Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
anatomy exam 4 ch. 13
front 1 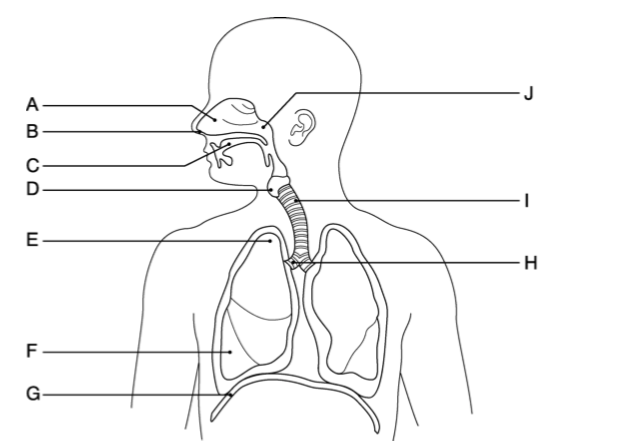 The nasal cavity is indicated by the letter __________. | back 1 Answer: A |
front 2  The right main (primary) bronchus is indicated by letter __________. | back 2 Answer: H |
front 3  The trachea is indicated by letter __________. | back 3 Answer: I |
front 4  The diaphragm muscle is indicated by letter __________. | back 4 Answer: G |
front 5  The oral cavity is indicated by letter __________. | back 5 Answer: C |
front 6  The base of the right lung is indicated by letter __________. | back 6 Answer: F |
front 7  The nostrils are indicated by letter __________. | back 7 Answer: B |
front 8  The apex of the right lung is indicated by letter __________. | back 8 Answer: E |
front 9  The larynx is indicated by letter __________. | back 9 Answer: D |
front 10  The pharynx is indicated by letter __________. | back 10 Answer: J |
front 11 The three mucosa-covered projections into the nasal cavity that greatly increase surface area of mucosa exposed to air are called __________. | back 11 Answer: conchae |
front 12 The anterior portion of the palate that is supported by bone is called the __________. | back 12 Answer: hard palate |
front 13 The three regions of the pharynx are the __________. | back 13 Answer: nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx |
front 14 Inflammation of the sinuses that can cause marked changes in voice quality is called __________. | back 14 Answer: sinusitis |
front 15 The large shield-shaped thyroid cartilage that protrudes anteriorly is commonly called the __________. | back 15 Answer: Adam's apple |
front 16 The mucosa-lined windpipe that extends from the larynx to the level of the fifth thoracic vertebra is called the __________. | back 16 Answer: trachea |
front 17 Clusters of lymphatic tissue in the pharynx are referred to as __________. | back 17 Answer: tonsils |
front 18 The opening between the vocal folds is called the __________. | back 18 Answer: glottis |
front 19 The C-shaped rings that reinforce the trachea are constructed of __________ cartilage. | back 19 Answer: hyaline |
front 20 The flap of elastic cartilage that protects the opening of the larynx is called the __________. | back 20 Answer: epiglottis |
front 21 Folds of mucous membrane called __________ vibrate to provide speech. | back 21 Answer: vocal folds or true vocal cords |
front 22 The serous membrane that surrounds each lung is created by a parietal and visceral __________. | back 22 Answer: pleura |
front 23 The division of the trachea produces two tubes called the right and left main (primary) __________. | back 23 Answer: bronchus |
front 24 Dust cells" that wander in and out of the alveoli, picking up bacteria, carbon particles, and other debris, are actually __________. | back 24 Answer: macrophages |
front 25 The air sacs of the lungs are called __________. | back 25 Answer: alveoli |
front 26 The process of moving air into and out of the lungs is commonly called breathing or __________. | back 26 Answer: pulmonary ventilation |
front 27 Gas exchange between the blood and tissue cells is called __________. | back 27 Answer: internal respiration |
front 28 The inspiratory muscles that contract so we can inspire air are the __________ and __________. | back 28 Answer: diaphragm; external intercostals |
front 29 The presence of air in the intrapleural space is known as __________. | back 29 Answer: pneumothorax |
front 30 Normal quiet breathing moves about __________ mL of air into and out of the lungs with each breath. | back 30 Answer: 500 |
front 31 A mechanism that clears the upper respiratory passages, which is similar to a cough except that the expelled air is directed through the nasal cavities instead of the oral cavity, is called a __________. | back 31 Answer: sneeze |
front 32 Air that remains in the conducting zone passageways and never reaches the alveoli is called the __________. | back 32 Answer: dead space volume |
front 33 Respiratory capacities are measured with a __________. | back 33 Answer: spirometer |
front 34 During __________, oxygen binds to hemoglobin to form oxyhemoglobin. | back 34 Answer: external respiration |
front 35 __________ is an odorless, colorless gas which binds preferentially with the same binding site on hemoglobin. | back 35 Answer: Carbon monoxide |
front 36 Most carbon dioxide is dissolved in blood plasma and transported as __________. | back 36 Answer: bicarbonate ion |
front 37 Inadequate oxygen delivery to body tissues is called __________. | back 37 Answer: hypoxia |
front 38 The portions of the brain that contain respiratory centers and set the breathing rate are the __________ | back 38 Answer: medulla oblongata and pons |
front 39 A normal respiratory rate of about 12-15 breaths per minute is called __________. | back 39 Answer: eupnea |
front 40 The most important stimulus for breathing in a healthy person is the body's need to rid itself of the blood gas called __________. | back 40 Answer: carbon dioxide |
front 41 In order to return acidic blood pH to normal, breathing becomes deeper and more rapid, a phenomenon known as __________. | back 41 Answer: hyperventilation |
front 42 The fatty molecule made by alveolar cells known as __________ reduces surface tension prevents alveoli collapse between breaths. | back 42 Answer: surfactant |
front 43 Gas exchange occurs in the A) larynx B) alveoli C) pharynx D) nose E) trachea | back 43 Answer: B) alveoli |
front 44 The respiratory conducting passageways perform all of the following functions EXCEPT: A) humidify air B) exchange gases D) purify air | back 44 Answer: B) exchange gases |
front 45 Which one of the following terms does NOT apply to the nose: A) external nares B) nasopharynx C) nasal cavity D) nostrils | back 45 Answer : B) nasopharynx |
front 46 What is the role of mucus in the nasal cavity: A) act as a resonance chamber for speech B) trap incoming bacteria and other foreign debris C) increase the air turbulence in the nasal cavity D) lighten the skull | back 46 Answer : B) trap incoming bacteria and other foreign debris |
front 47 The nasal cavity is separated from the oral cavity by: A) the hard palate B) the soft palate D) both the hard and soft palate | back 47 Answer : D) both the hard and soft palate |
front 48 Which one of the following bones does NOT contain paranasal
sinuses: B) mandible C) ethmoid D) maxilla E) sphenoid | back 48 Answer : B) mandible |
front 49 Which tonsil(s) is/are located in the oropharynx at the end of the soft palate: A) lingual tonsils B) thymus gland C) adenoid D) palatine tonsils E) pharyngeal tonsil | back 49 Answer : D) palatine tonsils |
front 50 Air from the nasal cavity enters the superior portion of the pharynx called the A) laryngopharynx B) oropharynx D) palatopharynx E) nasopharynx | back 50 Answer : E) nasopharynx |
front 51 The pharynogotympanic tubes, which drain the middle ear, open into the: A) nasopharynx B) laryngopharynx C) oropharynx D) tracheopharynx E) palatopharynx | back 51 Answer : A) nasopharynx |
front 52 Contaminated mucus is removed from the lower respiratory passageways, such as the trachea, by: A) flagella B) contractions of smooth muscles C) yawning D) cilia | back 52 Answer : D) cilia |
front 53 Following the removal of the larynx, a person would be unable
to: B) hear C) eat D) sneeze E) breathe | back 53 Answer : A) speak |
front 54 The opening between the vocal cords is called the: A) esophagus B) larynx C) glottis D) epiglottis | back 54 Answer : C) glottis |
front 55 The flap of elastic cartilage that protects food from entering the larynx when swallowing is the: A) trachea B) Adam's apple C) thyroid cartilage D) epiglottis E) glottis | back 55 Answer : D) epiglottis |
front 56 Vibration due to exhaled air that results in speech is a function of the: A) glottis B) complete voice box C) true vocal cords D) epiglottis | back 56 Answer: D) epiglottis |
front 57 Terminal bronchioles eventually terminate in: A) diaphragm B) glottis D) alveoli | back 57 Answer: D) alveoli |
front 58 The serous membrane covering the surface of the lungs is called the: A) main (primary) bronchi B) pleurisy D) parietal pleura E) visceral pleura | back 58 Answer: E) visceral pleura |
front 59 Which one of the following is NOT true of the lungs: A) the right lung has three lobes B) the bases rest on the diaphragm C) the left lung has two lobes D) the narrower portion of each lung is called the apex E) both lungs have two lobes | back 59 Answer: E) both lungs have two lobes |
front 60 When oxygen enters the respiratory system, what is the next structure to which it travels immediately upon leaving the trachea: A) alveoli C) pleura E) tertiary bronchi | back 60 Answer: D) main (primary) bronchi |
front 61 Which one of the following structures is NOT part of the respiratory zone: A) alveoli B) alveolar ducts D) primary bronchi E) alveolar sacs | back 61 Answer: D) primary bronchi |
front 62 Which of the following is NOT one of the four main events of respiration: A) external respiration B) pulmonary ventilation C) respiratory gas transport D) residual volume | back 62 Answer: D) residual volume |
front 63 Exchange of both oxygen and carbon dioxide through the respiratory membrane occurs by: A) facilitated diffusion B) simple diffusion C) endocytosis D) osmosis | back 63 Answer: B) simple diffusion |
front 64 The lipid molecule critical to lung function that coats the
gas-exposed alveolar surfaces is called: B) renin C) kinin D) interferon E) lecithin | back 64 Answer: A) surfactant |
front 65 Air moving in and out of the lungs is called: A) internal respiration B) expiration D) inspiration | back 65 Answer: C) pulmonary ventilation |
front 66 Which one of the following is NOT true of inspiration: B) relaxation of the external intercostal muscles helps increase the size of the thoracic cavity C) contraction of the diaphragm muscle helps increase the size of the thoracic cavity D) air continues to move into the lungs until intrapulmonary pressure equals atmospheric pressure E) the decreased gas pressure produces a partial vacuum that forcibly sucks air in | back 66 Answer: B) relaxation of the external intercostal muscles helps increase the size of the thoracic cavity |
front 67 The gas exchange that occurs between blood and tissue cells at systemic capillaries is called: A) external respiration B) expiration D) internal respiration | back 67 Answer: D) internal respiration |
front 68 Expiration (exhalation) occurs when: B) intrapulmonary pressure decreases D) diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax E) air moves into the lungs | back 68 Answer: D) diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax |
front 69 Which nonrespiratory air movement clears the upper respiratory
passageways: B) sneezing C) hiccupping D) coughing E) yawning | back 69 Answer: B) sneezing |
front 70 The presence of air in the intrapleural space is known as: A) atelectasis B) pneumothorax C) hypoxia D) asthma E) pleurisy | back 70 Answer: B) pneumothorax |
front 71 The respiratory movement representing the total amount of exchangeable air is the: A) tidal volume B) dead space volume D) expiratory reserve volume E) vital capacity | back 71 Answer: E) vital capacity |
front 72 The amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled after a tidal expiration is about: A) 1200 mL B) 4800 mL C) 500 mL D) 6000 mL E) 2100 mL | back 72 Answer: A) 1200 mL |
front 73 The amount of air exchanged during normal quiet breathing is about: A) 4800 mL B) 1200 mL C) 500 mL D) 6000 mL E) 2100 mL | back 73 Answer: C) 500 mL |
front 74 Carbon dioxide dissolves in blood plasma for transport as: A) oxyhemoglobin B) carbohemoglobin C) carbon monoxide D) bicarbonate ion E) deoxyhemoglobin | back 74 Answer: D) bicarbonate ion |
front 75 Oxygen binds with hemoglobin in the blood to form: A) oxyhemoglobin B) plasma D) carbon dioxide E) carbonic acid | back 75 Answer: A) oxyhemoglobin |
front 76 The bluish cast that results from inadequate oxygenation of the skin and mucosa is called: A) melanosis B) erythema C) albinism D) cyanosis E) xanthosis | back 76 Answer: D) cyanosis |
front 77 Where are the respiratory centers housed which control involuntary breathing rates: A) thalamus and corpus callosum B) hypothalamus and thalamus C) cerebellum and occipital lobe D) medulla and pons | back 77 Answer: D) medulla and pons |
front 78 Cessation of breathing is called: B) hyperpnea C) dyspnea D) eupnea E) tachypnea | back 78 Answer: A) apnea |
front 79 Hypoventilation dramatically increases carbonic acid concentration and involves: A) irregular breathing B) extremely slow breathing C) extremely fast breathing D) extremely deep breathing E) intermittent breathing | back 79 Answer: B) extremely slow breathing |
front 80 Hyperventilation leads to all of the following except: A) brief periods of apnea B) buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood C) cyanosis D) dizziness E) fainting | back 80 Answer: B) buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood |
front 81 The most important chemical stimulus leading to increased rate and depth of breathing is: A) decreased oxygen level in the blood B) decreased carbon dioxide in the blood C) increased blood pH D) increased hydrogen ion in the blood E) increased carbon dioxide in the blood | back 81 Answer: E) increased carbon dioxide in the blood |
front 82 Which one of the following is NOT a feature of COPD: B) most patients have a history of smoking D) most COPD victims are hypoxic | back 82 Answer: A) most patients have a genetic predisposition to COPD |
front 83 Which congenital respiratory disease results in the oversecretion of mucus and clogging of respiratory passageways: A) cystic fibrosis B) atelectasis C) asthma E) emphysema | back 83 Answer: A) cystic fibrosis |
front 84 The molecule that prevents lung collapse by lowering the surface tension of the water film lining each alveolar sac is called: A) resorbin B) renin C) lecithin D) fibrosin E) surfactant | back 84 Answer: E) surfactant |
front 85 Surfactant is usually present in fetal lungs in adequate quantities by: A) 22-24 weeks of pregnancy B) 24-26 weeks of pregnancy C) 26-28 weeks of pregnancy D) 28-30 weeks of pregnancy E) 20-22 weeks of pregnancy | back 85 Answer: D) 28-30 weeks of pregnancy |
front 86 The abbreviation IRDS stands for: B) intermittent respiratory distress state C) infant respiratory disease state D) intermittent respiratory disease syndrome E) infant respiratory distress syndrome | back 86 Answer: E) infant respiratory distress syndrome |
front 87 What is the most common cause for lung cancer: A) diet B) smoking C) hereditary D) asthma | back 87 Answer: B) smoking |
front 88 The respiratory rate in adults is: B) 12-18 respirations per minute C) 5-10 respirations per minute D) 30 respirations per minute | back 88 Answer: B) 12-18 respirations per minute |
front 89 The homeostatic imbalance associated with the death of many full-term
newborn infants is called: B) CTRL C) CF D) COPD E) IRDS | back 89 Answer: A) SIDS |
front 90 Obstruction of the trachea by a piece of food can lead to: A) pneumothorax B) hemothorax C) pleurisy D) pulmonary tamponade E) aspiration pneumonia | back 90 Answer: E) aspiration pneumonia |
front 91 Which of these age-related disorders is related to loss of elasticity of the lungs and hypoxia: A) sudden infant death syndrome B) asthma D) pneumonia E) tuberculosis | back 91 Answer: C) sleep apnea |
front 92 Which one of the following is NOT true of lung cancer: B) it is generally more prevalent in males than females C) its incidence is currently increasing D) most types of lung cancer are very aggressive | back 92 Answer: B) it is generally more prevalent in males than females |
front 93 The ciliated cells of the nasal mucosa propel contaminated mucus posteriorly toward the pharynx. True or False | back 93 True |
front 94 The nasal cavity is separated from the oral cavity by the nasal conchae. True or False | back 94 False |
front 95 There are only three paranasal sinuses located in the frontal, sphenoid, and parietal bones. True or False | back 95 False |
front 96 The portion of the pharynx continuous with the mouth is termed the oropharynx. True or False | back 96 True |
front 97 The tonsils are located in the larynx. True or False | back 97 False |
front 98 The larynx routes air and food into their proper channel and plays an important role in speech production. True or False | back 98 True |
front 99 The "guardian of the airways" that prevents food from entering the superior opening of the larynx is the thyroid cartilage. True or False | back 99 False |
front 100 The function of the C-rings of hyaline cartilage in the trachea is to keep the airway patent or open for breathing. True or False | back 100 True |
front 101 The emergency surgical opening of the trachea is called a tracheostomy. True or False | back 101 True |
front 102 Each main (primary) bronchus enters the lung at the apex. True or False | back 102 False |
front 103 The lungs are housed in the mediastinum of the thoracic cavity. True or False | back 103 False |
front 104 The bronchioles are the smallest of the conducting passageways in the lungs. True or False | back 104 True |
front 105 The parietal pleura is superficial to the visceral pleura. True or False | back 105 True |
front 106 The respiratory membrane is the air-blood barrier, where gases are exchanged. True or False | back 106 True |
front 107 The respiratory zone includes the respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, and alveoli. True or False | back 107 True |
front 108 The process of breathing is known as pulmonary ventilation. True or False | back 108 True |
front 109 Inspiration results when the diaphragm and external intercostal muscles relax. True or False | back 109 False |
front 110 Expiration occurs when the thoracic and intrapulmonary volumes decrease and the intrapulmonary pressure increases True or False | back 110 True |
front 111 The amount of air that can be forcibly inhaled over the tidal volume is around 3100 mL. True or False | back 111 True |
front 112 Normal quiet breathing, known as tidal volume, is around 500 mL of air. True or False | back 112 True |
front 113 Sudden inspirations resulting from spasms of the diaphragm are hiccups. True or False | back 113 True |
front 114 Bronchial sounds are produced as air fills the alveoli of the lungs. True or False | back 114 False |
front 115 Wheezing is a whistling sound associated with diseased respiratory tissue, mucus, or pus. True or False | back 115 True |
front 116 According to the laws of diffusion, movement of a respiratory gas occurs toward the area of higher concentration of that particular respiratory gas. True or False | back 116 False |
front 117 The general term for inadequate oxygen delivery to body tissues regardless of the cause is called hypoxia. True or False | back 117 True |
front 118 Venous blood in systemic circulation is poorer in oxygen and richer in carbon dioxide. True or False | back 118 True |
front 119 Hyperpnea results from exercise when breathing becomes deeper and more vigorous. True or False | back 119 True |
front 120 The lungs of the fetus are filled with air late in pregnancy. True or False | back 120 False |
front 121 Changes in oxygen levels in the blood are the most important stimuli for breathing in a healthy person. True or False | back 121 False |