Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
PCB3063 Ch 2
front 1  What is the name of the scientist shown in the image who is considered the father of genetics? Multiple choice question. | back 1 Gregor Mendel |
front 2 The offspring of a pea plant with purple flowers and a pea plant with white flowers would be called ______. | back 2 hybrids |
front 3 A cross between a true breeding tall plant and a true breeding short plant is an example of ______. | back 3 a hybridization experiment |
front 4 Why was the common garden pea, Pisum sativum, that Mendel used in his genetic experiments an ideal specimen to study genetic crosses? | back 4 He used true breeding Pisum sativum plants with two distinct genotypes and phenotypes. Reason: The Pisum sativum plants were true breeding with two distinct genotypes and phenotypes. Crosses between tall plants produced tall plants. Crosses between short plants produced short plants. Crosses between tall and short plants produced a combination of tall and short plants which was the basis of Mendel's statistical analysis. Reason: The Pisum sativum plants were true breeding with two distinct genotypes and phenotypes. Crosses between tall plants produced tall plants. Crosses between short plants produced short plants. Crosses between tall and short plants produced a combination of tall and short plants which was the basis of Mendel's statistical analysis. |
front 5 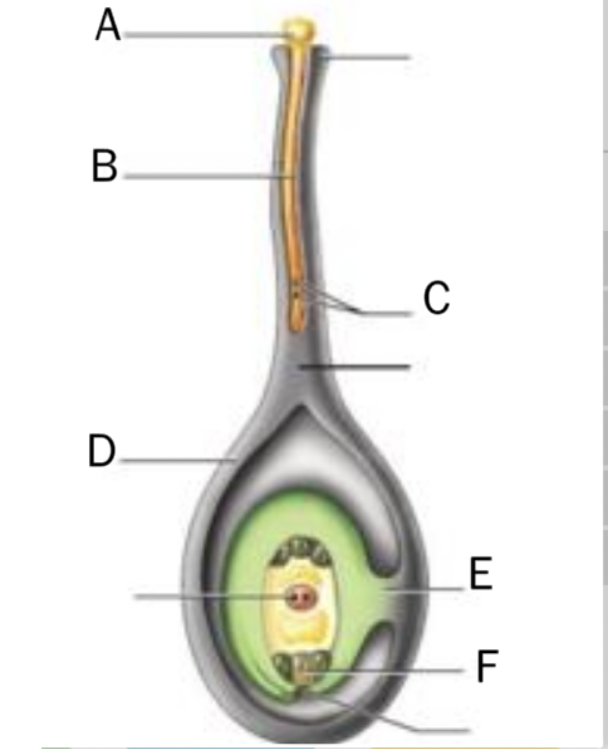 Identify the reproductive structures of a pollinated pea plant. Instructions | back 5
|
front 6 Select all of the true statements regarding Gregor Johann Mendel. | back 6 Mendel is regarded as a pioneer of genetics. Mendel initially failed the licensing exam to continue teaching. Mendel was an Augustinian priest/monk. |
front 7 List the events of pollination in the correct order, putting the first event at the top. InstructionsChoice 1 of 5. Second sperm fuses with central cell containing polar nuclei to create the endosperm toggle button Second sperm fuses with central cell containing polar nuclei to create the endosperm Choice 2 of 5. Sperm travel to egg where fertilization occurs toggle button Sperm travel to egg where fertilization occurs Choice 3 of 5. Pollen grain lands on stigma toggle button Pollen grain lands on stigma Choice 4 of 5. Pollen tube forms toggle button Pollen tube forms Choice 5 of 5. Sperm are produced in pollen grains and eggs are formed in the ovules toggle button Sperm are produced in pollen grains and eggs are formed in the ovules | back 7 no data |