Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Central Science: Chapter 8
front 1 Which of the following has eight valence electrons? | back 1 E |
front 2 Which of the following does not have eight valence electrons? | back 2 A |
front 3 Lattice energy is ________. | back 3 A |
front 4 In ionic bond formation, the lattice energy of ions ________ as the
magnitude of the ion charges ________ and the radii ________. | back 4 D |
front 5 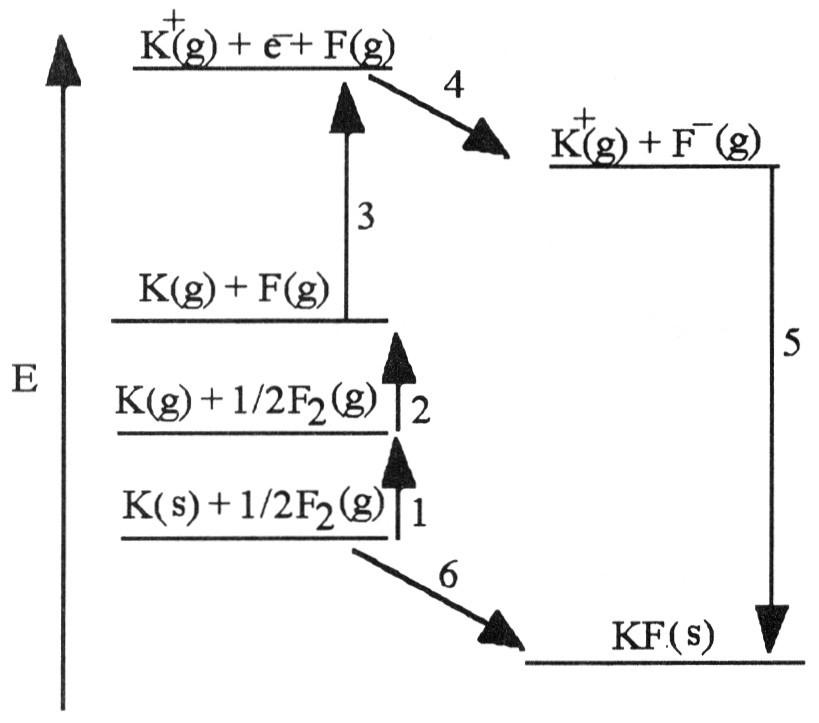 The diagram below is the Born-Huber cycle for the formation of crystalline potassium fluoride. 5) Which energy change corresponds to the electron affinity of
fluorine? | back 5 C |
front 6  Which energy change corresponds to the first ionization energy of
potassium? | back 6 D |
front 7 Using the Born-Haber cycle, the ΔH°f of KBr is equal to
________. | back 7 E |
front 8 The type of compound that is most likely to contain a covalent bond
is ________. | back 8 C |
front 9 In which of the molecules below is the carbon-carbon distance the
shortest? | back 9 B |
front 10 Of the molecules below, the bond in ________ is the most
polar. | back 10 D |
front 11 Which of the following has the bonds correctly arranged in order of
increasing polarity? | back 11 B |
front 12 Which of the following bonds would be considered non-polar
covalent? | back 12 B |
front 13 The Lewis structure of N2H2 shows ________. | back 13 C |
front 14 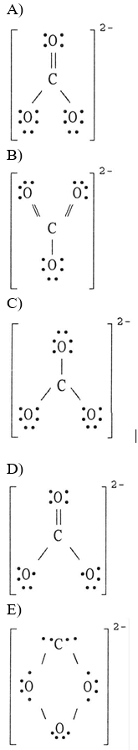 The Lewis structure of the CO32- ion is ________. | back 14 A |
front 15 How many electrons are in the Lewis structure of a nitrite ion
(NO2-)? | back 15 A |
front 16 Resonance structures differ by ________. | back 16 E |
front 17 The oxidation number of iron in Fe2O3 is ________. | back 17 C |
front 18 To convert from one resonance structure to another, ________. | back 18 C |
front 19 For ________ forms of a molecule or ion, the observed structure is an
average of the ________ forms. | back 19 B |
front 20 (i) NO2- (ii) NO3- (iii) SO3 2- (iv) SO4 2- (v) BrO3- There can be two equivalent best resonance structures of
________. | back 20 A |
front 21 (i) NO2- (ii) NO3- (iii) SO3 2- (iv) SO4 2- (v) BrO3- There can be three equivalent best resonance structures of
________. | back 21 A |
front 22 A valid Lewis structure of ________ cannot be drawn without violating
the octet rule. | back 22 B |
front 23 Based on the octet rule, boron will most likely form a ________
ion. | back 23 C |
front 24 Which of the following does not have eight valence electrons? | back 24 E |
front 25 Which of the following Lewis structures would be an expansion to the
octet rule? | back 25 D |
front 26 The central atom in ________ does not violate the octet rule. | back 26 C |
front 27 Which of the following Lewis structures would be an expansion to the
octet rule? | back 27 E |
front 28 A valid Lewis structure of ________ cannot be drawn without violating
the octet rule. | back 28 C |
front 29 Which of the following Lewis structures would be an incomplete
octet? | back 29 C |
front 30 Why don't we draw double bonds between the Be atom and the Cl atoms
in BeCl2? | back 30 A |
front 31 Which of the following atoms may have an expansion to the
octet? | back 31 A |
front 32 Bond enthalpy is ________. | back 32 A |
front 33 Given that the average bond energies for C-H and C-Br bonds are 413
and 276 kJ/mol, respectively, the heat of atomization of bromoform
(CHBr3) is ________ kJ/mol. | back 33 A |
front 34 Of the bonds C-C, C=C, and C≡C, the C-C bond is ________. | back 34 C |
front 35 ) Of the bonds C-N, C=N, and C≡N, the C-N bond is ________. | back 35 D |
front 36 As the number of covalent bonds between two atoms increases, the
distance between the atoms ________ and the strength of the bond
between them ________. | back 36 D |
front 37 Of the possible bonds between carbon atoms (single, double, and
triple), ________. | back 37 D |
front 38 Most explosives are compounds that decompose rapidly to produce
________ products and a great deal of ________. | back 38 E |
front 39 Dynamite consists of nitroglycerine mixed with diatomaceous earth or
cellulose. What is another name for dynamite? | back 39 C |
front 40 ________ is an explosive made of nitroglycerine and an absorbent such
as diatomaceous earth. | back 40 B |
front 41 Based on the octet rule, magnesium most likely forms a ________
ion. | back 41 A |
front 42 Based on the octet rule, phosphorus most likely forms a ________
ion. | back 42 B |
front 43 Based on the octet rule, aluminum most likely forms an ________
ion. | back 43 A |
front 44 Based on the octet rule, iodine most likely forms an ________
ion. | back 44 E |
front 45 The electron configuration of the phosphide ion (P3-) is
________. | back 45 E |
front 46 The electron configuration of the sulfide ion (S2-) is
________. | back 46 E |
front 47 The halogens, alkali metals, and alkaline earth metals have ________
valence electrons, respectively. | back 47 D |
front 48 The only noble gas without eight valence electrons is
________. | back 48 C |
front 49 Which of the following would have to lose two electrons in order to
achieve a noble gas electron configuration? A) O, Se | back 49 B |
front 50 Which of the following would have to lose three electrons in order to
achieve a noble gas electron configuration? A) Si, P | back 50 B |
front 51 Which of the following would have to gain two electrons in order to
achieve a noble gas electron configuration? A) Br | back 51 D |
front 52 For a given arrangement of ions, the lattice energy increases as
ionic radius ________ and as ionic charge ________. | back 52 A |
front 53 For a given arrangement of ions, the lattice energy decreases as
ionic radius ________ and as ionic charge ________. | back 53 B |
front 54 The electron configuration of the S2- ion is ________. | back 54 D |
front 55 The electron configuration of the P3- ion is ________. | back 55 C |
front 56 What species has the electron configuration [Ar]3d2? | back 56 C |
front 57 What species has the electron configuration [Ar]3d4? | back 57 B |
front 58 What is the electron configuration for the Co2+ ion? | back 58 B |
front 59 What is the electron configuration for the Fe3+ ion? | back 59 C |
front 60 What is the electron configuration for the Cu2+ ion? | back 60 C |
front 61 The formula of palladium (IV) sulfide is ________. | back 61 D |
front 62 Elements from opposite sides of the periodic table tend to form
________. | back 62 B |
front 63 Determining lattice energy from Born-Haber cycle data requires the
use of ________. | back 63 D |
front 64 A ________ covalent bond between the same two atoms is the
longest. | back 64 A |
front 65 How many hydrogen atoms must bond to silicon to give it an octet of
valence electrons? | back 65 D |
front 66 A double bond consists of ________ pairs of electrons shared between
two atoms. | back 66 B |
front 67 A triple bond consists of ________ pairs of electrons shared between
two atoms. | back 67 C |
front 68 What is the maximum number of double bonds that a hydrogen atom can
form? | back 68 A |
front 69 What is the maximum number of double bonds that a carbon atom can
form? | back 69 D |
front 70 What is the maximum number of triple bonds that a carbon atom can
form? | back 70 B |
front 71 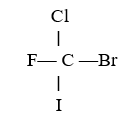 In the molecule below, which atom has the largest partial negative charge? A) Cl | back 71 B |
front 72 The ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons is best
quantified by the ________. | back 72 C |
front 73 Given the electronegativities below, which covalent single bond is
most polar? A) C—H | back 73 C |
front 74 Electronegativity ________ from left to right within a period and
________ from top to bottom within a group. | back 74 C |
front 75 Electropositivity ________ from left to right within a period and
________ from top to bottom within a group. | back 75 A |
front 76 A nonpolar bond will form between two ________ atoms of ________
electronegativity. | back 76 E |
front 77 The ion ICl4- has ________ valence electrons. | back 77 C |
front 78 The ion NO- has ________ valence electrons. | back 78 E |
front 79 The ion PO43- has ________ valence electrons. | back 79 E |
front 80 The Lewis structure of AsH3 shows ________ nonbonding electron
pair(s) on As. | back 80 B |
front 81 The Lewis structure of PF3 shows that the central phosphorus atom has
________ nonbonding and ________ bonding electron pair(s). | back 81 B |
front 82 The Lewis structure of HCN (H bonded to C) shows that ________ has
________ nonbonding electron pair(s). | back 82 B |
front 83 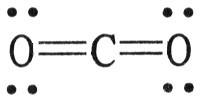 The formal charge on carbon in the molecule below is ________. A) 0 | back 83 A |
front 84 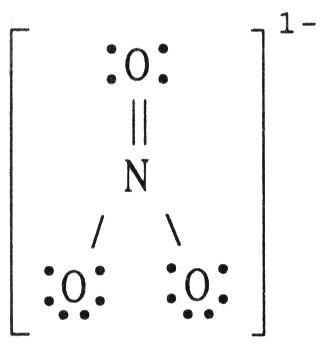 The formal charge on nitrogen in NO3- is ________, where the Lewis structure of the ion is: A) -1 | back 84 C |
front 85 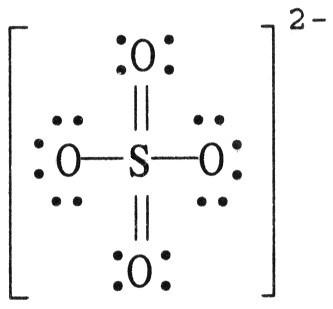 The formal charge on sulfur in SO42- is ________, where the Lewis structure of the ion is: A) -2 | back 85 B |
front 86 In the Lewis structure of ClF, the formal charge on Cl is ________,
and the formal charge on F is ________. | back 86 B |
front 87 In the Lewis structure of HCO3-, the formal charge on H is ________,
and the formal charge on C is ________. | back 87 B |
front 88 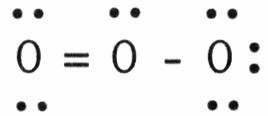 In the resonance form of ozone shown below, the formal charge on the central oxygen atom is ________. A) 0 | back 88 B |
front 89 How many equivalent resonance forms can be drawn for CO32-? (Carbon
is the central atom.) | back 89 C |
front 90 How many equivalent resonance forms can be drawn for the nitrate
ion? | back 90 C |
front 91 How many equivalent resonance structures can be drawn for the
molecule of SO3 without having to violate the octet rule on the sulfur
atom? | back 91 E |
front 92 How many different types of resonance structures can be drawn for the
ion SO32-? | back 92 C |
front 93 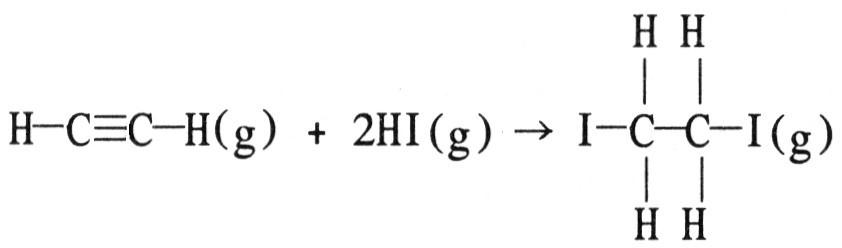 Using the table of average bond energies below, the ΔH for the reaction is ________ kJ. Bond: C≡C C-C H-I C-I C-H A) +160 | back 93 C |
front 94 Using the table of average bond energies below, the ΔH for the reaction is ________ kJ. H-C≡C-H (g) + H-Cl (g) → H2C=CHCl (g) A) +741 | back 94 B |
front 95 Using the table of average bond energies below, the △H for the reaction is ________ kJ. H3C-O-H (g) → C≡O (g) + 2H2 (g) A) +276 | back 95 C |
front 96 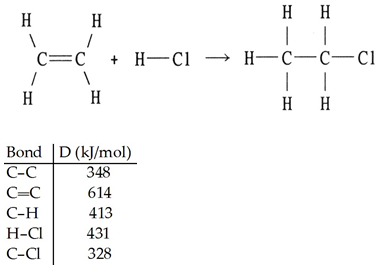 Using the table of bond dissociation energies, the ΔH for the following gas-phase reaction is ________ kJ. A) -44 | back 96 A |
front 97 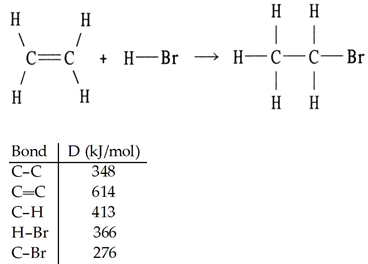 Using the table of bond dissociation energies, the ΔH for the reverse of following gas-phase reaction is ________ kJ. A) +57 | back 97 A |
front 98 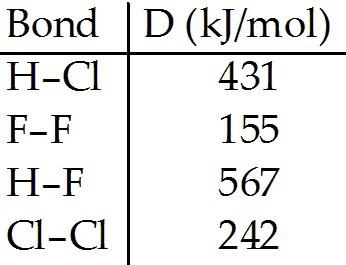 Using the table of bond dissociation energies, the ΔH for the
following reaction is ________ kJ. A) -359 | back 98 A |
front 99 There are ________ paired and ________ unpaired electrons in the
Lewis symbol for a fluorine atom. | back 99 C |
front 100 The ________ ion has a noble gas electron configuration. | back 100 A |
front 101 The ________ ion has a noble gas electron configuration. | back 101 A |
front 102 The ________ ion has eight valence electrons. | back 102 A |
front 103 There are ________ unpaired electrons in the Lewis symbol for an
oxygen atom . | back 103 C |
front 104 What is the principal quantum number of the last shell for the
element barium? | back 104 D |
front 105 The oxide of which of the following metals should have the greatest
lattice energy? | back 105 D |
front 106 The ________ ion is represented by the electron configuration
[Ar]3d2. | back 106 A |
front 107 Which of the following species does the noble gas electron
configuration [Kr]4d10 represent? | back 107 C |
front 108 Which of the following noble gas electron configurations represents
the Ru+ cation? | back 108 E |
front 109 Ni2+ ions are represented by the electron configuration
________. | back 109 A |
front 110 How many single covalent bonds must a chlorine atom form to have a
complete octet in its valence shell? | back 110 B |
front 111 The most electronegative atom of the ones listed below is
________. | back 111 A |
front 112 Of the atoms below, ________ is the most electronegative. | back 112 E |
front 113 Of the atoms below, ________ is the most electronegative. | back 113 A |
front 114 Of the atoms below, ________ is the least electronegative. | back 114 A |
front 115 Of the bonds below, ________ is the least polar. | back 115 B |
front 116 Which two bonds are most similar in polarity? | back 116 A |
front 117 There are ________ valence electrons in the Lewis structure of
CH3Cl. | back 117 A |
front 118 How many valence electrons are in the Lewis structure of
CH3OCH3.? | back 118 C |
front 119 In the Lewis symbol for a nitrogen atom, there are ________ paired
and ________ unpaired electrons. | back 119 A |
front 120 The oxidation number of phosphorus in PF5 is ________. | back 120 A |
front 121 The central atom in ________ violates the octet rule. | back 121 A |
front 122 Of the following, ________ cannot accommodate more than an octet of
electrons. | back 122 C |
front 123 How many covalent bonds are in the Lewis Structure of
CH3CHCl2.? | back 123 C |
front 124 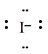 The electron configuration that corresponds to the Lewis symbol, [see img] is ________. | back 124 [Ne]3s23p6 |
front 125 Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction for which △H°rxn is the lattice energy for sodium chloride. | back 125 NaCl (s) → Na+ (g) + Cl- (g) |
front 126 Using the noble gas shorthand notation, write the electron configuration for Fe2+. | back 126 [Ar]3d6 |
front 127 Give the electron configuration of Zn2+. | back 127 [Ar]3d10 |
front 128 Which halogen, bromine or iodine, will form the more polar bond with phosphorus? | back 128 bromine |
front 129 Draw the Lewis structure of ICl2+. | back 129 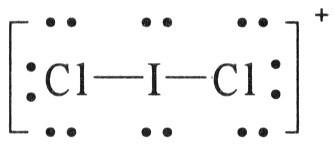 |
front 130 ) If more than one Lewis structure can be drawn then the molecule or ion is said to have ________ forms. | back 130 resonance |
front 131 How many resonance forms exist for benzene? | back 131 two |
front 132 If the bonds in the reactants of a reaction are weaker than the bonds in the product, the reaction is ________. | back 132 exothermic |
front 133 Which two elements in period 2 form compounds that can violate the octet rule? | back 133 boron and beryllium |
front 134 Polyatomic ions with an even number of electrons will follow the ________ rule. | back 134 octet |
front 135 The strength of a ________ bond is measured by its bond enthalpy. | back 135 covalent |
front 136 An exothermic reaction should have ________ chemical bonds and decompose to a molecule with ________ bonds. | back 136 weak, strong |
front 137 Calculate the bond energy of C—F given that the heat of atomization of CHFClBr is 1502 kJ/mol, and that the bond energies of C—H, C—Br, and C—Cl are 413, 276, and 328 kJ/mol, respectively. | back 137  |
front 138 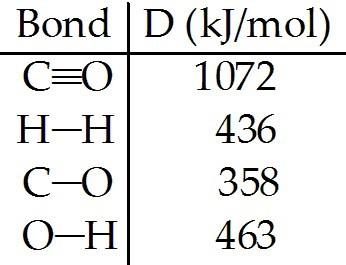 The reaction below is used to produce methanol: CO (g) + 2H2 (g) → CH3OH (l) △Hrxn = -128 kJ (a) Calculate the C—H bond energy given the following data: [see img] (b) The tabulated value of the (C-H) bond energy is 413 kJ/mol. Explain why there is a difference between the number you have calculated in (a) and the tabulated value. | back 138 (a) (b) |
front 139 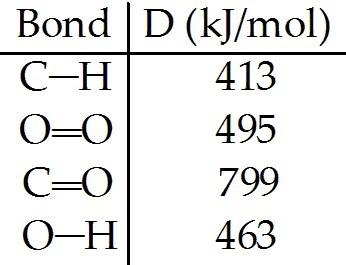 From the information given below, calculate the heat of combustion of methane. Start by writing the balanced equation. | back 139 CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O |
front 140 Atoms surrounded by eight valence electrons tend to lose electrons. | back 140 false |
front 141 The greater the lattice energy, the greater the charges on the participatory ions and the smaller their radii. | back 141 true |
front 142 Most transition metals do not form ions with a noble gas configuration. | back 142 true |
front 143 When a metal gains an electron, the process is endothermic. | back 143 false |
front 144 Electron affinity is a measure of how strongly an atom can attract additional electrons. | back 144 true |
front 145 As electronegativity difference increases, bond length will decrease. | back 145 true |
front 146 In some molecules and polyatomic ions, the sum of the valence electrons is odd and as a result the octet rule fails. | back 146 true |
front 147 A positive change in bond enthalpy is required to break a bond. | back 147 true |