Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
ABO - Anatomy
front 1 Cornea | back 1 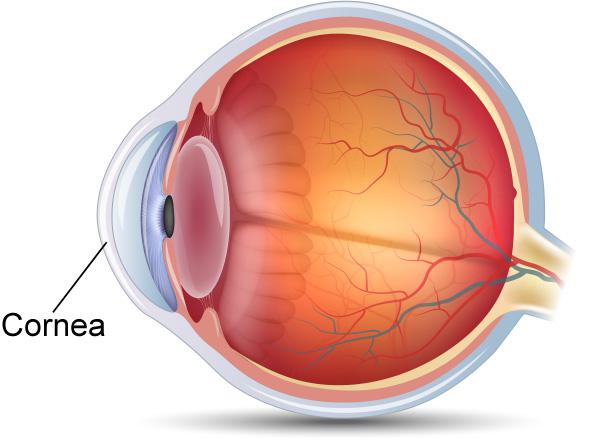 The refractive, transparent, anterior wall of the eye, equal to 43 diopters power. It is the most important part of the focusing system of the eye and brings objects into focus on the retina. The cornea is the fastest healing part of the body. |
front 2 Anterior Chamber | back 2 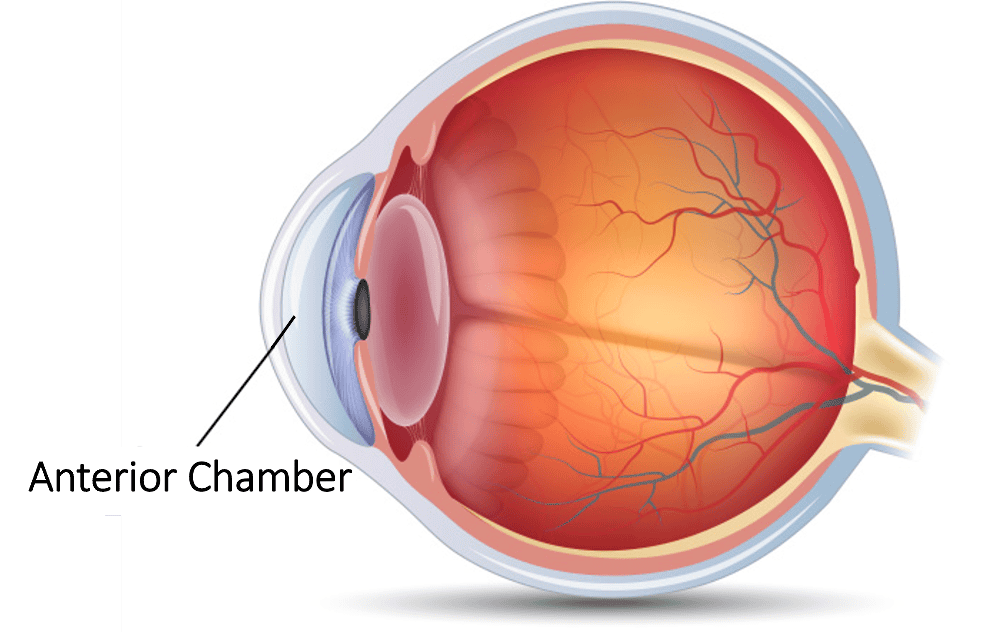 Front cavity or compartment of the eye, located between the cornea and iris. Contains the aqueous humor. |
front 3 Anterior Chamber Angle | back 3 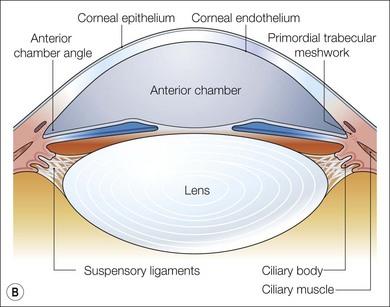 The structure formed by the junction of the iris with the corneo-sclera. Normal fluid drainage from the eye occurs through the trabecular meshwork which lies in the chamber angle. Malfunction of the chamber angle is the cause of glaucoma (high pressure in the eye). |
front 4 Iris | back 4 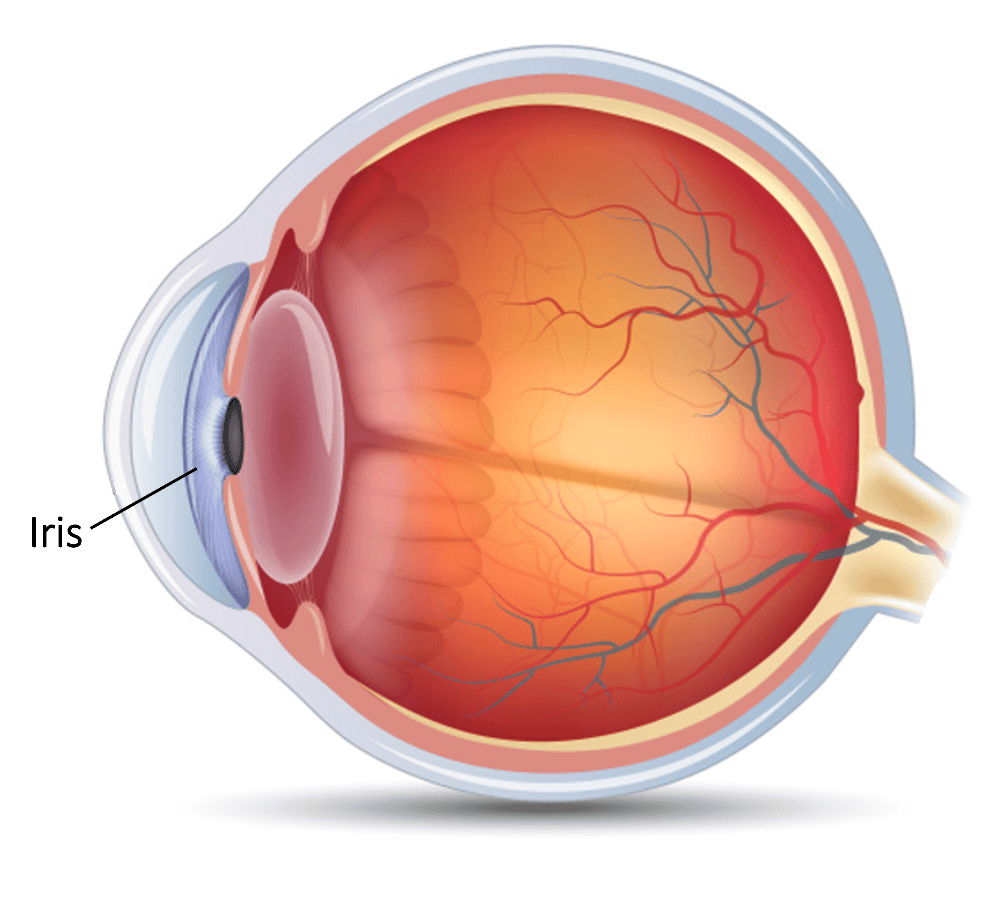 The colored, circular membrane suspended behind the cornea and
immediately |
front 5 Pupil | back 5 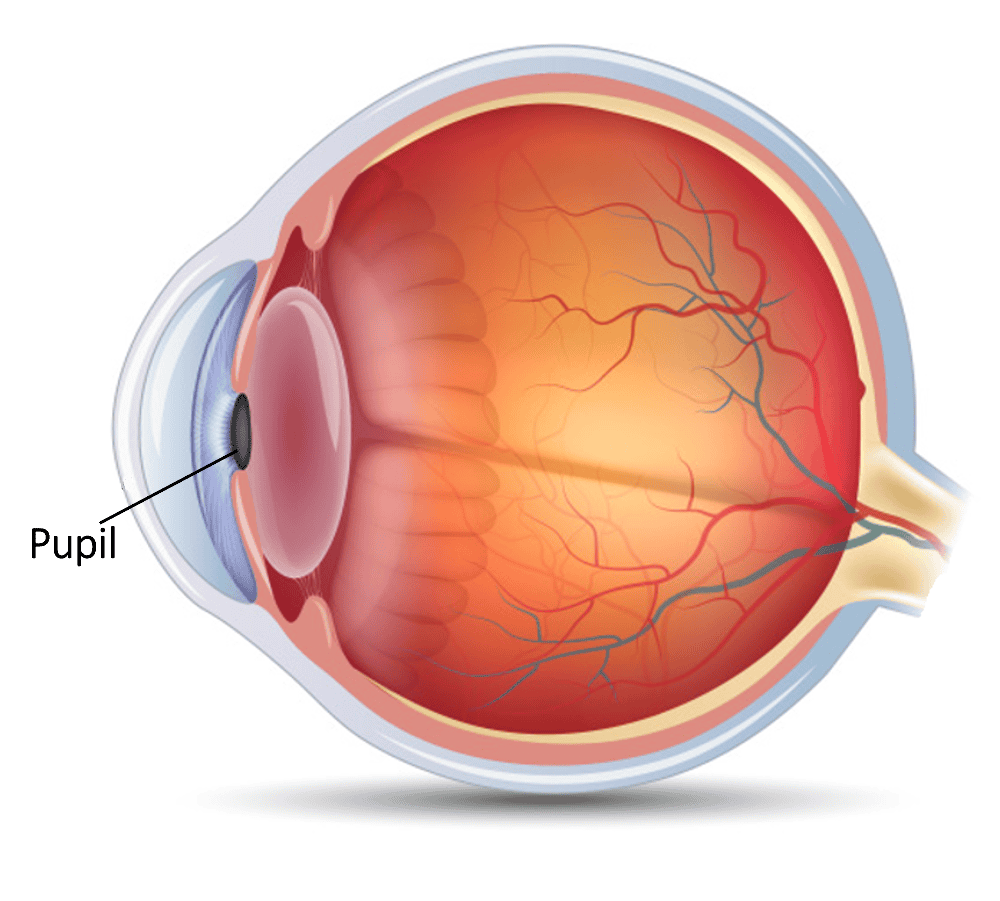 The central opening of the iris through which light is permitted to enter the eye. |
front 6 Crystalline Lens | back 6 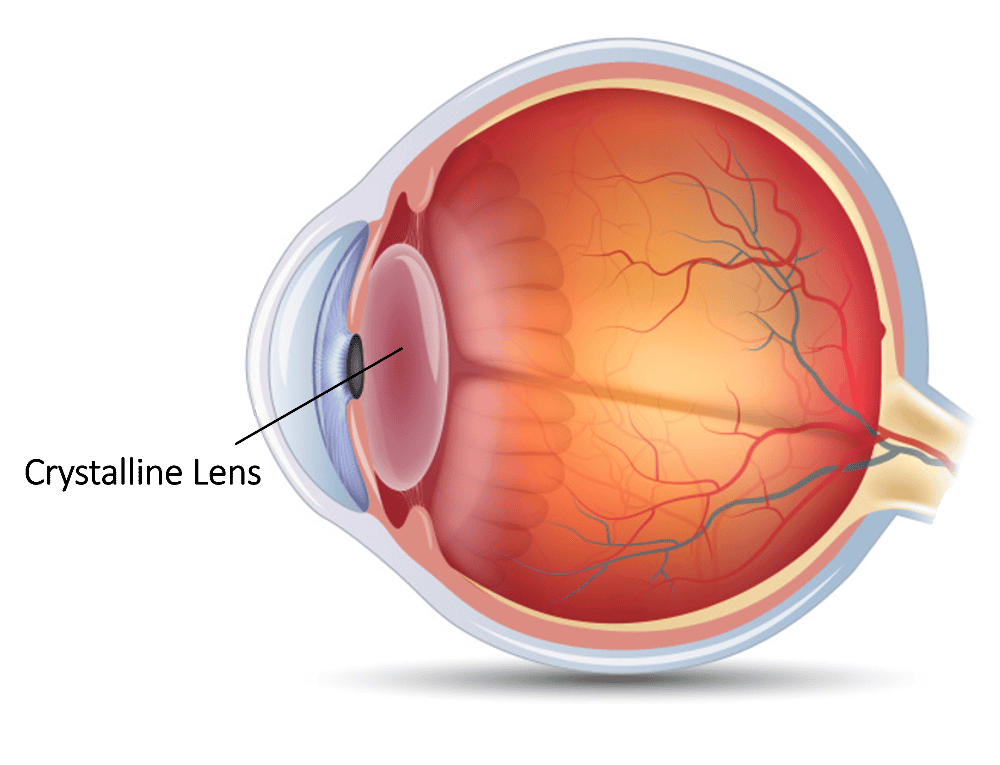 A transparent, colorless body suspended in the front part of the
eyeball, between |
front 7 Ciliary Body | back 7  A thick ring of tissue lying at the base of the iris. Its muscle fibers serve to change the curvature of the lens and thereby provide fine focusing of light onto the retina. |
front 8 Zonules | back 8 Threadlike filamentous attachments which hold the crystalline lens in place in the eye. |
front 9 Vitreous Humor | back 9 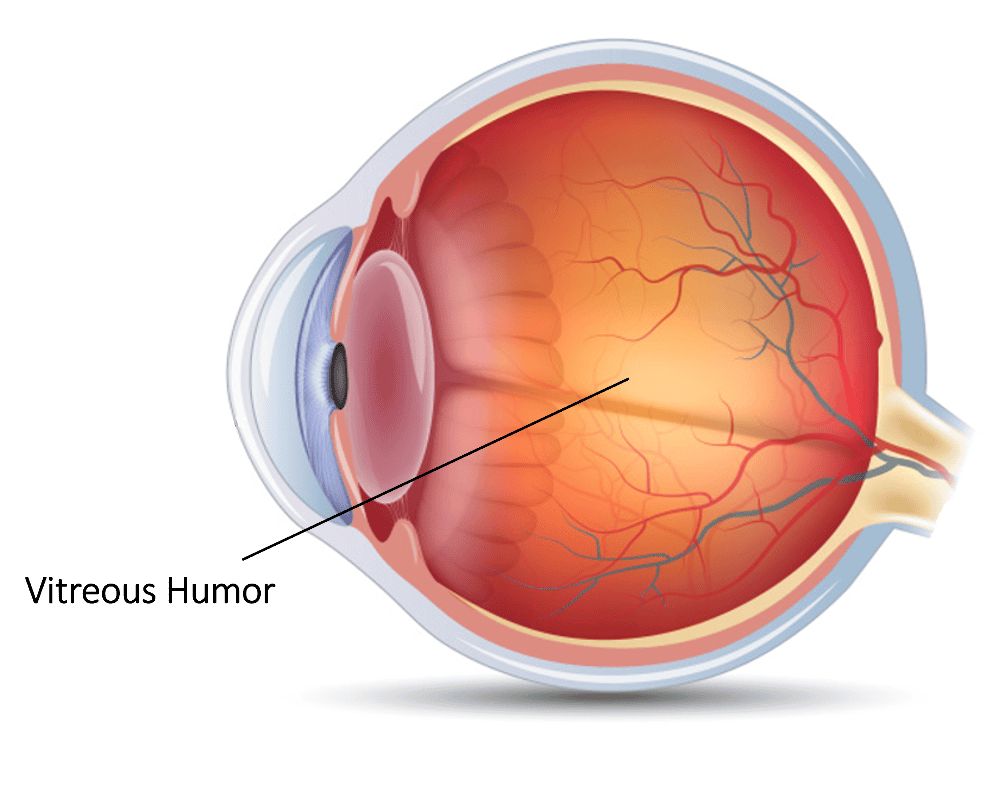 The clear jelly which fills the space between the lens and the retina. It helps to keep the retina intact. Eighty percent of the eye is filled with vitreous. |
front 10 Sclera | back 10 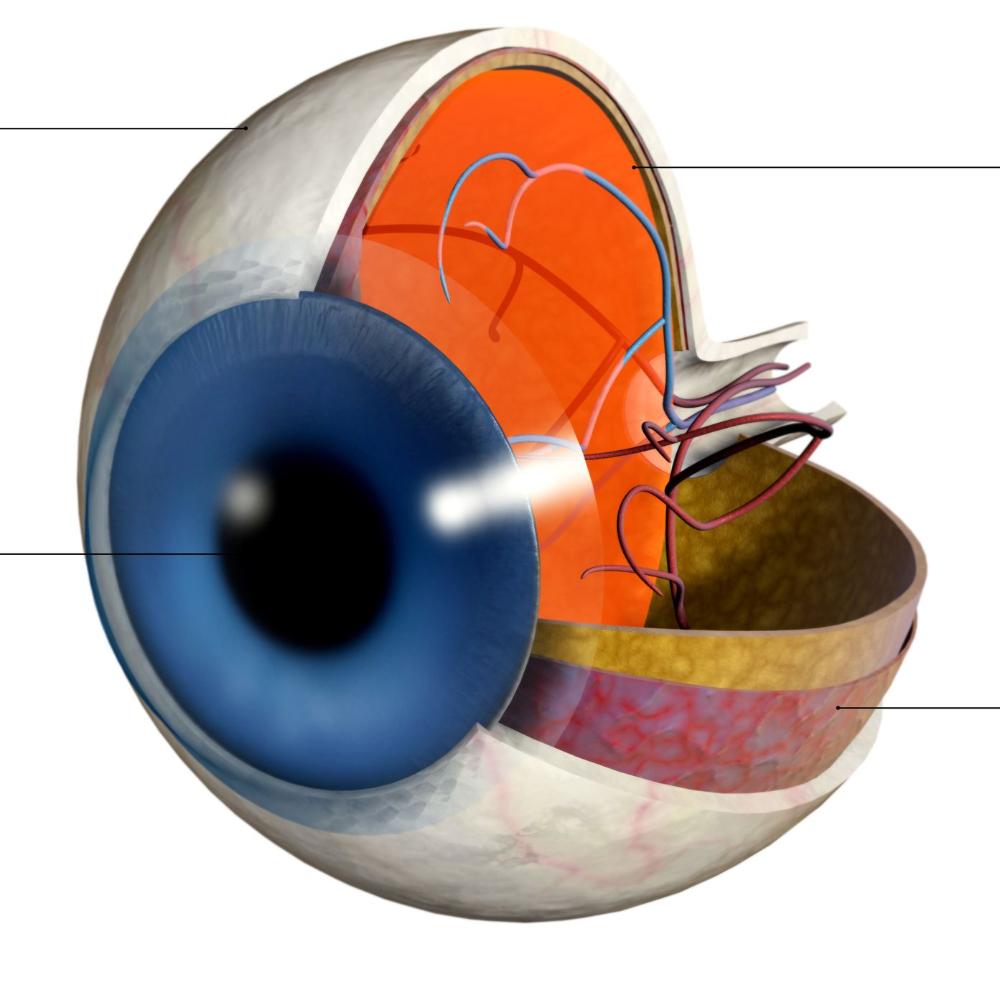 The sclera is tough and fibrous, protecting the interior components of the eye from injury, and makes up the exterior coating of the eye. The sclera forms the entire visible white exterior of the eye. |
front 11 Choroid | back 11  A spongy layer filled with blood vessels. It lies between the sclera and the retina. The choroid nourishes the outer layers of the retina. |
front 12 Retina | back 12 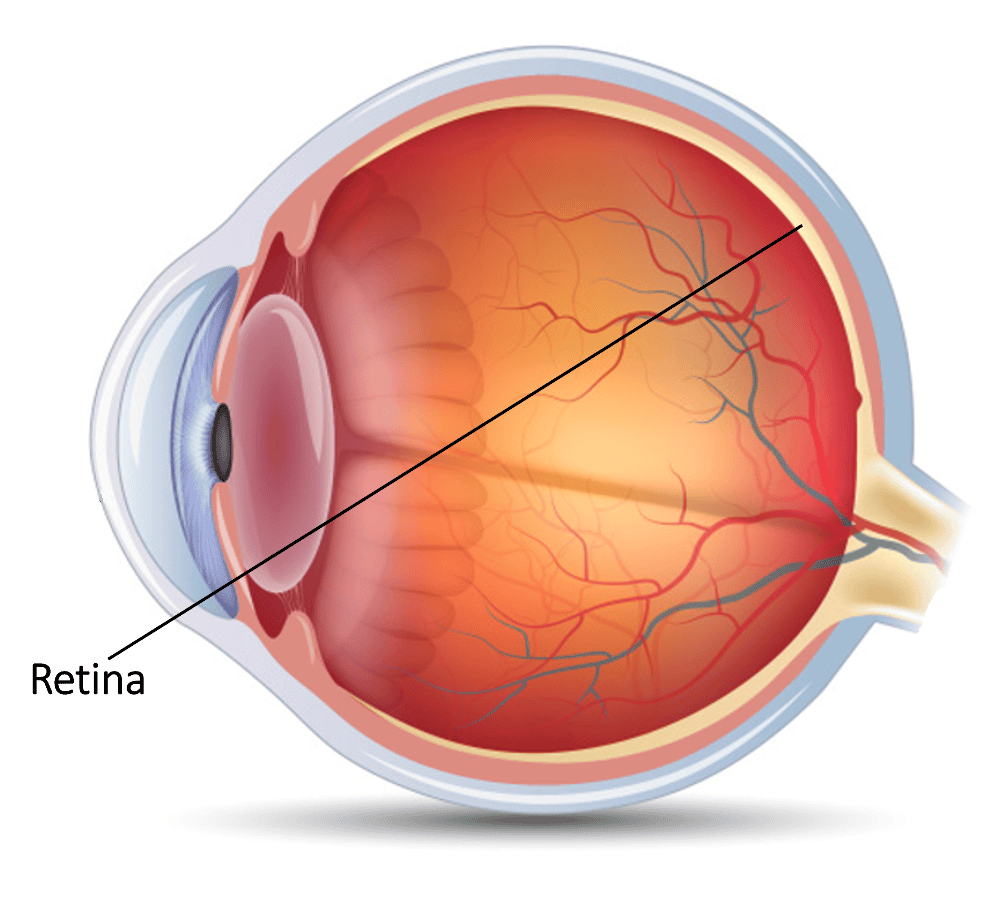 The vital thin layer of tissue composed of millions of visual cells which lines the inside back two-thirds of the eye. The retina is analogous to a film in a camera. It receives light and sends tiny electrical impulses to the brain to give sight. |
front 13 Optic Nerve | back 13 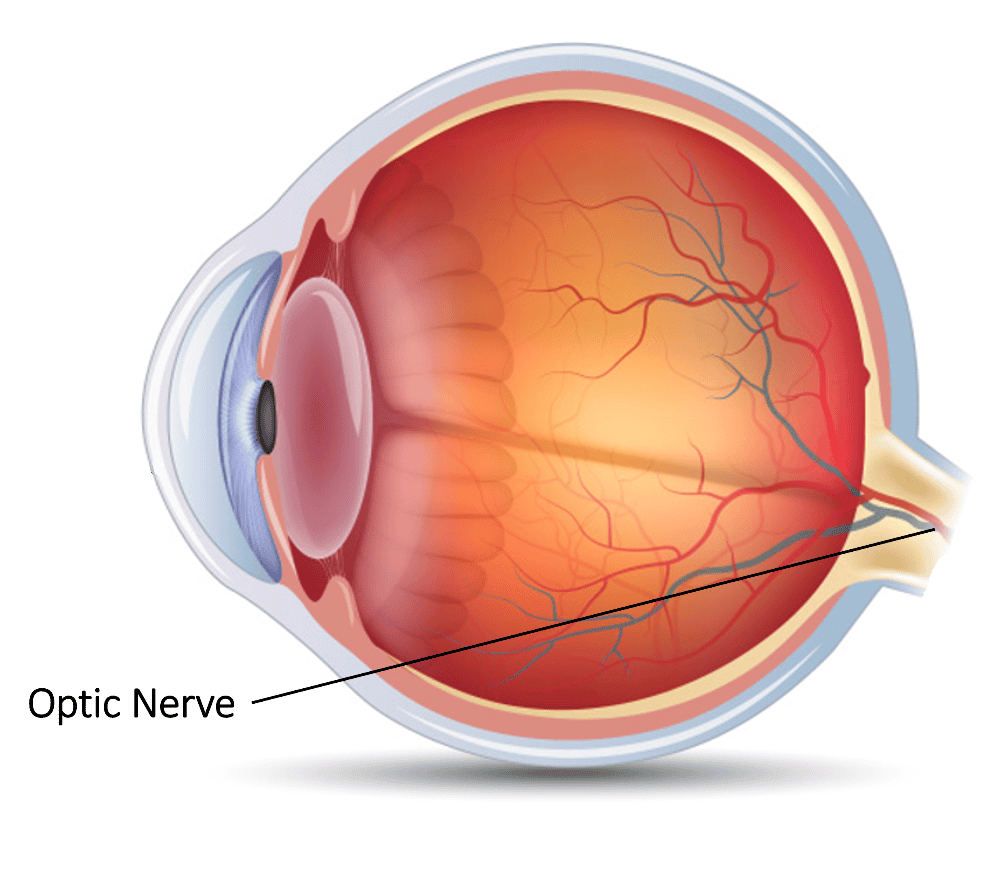 A cable-like structure composed of thousands of nerve fibers which carry impulses from the retina to the brain where visual perception occurs. |
front 14 Macula | back 14 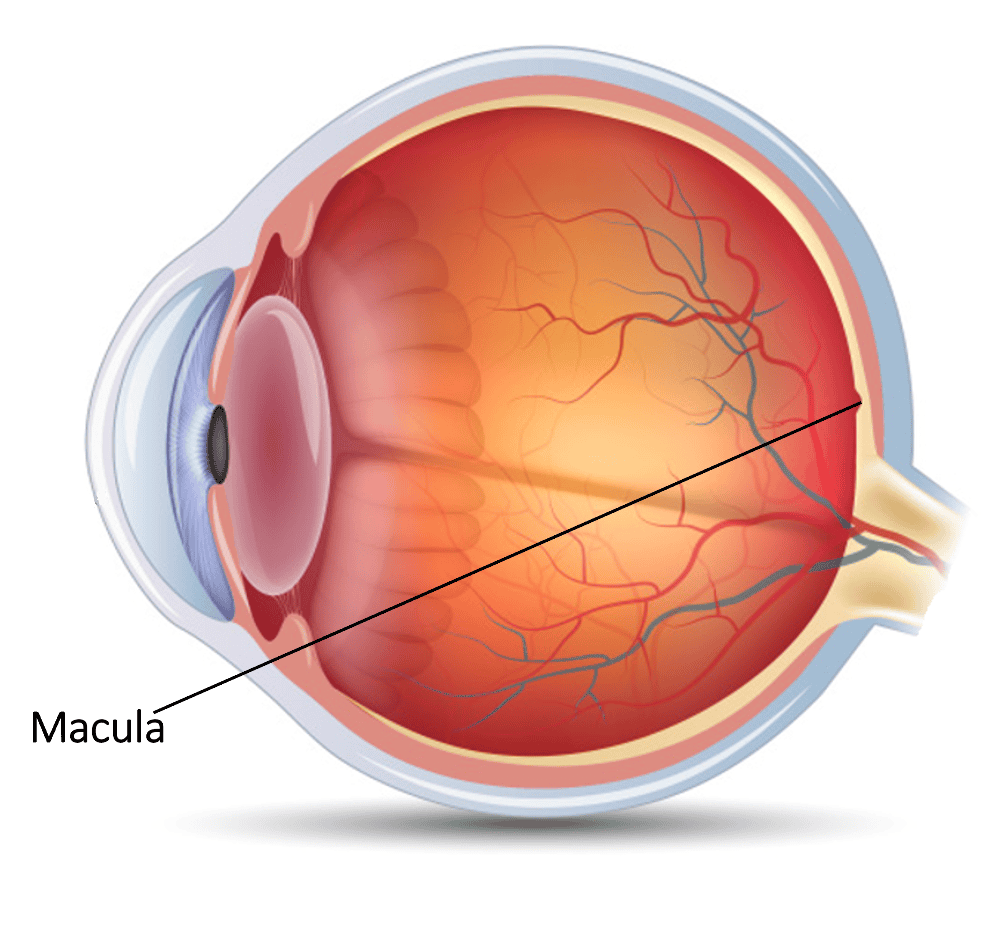 The highly developed central zone of the retina. The macula gives critical vision for reading and discrimination small objects. |
front 15 Optic Disc | back 15 The optic disc or optic nerve head is the point of exit for ganglion cell axons leaving the eye. Because there are no rods or cones overlying the optic disc, it corresponds to a small blind spot in each eye. |
front 16 Palpebra | back 16 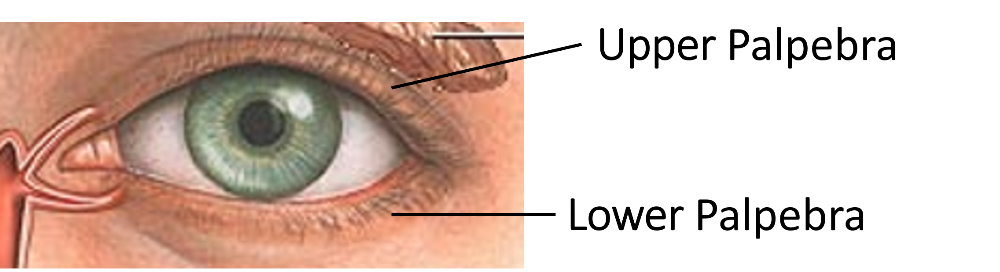 Eyelid. Protects the eye, helps remove foreign bodies. |
front 17 Canthus | back 17 The angle at either end of the slit between the eyelids. |
front 18 Cones | back 18 Light sensitive cells in the retina responsible for color vision, daytime vision, and the central portion of the visual field. |
front 19 Rods | back 19 Specialized visual cell in the retina responsible for peripheral and night vision. |
front 20 Conjunctiva | back 20 The clear membrane that lines the eyelids and covers the exposed
surface of the |