Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
A&P Chapter 12
front 1 After birth Schwanncells | back 1 increase their presence and amount of myelination in the peripheral nervous system. |
front 2 Which organelle is a common site of protein synthesis in neurons? | back 2 Nissl body |
front 3 Which electrical signal can allow for rapid long-distance communication within the nervous system? | back 3 nerve action potential |
front 4 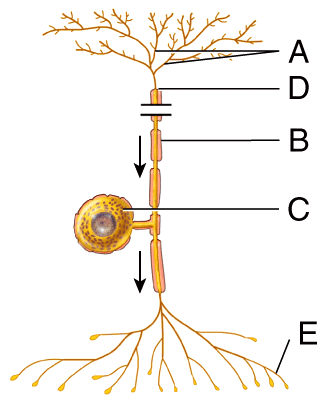 Which of the following structures is labeled A in the diagram? | back 4 dendrites |
front 5  Which of the structures in this diagram would be included in a ganglion? | back 5 C |
front 6 _____ is a neurotransmitter that is made on demand and can be used for microbial defense. ______ is a neurotransmitter that is made on demand and is used for vasodilation and special sensory recognition. | back 6 nitric oxide; carbon monoxide |
front 7 Na+/K+–ATPase is considered to be an electrogenic pump because | back 7 it contributes to the negativity of the resting membrane potential. |
front 8 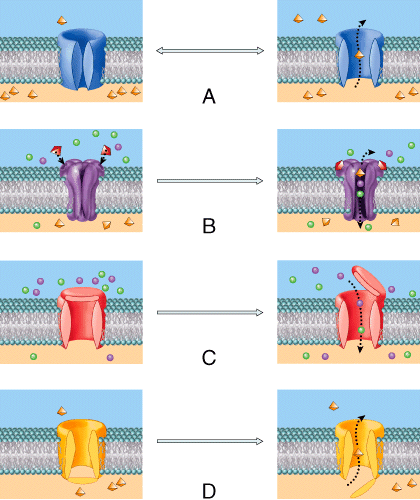 In this diagram, which of the channels is predominantly located on sensory neurons somas and dendrites and responds to vibration, touch, and stretch? | back 8 C |
front 9 The nervous system can distinguish between a light touch and a heavier touch because | back 9 the frequency of impulses sent to sensory centers is changing. |
front 10 Which ion channelsare used in the production of electrical signals in neurons? Select all that apply | back 10 Leak channel Voltage-gated channel Ligand-gated channel Mechanically gated channel |
front 11 This type of neural circuit consists of a single presynaptic neuron synapsing with several postsynaptic neurons. | back 11 Diverging circuit |
front 12 Which division of the peripheral nervous system only innervates the gastrointestinal tract’s wall? | back 12 Enteric nervous system |
front 13 In an action potential, the electric current that flows is generated by the movement of ______ across the membrane. | back 13 Ions |
front 14 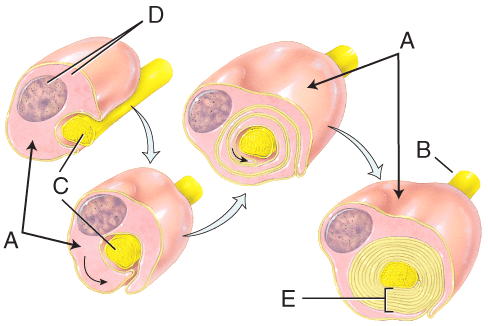 In this diagram, which structure would be produced by oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system? | back 14 E |
front 15 During an action potential’s ___________, a second stimulus can be produced only if the stimulus is greater than the threshold stimulus. This event corresponds to the period when the __________ remain open and sodium inactivation gates have reopened. | back 15 relative refractory period; potassium voltage-gated channels |
front 16 A postsynaptic neuron responds to acetylcholine neurotransmitter by creating | back 16 either EPSP or IPSP |
front 17 Acetylcholine is _________ at the neuromuscular junctions and ________ at cardiac muscle in the parasympathetic pathway. | back 17 excitatory; inhibitory |
front 18 During an action potential’s ___________, a second stimulus will not produce a second action potential (no matter how strong that stimulus is). This event corresponds to the period when the __________ remain open and the sodium inactivation gates have not reopened. | back 18 absolute refractory period; voltage-gated potassium channels |
front 19 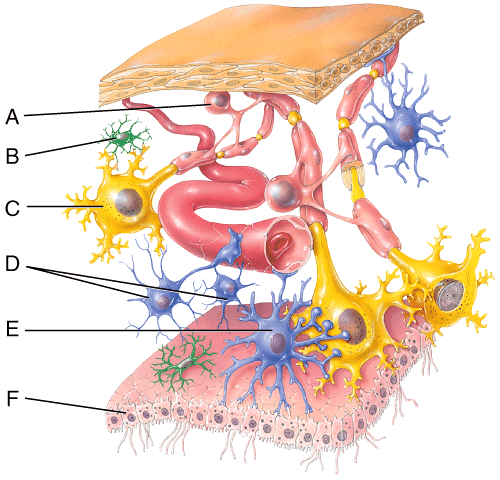 Which of the labeled cells in the diagram is a neuroglial cell that produces and assists in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid? | back 19 F |
front 20  In this diagram, which of these types of channels contributes to more potassium diffusing down their concentration gradient compared to sodium? | back 20 A |
front 21 In temporal summation, a single presynaptic neuron stimulates the creation of action potentials in a postsynaptic neuron when it | back 21 fires at a fast enough rate that the sum of EPSPs in the postsynaptic neuron moves above threshold. |
front 22 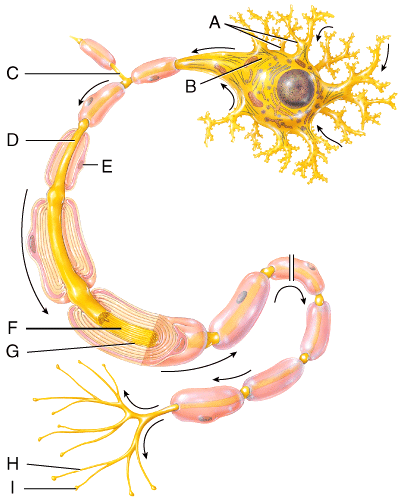 Which part of the neuron in this diagram would be called a nerve fiber? Select all that apply. | back 22 A, D, E |
front 23 Plasticity means the ability to | back 23 change based on experience. |
front 24  Which of the structures in this diagram contains a higher amount of voltage-gated sodium channels where action potentials are propagated? | back 24 B |
front 25  Which of the cells in this diagram sends electrical signals to glands, muscles and other neurons? | back 25 C |
front 26  In this diagram, where is a node of Ranvier? | back 26 B |
front 27 Which of these allows more potassium to exit the neuron and helps in maintaining the resting membrane potential? | back 27 leak channel |
front 28 Electrical excitability is seen in which cell? Select all that apply. | back 28 Muscle cells Neurons |
front 29 Manic-depressive illness is associated with | back 29 bipolar disorder. |
front 30 What specific type of unipolar neuron detects a sharp pain? | back 30 nociceptor |
front 31  Which of the cells in the diagram produces a myelin sheath but lacks a neurolemma? | back 31 A |
front 32 When a graded potential summates to threshold at the axon hillock, | back 32 voltage-gated Na+ channels open rapidly. |
front 33 What events must occur for the creation of an action potential? Select all that apply. | back 33 Summation of depolarizing graded potential. Threshold at the trigger zone. |
front 34 An excitatory neurotransmitter ______ the postsynaptic membrane. | back 34 depolarizes |
front 35 Wallerian degeneration refers to | back 35 degeneration of the distal end of axon and myelin sheath after neural injury. |
front 36 Diffusion, enzymatic degradation, and uptake by cells are all ways to | back 36 remove a neurotransmitter |
front 37  Which part of the neuron in this diagram produces proteins that can regenerate damaged axons in the PNS? | back 37 B |
front 38 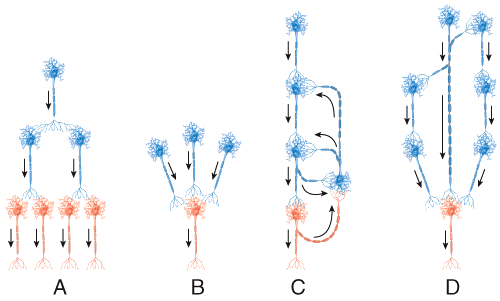 Which diagram represents a circuit that helps coordinated muscular activities, breathing, and short-term memory? | back 38 C |
front 39 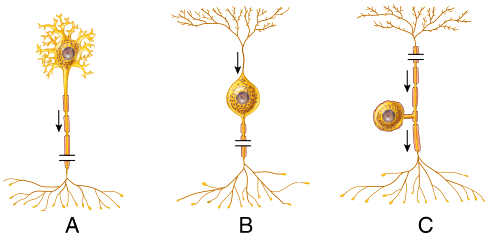 The neuron labeled B in this diagram would be classified as what type of functional neuron? | back 39 special senses neuron |
front 40  In this diagram, which of these types of channels represents a gate that opens to a depolarizing event? | back 40 D |
front 41 In this diagram, which structure electrically insulates the axon of a neuron to increase the speed of nerve impulse conduction? | back 41 E |
front 42 Which of the following types of neurons is exclusively found in the cerebellum? | back 42 Purkinje cells |
front 43 Hearing your cell phone ring in an quiet lecture hall is an example of which nervous system functions? | back 43 Sensory function |
front 44 Saltatory conduction is described by which statements? 1) current passes through the entire unmyelinated axon membrane
| back 44 2,3,4 |
front 45 In the process of spatial summation, _____ are added together and _____ are subtracted from that total to determine whether _____ will be created at the trigger zone of the postsynaptic neuron. | back 45 EPSPs; IPSPs; action potentials |
front 46 These statements describe what part of an action potential? • Sodium activation gates are closed | back 46 Relative refractory period |
front 47 During the resting state of a voltage-gated Na+channel, 1. the inactivation gate is open. 2. the activation gate is closed. 3. the channel is permeable to Na+. | back 47 both 1 and 2 are true. |
front 48 Which types of membrane channels can cause an IPSP on a neuron when acetylcholine binds to the receptor? Select all that apply. | back 48 Ionotropic ligand-gated channels |
front 49  Which diagram represents the type of circuit commonly used to send sensory signals to multiple areas of the brain? | back 49 A |
front 50  Which of the labeled cells in the diagram is a neuroglial cell that can be found in gray or white matter and makes contact with blood capillaries, neurons and pia mater of brain and spinal cord? | back 50 A |
front 51 Which of the neurons is located deep in the dermis or hypodermis and detect deep pressure? | back 51 Pacinian corpuscle |
front 52 Which neurotransmitters are used in virtually all of the inhibitory synapses found in the spinal cord? | back 52 gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glycine |
front 53  Which part of the neuron in this diagram will contain voltage-gated ion channels? | back 53 G |
front 54 Which is a function of the nervous system? Select all that apply. | back 54 Sensory function Integrative function Motor function |
front 55  Which diagram represents the type of circuit used to solve algorithms and geometry? | back 55 D |
front 56  In the diagram, where do graded potentials occur? Select all that apply?. | back 56 A, B |
front 57 All of the following statements are true for which type of cell?
| back 57 Polarized cell |
front 58 __________ open and close in response to physical deformation of receptors. | back 58 Mechanically gated channels |
front 59 A depolarizing graded potential | back 59 makes the membrane less polarized. |
front 60 Faster communication and synchronization are two advantages of | back 60 electrical synapses |
front 61 Which type of central nervous system tissue contains neuronal cell bodies, dendrites, unmyelinated axons, axon terminals, and neuroglial cells? | back 61 Gray matter |
front 62  Which diagram represents the type of circuit involved in controlling the movement of the biceps brachii and triceps brachii skeletal muscles? | back 62 B |
front 63 Chromatolysis refers to | back 63 break up of Nissl bodies after neural injury. |
front 64 With respect to neurons, the term “nerve fiber” refers to what structure? Select all that apply. | back 64 Axon, Dendrite |
front 65 This type of neuron has one dendrite and one axon emerging from the cell body. | back 65 Bipolar neuron |
front 66 The motor portion of the autonomic nervous system can be divided into | back 66 sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. |
front 67 Which of the following types of neurons is the most common type of neuron found in the brain and spinal cord? | back 67 multipolar neuron |
front 68  Which of the labeled cells in the diagram is a neuroglial cell that removes debris and acts as a phagocyte? | back 68 B |