Learning Outcome 5.5 Exercises: Exercise 7, 8. | back 62  |
front 63  Chapter 5.6 Abbreviations | back 63 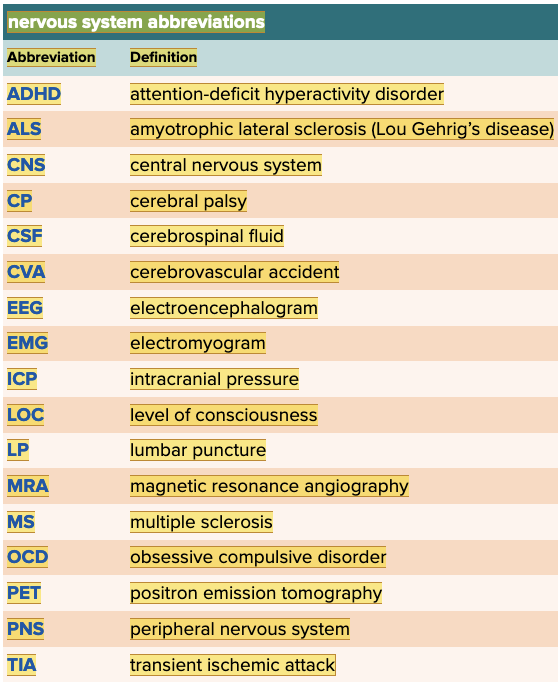 Chapter 5.6 Abbreviations
|
front 64  Learning Outcome 5.6 Exercises: Exercise 1, 2. | back 64 no data |
front 65  Learning Outcome 5.6 Exercises: Exercise 3. | back 65  |
front 66 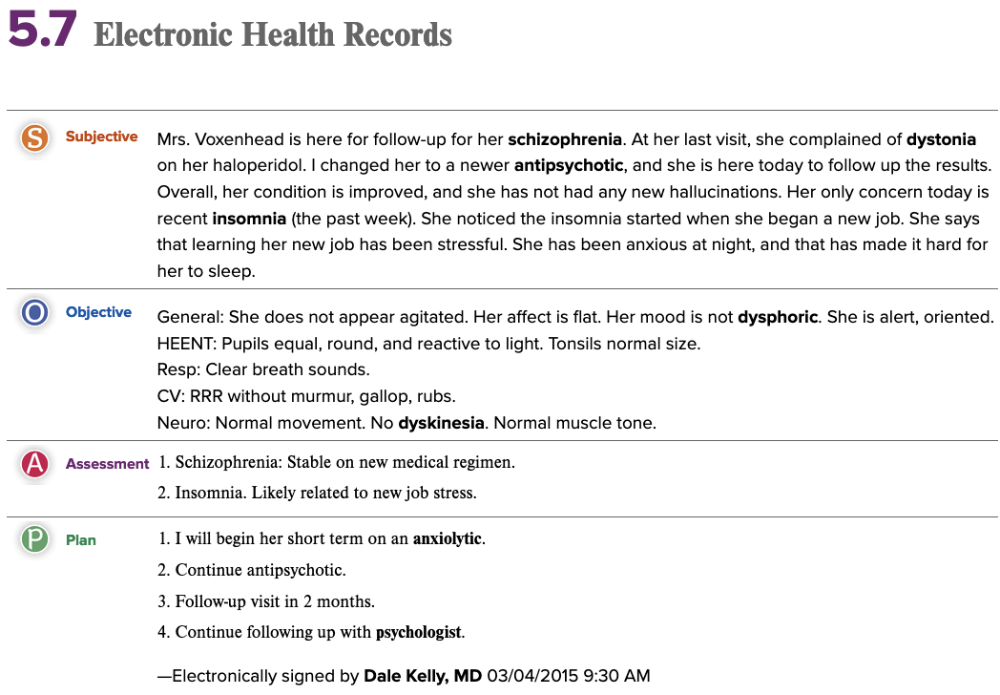 Chapter 5.7 Electronic Health Records | back 66  Chapter 5.7 Electronic Health Records |
front 67  Learning Outcome 5.7 Exercises: Exercise 1, 2, 3, 4. | back 67  |
front 68  Chapter 5.7 Electronic Health Records Emergency Department Visit | back 68  Chapter 5.7 Electronic Health Records Emergency Department Visit |
front 69  Learning Outcome 5.7 Exercises: Exercise 5, 6, 7, 8. | back 69  |
front 70  Chapter 5.7 Electronic Health Records Brief Admission Summary Letter | back 70 no data |
front 71  Learning Outcome 5.7 Exercises: Exercise 9, 10, 11, 12. | back 71  |
front 72 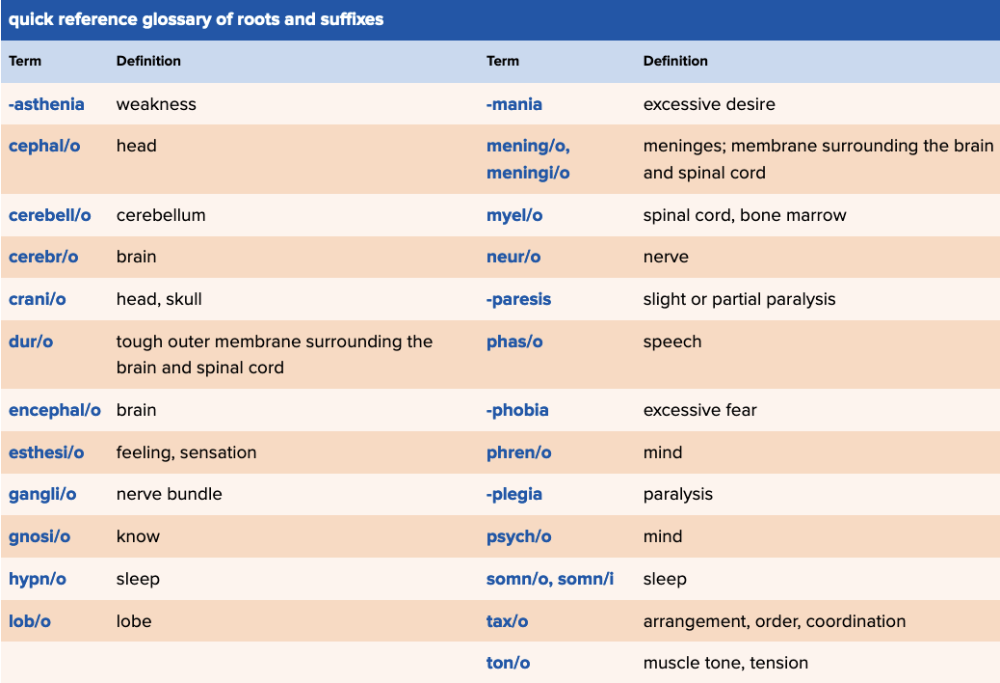 Chapter 5 Quick Reference
| back 72 no data |
front 73 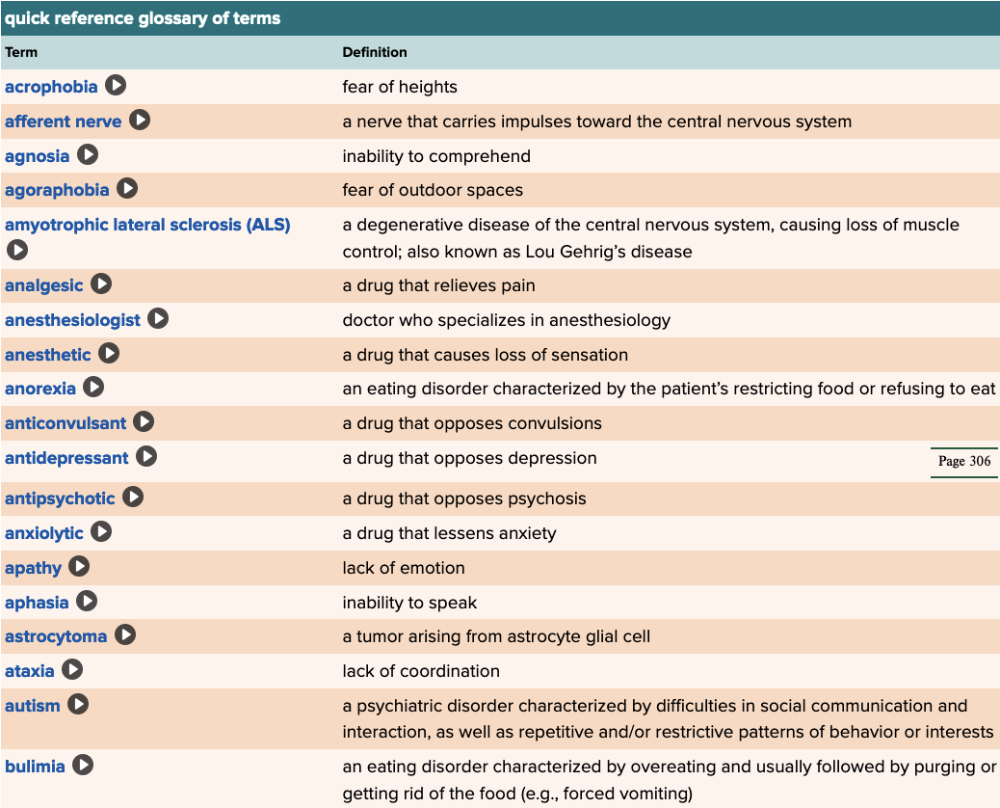 Chapter 5 Quick Reference
| back 73 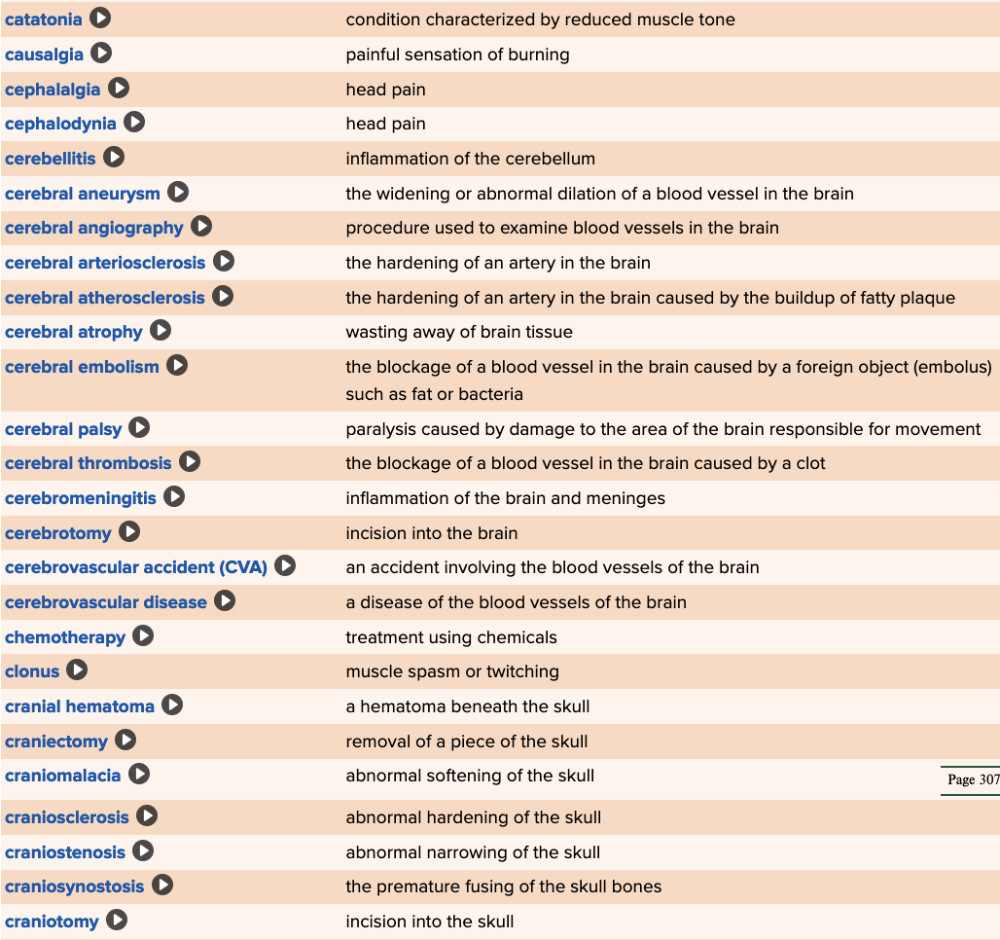 Chapter 5 Quick Reference
|
front 74 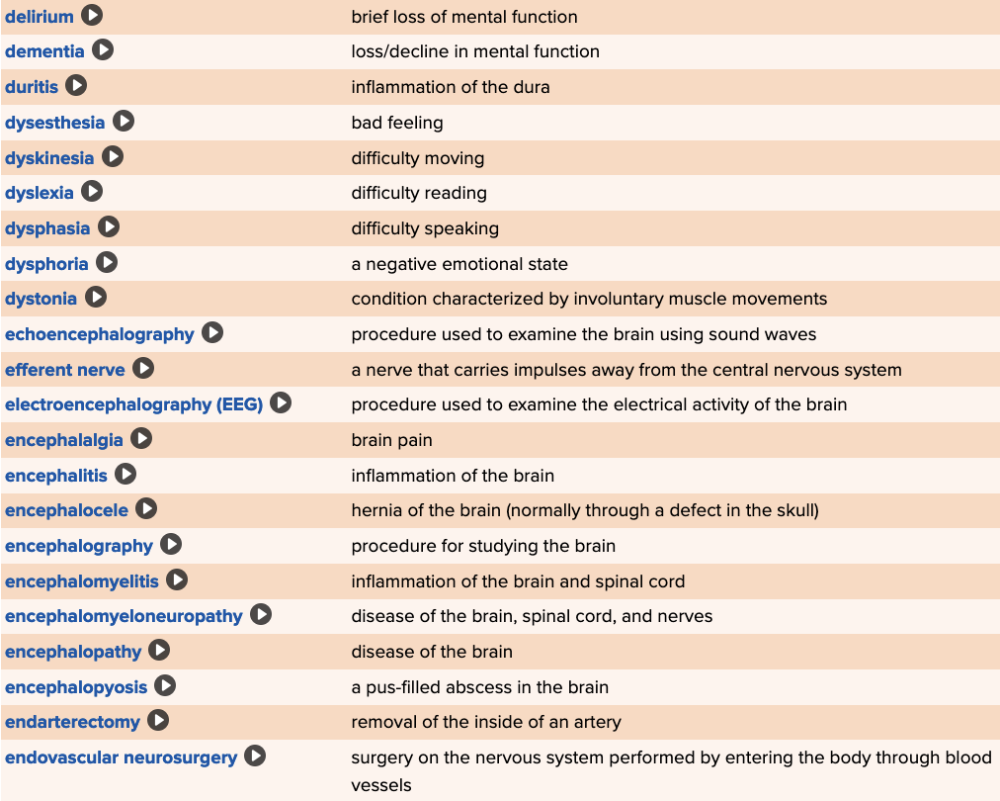 Chapter 5 Quick Reference
| back 74 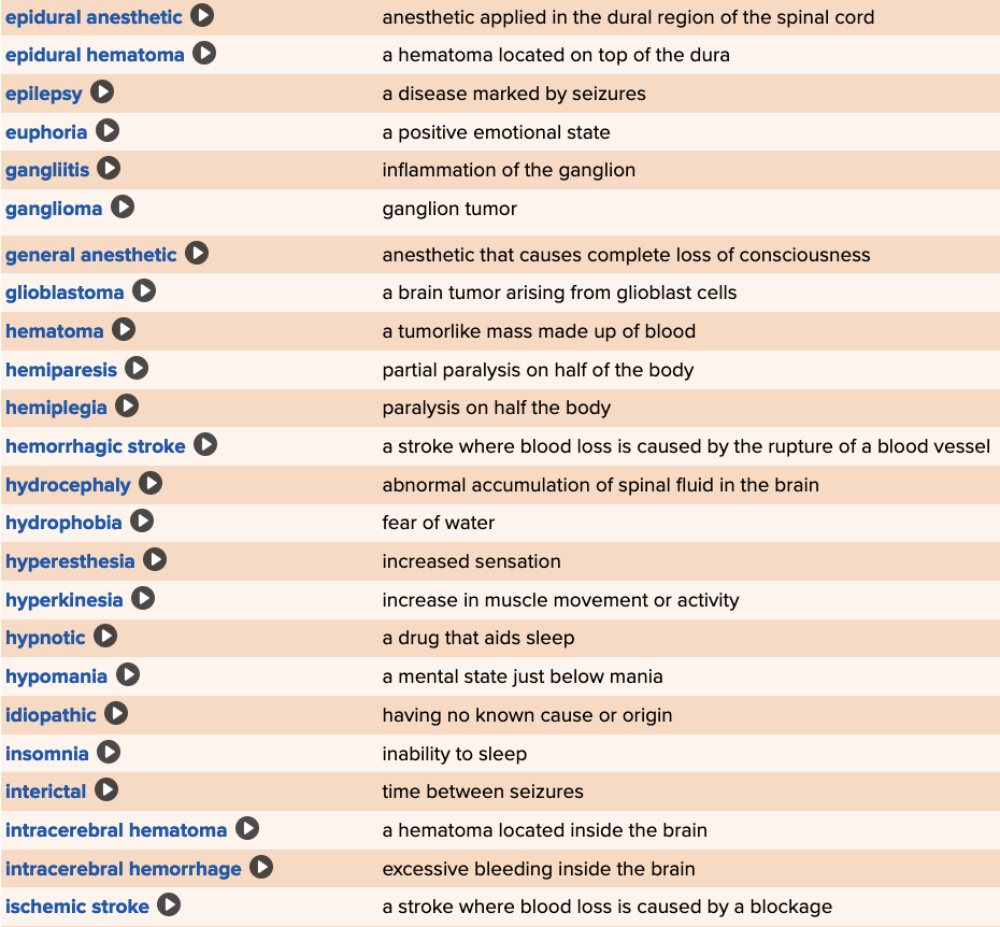 Chapter 5 Quick Reference
|
front 75 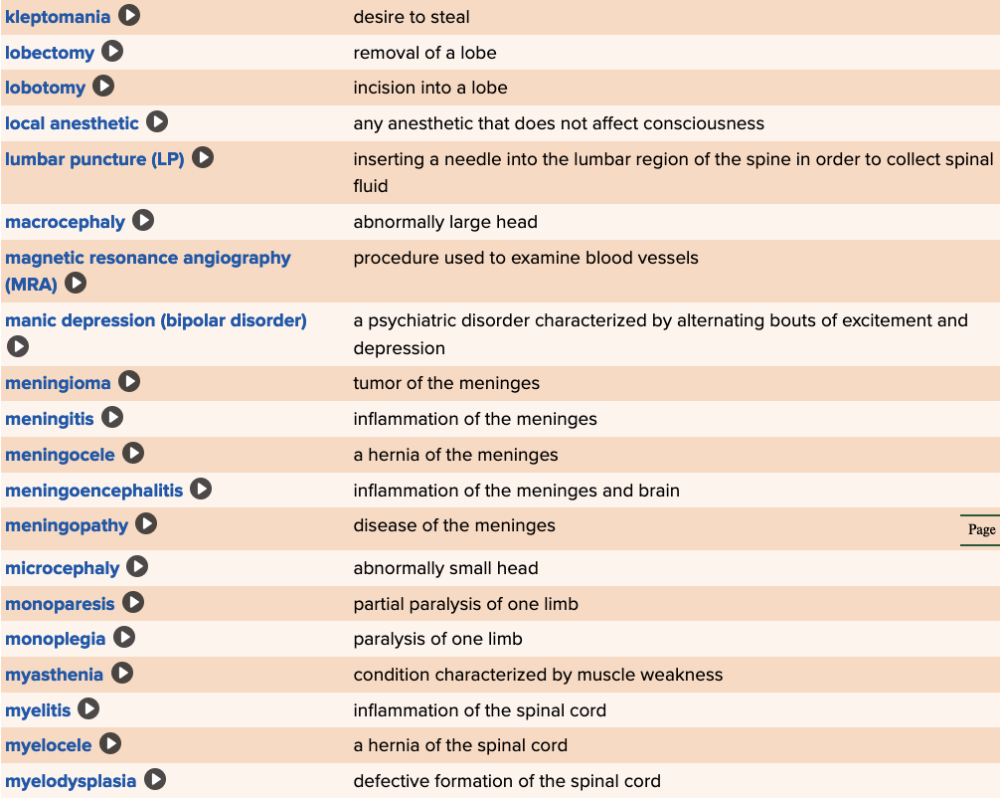 Chapter 5 Quick Reference
| back 75 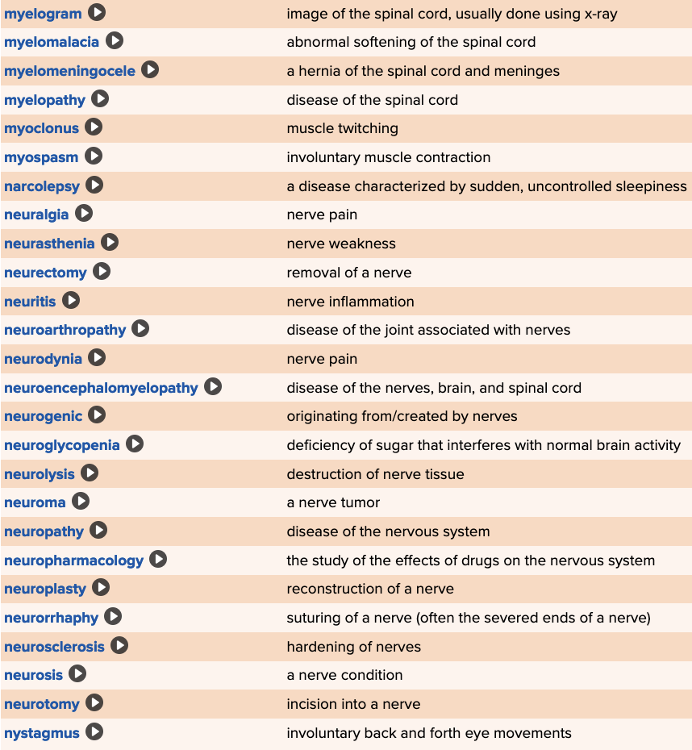 Chapter 5 Quick Reference
|
front 76 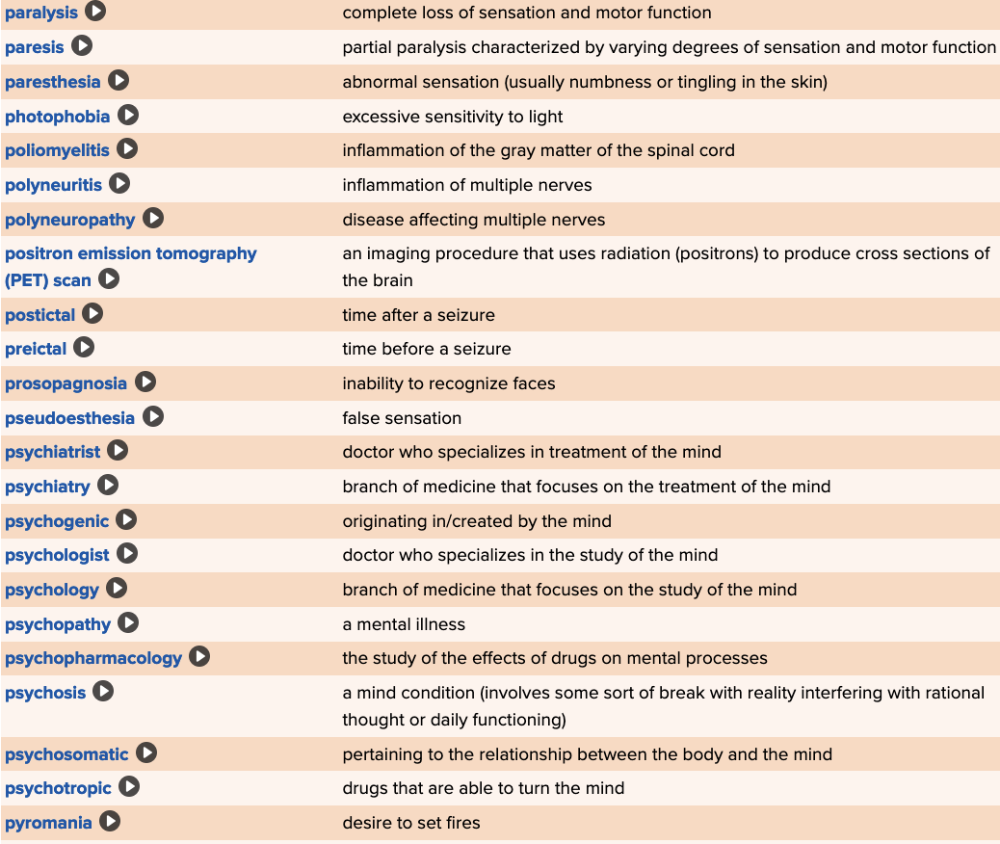 Chapter 5 Quick Reference
| back 76 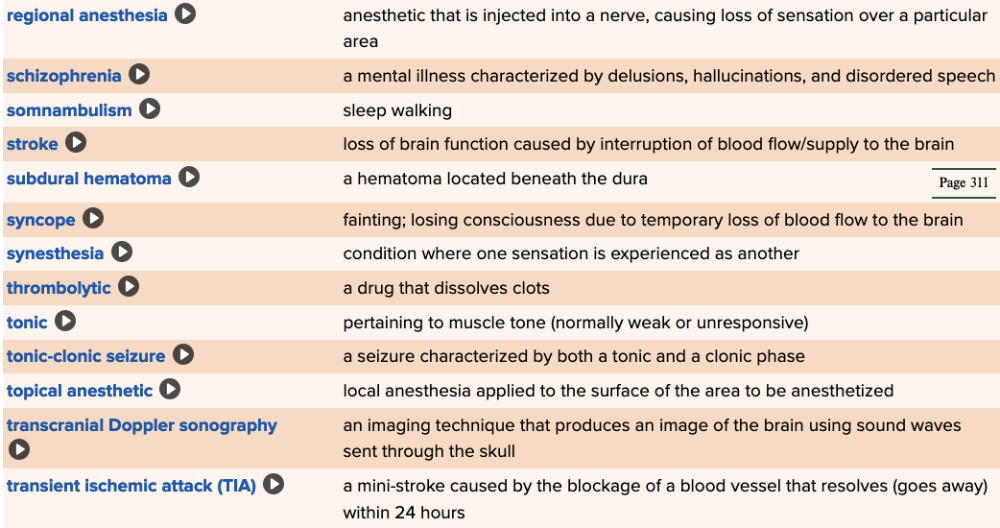 Chapter 5 Quick Reference
|
front 77 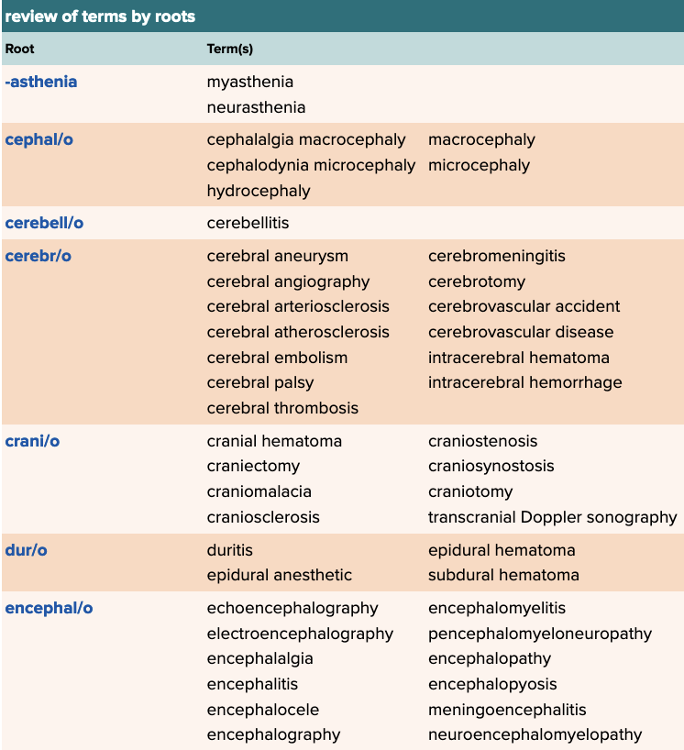 Chapter 5 Quick Reference
| back 77 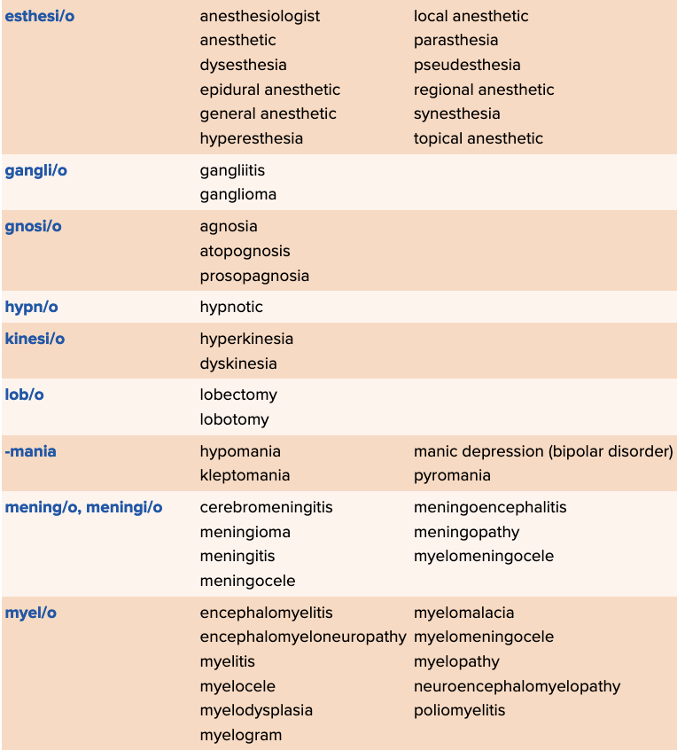 Chapter 5 Quick Reference
|
front 78 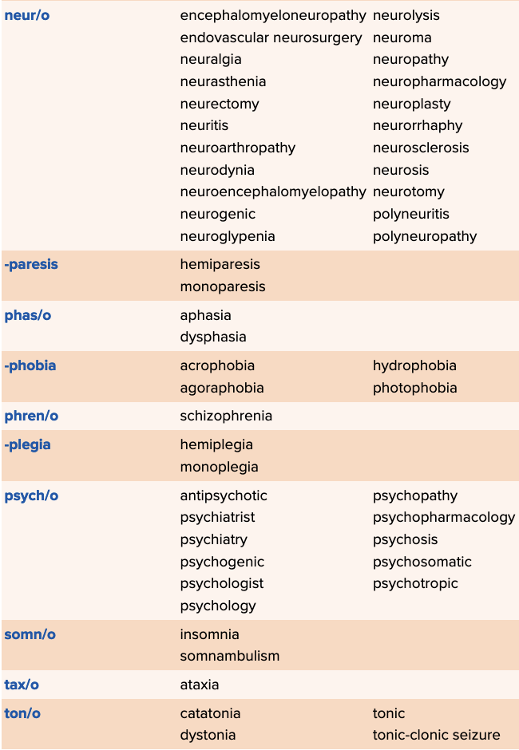 Chapter 5 Quick Reference
| back 78  Chapter 5 Quick Reference
|
front 79  Chapter 5 Review Exercises: Exercise 1, 2. | back 79 no data |
front 80  Chapter 5 Review Exercises: Exercise 3. | back 80 no data |
front 81  Chapter 5 Review Exercises: Exercise 4. | back 81 no data |
front 82  Chapter 5 Review Exercises: Exercise 5. | back 82 no data |
front 83  Chapter 5 Review Exercises: Exercise 6. | back 83 no data |
front 84  Chapter 5 Review Exercises: Exercise 7, 8. | back 84 no data |
front 85  Chapter 5 Review Exercises: Exercise 9. | back 85 no data |
front 86  Chapter 5 Review Exercises: Exercise 10. | back 86 no data |
front 87  Chapter 5 Review Exercises: Exercise 11. | back 87  |
front 88  Chapter 5 Review Exercises: Exercise 11. | back 88 no data |
front 89  Chapter 5 Review Exercises: Exercise 12, 13. | back 89 no data |
front 90 Select all that apply Which of the following is a unified collection of cells known as the central nervous system? Multiple select question.
| back 90
|
front 91 Select all that apply Which of the following make up the central nervous system? Multiple select question.
| back 91
|
front 92 Which of the following terms relates to the brain? Multiple choice question.
| back 92 Encephalitis |
front 93 The term "Little brain" means ______. | back 93 cerebellum |
front 94 Which of the following is a commonly used meaning for a brain operation that changes one's personality? Multiple choice question.
| back 94 Lobotomy |
front 95 Select all that apply The two parts of the nervous system are the ______ Multiple select question.
| back 95
|
front 96 What is the root for skull? Multiple choice question.
| back 96 Crani/o |
front 97 How many hemispheres does the brain have? Multiple choice question.
| back 97 Two |
front 98 The term that means half the head that comes from the word hemicranias is called ______. | back 98 migraine |
front 99 Select all that apply Which of the following roots mean "brain"? Multiple select question.
| back 99
|
front 100 The definition of the root "dur/o" is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 100 dura |
front 101 Select all that apply Which of the following terms relate to the cerebellum? Multiple select question.
| back 101
|
front 102 Select all that apply Which of the following is the Greek word meaning neuron? Multiple select question.
| back 102
|
front 103 Lobes are smaller subdivisions of an ______. | back 103 organ |
front 104 In the Roman translation, the term ganglion means ______. | back 104 knot |
front 105 The root for head is called ______. | back 105 cephal/o, crani/o, cephal, or cephalo |
front 106 Which of the following is the Greek meaning for the root myel/o? Multiple choice question.
| back 106 The innermost part |
front 107 The root for "skull" is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 107 crani/o |
front 108 Select all that apply The meaning of the root esthesi/o is ______. Multiple select question.
| back 108
|
front 109 The root for dura is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 109 dur/o |
front 110 The root for "speech" is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 110 phas/o |
front 111 The definition of the root neur/o is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 111 nerve |
front 112 Select all that apply The root for "mind" is ______. Multiple select question.
| back 112
|
front 113 The definition of the root gangli/o is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 113 nerve bundle |
front 114 Select all that apply Some roots for sleep are ______. Multiple select question.
| back 114
Ex. There is somn/i as well. |
front 115 The root for "spinal cord" is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 115 myel/o |
front 116 The definition of gnosi/o is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 116 know |
front 117 The root for "feeling or sensation" is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 117 esthesi/o |
front 118 The definition of "excessive desire" is ______. | back 118 -mania |
front 119 The definition of the root phas/o is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 119 speech |
front 120 Select all that apply The definition of -phobia is excessive ______. Multiple select question.
| back 120
|
front 121 The definition of "psych/o" is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 121 mind |
front 122 The suffix "-paresis" means slight or partial ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 122 paralysis |
front 123 Select all that apply Roots for sleep are ______. Multiple select question.
| back 123
|
front 124 The root meaning "muscle tone, tension, or pressure" is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 124 ton/o |
front 125 The root for "know" is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 125 gnosi/o |
front 126 Select all that apply The medical term root "tax/o" means ______. Multiple select question.
| back 126
|
front 127 Which of the following terms characterize bipolar depression's intense mood swings? Multiple choice question.
| back 127 Manic |
front 128 Select all that apply The suffixes that relate to paralysis are ______. Multiple select question.
| back 128
|
front 129  Match the condition to the definition related to the suffix "phobia." | back 129 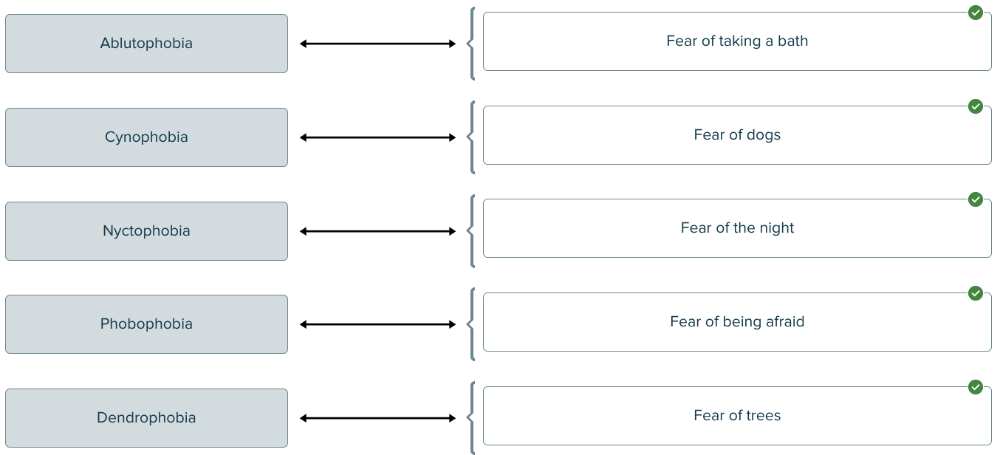 |
front 130 Select all that apply Which of the following comes from the Greek term "paresis"? Multiple select question.
| back 130
|
front 131 The definition of the suffix "-asthenia" is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 131 weakness. |
front 132 Select all that apply The root "ton/o" means ______. Multiple select question.
| back 132
|
front 133 The most common psychiatric issue that providers treat is ______. | back 133 emotions, emotion, depression, or anxiety |
front 134 Which of the following is the practice of removing and displaying the head and skin of a dead animal? Multiple choice question.
| back 134 Taxidermy |
front 135 A loss or decline in mental function is ______. Multiple choice question. aphasia ataxia myospasm dementia | back 135 dementia |
front 136 The Greek meaning of plegia is ______.
| back 136 to strike |
front 137 Which of the following terms would be associated with the suffix phobia? Multiple choice question.
| back 137 Excessive fear or sensitivity |
front 138  Match each impairment term with the word analysis. | back 138 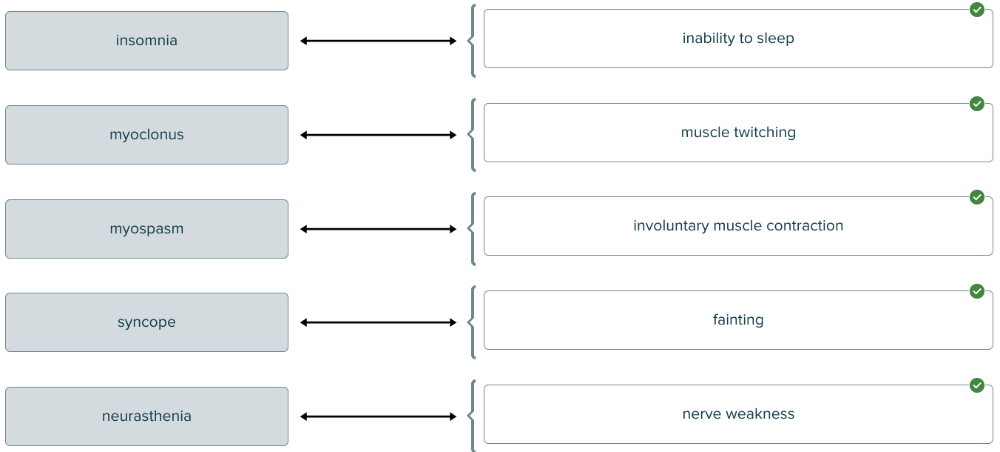 |
front 139 The suffix meaning "weakness" is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 139 -asthenia |
front 140 Select all that apply Terms meaning head pain are ______. Multiple select question.
| back 140
|
front 141 Which of the following is defined by a sudden state of confusion and abrupt loss of awareness of the surroundings? Multiple choice question.
| back 141 Delirium |
front 142 The condition characterized by partial paralysis on half the body is ______. | back 142 hemiparesis |
front 143 The inability to speak is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 143 aphasia |
front 144 Increased sensation is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 144 hyperesthesia |
front 145 Select all that apply The suffixes that relate to paralysis are ______. Multiple select question.
| back 145
|
front 146 The condition for fear of heights is ______. | back 146 acrophobia |
front 147 The inability to sleep is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 147 insomnia |
front 148 Which of the following is when electrodes are placed on the skull and the brain for monitoring? Multiple choice question.
| back 148 EEG |
front 149 Select all that apply Terms meaning "nerve pain" are ______. Multiple select question.
| back 149
|
front 150 A procedure used to examine the electrical activity of the brain is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 150 electroencephalography |
front 151  Match the paralysis term to the definition. | back 151 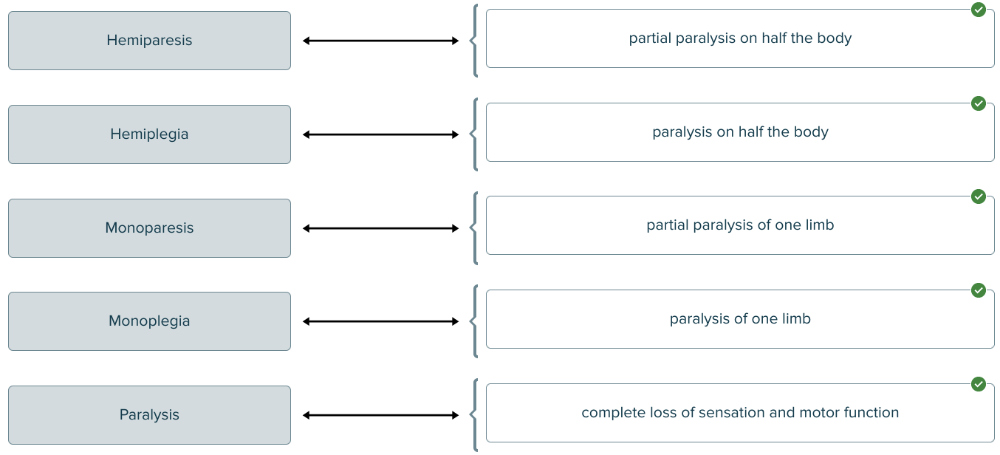 |
front 152 An image of the spinal cord is a ______. | back 152 myelogram |
front 153  Match each sensation/feeling term with its definition. | back 153 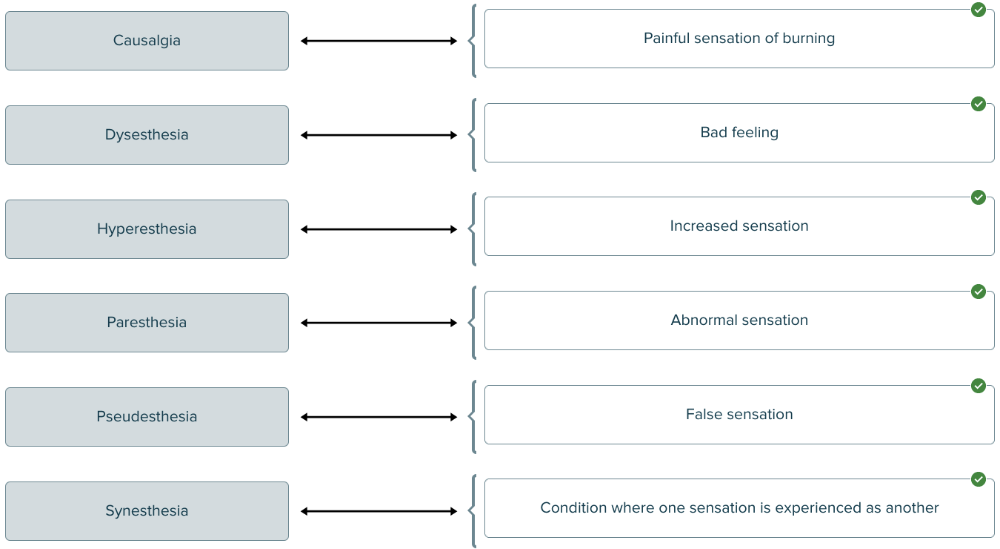 |
front 154 Which of the following terms is associated with duritis? Multiple choice question.
| back 154 Inflammation of the dura |
front 155  Match each phobia/mania term with its definition. | back 155 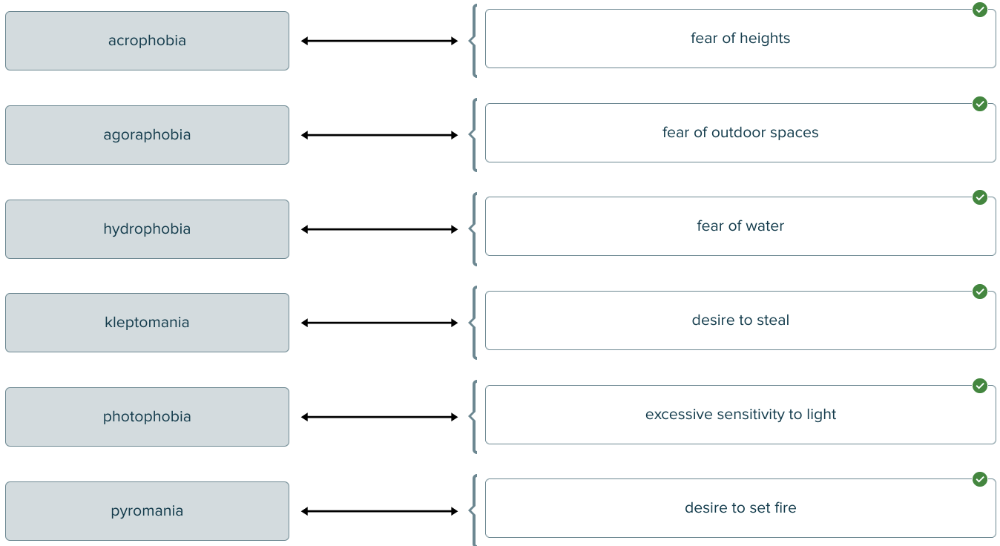 |
front 156 A condition of having an abnormally large head is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 156 macrocephaly |
front 157 The most common lab work done in the evaluation of the neurologic system focuses on testing a patient’s ______ fluid. | back 157 cerebrospinal |
front 158 Select all that apply Which of the following is/are terms associated with an EEG? Multiple select question.
| back 158
|
front 159 An increase in muscle movement or activity is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 159 hyperkinesia |
front 160 An imaging technique that produces an image of the brain using sound waves sent through the skull is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 160 transcranial doppler sonography |
front 161 Nerve weakness is defined as ______. | back 161 neurasthenia |
front 162  Match each structure term with its definition. | back 162 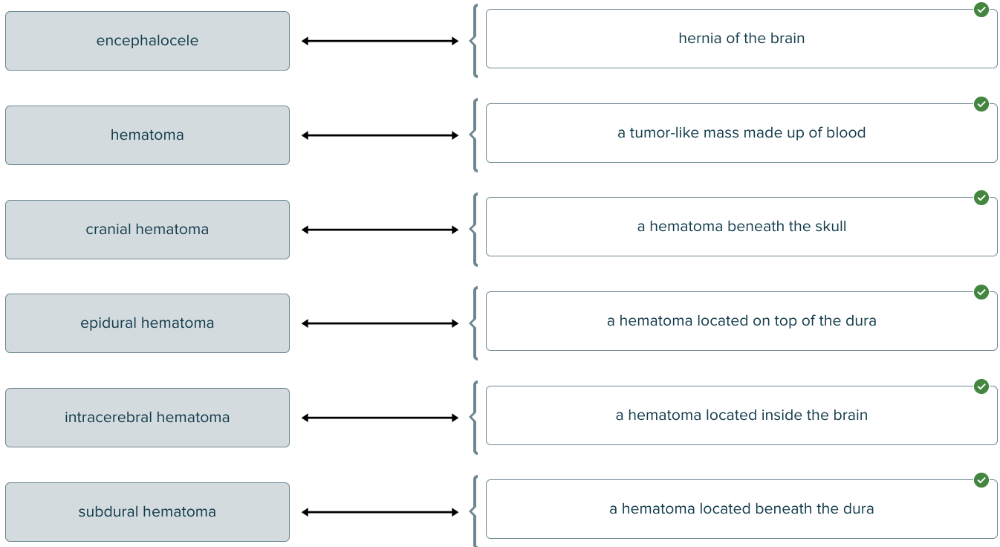 |
front 163 Select all that apply Nerves that carry impulses away from the CNS are ______. Multiple select question.
| back 163
|
front 164 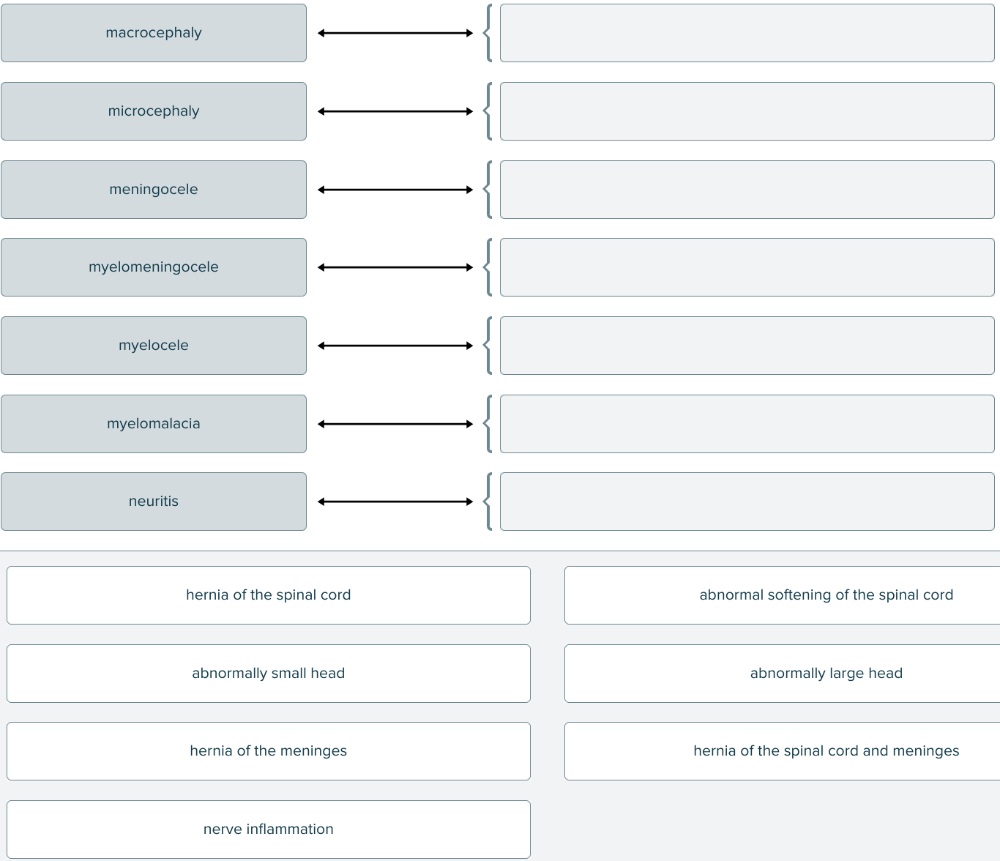 Match each term associated with structure with its definition. | back 164 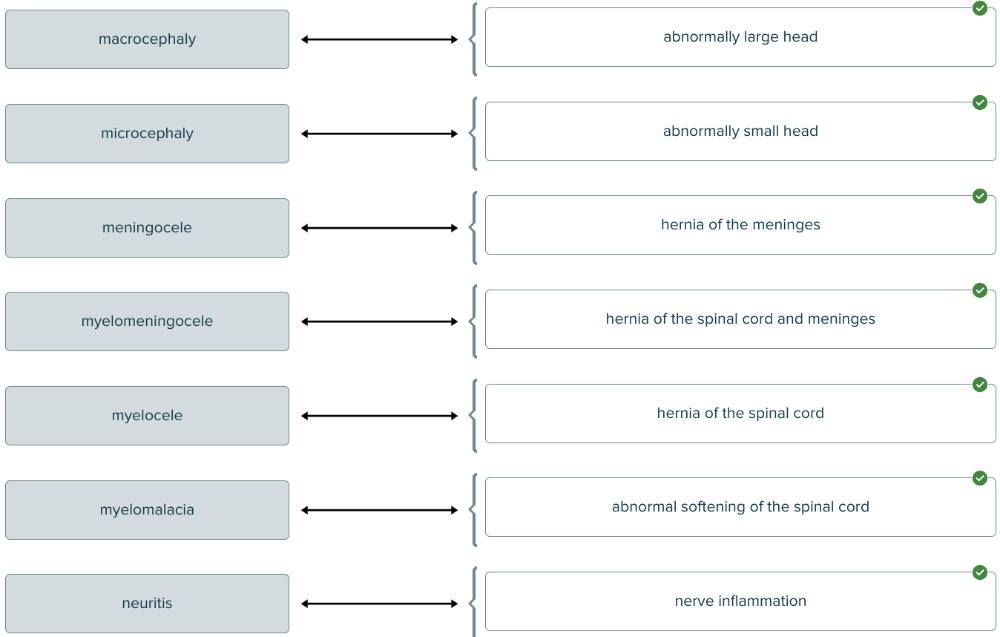 |
front 165 Select all that apply Which of the following is the root for the term idiopathic? Multiple select question.
| back 165
Ex.
Reason: root for postictal
Reason: suffix |
front 166 Which of the following is when electrodes are placed on the skull and the brain for monitoring? Multiple choice question.
| back 166 EEG |
front 167 Which of the following is defined as a premature closure of the bone/s? Multiple choice question.
| back 167 Craniosynostosis |
front 168 The inability to comprehend is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 168 agnosia |
front 169 Which of the following is a stroke when blood loss is caused by a blockage? Multiple choice question.
| back 169 Ischemic Stroke |
front 170 Involuntary back and forth eye movement is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 170 nystagmus |
front 171 The blockage of a blood vessel on the brain caused by a blood clot is called a cerebral ______. | back 171 thrombosis |
front 172 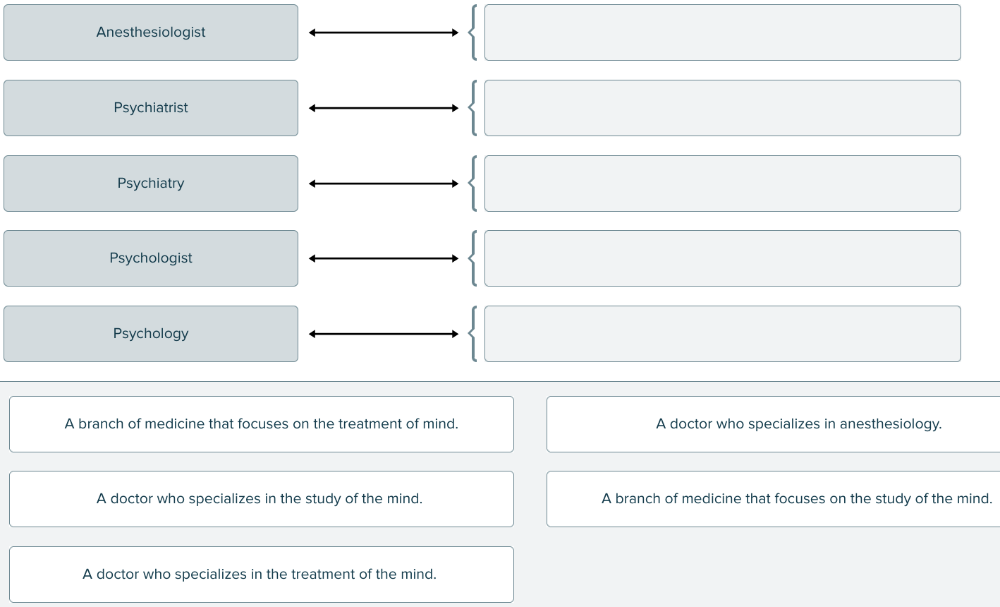 Drag and drop the definitions against the corresponding terms related to a specialty or specialist. | back 172 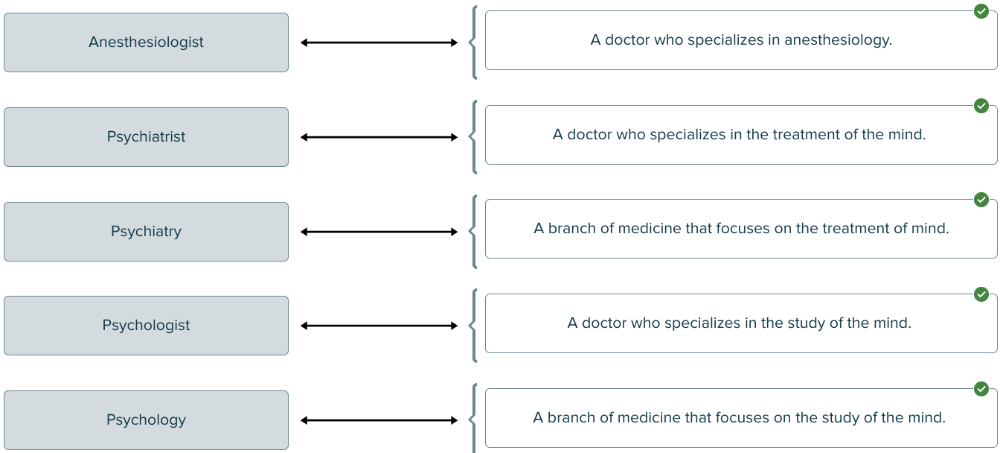 |
front 173 Abnormal accumulation of spinal fluid in the brain is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 173 hydrocephaly |
front 174 Which of the following is defined as having no known origin or cause? Multiple choice question.
| back 174 Idiopathic |
front 175 Select all that apply Select the central nervous system tumors. Multiple select question.
| back 175
|
front 176 Which of the following is defined as an accident involving the blood vessels of the brain? Multiple choice question.
| back 176 CVA (Cerebrovascular Accident) |
front 177 Disease of the brain is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 177 encephalopathy |
front 178 Which of the following is the definition of cerebral thrombosis? Multiple choice question.
| back 178 Blockage of the blood vessel in the brain caused by blood clots Ex.
Reason: This is craniomalacia
Reason: This is atherosclerosis
Reason: This is aneurysm |
front 179 Inflammation of the brain is is defined as ______. | back 179 encephalitis |
front 180 Which of the following is the term for abnormal softening of the skull. Multiple choice question.
| back 180 Craniomalacia |
front 181 Which of the following is inflammation of the spinal cord? Multiple choice question.
| back 181 Myelitis |
front 182 A positive emotional state is called ______. | back 182 euphoria |
front 183 Select all that apply Which of the following are common psychogenic problems? Multiple select question.
| back 183 Depression Anxiety |
front 184 Select all that apply Which of the following conditions are treated by psychiatric drugs? Multiple select question.
| back 184
|
front 185 Which of the following is a tumor of the meninges? Multiple choice question.
| back 185 Meningioma |
front 186 Which type of anesthesia is injected into a nerve, causing loss of sensation over a particular area? Multiple choice question.
| back 186 Regional Ex.
Reason: This anesthetic does not affect consciousness.
Reason: This anesthetic is applied in the dural region of the spinal cord. |
front 187  Match the term about diseases to its definition. | back 187 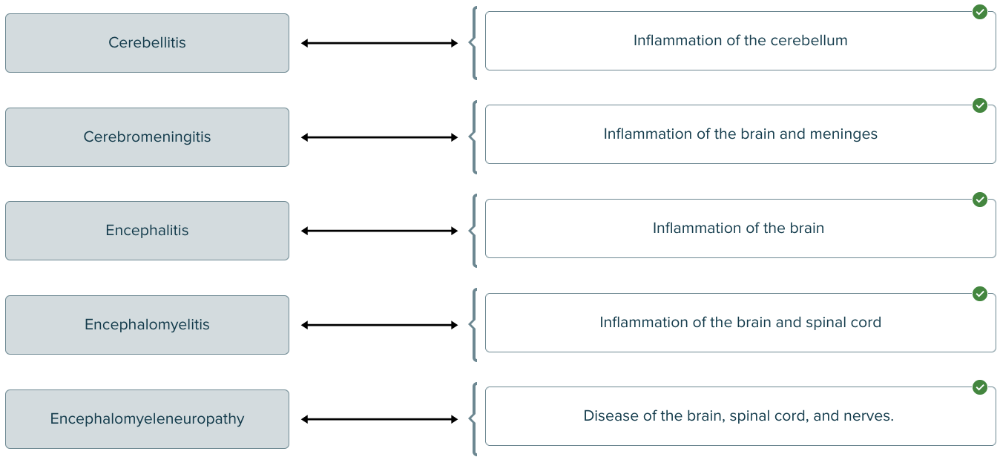 |
front 188 A drug that dissolves clots is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 188 thrombolytic |
front 189 Inflammation of the brain and meninges is ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 189 meningoencephalitis |
front 190 The term that defines a removal of a lobe is called ______. | back 190 lobectomy |
front 191 A negative emotional state is called ______. Multiple choice question.
| back 191 dysphoria |
front 192 An incision into a nerve is called ______. | back 192 Neurotomy |
front 193 The type of surgery that can be used to treat problems of the nervous system's support structures is ______. | back 193 neurosurgery |
front 194 The abbreviation for Lou Gehrig's disease is ______. | back 194 ALS |
front 195 Which of the following is anesthetic that causes complete loss of consciousness? Multiple choice question.
| back 195 General Anesthetic |
front 196 A drug that relieves pain is called ______. | back 196 analgesic |
front 197 Which type of surgical procedure is defined as removal of a piece of the skull? Multiple choice question.
| back 197 Craniectomy |
front 198 Which of the following is defined as an incision into a lobe? Multiple choice question.
| back 198 Lobotomy |
front 199  Match the central nervous system abbreviation to the definition. | back 199 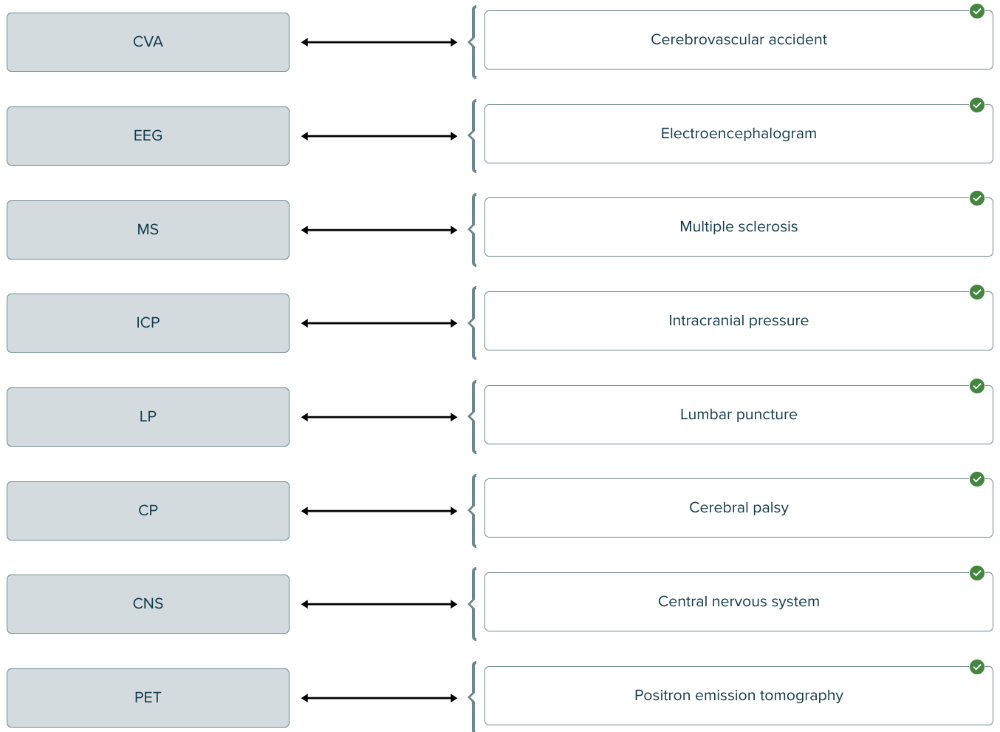 |