Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Human Anatomy & Physiology
front 1 1-Which of the following is not one of the functions of blood? | back 1 to protect vital organs |
front 2 2- The most abundant component of plasma is: | back 2 water |
front 3 3-Which of the following characteristics is not associated with
erythrocytes? | back 3 Capable of protein synthesis |
front 4 4-What is the oxygen-binding protein found in erythrocytes? hemoglobin | back 4 hemoglobin |
front 5 5-Bilirubin comes from the breakdown of: | back 5 heme molecules of hemoglobin that lack iron. |
front 6 6-During leukopoiesis, neutrophils are derived from __________. | back 6 myeloblasts |
front 7 7-Which type of leukocyte may produce antibodies? lymphocyte | back 7 lymphocyte |
front 8 8-Which of the following characteristics is not associated with
platelets? | back 8 They are incapable of oxidative catabolism. |
front 9 9-The enzyme that coverts fibrinogen to fibrin is __________. | back 9 thrombin |
front 10 10-Select the appropriate pathway for the steps of hemostasis. | back 10 vascular spasms, platelet plug formation, coagulation, clot retraction, thrombolysis |
front 11 11-In the common pathway of coagulation, what factor combines with
factor Va and calcium ions to form prothrombin activator? | back 11 Xa |
front 12 12-Which of the following donors will be suitable for a recipient
with type A+ blood? | back 12 A donor with O- blood 13- |
front 13 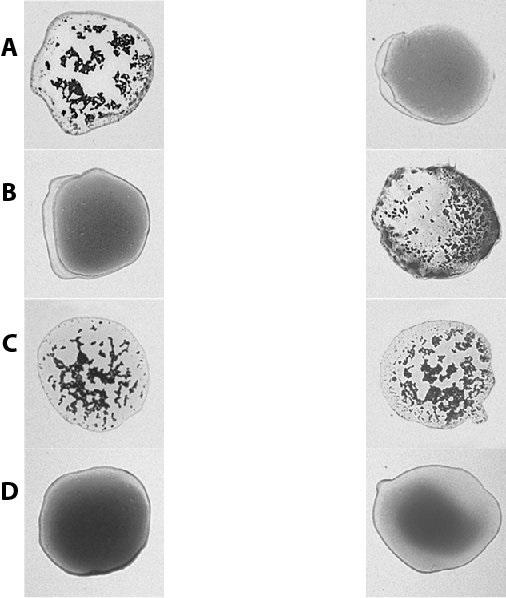 13-Match the following blood types. In the left column, the blood sample is combined with an anti-A antibody; in the right column, the blood sample is combined with an anti-B antibody. Type AB A | back 13 C |
front 14  14-Match the following blood types. In the left column, the blood sample is combined with an anti-A antibody; in the right column, the blood sample is combined with an anti-B antibody Type A | back 14 A |
front 15  15-Match the following blood types. In the left column, the blood sample is combined with an anti-A antibody; in the right column, the blood sample is combined with an anti-B antibody Type O D | back 15 D |
front 16  16- Match the following blood types. In the left column, the blood
sample is combined with an anti-A antibody; in the right column, the
blood sample is combined with an anti-B antibody | back 16 B |
front 17  17-Match the following blood types. In the left column, the blood sample is combined with an anti-A antibody; in the right column, the blood sample is combined with an anti-B antibody Lacks the A and B antigens B | back 17 D |
front 18  18-Match the following blood types. In the left column, the blood sample is combined with an anti-A antibody; in the right column, the blood sample is combined with an anti-B antibody Possesses both the A and B antigens | back 18 C |
front 19 19-Jerry is an alcoholic and does not eat enough food. He has been
diagnosed with a vitamin deficiency. What blood disorder is the most
likely a result of this deficiency? | back 19 pernicious anemia |
front 20 20-Platelets form from large cells called __________. | back 20 megakaryocytes |
front 21 21-When is fibrin produced during the coagulation cascade? | back 21 common pathway |
front 22 22-What ions are necessary for both the intrinsic and extrinsic
pathways to the coagulation cascade? | back 22 calcium ions |
front 23 23-When fibrin levels increase, thrombin production is inhibited.
This is an example of a __________. | back 23 negative feedback loop |
front 24 24-The process by which a blood clot dissolves is called __________. | back 24 thrombolysis |