Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
CH 10- Muscle Tissue
front 1 Muscle that has a striped appearance is described as | back 1 striated |
front 2 Which element is important in directly
triggering | back 2 calcium (Ca++) |
front 3 Which of the following properties is not common to all three muscle
tissues? | back 3 at rest, uses shielding proteins to cover actin-binding sites |
front 4 The correct order for the smallest to the largest unit of
organization in muscle tissue is ________. | back 4 filament, myofibril, muscle fiber, fascicle |
front 5 Depolarization of the sarcolemma means ________. | back 5 the inside of the membrane has become less |
front 6 In relaxed muscle, the myosin-binding site on actin is | back 6 tropomyosin |
front 7 According to the sliding filament model, binding sites | back 7 calcium ion levels rise |
front 8 The cell membrane of a muscle fiber is called | back 8 sarcolemma |
front 9 Muscle relaxation occurs when ________. | back 9 calcium ions are actively transported into sarcoplasmic reticulum |
front 10 During muscle contraction, the cross-bridge detaches | back 10 calcium ions bins to troponin |
front 11 Thin and thick filaments are organized into functional | back 11 sarcomeres |
front 12 During which phase of a twitch in a muscle fiber is | back 12 contraction phsase |
front 13 Muscle fatigue is caused by ________. | back 13 exhaustion of energy reserves and buildup of lactic acid levels |
front 14 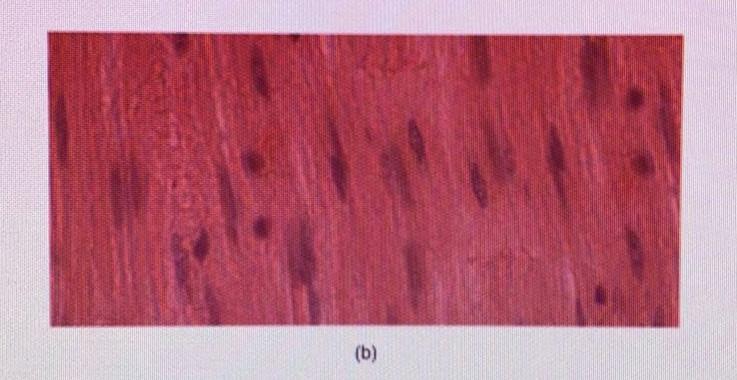 | back 14 smooth |
front 15 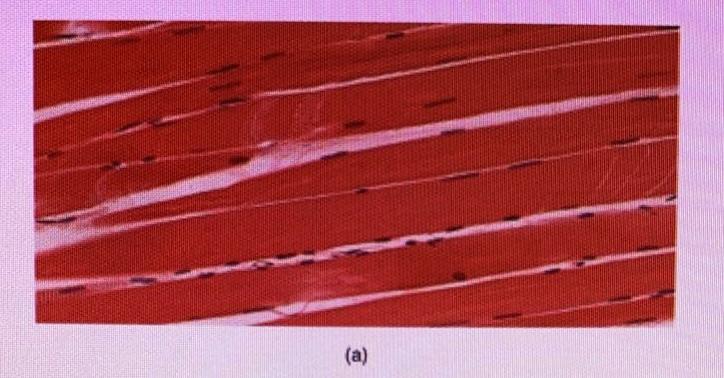 Which type of muscle tissue is this? | back 15 skeletal |
front 16 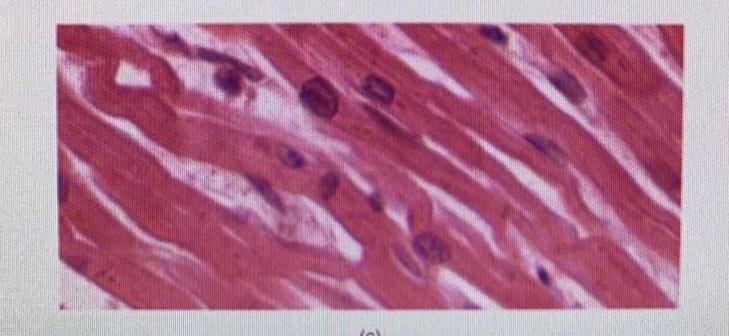 Which type of muscle tissue is this? | back 16 cardiac |
front 17 A sprinter would experience muscle fatigue sooner than | back 17 anaerobic metabolism in the muscles of the sprinter |
front 18 What aspect of creatine phosphate allows it to supply | back 18 phosphate bonds |
front 19 Drug X blocks ATP regeneration from ADP and | back 19 none of the above |
front 20 The muscles of a professional sprinter are most likely | back 20 80 percent fast-twitch muscle fibers and 20 percent slow-twitch muscle fibers |
front 21 The muscles of a professional marathon runner are | back 21 20 percent fast-twitch muscle fibers and 80 percent slow-twitch muscle fibers |
front 22 Which of the following statements is true? | back 22 fast fibers have large glycogen reserves. |
front 23 Which of the following statements is false? | back 23 slow fibers have a small network of capillaries. |
front 24 Cardiac muscles differ from skeletal muscles in that | back 24 contain intercalated discs |
front 25 If cardiac muscle cells were prevented from undergoing | back 25 stop contracting |
front 26 Smooth muscles differ from skeletal and cardiac | back 26 lack myofibrils |
front 27 Which of the following statements describes smooth | back 27 they are resistant to fatigue |
front 28 From which embryonic cell type does muscle
tissue | back 28 myoblast cells |
front 29 Which cell type helps to repair injured muscle fibers? | back 29 satellite cells |
front 30 Skeletal muscle is _________ | back 30 attached to tendons/bones, striated, under voluntary control, multinucleated |
front 31 Cardiac muscle __________ | back 31 forms most of the wall of the heart, striated, involuntary control, one centrally located nucleus |
front 32 Smooth muscle | back 32 non-striated, involuntary, one centrally located nucleus, found in walls of hollow internal structures |
front 33 The four properties of muscle tissue include___________ | back 33 excitability, contractility, extensibility, and elasticity |
front 34 excitability | back 34 ability to respond to stimuli by producing electrical signals |
front 35 contractility | back 35 ability to contract and generate force when stimulated |
front 36 extensibility | back 36 ability to be stretched without damaging the tissue |
front 37 elasticity | back 37 ability to return to original shape after contraction or extension |
front 38 Each skeletal muscle is considered an ______ | back 38 organ |
front 39 deep fascia is composed of _____ | back 39 dense irregular connective tissue around muscle with similar functions |
front 40 epimysium_____ | back 40 surrounds the whole muscle |
front 41 perimysium______ | back 41 surrounds bundles (fascicles) of 10-100 muscle cells |
front 42 endomysium______ | back 42 separates individual muscle fibers |
front 43 aponeurosis _____ | back 43 a sheet-like tendon joining one muscle with another or bone; formed when all connective tissue components come together |
front 44 Each skeletal muscle is typically supplied by ______ | back 44 a nerve, artery, and two veins |
front 45 capillaries in skeletal muscle_____ | back 45 bring oxygen and nutrients and remove heat and wastes |
front 46 How do mature muscle cells develop? | back 46 from 100 myoblasts that fuse together in the fetus |
front 47 What fills the sarcoplasm? | back 47 myofibrils, glycogen, and myoglobin (red-colored, oxygen-binding protein) |
front 48 The filaments of myofibrils are arranged into ______ | back 48 sarcomeres |
front 49 Four steps of contraction cycle include: | back 49 1) ATP hydrolysis 2) attachment of myosin to actin to form crossbridges 3) power stroke 4) detachment of myosin from actin |
front 50 Four steps of nerve impulse illiciting muscle action potential | back 50 1) release of ACh 2) activation of ACh receptors 3) production of muscle action potential 4) termination of ACh activity |