Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Human Anatomy & Physiology
front 1 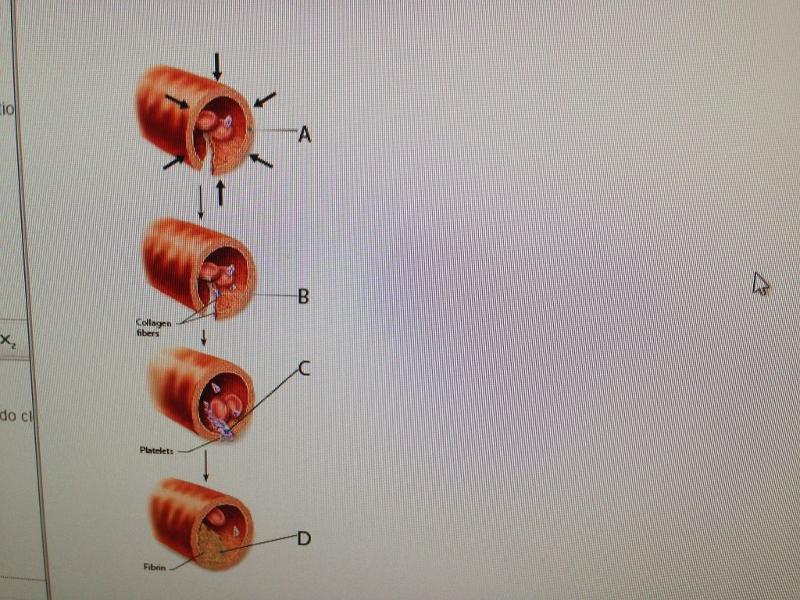 1.Art-based Question | back 1 D |
front 2 2.Hemostasis is important for __________. | back 2 stoppage of bleeding |
front 3 3.Which step in hemostasis involves activation of formed elements in
the blood? | back 3 platelet plug formation |
front 4 4.Which of the following represents a difference between extrinsic
and intrinsic blood clotting pathways? | back 4 One is faster than the other. |
front 5 5.Which of the following would NOT lead to a bleeding
disorder? | back 5 excess calcium in the diet |
front 6 6.A person who lacks agglutinogen A but has agglutinogen B would have
blood type __________. | back 6 B |
front 7 7.Choose the incompatible transfusion. | back 7 Donate type B blood to a recipient with type O blood. |
front 8 8. | back 8 AB |
front 9 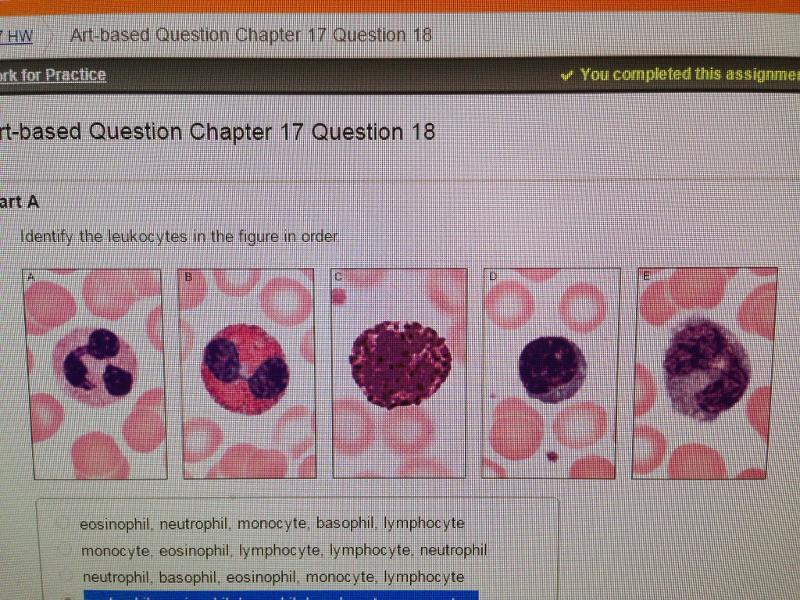 9.Art-based Question | back 9 neutrophil, eosinophil, basophil, lymphocyte, monocyte |
front 10 10.From which cell do the granulocytes
descend? | back 10 myeloblast |
front 11 11.On a blood smear slide prepared using Wright's stain, you observe
a large cell with a U-shaped nucleus and pale blue cytoplasm. This
cell is most likely a(n) __________. | back 11 monocyte |
front 12 12.Which type of leukocyte is responsible for antibody production? | back 12 lymphocytes |
front 13 13.Which of the following does NOT stimulate erythrocyte
production? | back 13 hyperventilating |
front 14 14.Which of the following are primary lymphoid organs? | back 14 bone marrow and thymus |
front 15 15.Which of the following areas in a secondary lymphoid organ allows
intimate contact between blood and the lymphocytes? | back 15 white pulp of the spleen |
front 16 16-Where in the lymph node do the T cells first encounter antigens
presented by dendritic cells? | back 16 deep in the cortex |
front 17 17.Collections of lymphoid tissues, called MALT, are strategically
placed throughout the respiratory, digestive, and genitourinary
systems. Which one of these is located at the end of the small
intestine? | back 17 Peyer’s patches |
front 18 18.There is a decrease in our ability to fight infection as we age. Which lymphoid organ may have a role in this decline? spleen | back 18 thymus |
front 19 19.Besides lymph nodes, where would you expect to find proliferating
(dividing) B cells? | back 19 in the spleen |
front 20 20. Which of the following mechanisms is NOT used to propel lymph
through lymphatic vessels? | back 20 small heart-like pumps |
front 21 21. Adjacent cells in lymphatic capillaries overlap each other
loosely. What is the unique structural modification that increases
their permeability? | back 21 minivalves |
front 22 22.Which of the following promotes closure of the minivalves
associated with lymph capillaries? | back 22 increasing pressure inside the lymph capillary |
front 23 23. Lymph from what regions of the body is drained into the right
lymphatic duct? | back 23 thorax |
front 24 24.What is the name of the enlarged sac to which the lumbar trunks
and the intestinal trunk return lymph? | back 24 cisterna chyli |
front 25 25.What region of the lymph node contains follicles filled with
dividing B cells? | back 25 cortex |
front 26 27.Which lymph cells produce antibodies? | back 26 plasma cells |
front 27 27. Which statement describes the origin of lymph fluid? | back 27 Lymph is excess fluid formed from plasma that accumulates in the tissues as interstitial fluid. |
front 28 28. Where are the three large clusters of superficial lymph
nodes? | back 28 the cervical, inguinal, and axillary regions |
front 29 29.Once collected, lymph ultimately drains into
__________. | back 29 venous circulation |
front 30 30. Art-based Question | back 30 C |
front 31 31.Which of the following is a role of lymph nodes? | back 31 They filter lymph. |
front 32 32.Which part of the spleen is the site of immune
function? | back 32 white pulp |
front 33 33. After surgical removal of the spleen (i.e., a splenectomy), some
other organs take over most of its functions. Which of the following
spleen functions in the adult can not be performed by bone
marrow? | back 33 removal of aged and damaged red blood cells from the blood |
front 34 34. Which of the following lymph organs is NOT matched with its
function? | back 34 Peyer's patches: mature B cells |
front 35 35. Peyer's patches are mucosa-associated lymph tissue located in the
__________. | back 35 wall of the small intestine |
front 36 36-The muscular layer in the wall of a blood vessel is the tunica interna. | back 36 tunica media. |
front 37 37-Compared to arteries, veins | back 37 have thinner walls. |
front 38 38-Capillaries that have a complete lining are called
| back 38 continuous capillaries. |
front 39 39-The smallest arterial branches are called the | back 39 precapillary arterioles. |
front 40 40-The layer between the tunica media and the tunica externa in a
large artery is the | back 40 external elastic membrane. |
front 41 41-The thoroughfare channel ends at the | back 41 venule. |
front 42 42-Which of the following layers of a vessel contains collagen fibers
with scattered bands of elastic fibers? | back 42 tunica externa |
front 43 43-After blood leaves the capillaries, it enters the | back 43 venules. |
front 44 44-Which layer of a blood vessel contains concentric sheets of smooth
muscle tissue? external elastic membrane | back 44 tunica media |
front 45 45-The large vessels that return blood to the heart are called arterioles. | back 45 veins. |
front 46 46-11. | back 46 internal elastic membrane. |
front 47 47-Which of the following is the innermost layer of a blood vessel?
| back 47 tunica intima |
front 48 48-Venoconstriction ________ the amount of blood within the venous
system, which ________ the volume in the arterial and capillary
systems. | back 48 reduces; increases |
front 49 49-Venous valves are responsible for | back 49 channeling blood toward the heart. |
front 50 50-Venae cavae are the largest of what type of vessel? | back 50 vein |
front 51 51-The layer of the arteriole wall that can produce vasoconstriction
is the | back 51 tunica media. |
front 52 52-Of the following arteries, the one that is an elastic artery is
the subclavian artery. | back 52 the subclavian artery. |
front 53 53-Which of the following lumen diameters would be typical of a
muscular artery? | back 53 0.4 cm |
front 54 55-Which vessel is known as a resistance vessel? | back 54 arteriole |
front 55 55-The main control of peripheral resistance occurs in the
| back 55 arterioles. |
front 56 56-Resistance is a force that decreases blood flow. | back 56 decreases blood flow. |
front 57 57-Total peripheral resistance is related to all of the following,
except the | back 57 osmolarity of interstitial fluids. |