Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter Question Blood Vessels
front 1 Which branch of the Autonomic Nervous System innervates blood vessels? Which layers of the blood vessel wall do these nerves innervates? What are effectors (cells that carry out the response)? | back 1 Smooth muscle is regulated by sympathetic vasomotor nerve fibers of the autonomic nervous system. These nerves innervate the tunica media. The effectors are smooth muscle cells |
front 2 When vascular smooth muscle contracts, what happens to the diameter of the blood vessel? What is this called? | back 2 When smooth muscle contract there is a reduction in lumen diameter, this is called vasoconstriction. |
front 3 Name the type of artery that matches each description:
| back 3 (a)elastic arteries - major role in dampening the pulsatile pressure of heart contractions
|
front 4 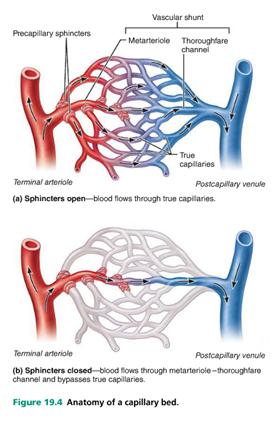 Look at figure 19.4 and assume that the capillary bed depicted is in your calf muscle.
| back 4 Capillary bed A |
front 5 (a) What is the function of valves in veins?
| back 5 a) Valves prevent blood from flowing backwards
|
front 6 In the systemic circuit, which contains more blood-arteries or veins- or is it the same? | back 6 Veins contain more blood than arteries. At any given time there is 60% of the body’s blood in the veins |
front 7 List 3 factors that determine resistance in a vessel?
| back 7 blood viscosity
|
front 8 Suppose vasoconstriction decreases the diameter of a vessel to one-third its size. What happens to the rate of flow through that vessel?
| back 8 The rate of flow would decrease 81-fold from its original flow. (3X3x3x3=27) |
front 9 Describe the baroreceptor reflex changes that occur to maintain blood pressure when you rise from a lying-down to a standing position. | back 9 When you stand up, the baroreceptors will sense a drop in your blood pressure. They quickly take action to make sure that blood continues to flow to the brain, kidneys, and other important organs. The baroreceptors cause the heart to beat faster and harder. They also cause the small arteries (arterioles) and veins to narrow. |
front 10 The kidneys play an important role in maintaining MAP by influencing which variable?
| back 10 The kidneys play an important role by influencing blood volume.
|
front 11 Suppose you are in a bicycle race.
| back 11 The smooth muscle relaxes, dilating the vessels and supplying more oxygen and nutrients to the exercising muscles.
|
front 12 If many arterioles in your body dilated at once, you would expect MAP to plummet. What prevents MAP from decreasing during your bicycle race? | back 12 Extrinsic mechanisms, primarily the SNS, and cardiac output increases |
front 13 Suppose OPif rises dramatically - say because of a serious bacterial infection in the surrounding tissue.
| back 13 a) an increase in interstial fluid osmotic pressure would pull more fluid from the capillaries causing edema
|
front 14 Your neighbor, Bob, calls you because he thinks he is having an allergic reaction to a medication. You find Bob on the verge of losing consciencness and having trouble breathing. When paramedics arrive, they note his blood pressure is 63/38 and he has a rapid, theady pulse.
| back 14 Bob is suffering from anaphylactic shock due to an allergic reaction to his medication. His blood pressure is low because of widespread vasodilation triggered by the massive release of histamine. His rapid heart rate is a result of the baroreceptor reflex triggered by his low blood pressure. This activates his sympathetic nervous system, increasing heart rate, in an attempt to raise his blood pressure. |
front 15 Which paired artery supplies most of the tissues of the head except for the brain and orbits? | back 15 the external carotid arteries supplies most of the tissue of the head. |
front 16 Name the arterial anastomosis at the base of the cerebrum? | back 16 the cerebral arterial circle, aka the circle of willis |
front 17 Name the four unpaired arteries that emerge from the abdominal aorta. | back 17 celiac trunk
|
front 18 You are assessing the circulation in the leg of a diabetic patient at the clinic. Name the artery you palpitate in each of these three locations. | back 18 Behind the knee,
|
front 19 In what important way does the area drained by the vertebral veins differ from the area served by the vertebral arteries? | back 19 The vertebral arteries supply the brain with oxygenated blood but the vertebral veins do not drain much of the deoxygenated blood from the brain. |
front 20 Which veins drain the dural venous sinuses and where do these veins terminate? | back 20 the internal jugular veins, each internal jugular vein joins a subclavian vein to form a brachiocephalic vein |
front 21 What is a portal system?
| back 21 a system where two capillary beds occur in series
|
front 22 Name the leg veins that often become varicosed? | back 22 The great and small saphenous veins |
front 23 List three differences between systemic arteries and veins with respect to their general pathways and courses? | back 23 arteries run deep, veins run deep and superficial
|
front 24 Name three fetal shunts that are occludes shortly after birth. Which structures does each shunt bypass? | back 24 The foramen ovale and the ductus arteriosus both bypass the fetal lungs. The ductus venosus bypasses the liver |
front 25 Name three common age-related vascular problems? | back 25 varicose veins
|