Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
A&P Final Review
front 1 A mismatch of blood types during a transfusion is dangerous because ________. A) white blood cells from the donor's blood cause inflammation B) antibodies in the donor's plasma will attack and kill the recipient's healthy blood cells C) clotting factors in the donor's blood will cause unwanted clots known as thrombus D) preformed antibodies in the recipient's blood will bind and clump (agglutinate) the donated cells | back 1 D) preformed antibodies in the recipient's blood will bind and clump (agglutinate) the donated cells |
front 2 If you centrifuge (spin) whole blood you will find the band of white blood cells and platelets (the Buffy coat) is much thinner than the packed red blood cells below it. This difference reflects the fact that ________. A) white blood cells are fewer in number than red blood cells B) white blood cells are smaller than red blood cells C) platelets are larger than red blood cells D) platelets are larger than white blood cells | back 2 A) white blood cells are fewer in number than red blood cells |
front 3 If you centrifuge (spin) whole blood, you will find the red blood cells (erythrocytes) at the bottom of the tube and white blood cells atop them. This implies that ________. A) red blood cells are larger than white blood cells B) white blood cells are fewer in number than red blood cells C) white blood cells are smaller than red blood cells D) red blood cells have a greater density than white blood cells | back 3 D) red blood cells have a greater density than white blood cells |
front 4 True or False? Positive chemotaxis is a feedback system that signals leukocyte migration into damaged areas. | back 4 TRUE |
front 5 The cells responsible for producing platelets are called _____. A) megakaryocytes. B) lymphoid stem cells. C) myeloblasts. D) monoblasts. E) erythrocytes. | back 5 A) megakaryocytes. |
front 6 True or False A person with type B blood could receive blood from a person with either type B or type O blood. | back 6 TRUE |
front 7 What is the average normal pH range of blood? A) 4.65-4.75 B) 8.35-8.45 C) 7.75-7.85 D) 7.35-7.45 | back 7 D) 7.35-7.45 |
front 8 True or False? When erythrocytes are destroyed, some of the heme is converted into bilirubin and then secreted as bile. | back 8 TRUE |
front 9 True or False? Basophils increase in number when parasitic invasion occurs. | back 9 FALSE |
front 10 True or False? Granulocytes called neutrophils are phagocytic and are the most numerous of all white blood cell types. | back 10 TRUE |
front 11 Loss of fibrinogen within the plasma would most likely cause which of the following? A) fever with pain B) loss of blood clotting C) edema (swelling) D) pallor (pale skin) | back 11 B) loss of blood clotting |
front 12 True or False? The immediate response to blood vessel injury is clotting. | back 12 FALSE |
front 13 A person with an extremely high count of neutrophils is likely suffering ________. A) a bacterial infection B) a viral infection C) anemia D) polycythemia | back 13 A) a bacterial infection |
front 14 When neither anti-A serum nor anti-B serum clot on a blood plate with donor blood, the blood is type ________. A) A B) B C) O D) AB | back 14 C) O |
front 15 Which blood type is generally called the universal donor? A) A B) B C) AB D) O | back 15 D) O |
front 16 Which of the choices below is the parent cell for all formed elements of blood? A) normoblast B) hemocytoblast C) polymorphonuclear cell D) megakaryocyte | back 16 B) hemocytoblast |
front 17 True or False? Leukemia refers to cancerous conditions involving white blood cells | back 17 TRUE |
front 18
A patient's hematocrit shows an unusually large buffy coat.
What is a likely cause of this?
| back 18 c. severe infection |
front 19 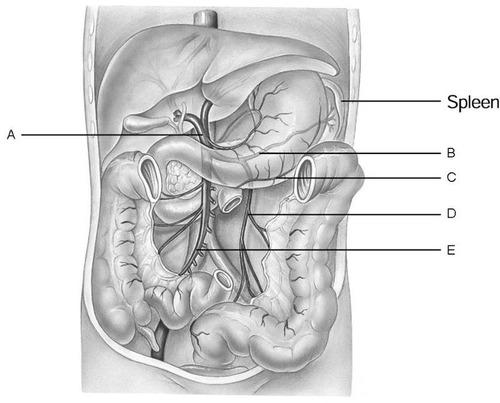
Using Figure 19.2, match the following:
| back 19 B |
front 20 
Using Figure 19.2, match the following:
| back 20 D |
front 21  Using Figure 19.2, match the following: superior mesenteric vein | back 21 E |
front 22  Using Figure 19.2, match the following: hepatic portal vein | back 22 A |
front 23  Using Figure 19.2, match the following: right gastroepiploic vein | back 23 C |
front 24
Blood flow to the skin ________.
| back 24 B) increases when environmental temperature rises |
front 25 True or False? An increase in blood viscosity will cause an increase in peripheral resistance. | back 25 TRUE |
front 26 True or False? The left side of the heart pumps the same volume of blood as the right. | back 26 TRUE |
front 27 In red bone marrow newly formed blood cells enter the circulation. You would expect to see many ________ type of capillaries in red bone marrow. A) metarterioles B) continuous capillaries C) sinusoid capillaries D) fenestrated capillaries | back 27 C) sinusoid capillaries |
front 28 Due to the branching of arteries the type of arteries that would be most numerous would be ________. A) arterioles B) pulmonary arteries C) muscular arteries D) elastic arteries | back 28 A) arterioles |
front 29 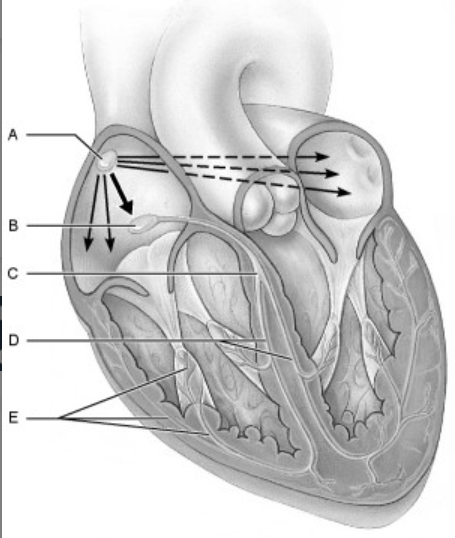 Using Figure 18.1, match the following: | back 29 E |
front 30  Using Figure 18.1, match the following: | back 30 A |
front 31  Using Figure 18.1, match the following: | back 31 C |
front 32  Using Figure 18.1, match the following: | back 32 B |
front 33  Using Figure 18.1, match the following: | back 33 D |
front 34 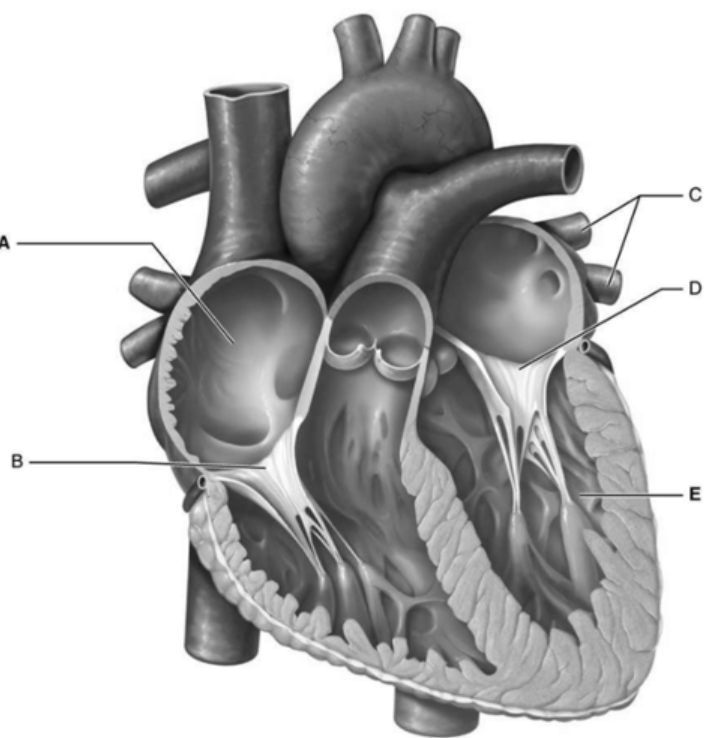 Using Figure 18.4, match the following: | back 34 B |
front 35  Using Figure 18.4, match the following: | back 35 D |
front 36  Using Figure 18.4, match the following: | back 36 A |
front 37  Using Figure 18.4, match the following: | back 37 E |
front 38  Using Figure 18.4, match the following: | back 38 C |
front 39
Which chambers of the heart contain oxygenated blood?
| back 39 D. The left atrium and ventricle |
front 40 Which of the following is the most significant source of blood flow resistance? A) blood viscosity B) blood vessel diameter C) total blood vessel length D) blood vessels type | back 40 B) blood vessel diameter |
front 41 Which of the following does not contribute to venous blood pressure? A) skeletal muscle activity B) venous anastomosis C) constriction of smooth muscle around veins by the sympathetic nervous system D) increased abdominal pressure during breathing | back 41 A) skeletal muscle activity |
front 42 Atherosclerosis causes elastic arteries to become less stretchy. How does this affect pulse pressure? A) Pulse pressure is unaffected by atherosclerosis. B) Pulse pressure is temporarily increased. C) Pulse pressure is temporarily decreased. D) Pulse pressure is chronically decreased. E) Pulse pressure is chronically increased. | back 42 E) Pulse pressure is chronically increased. |
front 43 The receiving chambers of the heart include the ________. A) right atrium and ventricle B) right and left ventricles C) right and left atria D) left atrium and ventricle | back 43 C) right and left atria |
front 44
Peripheral resistance ________.
| back 44 C) increases as blood viscosity increases |
front 45 True or False? The myocardium receives its blood supply from the coronary arteries. | back 45 TRUE |
front 46 Which will not occur if blood pressure drops below homeostatic levels? A) The cardioacceleratory center of the medulla will be activated B) Barorecptors in the carotid sinuses and aortic arch will be stimulated C) Vasomotor center of the medulla will trigger vasoconstriction | back 46 B) Barorecptors in the carotid sinuses and aortic arch will be stimulated |
front 47 Which is NOT a vessel that brings blood directly into the right atrium? A) superior vena cava B) inferior vena cava C) pulmonary vein D) coronary sinus | back 47 C) pulmonary vein |
front 48
Permitting the exchange of nutrients and gases between the
blood and tissue cells is the primary function of ________.
| back 48 D) capillaries |
front 49 Which coronary artery is the most responsible for supplying blood to the myocardial tissue of the left atrium? A) anterior interventricular artery B) posterior interventricular artery C) right marginal artery D) circumflex artery | back 49 D) circumflex artery |
front 50 True or False? Anastomoses among coronary arterial branches provide collateral routes for blood delivery to the heart muscle. | back 50 TRUE |
front 51
Which of the following signs of hypovolemic shock is a
relatively late sign?
| back 51 D) rapidly falling blood pressure |
front 52
Compared to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle ________.
| back 52 A) has gap junctions that allow it to act as a functional syncytium |
front 53 Which of the following is NOT a part of the lymphatic system? A) lymph nodes B) lymph C) lymphatic vessels D) erythrocytes | back 53 D) erythrocytes |
front 54 Lymph leaves a lymph node via ________. A) afferent lymphatic vessels B) efferent lymphatic vessels C) the cortical sinus D) the subcapsular sinus | back 54 B) efferent lymphatic vessels |
front 55 Which of the following is NOT a function of the lymphatic system? A) transporting dietary fats B) transporting respiratory gases C) draining excess interstitial fluid D) carrying out immune responses | back 55 B) transporting respiratory gases |
front 56 Peyer's patches are found in the distal portion of the ________. A) large intestine B) stomach C) small intestine D) esophagus | back 56 C) small intestine |
front 57 True or False? Like blood, lymph flows both to and from the heart. | back 57 FALSE |
front 58
The lymphatic capillaries are ________.
| back 58 A) more permeable than blood capillaries |
front 59 True or False? When tissues are inflamed, lymphatic capillaries develop openings that permit uptake of large particles such as cell debris, pathogens, and cancer cells. | back 59 TRUE |
front 60 Select the correct statement about lymph transport. A) Under normal conditions, lymph vessels are very high-pressure conduits. B) Lymph transport is only necessary when illness causes tissue swelling. C) Lymph transport is faster than that occurring in veins. D) Lymph transport depends on the movement of adjacent tissues, such as skeletal muscles. | back 60 D) Lymph transport depends on the movement of adjacent tissues, such as skeletal muscles. |
front 61 A flu vaccine is needed seasonally to be effective but a polio vaccine is only needed once. The best explanation of this is ________. A) the flu vaccine is substantially weaker than the polio vaccine B) exposure to flu vaccine produces no memory cells from proliferating B-lymphocytes C) the polio virus is substantially weaker than the flu virus D) the flu has several strains that change seasonally | back 61 D) the flu has several strains that change seasonally |
front 62 True or False? Peyer's patches are clusters of lymphoid tissue found primarily in the large intestine. | back 62 FALSE |
front 63 Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues include all of the following EXCEPT ________. A) palatine tonsils B) islets of Langerhans C) lingual tonsils D) Peyer's patches | back 63 B) islets of Langerhans |
front 64 A vaccine is effective because ________. A) B-lymphocytes are unable to mount an immune response the first time they are exposed to a new pathogen B) the secondary response of the adaptive immunity is faster and more efficient the primary response C) the vaccine contains the lymphocytes necessary to fight infection D) the vaccine contains the antibodies necessary to fight infection | back 64 B) the secondary response of the adaptive immunity is faster and more efficient the primary response |
front 65 The redness and heat of an inflamed area are due to a local hyperemia caused by ________. A) phagocyte mobilization B) complement production C) vasoconstriction D) vasodilation | back 65 D) vasodilation |
front 66 True or False? Fever is often a beneficial immune response because it can speed the activities of leucocytes. | back 66 TRUE |
front 67 Which of the following is not a type of T cell? A) helper B) antigenic C) cytotoxic D) regulatory | back 67 B) antigenic |
front 68 An advantage to adaptive immunity is ________. A) the use of antibodies that cause cell lysis and kill invading cells B) the ability of its individual cells to respond to many different pathogens C) its memory cells that provide quicker, larger and more efficient immune response upon second exposure to an antigen D) its need for several cells to be activated over several days on first exposure | back 68 C) its memory cells that provide quicker, larger and more efficient immune response upon second exposure to an antigen |
front 69 Which of the following does NOT contain a mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue? A) appendix B) tonsil C) Peyer's patch D) thymus | back 69 D) thymus |
front 70 The thymus is the only lymphoid organ that does NOT ________. A) directly fight antigens B) have lymphocytes C) have a cortex and medulla D) produce hormones | back 70 A) directly fight antigens |
front 71 Natural killer (NK) cells ________. A) can kill cancer cells before the immune system is activated B) are also called cytotoxic T cells C) are cells of the adaptive immune system D) are a type of phagocyte | back 71 A) can kill cancer cells before the immune system is activated |
front 72 B lymphocytes develop immunocompetence in the ________. A) bone marrow B) lymph nodes C) thymus D) spleen | back 72 A) bone marrow |
front 73 True or False? The lymphatic capillaries function to absorb the excess protein-containing interstitial fluid and return it to the bloodstream. | back 73 FALSE |
front 74 Which of the following is associated with passive immunity? A) booster shot of vaccine B) exposure to an antigen C) infusion of weakened viruses D) passage of IgG antibodies from a pregnant mother to her fetus | back 74 D) passage of IgG antibodies from a pregnant mother to her fetus |
front 75 Tonsils have blind-ended structures called ________ that trap bacteria and particulate matter. A) tonsillar crypts B) germinal centers C) tonsillar corpuscles D) lymphoid follicles | back 75 A) tonsillar crypts |
front 76 True or False? Anaphylactic shock is a rare but severe allergic response that may occur if the allergen enters the blood stream. | back 76 TRUE |
front 77 True or False? Lymphatic capillaries are permeable to proteins. | back 77 TRUE |
front 78 Vaccines work by ________. A) boosting innate immunity with cytokines B) providing the necessary antibodies to fight infections C) suppressing inflation to help speed healing D) priming the adaptive immunity with a relatively harmless primary exposure | back 78 D) priming the adaptive immunity with a relatively harmless primary exposure |
front 79 Lymph traveling from the left arm would enter the venous circulation via the _______. A) axillary nodes | back 79 B) thoracic duct |
front 80 True or False? Lymph capillary permeability is due to minivalves and protein filaments. | back 80 TRUE |
front 81 Which of the following statements regarding the thymus is FALSE? A) It has follicles similar to those in the spleen. B) It does not directly fight antigens. C) It functions strictly in T lymphocyte maturation. D) Its stroma consists of epithelial tissue. | back 81 A) It has follicles similar to those in the spleen. |
front 82
Which of the following would be a component of the body's
first line of defense?
| back 82 D) mucous membranes |
front 83 Which lymphoid organ atrophies as we age? A) thymus B) appendix C) spleen D) tonsils | back 83 A) thymus |
front 84
A cellular component of the innate defenses includes _____.
| back 84 D) Natural killer cells |
front 85 The thymus is most active during ________. A) childhood B) fetal development C) middle age D) old age | back 85 A) childhood |
front 86 True or False? About 3 liters of fluid are lost to the tissue spaces every 24 hours and are returned to the bloodstream as lymph. | back 86 TRUE |
front 87 Inflammation ________. A) is caused by bacterial activity to enhance the spread of disease B) brings more leukocytes to the sight of infection C) is caused by viral activity to enhance the spread of the disease D) slows the healing process with swelling that can impair bodily function | back 87 B) brings more leukocytes to the sight of infection |
front 88 True or False? In a case of immediate hypersensitivity the immune system responds with an allergic response on the first exposure to the allergen. | back 88 FALSE |
front 89 The tonsils located at the base of the tongue are the ________. A) pharyngeal tonsils B) Peyer's tonsils C) palatine tonsils D) lingual tonsils | back 89 D) lingual tonsils |
front 90 Lymphoid tissue that appears as a swelling of the mucosa in the oral cavity is called a(n) ________. A) Peyer's patch B) thymus C) tonsil D) appendix | back 90 C) tonsil |
front 91 True or False? The functions of the nasal conchae are to enhance the air turbulence in the cavity and to increase the mucosal surface area exposed to the air. | back 91 TRUE |
front 92
Factors that influence the rate and depth of breathing include ________.
| back 92 B) voluntary cortical control |
front 93
Which of the following is not normally found in saliva?
| back 93 E) Protease |
front 94
Surfactant helps to prevent the alveoli from collapsing by ________.
| back 94 B) interfering with the cohesiveness of water molecules, thereby reducing the surface tension of alveolar fluid |
front 95 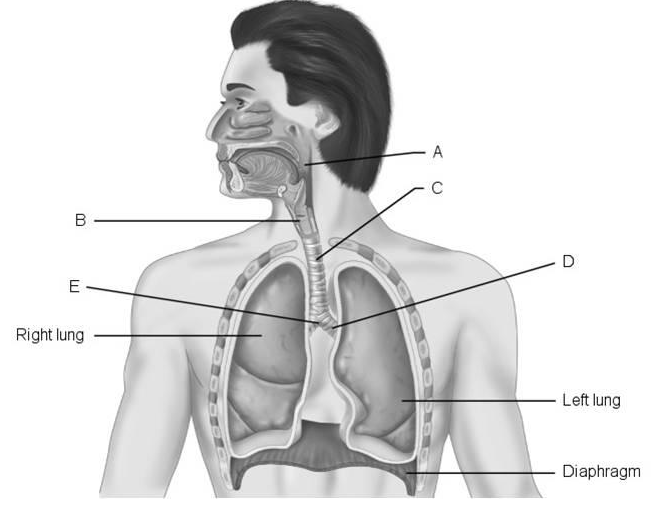
Using Figure 22.1, match the following:
2) Pharynx. 3) Larynx. 4) Carina of trachea. 5) Trachea. | back 95 1) D 2) A 3) B 4) E 5) C |
front 96
Inspiratory capacity is ________.
| back 96 A) the total amount of air that can be inspired after a tidal expiration |
front 97 True or False? Nasal conchae mainly work on inhalation to warm and moisten air. They serve minor functions for exhalation. | back 97 FALSE |
front 98 Which of the following maintains the patency (openness) of the trachea? A) pseudostratified ciliated epithelium B) C-shaped cartilage rings C) surfactant production D) surface tension of water | back 98 B) C-shaped cartilage rings |
front 99 Which of the following is not true of saliva? A) moistens food and aids in compacting of the bolus B) cleanses the mouth C) contains enzymes that begin the breakdown of carbohydrates D) contains acids which aid in chemical digestion | back 99 D) contains acids which aid in chemical digestion |
front 100 A ruptured appendix is life threatening because ________. A) it is likely to cause severe internal bleeding B) the large intestine will no longer be able to receive digested material from the small intestine C) loss of the appendix's function will cause an immune deficiency in the digestive system D) it is likely to cause massive infection of the abdominopelvic cavity | back 100 D) it is likely to cause massive infection of the abdominopelvic cavity |
front 101 True or False? The lingual tonsil is found on the posterior surface of the root of the tongue | back 101 TRUE |
front 102 Choose the incorrect statement regarding bile. A) Bile functions to emulsify fats. B) Bile contains enzymes for digestion. C) Bile functions to carry bilirubin formed from breakdown of worn-out RBCs. D) Bile is both an excretory product and a digestive secretion. | back 102 B) Bile contains enzymes for digestion. |
front 103 True or False? The pancreas has both an endocrine and an exocrine function. | back 103 TRUE |
front 104 Most inspired particles such as dust fail to reach the lungs because of the ________. A) action of the epiglottis B) ciliated mucous lining in the nose C) porous structure of turbinate bones D) abundant blood supply to nasal mucosa | back 104 B) ciliated mucous lining in the nose |
front 105 From the esophagus to the anal canal, the walls of every organ of the alimentary canal are made up of the same four basic layers. Arrange them in order from the lumen. A) serosa, mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis externa B) mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and serosa C) submucosa, serosa, muscularis externa, and mucosa D) muscularis externa, serosa, mucosa, and submucosa | back 105 B) mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and serosa |
front 106 Select the best explanation for why protease enzymes are secreted in inactive forms. A) Inactive enzymes will simply be expelled with the feces if no protein is present in the digesting food, this will help to conserve energy. B) The immunoglobulins protecting the digestive tract would be digested without proper regulation of protein digesting enzymes. C) The enzymes would digest each other if they were not properly regulated. D) The cells producing inactive enzymes are themselves protected from the enzymes until they are safely within the lumen of the GI tract. | back 106 D) The cells producing inactive enzymes are themselves protected from the enzymes until they are safely within the lumen of the GI tract. |
front 107 True or False? Another term for swallowing is deglutition. | back 107 TRUE |
front 108 True or False? The circular folds of the small intestine enhance absorption by causing the chyme to spiral, rather than to move in a straight line, as it passes through the small intestine. | back 108 TRUE |
front 109 The function of the hepatic portal circulation is to ________. A) return glucose to the general circulation when blood sugar is low B) carry toxins to the kidney for disposal through the urinary tract C) distribute hormones throughout the body D) collect absorbed nutrients for metabolic processing in the liver | back 109 D) collect absorbed nutrients for metabolic processing in the liver |
front 110 True or False? The major means of propulsion through the alimentary canal is peristalsis. | back 110 TRUE |
front 111 The walls of the alveoli are composed of two types of cells, type I and type II alveolar cells. The function of type II alveolar cells is to ________. A) replace mucus in the alveoli B) protect the lungs from bacterial invasion C) trap dust and other debris D) secrete surfactant | back 111 D) secrete surfactant |
front 112 Pepsinogen, an inactive digestive enzyme, is secreted by the ________. A) parietal cells of the duodenum B) goblet cells of the small intestine C) Brunner's glands D) chief cells of the stomach | back 112 D) chief cells of the stomach |
front 113 Inspiration occurs when the ____________ is less than the ____________. A) intrapulmonary pressure is less than intrapleural
pressure. | back 113 B) intrapleural pressure is less than intrapulmonary pressure. |
front 114 The larynx contains ________. A) lateral cartilage ridges called false vocal folds B) the thyroid cartilage C) an upper pair of avascular mucosal folds called true vocal folds D) a cricoid cartilage also called the Adam's apple | back 114 B) the thyroid cartilage |
front 115 When we ingest large molecules such as lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins, they must undergo catabolic reactions whereby enzymes split these molecules. This series of reactions is called ________. A) mechanical breakdown B) absorption C) secretion D) chemical digestion | back 115 D) chemical digestion |
front 116 The absorptive effectiveness of the small intestine is enhanced by increasing the surface area of the mucosal lining. Which of the following accomplish this task? A) the vast array of digestive enzymes B) the rugae and haustra C) villi, and microvilli D) Brunner's glands and Peyer Patches | back 116 C) villi, and microvilli |
front 117 Which of the following is least involved in the mechanical breakdown of food, digestion or absorption of nutrients? A) the oral cavity B) the esophagus C) large intestine D) the small ingestion | back 117 B) the esophagus |
front 118 The chemical and mechanical processes of food breakdown are called ________. A) secretion B) ingestion C) absorption D) digestion | back 118 D) digestion |
front 119 True or False? The only essential function of the stomach is to begin the digestion of proteins. | back 119 FALSE |
front 120 All of the following are true of swallowing (deglutition) except one. Select the statement that is not true of swallowing. A) The involuntary portion of swallowing takes place in the pharynx. B) The mouth, pharynx and esophagus all take part in swallowing. C) The epiglottis assists in propelling food into the trachea. D) The voluntary phase of swallowing takes place within the mouth. | back 120 C) The epiglottis assists in propelling food into the trachea. |
front 121 Intrapulmonary pressure is the ________. A) difference between atmospheric pressure and respiratory pressure B) pressure within the pleural cavity C) pressure within the alveoli of the lungs D) negative pressure in the intrapleural space | back 121 C) pressure within the alveoli of the lungs |
front 122
Which of the following provide the greatest surface area for
gas exchange?
| back 122 C) alveoli |
front 123 True or False? All the chemical and mechanical phases of digestion from the mouth through the small intestine are directed toward changing food into forms that can pass through the epithelial cells lining the mucosa into the underlying blood and lymphatic vessels. | back 123 TRUE |
front 124 True or False? Under certain conditions, the vocal folds act as a sphincter that prevents air passage. | back 124 TRUE |
front 125
Respiratory control centers are located in the ________.
| back 125 A) medulla and pons |
front 126 Some antacid drugs block histamine receptors, resulting in reduction of the production and excretion of stomach acid. These drugs have the biggest effect on which of the following? A) surface epithelial cells B) chief cells C) mucous neck cells D) parietal cells | back 126 D) parietal cells |
front 127 True or False? Most nutrients are absorbed through the mucosa of the intestinal villi by active transport. | back 127 TRUE |
front 128 True or False? Strong emotions and pain, acting through the limbic system and hypothalamus, send signals to the respiratory centers that modulate respiratory rate and depth. | back 128 TRUE |
front 129 True or False? Smoking diminishes ciliary action and eventually destroys the cilia. | back 129 TRUE |
front 130 True or False? The lungs are perfused by two circulations: the pulmonary and the bronchial. The pulmonary circulation is for oxygenation of blood. The bronchial circulation supplies blood to the lung structures (tissue). | back 130 TRUE |
front 131 Tidal volume is air ________. A) exchanged during normal breathing B) remaining in the lungs after forced expiration C) inhaled after normal inspiration D) forcibly expelled after normal expiration | back 131 A) exchanged during normal breathing |
front 132 The function of goblet cells is to ________. A) provide protection against invading bacteria and other disease-causing organisms that enter the digestive tract in food B) secrete buffers in order to keep the pH of the digestive tract close to neutral C) produce mucus that protects parts of the digestive organs from the effects of powerful enzymes needed for food digestion D) absorb nutrients from digested food and store them for future use | back 132 C) produce mucus that protects parts of the digestive organs from the effects of powerful enzymes needed for food digestion |
front 133 Bile salts bind at their hydrophobic regions to large fat globules within the chyme that enters the duodenum. Bile salts break up the fat globule into smaller fat droplets. This role of bile salts is best described as ________. A) lipid emulsification B) lipid absorption C) lipid ingestion D) lipid digestion | back 133 A) lipid emulsification |
front 134 Which structure is lined with simple squamous epithelium? A) oropharynx B) alveolus C) trachea D) nasopharynx | back 134 B) alveolus |
front 135 Which vitamin requires intrinsic factor in order to be absorbed? A) K | back 135 C) B-12 |
front 136
Air moves out of the lungs when the pressure inside the lungs is
| back 136 B) greater than the pressure in the atmosphere. |
front 137 The sheets of peritoneal membrane that hold the digestive tract in place are called ________. A) mucosal lining B) lamina propria C) serosal lining D) mesenteries | back 137 D) mesenteries |
front 138 Select the description below that illustrates a difference between a sphincter and circular muscle. A) A sphincter is a thickening of circular muscle that can prevent the movement of digesting materials while circular muscle is involved in propulsion digesting material. B) Sphincters are found throughout the GI tract while circular muscle is found only in the proximal portion of the GI tract. C) A sphincter is composed of smooth muscle while circular muscle is composed of skeletal muscle tissue. D) Sphincters are found in the proximal portion of the GI tract while circular muscle is found in the distal portions. | back 138 A) A sphincter is a thickening of circular muscle that can prevent the movement of digesting materials while circular muscle is involved in propulsion digesting material. |
front 139 True or False? The paired lungs occupy the mediastinum of the thoracic cavity. | back 139 FALSE |
front 140 Which pressure actually keeps the lungs from collapsing? A) atmospheric pressure | back 140 D) transpulmonary pressure |
front 141 Peristaltic waves are ________. A) churning movements of the gastrointestinal tract that aid in mechanical breakdown of chyme B) segmental regions of the gastrointestinal tract C) waves of muscular contractions that propel contents from one point to another D) pendular movements of the gastrointestinal tract | back 141 C) waves of muscular contractions that propel contents from one point to another |
front 142 Which of the following would likely be absorbed in the stomach? A) a serving of pasta | back 142 B) a serving of alcohol |
front 143 Which of the following refers to the movement of air into and out of the lungs? A) pulmonary ventilation B) external respiration C) internal respiration D) gas exchange | back 143 A) pulmonary ventilation |
front 144 Gastric pits, as opposed to gastric glands, are completely lined with ________. A) mucous cells | back 144 A) mucous cells |
front 145 True or False? During normal quiet breathing, males breathe 25% more than females. | back 145 TRUE |
front 146 Which of the following is the best explanation of the benefit in the digestive system having the largest collection of lymphoid tissue (MALT) at the distal end of the small intestine? A) The alkaline secretion of the small intestine aid in the growth of bacteria and must be controlled. B) The body will actively excrete pathogens out the body, into the digestive system to be removed from the body in feces. C) The huge numbers of bacteria living in the large intestine must be prevented from entering the lumen of the small intestine and being absorbed with food's nutrients into the blood stream. D) The digestive systems first and foremost job is to digest and absorb nutrients so it puts off immunity for last. | back 146 C) The huge numbers of bacteria living in the large intestine must be prevented from entering the lumen of the small intestine and being absorbed with food's nutrients into the blood stream. D) The digestive systems first and |
front 147 The bolus is liquefied in the ________ and it is now called chyme. A) esophagus B) stomach C) small intestine D) mouth | back 147 B) stomach |
front 148
The ingestion of which nutrient type results in the greatest
food-induced thermogenesis?
| back 148 C) proteins |
front 149 True or False? Triglycerides and cholesterol do NOT circulate freely in the bloodstream. | back 149 TRUE |
front 150 True or False? The increased use of noncarbohydrate molecules for energy to conserve glucose is called glucose sparing. | back 150 TRUE |
front 151 Which of the choices below is NOT a mechanism of heat production? A) enhanced thyroxine release B) sweating C) vasoconstriction of cutaneous blood vessels D) shivering | back 151 B) sweating |
front 152
The most abundant dietary lipids are ________.
| back 152 D) triglycerides |
front 153
The process of breaking triglycerides down into glycerol and
fatty acids is known as ________.
| back 153 D) lipolysis |
front 154
Catabolism would be best described as a process that ________.
| back 154 C) breaks down complex structures to simpler ones |
front 155 True or False? For use as fuel, all food carbohydrates are eventually transformed to glucose. | back 155 TRUE |
front 156 Several hours after your last meal, declining blood glucose levels stimulate release of the hormone ________, which stimulates glycogenolysis, lipolysis and fat mobilization, and gluconeogenesis. A) glucagon B) thyroxine C) cortisol D) insulin | back 156 A) glucagon |
front 157
Which of the following statements best describes complete protein?
| back 157 D) must meet all the body's amino acid requirements for maintenance and growth |
front 158 Which of the following is a source of complex carbohydrates? A) soda B) fruit juice C) potatoes D) pudding | back 158 C) potatoes |
front 159
Which of the following is the major role of leptin in the body?
| back 159 A) promote weight loss with activity |
front 160
Glycogen is formed in the liver during the ________.
| back 160 B) absorptive state |
front 161
The term metabolism is best defined as ________.
| back 161 D) biochemical reactions involved in building cell molecules or breaking down molecules for energy |
front 162 True or False? The preferred energy fuel for the brain is fat. | back 162 FALSE |
front 163
Which of the following is NOT true of the basal metabolic rate (BMR)?
| back 163 D) It is best calculated when the subject is in the absorptive state. |
front 164
The most abundant dietary lipids are ________.
| back 164 D) triglycerides |
front 165 Red blood cells lack mitochondria. As a result, ATP production is solely through ________. A) glycolysis B) electron transport chain C) citric acid (Krebs) cycle D) aerobic respiration | back 165 A) glycolysis |
front 166 True or False? The body is considered to be in nitrogen balance when the amount of nitrogen ingested in lipids equals the amount excreted in urine. | back 166 FALSE |
front 167 True or False? Diets high in cholesterol and saturated fats tend to produce high HDL concentrations. | back 167 FALSE |
front 168 Which type of food molecule provides components for cellular structures like plasma membranes, myelin sheaths, and steroid hormones? A) protein | back 168 B) lipids |
front 169
Which of the following is the most important function of the liver?
| back 169 D) protein metabolism |
front 170 When proteins undergo deamination, the waste substance found in the urine is mostly ________. A) ammonia B) ketone bodies C) urea D) acetyl CoA | back 170 C) urea |
front 171
Lipogenesis occurs when ________.
| back 171 D) cellular ATP and glucose levels are high |
front 172
Which of the choices below is not a fate of carbohydrate taken
into the body?
| back 172 D) conversion to a nucleic acid |
front 173
Heat-loss mechanisms do not include ________.
| back 173 D) vasoconstriction of peripheral blood vessels |
front 174 True or False? The term essential nutrient refers to the chemicals that can be interconverted in the liver so that the body can maintain life and good health. | back 174 FALSE |
front 175 True or False? Except for lactose and some glycogen, the carbohydrates we ingest are mainly from animals. | back 175 FALSE |
front 176 True or False? There are NO nutritionally complete proteins. All animal products should be eaten with plant material to make a nutritionally complete protein. | back 176 FALSE |
front 177 True or False? Vitamins are inorganic compounds that are essential for growth and good health. | back 177 FALSE |
front 178
In the case of a person who consumes a normal, balanced diet,
proteins are essential to the body for all of the following except ________.
| back 178 A) production of energy |