Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Anatomy and Physiology 2 Wiley Chapter 23
front 1 Which of the following is NOT part of the upper respiratory system? | back 1 Trachea |
front 2 Which of the following is NOT a conducting zone action? | back 2 All of these are actions of the conducting zone |
front 3 Which of the following is NOT a factor that determines the rate of pulmonary and systemic gas exchange? | back 3 all of these are factors that determine the rate of pulmonary and systemic gas exchange |
front 4 Which of the following is a passageway for air, food and water? | back 4 pharynx |
front 5 Which structure prevents food or water from entering the trachea? | back 5 epiglottis |
front 6 The gas law that describes the pressure changes that occur during pulmonary ventilation is | back 6 Boyle's law |
front 7 Which structure is located anterior to the esophagus and carries air to the bronchi? | back 7 trachea |
front 8 Which of the following is the primary gas exchange site? | back 8 Alveolus |
front 9 Which of the below tissues maintains open airways in the lower respiratory system? | back 9 hyaline cartilage |
front 10 Which of the below tissues provides the functions of the inner layer of the conducting organs? | back 10 cilitated cuboidal epithelium with goblet cells |
front 11 The point where the trachea divides into right and left primary bronchi is a ridge called | back 11 carina |
front 12 Which of the below tissues forms the exchange surfaces of the alveolus? | back 12 simple squamous epithelium |
front 13 Which of the following are cells of the alveoli that produce surfactant? | back 13 type II alveolar cells |
front 14 Which of the following is NOT a factor that affects pulmonary ventilation? | back 14 all of these are factors that affect pulmonary ventilation |
front 15 Which of the following indicates the diffusion of gases at the alveoli of the lungs? | back 15 oxygen in the blood, carbon dioxide out of the blood |
front 16 Exhalation begins when | back 16 inspiratory muscles relax |
front 17 Which of the following is the sum of the residual and the expiratory reserve volume? | back 17 functional residual capacity |
front 18 Which of the following is NOT a factor that the rate of pulmonary and systemic gas exchange depends on? | back 18 force of contraction of diaphragm |
front 19 Which of the following is the dominant method of carbon dioxide transport? | back 19 dissolved in plasma as bicarbonate ions |
front 20 When blood pH drops, the amount of oxyhemoglobin ___ and oxygen delivery to the tissue cells ___. | back 20 decreases/increases |
front 21 Which of the following is a factor that does NOT affect hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen? | back 21 respiratory rate |
front 22 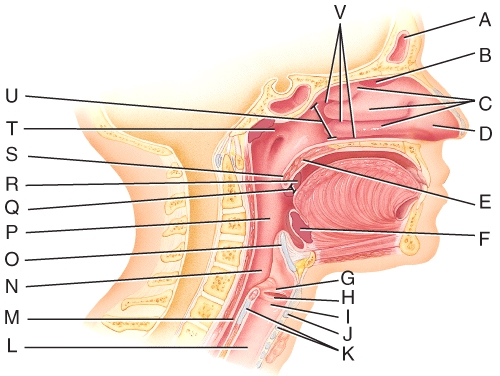 Where are the nasal conchae? | back 22 B) C |
front 23  Which tonsils are found in the oropharynx? | back 23 B) R |
front 24  Which structure is also referred to as the Adam's apple? | back 24 D) J |
front 25  Where is the larynx? | back 25 A) I |
front 26  Where is the uvula? | back 26 D) S |
front 27 A white baby boy is born after 7 months of gestation. He develops difficulty breathing and looks slightly blue. He is most likely suffering from- | back 27 respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) |
front 28 An individual is suffering from gangrene. This is a condition where circulation to tissues is interrupter causing a serious reduction in oxygenation to these tissues. Anaerobic bacteria invade the tissues and must be treated. If antibiotics don't work, an intelligent treatment may include- | back 28 hyberbaric oxygenation |
front 29 A man is found lying unconscious on the floor of his apartment during a very cold period. A space heater is nearby. His lips appear to be cherry red in color. He might be suffering from- | back 29 carbon monoxide poisoning |
front 30 An individual suffers a blood clot in an artery that delivers blood to his leg. The leg begins to take on a blue hue, becomes colder than the rest of his body and he experiences numbness in the leg. He is most likely experiencing- | back 30 ischemic hypoxia |
front 31 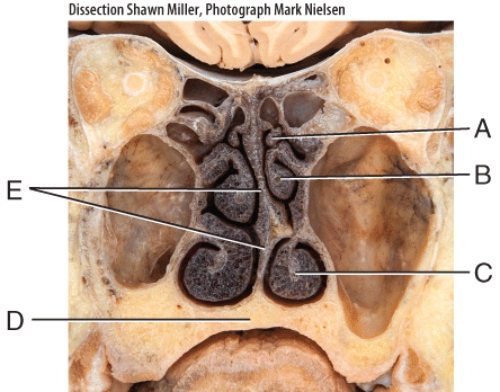 Where is the middle nasal concha? | back 31 B |
front 32  Where is the inferior nasal concha? | back 32 C |
front 33  What is E pointing to? | back 33 nasal septum |
front 34 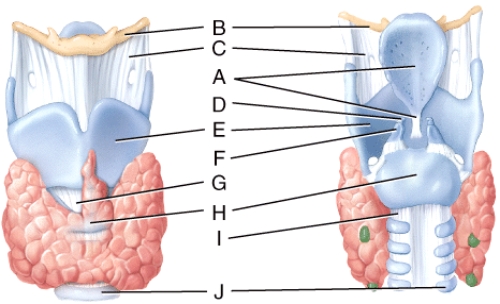 What is line D pointing to? | back 34 corniculate cartilage |
front 35  Where is the cricoid cartilage? | back 35 E) H |
front 36 An individual has an ideal weight of 125 pounds. Based on this fact, the estimated size of his anatomical (respiratory) dead space is- | back 36 125 milliliters |
front 37 The most important factor that determines the percentage of oxygen saturation of hemoglobin is? | back 37 Po2 |
front 38 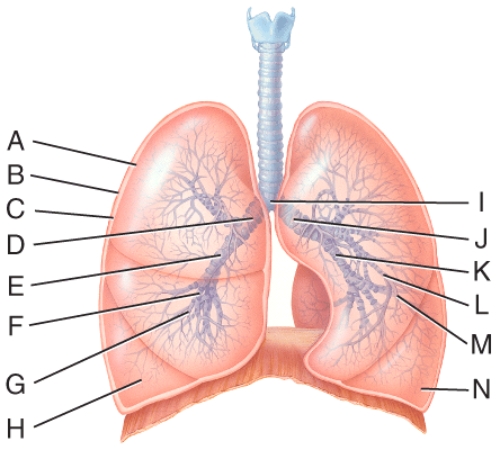 What is line J pointing to? | back 38 left primary bronchus |
front 39  Where is the right bronchiole? | back 39 B) G |
front 40 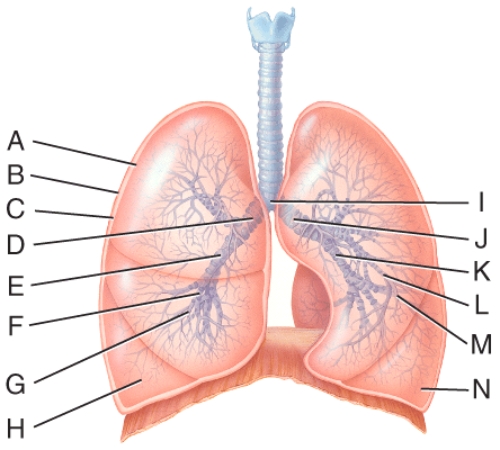 Which lines are pointing to tertiary bronchi? | back 40 F and L |
front 41  What is line B pointing to? | back 41 parietal pleura |
front 42 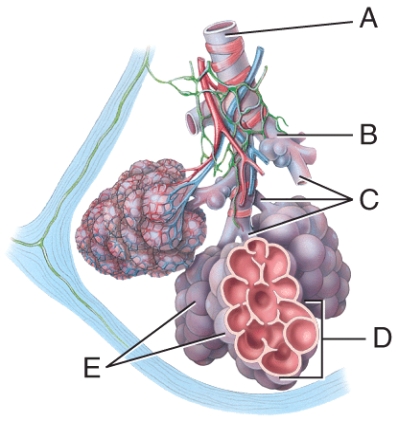 Which letter represents the primary gas exchange structure? | back 42 D) E |
front 43  What are lines C pointing to? | back 43 Alveolar ducts |
front 44  Where is the terminal bronchiole? | back 44 A |
front 45 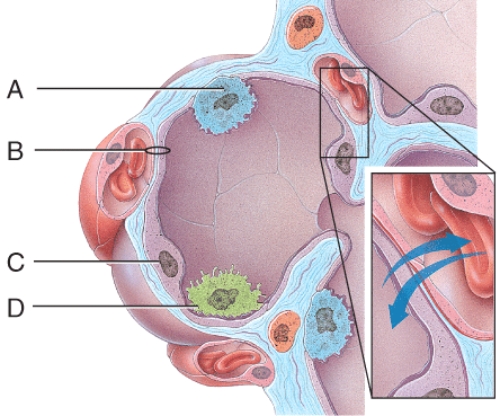 Which structure provides disease resistance within the lungs? | back 45 D |
front 46  Which cells are the main sites of gas exchange? | back 46 C |
front 47  Which cell secretes surfactant? | back 47 A |
front 48 If an individual experiences a broken rib which is displayed sufficiently to puncture a lung, even though the outer skin is not punctured, he will most likely develop- | back 48 ABC |
front 49 Normal quiet breathing is controlled by | back 49 all of these choices |
front 50 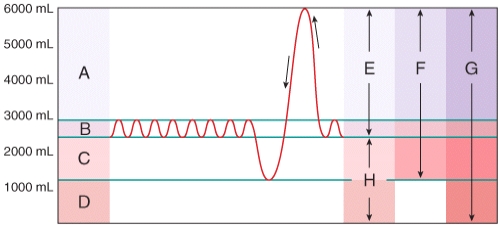 Which area in the figure is the sum of the tidal volume and the inspiratory reserve volume? | back 50 D) E |
front 51  Which area in the figure is the sum of the tidal volume and the inspiratory reserve volume and expiratory reserve volume? | back 51 E) F |
front 52  Which area in the figure is the sum of the vital capacity and residual volume? | back 52 C) G |
front 53  Which area in the figure is the sum of the residual volume and the expiratory reserve volume? | back 53 A) H |
front 54  Which area in the figure represents a very deep inhalation, much greater than the tidal volume? | back 54 B) A |
front 55  Which area in the figure represents the volume of a normal breath? | back 55 A) B |
front 56  Which area in the figure represents the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a deep exhalation? | back 56 C) D |
front 57  Which area in the figure represents a very deep exhalation, much greater than the tidal volume? | back 57 A) C |
front 58 Which of the following is a spasmodic contraction of the diaphragm followed by spasmodic closure of the rima glottidis, which produces a sharp sound on inhalation? | back 58 hiccuping |
front 59 Which of the following is an inhalation followed by many short convulsive exhalations during which the rima glottidis remains open and the vocal folds vibrate, accompanied by characteristic facial expressions? | back 59 laughing/crying |
front 60 Which of the following is a series of convulsive inhalations followed by a single prolonged exhalation where the rima glottidis closes earlier than normal after each inhalation so only a little air enters the lungs with each inhalation? | back 60 sobbing |
front 61 Which of the following is a deep inhalation through a widely opened mouth producing an exaggerated depression of the mandible, the precise cause of which is unknown? | back 61 yawning |
front 62 Which of the following is a long drawn and deep inhalation immediately followed by a shorter but forceful exhalation? | back 62 sighing |
front 63 Which of the following is a spasmodic contraction of the muscles of exhalation that forcefully expels air through the nose and mouth? | back 63 sneezing |
front 64 Which of the following is a long drawn and deep inhalation followed by a complete closure of the rima glottidis, which results in a strong exhalation, pushing the rima glottidis open and sending a blast of air through the upper respiratory passages? | back 64 coughing |
front 65 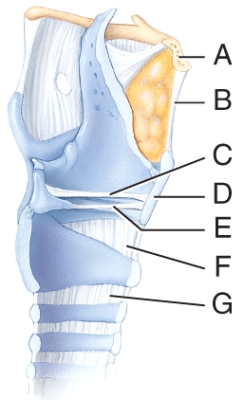 Which structure in the figure is the hyoid bone? | back 65 A |
front 66  Which structure in the figure is the ventricular fold? | back 66 C |
front 67  Which structure in the figure is the vocal fold? | back 67 D) E |
front 68 Where is the rhythmicity center for respiration? | back 68 in the medulla |
front 69 With which body system does the respiratory system work to regulate the pH of body fluids? | back 69 urinary |
front 70 The branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the ears, nose and throat is- | back 70 otolaryngology |
front 71 The surgical procedure used to cosmetically reshape the nose or to correct a deviated septum or fracture of the nose is called | back 71 rhinoplasty |
front 72 Coryza is the medical name for | back 72 the common cold |
front 73 During quiet inhalation, which respiratory muscles contract? | back 73 diaphragm and external intercostals |
front 74 The volume of one breath is called | back 74 tidal volume |
front 75 The sum of the partial pressures of nitrogen, oxygen, argon, carbon dioxide, water vapor and other gases in our environment is called | back 75 atmospheric pressure |
front 76 If each hemoglobin molecule has bound 3 oxygen molecules, the hemoglobin is considered to be saturated at what percentage? | back 76 75% |
front 77 The neurons of the pontine respiratory group transmit nerve impulses to the | back 77 medulla |
front 78 Exercise brings about an increase in | back 78 both a and b |
front 79 the cartilages and muscles of the larynx develop from the | back 79 fourth and sixth pharyngeal arches |
front 80 Which of the following is a forced exhalation against the closed rima glottidis as may occur during periods of straining while defecating? | back 80 valsalva maneuver |