Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
ABO - Pathology
front 1 Aphakia | back 1 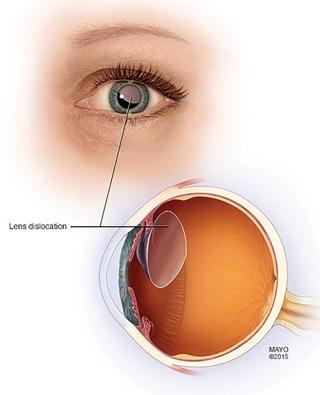 An absence of the crystalline lens of the eye (pseudophakia: having a false lens). |
front 2 Cataracts | back 2 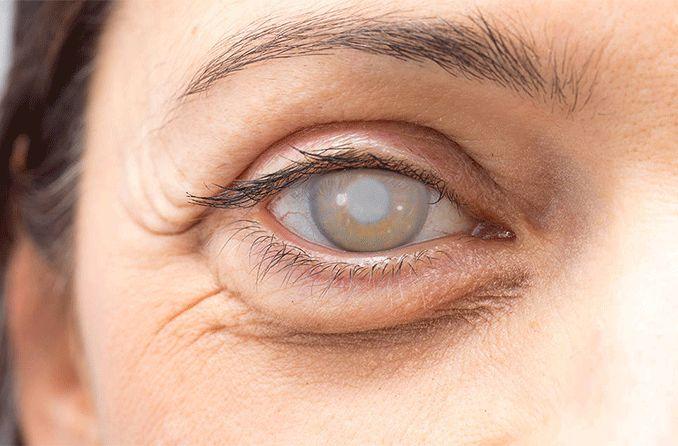 A condition when the crystalline lens of the eye becomes opaque.
Congenital cataract: one, which originates at
birth. |
front 3 Conjunctivitis | back 3 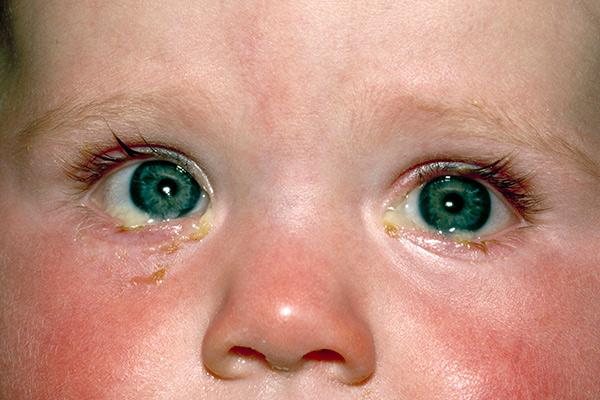 Inflammation of the conjunctiva; commonly referred to as "pink eye." |
front 4 Cycloplegia | back 4 Paralysis of the ciliary body; cycloplegic drops are used for diagnostic purposes. |
front 5 Glaucoma | back 5 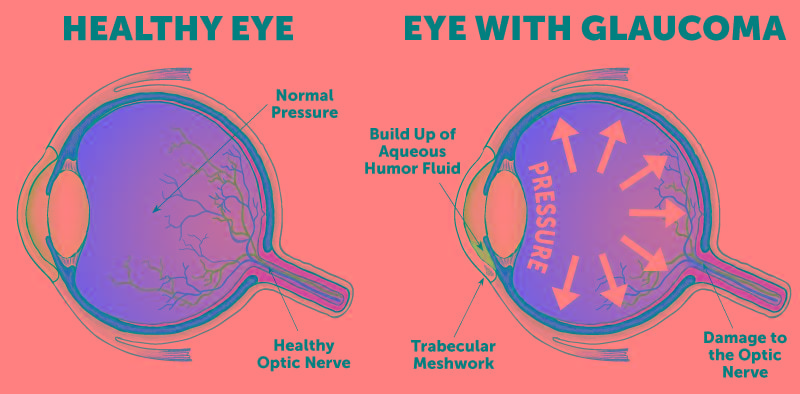 An ocular disease having as its primary characteristic a sustained
increase in |
front 6 Mydriasis | back 6 Prolonged or excessive dilation of the pupil of the eye. Mydriatic
drops cause |
front 7 Nystagmus | back 7 Rapid, involuntary oscillation of the eyeballs, usually the result of
brain or ear |
front 8 Photophobia | back 8 Abnormal sensitivity to light; light discomfort. |
front 9 Ptosis | back 9 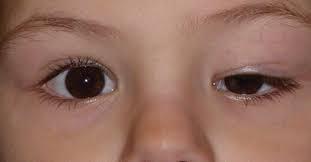 Paralytic drooping of the upper eyelid. |
front 10 Scotoma | back 10 A blind area of reduced vision in the visual field. |
front 11 Strabismus | back 11 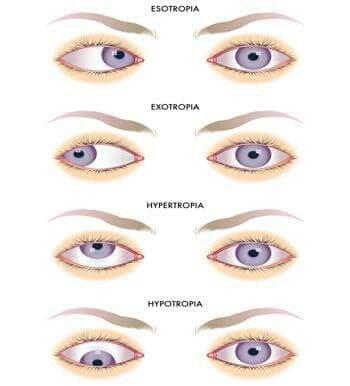 Failure of the two eyes to simultaneously direct their gaze at the
same object |