Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
lifespan exam 2 chapter 7-12
front 1 What are the major milestone of gross motor skills between 18-24 months? c7 | back 1 Runs awkwardly; climbs stairs with both feet on each steps; pushes and pull boxes or wheeled toys c7 |
front 2 What are the major milestone of gross motor skills between 2-3 years old? c7 | back 2 Runs easily; climb on furniture unaided; hauls and shove big toys around obstacles. c7 |
front 3 What are the major milestone of gross motor skills between 3-4 years old? c7 | back 3 Walks up stairs one foot per steps; skips on two feet; walks on tiptoe; pedals and steers tricycle; walk in any direction pullng large toys c7 |
front 4 What are the major milestone of gross motor skills between 4-5 years old? c7 | back 4 Walks up and down stairs one foot per step; stands. runs, and walks on tiptie c7 |
front 5 What are the major milestone of gross motor skills between 5-6 years old? c7 | back 5 Skips on alternate feet; walks on a line; sides, swings c7 |
front 6 What are the major milestone of fine motor skills between 18-24 months? c7 | back 6 Show clear hand preference; stacks four to six blocks; turns page one at a time; picks up things without overbalancing; unscrews lid on a jar c7 |
front 7 What are the major milestone of fine motor skills between 2-3 years old? c7 | back 7 picks up small objects; throws small ball while standing c7 |
front 8 What are the major milestone of fine motor skills between 3-4 years old? c7 | back 8 catches large ball between outstretched arms; cuts paper with scissors; holds pencil between thumb and fingers c7 |
front 9 What are the major milestone of fine motor skills between 4-5 years old? c7 | back 9 Strikes ball with bat; kicks and catches ball; thread beads on a string; grasp pencil properly c7 |
front 10 What are the major milestone of fine motor skills between 5-6 years old? c7 | back 10 plays ball games well; thread needles and sew large stitches c7 |
front 11 Define Corpus Callosum c7 | back 11 The membrane that connect the right and left hemispheres of the cerebral cortex. (The brain structure through which the left and right sides of the cerebral cortex communicate, grows and mature more during the early childhood years than in any other periods of life) c7 |
front 12 Define Lateralization c7 | back 12 The process through which brain functions are divided between the two hemisphere of the cerebral cortex. c7 |
front 13 Define Hippocampus c7 | back 13 The brain structure that is important in learning. (this involves transfer of information to long-term memory) c7 |
front 14 Define Handedness c7 | back 14 A strong preference for using one hand or the other that develops between 3 and 5 years of age c7 |
front 15 Define Infantile Amnesia c7 | back 15 The inability to remember much about the first three years of life. c7 |
front 16 Summary of eating patterns c7 | back 16 Children grow more slowly during the early childhood years therefore it may seem that they eat less than when they were babies. Moreover, parents should be more concern about nutritious food, not about the quantity of food the child is eating. c7 |
front 17 Summary of illness c7 | back 17 In the US, the average preschooler has six to seven colds each year along with one or two episodes of gastrointestinal illness. Study shows single-parent homes have more asthma, headaches, and generally higher vulnerability to illness than those who live with both biological parents. c7 |
front 18 Summary of accidents c7 | back 18 25% of all US childern under age 5 have atleast 1 accident. Accidents are the major cause of death in preschoolers and school-age children. Accidents are more common in boys. Drowning is the leading cause of 1-4 y/o and 5+ are motor vehicle accidents c7 |
front 19 Define Reticular Formation c7 | back 19 The part of the brain that regulates attention and concentration c7 |
front 20 Define Child Abuse c7 | back 20 Physical or psychological injury that results from an adults intentional exposure of a child to potentially harmful physical stimuli, sexual acts, or neglect c7 |
front 21 Define Neglect c7 | back 21 The failure of caregivers to provide emotional and physical support for a child. c7 |
front 22 Define PTSD (post-traumatic stress disorder) c7 | back 22 Involves extreme levels of anxiety, flashback memories of episodes or abuse, nightmares, and other sleeping disturbance. c7 |
front 23 Summary of abuse and neglect c7 | back 23 2/3 (66%) of abuse results in physical injury, 1/4 (25%) involves sexual abuse, 1/20 (5%) involves neglect, Responsible for 10% of Emergency visit, Between 1% and 5% suffer from physical abuse, 2000 infants and children die each year result of child abuse. Preventing abuse begins with education. c7 |
front 24 Define Piagets Preoperational stage c7 | back 24 Piagets second stage of cognitive development, during which children become proficient in the use of symbols in thinking and communicating but still have difficulty thinking logically c7 |
front 25 Define Semiotic (symbolic) function c7 | back 25 (18-24 month) The understanding that one object or behavior can represent another. i.e. a child pretending to feed a doll stands for a parent feeding a baby. c7 |
front 26 Egocentrism c7 | back 26 A child's belief that everyone see and experience the world as they way they do. i.e a child give a prism sees a mountain. c7 |
front 27 Define Theories of Mind c7 | back 27 A set of ideas constructed by a child or adult to explain to other peoples ideas, beliefs,desires, and behavior. c7 |
front 28 Define Fast Mapping c7 | back 28 The ability to categorically link new words to real-world referents c7 |
front 29 Define Myelinization c7 | back 29 Protective, fatty material wraps around nerve cells in the peripheral and central nervous system c7 |
front 30 Right, left, or ambidextrous handedness c7 | back 30 83% are right handed
|
front 31 Define Centration c7 | back 31 A childs tendency to focus on only one aspect of a situation, problem or object at a time. i.e. A child may complain that there is too little ice cream in a big bowl. Transfer same ice cream to a smaller bowl and the child will be more satisfied. c7 |
front 32 Define Conservation c7 | back 32 The understanding that matter can change based on three characteristics: Identity, Compensation, and Reversibility c7 |
front 33 Define Grammar Explosion c7 | back 33 The period during when the grammatical features of a childern's speech become more similar to those of adult speech c7 |
front 34 Define Phonological Awareness c7 | back 34 Children's understanding of the sound patterns of the language they are acquiring. (developed through word play such as nursing rhymes) c7 |
front 35 Define Social-Cognitive Theory c8 | back 35 The theoretical perspective that asserts that social and personality developments in early childhood is related to improvements in the cognitive domain (assumes that social and emotional changes in the child are the results of or at least are faciliated by-the enormous growth in cognitive abilities that happens during the preschool years) c8 |
front 36 Define Person Perception c8 | back 36 The ability to classify others according to categories such as age, gender, and race c8 |
front 37 Summary of Temperament to Personality c8 | back 37 A child's ability to control and submit to their impulse. If not they will learn that they will miss out on the fun of the game, therefore the control will help them develop their personality c8 |
front 38 Define Emotional Regulation c8 | back 38 The ability to control emotional state and emotion-related behavior c8 |
front 39 Define the Freuds Anal Stage (1-3 yrs) c8 | back 39 Stage where toilet training occurs. Control over bodily functions c8 |
front 40 Define the Freuds Phallic Stage (3-5 yrs) c8 | back 40 The stage where the foundation for later gender and moral development c8 |
front 41 Define Eriksons Stage of Autonomy VS Shame and Doubt c8 | back 41 Eriksons stage that centers around the toddlers new mobility and the accompanying desire for autonomy c8 |
front 42 Define Eriksons Stage of Initiative VS Guilt c8 | back 42 Eriksons stage that is ushered in by new cognitive skills, particularly the preschoolers ability to plan, which accentuates the wishes to take the initiative c8 |
front 43 Define Gender Identity c8 | back 43 The ability to correctly label oneself and others as male or female (by age 2 most can label themselves, 6-8 month later they can label others as well) c8 |
front 44 Define Gender Stability c8 | back 44 The understanding that gender is a stable, life long characteristic (most understand gender stability by age 4) c8 |
front 45 Define Gender Constancy c8 | back 45 The understanding that gender is a component of the self that is not altered by external appearance c8 |
front 46 Summary of Sex Role Knoweledge c8 | back 46 5-6 years old has found out that gender is permanent and is searching for a reliable rule about how boys and girls should behave. Children's pick up information watching adults and TV and treat them as morals rules. Later they understand, and gender concepts become more flexible. c8 |
front 47 Define Cross-gender Behavior c8 | back 47 Behavior that is atypical for ones own sex, but is typical for the opposite sex. i.e. Tomboyishness-girl plays with a truck-typical for boys, not as much for girls. More with girls then boys c8 |
front 48 Summary of attachements c8 | back 48 By age 2-3, attachments are just as strong but become less visible. Childrens who are securely attached to their parents experience fewer behavior problems. c8 |
front 49 Define Parenting Style c8 | back 49 The characteristic strategies that parents use to manage children's behavior c8 |
front 50 What are the four types of parenting styles c8 | back 50 1. The Authoritarian Type
|
front 51 Define The Authoritarian Parenting Style
| back 51 Low in nurturance and communication, but high in control and maturity demand. (More Common in Asian) c8 |
front 52 Define The Permissive Parenting Style
| back 52 High in nurturance and low in maturity demands, control, and communication c8 |
front 53 Define The Authoritative Parenting Style
| back 53 High in nurturance, maturity demands, control, and communication. (More common in white families and middle Class. Least common among asians. The best parenting style) c8 |
front 54 Define The Uninvolved Parenting Style
| back 54 Low in nurturance, maturity demands, control, and communication. (Structureless type-Also known as Neglecting Parenting Style) c8 |
front 55 Define Association Areas c9 | back 55 Parts of the brain where sensory, motor, and intellectual functions are linked-are myelinized to some degree by the time children enter middle childhood c9 |
front 56 Summary of Growth and Motor Development c9 | back 56 Each year children 6-12 grow about 2-3 inches and add about 6lbs. Hand, eyes, and fine motor coordination improves. Girls at this age are ahead in boys in their overall growth. By 12 girl attained 94% of their adult height, boys 84%. c9 |
front 57 Define Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) c9 | back 57 An injury to the head that results in diminished brain function such as a loss of consciousness, confusion, or drowsiness among school age children. Most who experience TBI fully recover c9 |
front 58 Define Asthma c9 | back 58 A chronic lung disease, characterized by sudden, potentially fatal attacks of breathing difficulty. 9% of school age students are diagnosed with asthma c9 |
front 59 Define excessive weight gain c9 | back 59 A pattern in which children gain more weight in a year than is appropriate for their age and height c9 |
front 60 Summary of Language c9 | back 60 Between 6-12, children continue to add words into their vocab astonishing rate from 5,000-10,000 new words per year c9 |
front 61 Define Piagets Concrete Operational Stage c9 | back 61 Piagets 3rd stage of cognitive development, during which children construct schemes that enable them to think logically about object and events in the real world. c9 |
front 62 Define Processing Efficiency c9 | back 62 The ability to make efficient use of short-term memory capacity. (it gets steadily faster with age) c9 |
front 63 Summary of Schooling c9 | back 63 Teaching style similar to Authoritative Parent Style-An approach that combines clear goals, good control, good communication, and high nurturance are more effective. Class size less than 20 are also more effective. c9 |
front 64 Define Literacy c9 | back 64 The ability to read and write
|
front 65 Define Reading Fluency c9 | back 65 The ability to read aloud with emotional expressiveness and minimal effort c9 |
front 66 Define English Language Learner (ELL) c9 | back 66 Non-English-speaking students either immigrant children or native born children c9 |
front 67 Define Bilingual Education c9 | back 67 An approach to second-language education in which children receive instruction in two different languages. c9 |
front 68 Define English-as-a-second-language (ESL) c9 | back 68 An approach to second-language education in which children attend English classes for part of the day and receive most of their academic instructions in English. c9 |
front 69 Define Achievement Test c9 | back 69 A test designed to assess specific information learned in school c9 |
front 70 Define Intelligent test c9 | back 70 Test that are usually paper-and-pencil multiple-choice test that can be given to large number of children at the same time (most US school require students to take this test at various points in their educational careers) c9 |
front 71 What are the 8 types of Intelligence c9 | back 71 1. Linguistic
|
front 72 Define linguistic intelliegence c9 | back 72 The ability to use language effectively c9 |
front 73 Define Logical/Mathematical Intelligence c9 | back 73 Facility with numbers and logical problem solving c9 |
front 74 Define Musical Intelligence c9 | back 74 The ability to appreciate and produce music c9 |
front 75 Define Spatial Intelligence c9 | back 75 The ability to appreciate spatial relationships c9 |
front 76 Define Bodily Kinesthetic Intelligence c9 | back 76 The ability to move in a coordinated way, combined with a sense of one's body in space c9 |
front 77 Define Naturalist Intelligence c9 | back 77 The ability to make fine discrimination among the plants and animals of the natural world or the patterns and designs of human artifacts c9 |
front 78 Define Interpersonal Intelligence c9 | back 78 Sensitivity to the behavior, moods, and needs of others c9 |
front 79 Define Intrapersonal Intelligence c9 | back 79 The ability t o understand oneself c9 |
front 80 Summary of Ethnic Differences in achievements c9 | back 80 Achievements differences may be due to philosophical belief that characterize some racial and ethnic groups. i.e. American tends to be individualistic focusing on oneself. c9 |
front 81 Define Learning Disability c9 | back 81 A disorder in which a child has difficulty mastering a specific academic skill, even though she possesses normal intelligence and no physical or sensory handicap (most often reading) |
front 82 Define Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) c9 | back 82 A mental disorder that causes children to have difficult attending to and completing task (10% of US school children has ADHD) c9 |
front 83 Summary of Freud and Erikson's perspective on Psychoanalytic c10 | back 83 Freud thought that the challenge of the middle childhood years was to form emotional bonds with peers and to move beyond those that were developed with parents in earlier years. Erikson Accepted Freuds view and added that was the time when they experience the crisis "industry vs inferiority" c10 |
front 84 Define Industry vs Inferiority
| back 84 During this stage Erikson said, children develop a sense of their own competence through the achievement of culturally define learning goals-failure to master these lead to sense of inferiority
|
front 85 Define Trait c10 | back 85 A stable pattern of responding to situations c10 |
front 86 Define Bandura's Reciprocal Determinism c10 | back 86 Model in which personal, behavioral, and environmental factors interact to influence personality development c10 |
front 87 Explain Bandura's Reciprocal Determinism Chart c10 | back 87 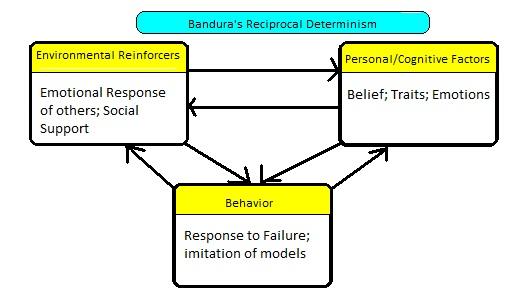 c10 |
front 88 What are the Big 5 Personality Traits c10 | back 88 1. Extraversion
|
front 89 Define Extraversion
| back 89 Active, Assertive, Enthusiastic, Outgoing--High activity level; Sociability; positive emotionality; talkativeness c10 |
front 90 Define Agreeableness
| back 90 Affectionate, forgiving, generous, kind, sympathetic, trusting--Perhaps high approach/positive emotionality; perhaps effortful control c10 |
front 91 Define Conscientiousness
| back 91 Efficient, organized, prudent, reliable, responsible--Effortful control/task persistence c10 |
front 92 Define Neuroticisim also known as Emotional Instability
| back 92 Negative Emotionality; Irritability c10 |
front 93 Define Openness/Intellect
| back 93 Approach; low inhibition c10 |
front 94 Example of Reciprocal Determinism c10 | back 94 When a child with a difficult temperament (personal component) throws a tantrum, the parents may ignore him (environmental component), leading him to become enraged and to misbehave even more (behavioral component). But if parents respond to an easygoing child's tantrum with inattention, the child may respond by stopping the tantrum to regain his parents attention. c10 |
front 95 Define Psychological Self c10 | back 95 A persons understanding of his or her enduring psychological characteristic/ones stable, internal traits c10 |
front 96 Define Self-Efficacy c10 | back 96 Belief in ones capacity to cause an intended event to occur or to perform a task c10 |
front 97 Define Self-Esteem c10 | back 97 A global evaluation of ones own worth (sums up all of the separate assessments a child makes about his skills in different areas. c10 |
front 98 Define Behavioral Comparison c10 | back 98 A description that involved comparing a childs behavior or physical features with those of another child or with a norm. i.e. Billy runs a lot faster then Jason c10 |
front 99 Define Psychological Construct c10 | back 99 Any statement that involved some internal personal trait. i.e. Sarah is so kind c10 |
front 100 Summary of how self esteem develop 1
| back 100 Self Esteem is strongly influenced by mental comparisons of children's ideal selves and their actual experiences. The key to self esteem is the amount of discrepancy between what the child desires and what he thinks he has achieved. The second major influence on a child's self esteem is the overall support the child feels she is receiving from the important people around them. c10 |
front 101 Summary of how self esteem develop 2
| back 101 To develop high self-esteem, children must first acquire the sense that they are liked and accepted in their families, by both parents and siblings. Next they need to be able to find friends with whom they can develop stable relationships. c10 |
front 102 Summary of The Child as Psychologist c10 | back 102 6-12 years old descriptions of other people will focus almost exclusive on external features-what the person looks like, where he lives, what he does, etc. i.e. He is very tall, dark brown hair, he goes to our school, I don't think he has any brothers or sisters etc.. c10 |
front 103 Define Moral Relativism Stage
| back 103 The second of Piagets stages or moral development, in which children's understand that many rules can be change through social agreements. Children's realize that the important thing about a game is that all players follow the same rules, regardless of what those rules are. c10 |
front 104 Define Moral Realism Stage
| back 104 The first of Piagets stages of Moral Development, in which children believes rules are inflexible and can not be change. i.e. children's believe that the rules of games can't be change because they are authorities such as parents, governments officials, or religious figures |
front 105 Define Self-Regulating
| back 105 Children's ability to conform to parental standards of behavior without direct supervision. i.e. Bike riding, skate boarding, without parents supervision c10 |
front 106 Summary of Relationships with Parents c10 | back 106 Middle childhood (6-12 yrs) is a period of increasing independence of child from family. Children who have close, warm relationships with their parents tend to be socially competent with peers c10 |
front 107 Summary of Gender Self-Segregation c10 | back 107 Boys play with boys and girls play with girls in their own kinds of games. Gender is more important among 6-12 then race, age, etc. Rough play in common in boys, less in girls. Boys establish hierarchies through roughness, girls through social skills. Boys are more accepting of newcomers and play with larger group, girls play in pairs or in small exclusive groups. Boys are more competitive, girls are more compliance. c10 |
front 108 Define Relational Aggression c10 | back 108 Aggression aimed at damaging another person's self-esteem or peer relationships, such as by ostracism or threats of ostracism (banning from the group, or threats to be banned from the group), cruel gossiping, or facial expressions of disdain. (more likely in girls then boys, begins in early preschool) c10 |
front 109 Define Retaliatory Aggression c10 | back 109 Aggression to get back at someone who has hurt you increasing in both boys and girls during the 6-12 year old period c10 |
front 110 Define Bullying c10 | back 110 A complex form of aggression in which a bully routinely aggresses against one or more habitual victims. They exhibit physical, verbal, and/or relational aggression toward their victims c10 |
front 111 Define Social Status c10 | back 111 An individual child's classification as popular, rejected, or neglected c10 |
front 112 Define Popular Social Status among children's c10 | back 112 children that are usually good at accurately assessing other's feelings at regulating their own emotions c10 |
front 113 Define Withdrawn/Rejected Status among children's c10 | back 113 Children that realize that they are dislike by peers, after repeated attempt to gain acceptance they give up and become socially withdrawn (often feel loneliness) c10 |
front 114 Define Aggressive/Rejected Status among children's c10 | back 114 Children's that are often disruptive, uncooperative, bossy, and usually believe that their peers likes them (many are unable to control) c10 |
front 115 Define Popular Social Status among children's c10 | back 115 Children's that are much less stable over time than those of rejected ones. They may sometimes move to the popular category when they become part of a new peer group. c10 |
front 116 Summary of The Effects of Poverty on Families and Children c10 | back 116 Children's living in poverty-neighborhoods show symptoms of PTSD. Including sleep disturbances, irritability, inability to concentrate, and angry outburst. Many experience flashback or intrusive memories of traumatic events, some persist into adulthood. (Lower income family have lower IQ) c10 |
front 117 Define Adolescence c11 | back 117 The transitioninal period between childhood and adulthood c11 |
front 118 Define Prefrontal Cortex (PFC) c11 | back 118 The part of the frontal lobe that is just behind the forehead. It is responsible for executive processing c11 |
front 119 Summary of the Brain c11 | back 119 There are two major brain growth spurt in the teenage years. One from 13-15 the second one begins around 17 and continues into early adulthood c11 |
front 120 What is the brain growth spurt between 13-15 c11 | back 120 During this spurt, the cerebral cortex become thicker, the neuronal pathways become more efficient;- more energy is produce and consumed by the brain than any other years;- teens are enable to think abstractly and reflect on their cognitive process, profound in changes of the prefrontal cortex c11 |
front 121 What is the brain growth spurt that begins around 17 and continue into early adulthood c11 | back 121 During this spurt, the frontal lobes of the cerebral cortex are the focus of development. This area of the brain controls logic and plainning. c11 |
front 122 Define Executive Processing c11 | back 122 Skills that enable us to consciously control and organize our though processes. c11 |
front 123 Summary of Physical Growth in Height c11 | back 123 An adolescent may grow 3-6 inches a year for several years until they reach their adult size. Girls attain most of their height by 16 while boys continue to grow until 18-20 c11 |
front 124 Summary of Shape and Proportions c11 | back 124 During the growth spurt, the normal cephalocaudal and proximodistal patterns are reverse. Teens hands and feet are the first to grow to adult size, follow by arms and legs, the trunk is usually the slowest-growing part. (good sign is shoe size increasing) c11 |
front 125 Summary of Other Body Systems c11 | back 125 By 17-18 boys finally catch up with girls in joint development. Men 40% body fat, Females 24% body fat. Boy usually have greater endurance because of their lower level of body fats. During teenage years, the heart and lungs increases considerably in size, and the heart rate drops. |
front 126 Define Puberty c11 | back 126 The physical changes which culminate in sexual maturity (changes both seen and unseen that are needed for reproductive maturity) c11 |
front 127 Major Hormones That Contributes to Physical Growth and Development c11 | back 127 c11 |
front 128 Define Primary Sex Characteristics c11 | back 128 The sex organs; Ovaries, Uterus, and Vagina in the female;-Testes and Penis in the male c11 |
front 129 Define Pituitary Gland c11 | back 129 The gland that control all other glands in the body, signal a child's adrenal glands to step up and produce androgen. (triggers glads to release hormones) c11 |
front 130 Define Menarche c11 | back 130 The first menstruation cycle within girls. Typically occurs 2 years after the beginning of other visible changes and is succeeded only by the final stage of breast and pubic hair development. 10% experience menarche earlier than 11, 90% each it by 14. Possible pregnancy after menarche. c11 |
front 131 Define Secondary Sex Characteristics c11 | back 131 Body part such as breast in females, changing voice pitch and beard growth in boys, and growth of pubic hair in both sex. c11 |
front 132 Summary of Timing with Puberty in girls c11 | back 132 Early developing girls are more like to have negative body images such as thinking they are too fat; get in trouble in school and at home; more likely to become sexually active; and more likely to get depress then girls who are average in developing. c11 |
front 133 Summary of Timing with Puberty in boys c11 | back 133 Early developing boys often occupy leadership roles and are more academically and economically successful in adulthood. c11 |
front 134 Summary of Teen Pregnancy Statistic c11 | back 134 In US the annual pregnancy rate 40 pregnancy per 1000 teen. (1 pregnancy per 1,000 girls younger than 15; 22 per 1000 at 15-17; and 70 per 1000 among 18-19 years old.) Of that 17% are African American, 8% are Whites, 14% are Hispanics. c11 |
front 135 Summary of Adolescent Pregnancy c11 | back 135 When teens become pregnant, about 1/3 (33%) end up in abortion, 14% result in miscarriages. 7% White, and 1% African American place their babies up for adoption c11 |
front 136 Gland-Hormones-and the Aspect of Growth Influenced
| back 136 Hormones(Thyroxine)-Normal Brain Development and overall rate of growth c11 |
front 137 Gland-Hormones-and the Aspect of Growth Influenced
| back 137 Hormones (Adrenal Androgen) -Some changes at puberty, particularly the development of secondary sex characteristic in girls c11 |
front 138 Gland-Hormones-and the Aspect of Growth Influenced
| back 138 Hormones (testosterone) -Crucial in the formation of male genitals prenatally; also triggers the sequence of changes in primary and secondary sex characteristics at puberty in the male c11 |
front 139 Gland-Hormones-and the Aspect of Growth Influenced
| back 139 Hormones (estrogen/estradiol) development of the menstrual cycle and breast in girls; has less to do with other secondary sex characteristics than testosterone does for boys c11 |
front 140 Gland-Hormones-and the Aspect of Growth Influenced
| back 140 Hormones (General Growth Hormones, Thyroid stimulating hormones and other activating hormones) -Rate of physical maturation; signals other glands to secrete c11 |
front 141 Summary of Sexual Minority Youth c11 | back 141 The emergence of physical attraction to members of the opposite sex. For some they are attractive to the same sex, or both sex. c11 |
front 142 Define Heterosexuality c11 | back 142 Physical Attraction to the opposite sex c11 |
front 143 Define Homosexuality c11 | back 143 Physical attractions to the same sex c11 |
front 144 Define Bisexuality c11 | back 144 Physical attractions to both sex c11 |
front 145 Define Transgenderism c11 | back 145 One who is convinced that their psychological gender is inconsistent with their biological sex c11 |
front 146 Summary of Drugs, Alcohol, and Tobacco c11 | back 146 Illicit drug use is declining, but still a problem because of the risk to which teens expose themselves, such as drunk driving and the possibility of life long addictions. c11 |
front 147 Summary of Depression and Suicide c11 | back 147 5% adolescents are in the midst of depression. 11% males and 22% females have reported depressions in teens. 15% of high school students have thought about suicide, 7% has attempted, 1 in 10,000 has succeeded. Boys are 4 times as high in comiting suicide than girls. c11 |
front 148 Contributing factors to suicide c11 | back 148 -Triggering stressful event such as rejection or humiliation i.e Breaking up with gf/bf or failure
|
front 149 Piagets Formal Operational Stage c11 | back 149 The fourth stage during which adolescents learn to reason logically about abstract concepts. Typically around 12-16 years of age c11 |
front 150 Define Task Goal c11 | back 150 Goals based on a personal standard and a desire to become more competent at something (goal based on a desire for self improvement) c11 |
front 151 Define Ability Goal c11 | back 151 Goals based on a desire to be superior to others. (being better than another person at something. c11 |
front 152 Summary on Transition to Secondary School c11 | back 152 Both method of 6-3-3 and 5-3-4 has not been working, students show losses in achievement and self-esteem transitioning to high school. Educators and developmentalists are searching for explanations and practical remedies to solve the transitioning period. c11 |
front 153 Define Identity c12 | back 153 An understanding of one's unique characteristics and how they have been, are, and will be manifested across ages, situations, and social roles c12 |
front 154 Define Identity Crisis c12 | back 154 A period during which an adolescent is troubled by his lack of an Identity (Eriksons term for the psychological state of emotional turmoil that arises when an adolescents sense of self becomes "unglued" so that a new, more mature sense of self can be achieved) c12 |
front 155 Define Genital Stage c12 | back 155 The period during which psychosexual maturity is reached c12 |
front 156 Define Identity vs Role Confusion c12 | back 156 The stage during which adolescents attain a sense of who they are c12 |
front 157 Marcia's Theory of Identity Achievement c12 | back 157 The person has been through a crisis and has reached a commitment to idealogical, occupational, or other goals c12 |
front 158 Marcia's Theory of Moratorium c12 | back 158 A crisis in progress, but no commitment has yet been made c12 |
front 159 Marcia's Theory of foreclosure c12 | back 159 The person has made a commitment without having gone through a crisis. No reassessment of old positions has been made. Instead, the young person simply accept a parentally or culturally define commitment c12 |
front 160 Marcia's Theory of Identity Diffusion c12 | back 160 The young person is not in the midst of a crisis and has not made a commitment. Diffusion may thus represent either an early stage in the process or a failure to reach a commitment after a crisis c12 |
front 161 Marcia's Crisis c12 | back 161 a period of decision making when old values and old choices are reexamined. This may occur as a sort of upheaval-or it may occur gradually c12 |
front 162 What are Marcia's 4 Identity Status c12 | back 162 1. Identity Achievement
|
front 163 Summary of Self-Understanding c12 | back 163 As children's ages, their self-concepts becomes more focused on enduring internal characteristics. i.e "Who am I?" (I am tall, I have blue eyes) to (I am a Democrat, I believe in God.) c12 |
front 164 Summary of Self Esteem c12 | back 164 Self esteem shifts during teenage years. At 19-20 years old, they have higher self esteem then at 8-10 years old. It very often drops abruptly. Teens with high self-esteem are better able to resist peer pressure, get higher grades in school, and are less likely to be depress. c12 |
front 165 Define Gender Role Identity c12 | back 165 The Gender related aspect of the psychological self. i.e Masculine most likely males, feminine mostly females. c12 |
front 166 Define Masculine c12 | back 166 One who perceives themselves as having masculine quantities c12 |
front 167 Define Feminine c12 | back 167 One who perceives themselves as having feminine quantities c12 |
front 168 Define Androgynous c12 | back 168 One who perceives themselves as having both Masculine and Feminine quantities c12 |
front 169 Define Undifferentiated c12 | back 169 One who perceives themselves as lacking both masculine and feminine quantities. c12 |
front 170 Define Ethnic Identity c12 | back 170 A sense of belonging to an ethnic group. (self identification as a member of their specific group, commitment to that group, and its values and attitudes, and some attitudes about the group that they being c12 |
front 171 Phinny's Second Stage "Ethnic Identity Search" c12 | back 171 One who compare his own ethnic group with others, to try to arrive at his own judgement c12 |
front 172 Phinny's Ethnic Identity Achievement stage c12 | back 172 A person who develops two Identity. One to the dominate culture, and one to the ethnic group which they belong to. c12 |
front 173 Define Conventional Morality
| back 173 Rules or norms of a group to which the individual belongs become the basis of moral judgments, whether that group is family, the peer group, a church, or the nation. c12 |
front 174 Define Postconventional Morality
| back 174 The level of moral reasoning in which judgments are based on an integration of individual rights and the needs of society. c12 |
front 175 Summary of Kohlberg's Culture and Moral Reasoning c12 | back 175 Justice is an important moral concept througout the world, and thus it isn't surprising that Kohlberg's stage sequence has been so strongly supported in cross-cultural research c12 |
front 176 Define Cyberbullying c12 | back 176 A form of aggression in which electronic communication are used to intentionally inflict harm on others i.e. disturbing photo, emails etc.. c12 |
front 177 Define Delinquency c12 | back 177 Antisocial behavior that includes law breaking. i.e. rape and murder c12 |
front 178 Children's and Adolescents comments about how to solve disagreements between friends c12 | back 178 5 yrs old- Go away from her and come back later when you're not fighting
|
front 179 Summary of Peer Groups c12 | back 179 Adolescents chooses to socialize with a group that shares their values, attitudes, behaviors, and identity status. Like friendships, peer groups become relatively stable. Peer groups structures can change over the years of adolescence. c12 |
front 180 Summary of Peer Group Relationships c12 | back 180 Although adults often assume that sexual desires are the basis of relationships, it appears that social factors are just as important. c12 |