Alkens alkynes
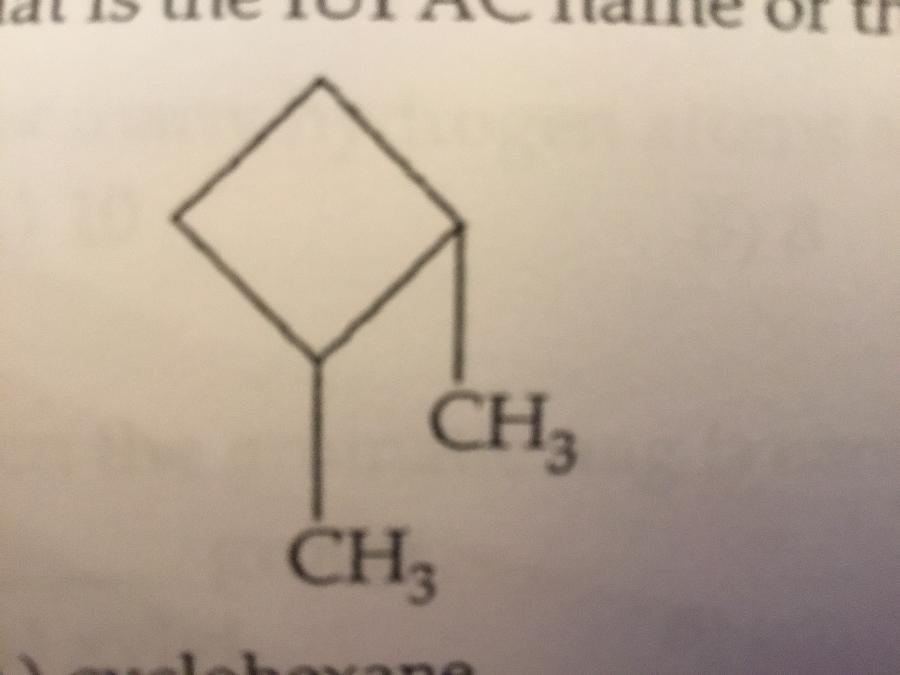
What is the IUPAC name of the molecule shown?
A. Cyclohexane
B. 3,4-dimethylcyclobutane
C. Dimethylcyclobutane
D. 2,3-dimethylcyclobutane
E. 1,2-dimethylcyclobutane
E. 1,2-dimethylcyclobutane
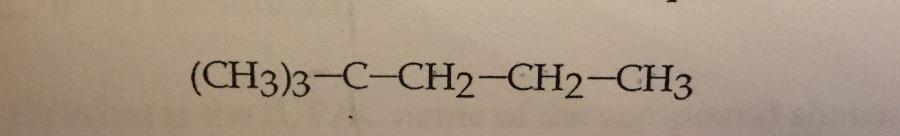
What is the IUPAC name of the compound shown?
a. Heptane
B. 2,2-dimethylpentane
c. 1,1,1-trimethylbutane
d. 2-dimethylpentane
e. 2-ethylhexane
B. 2,2-dimethylpentane
The functional group illustrated by R-O-R’ is an.
A. Alcohol
B. Aldehyde
C. Ester
D. Ether
E. Alkyl
D. Ether.
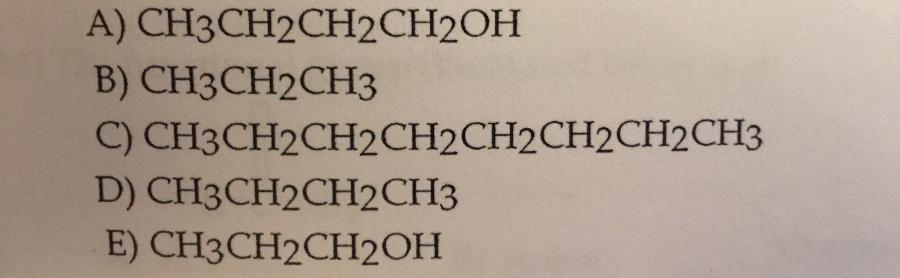
Which compound shown it the most soluble in water?
E.
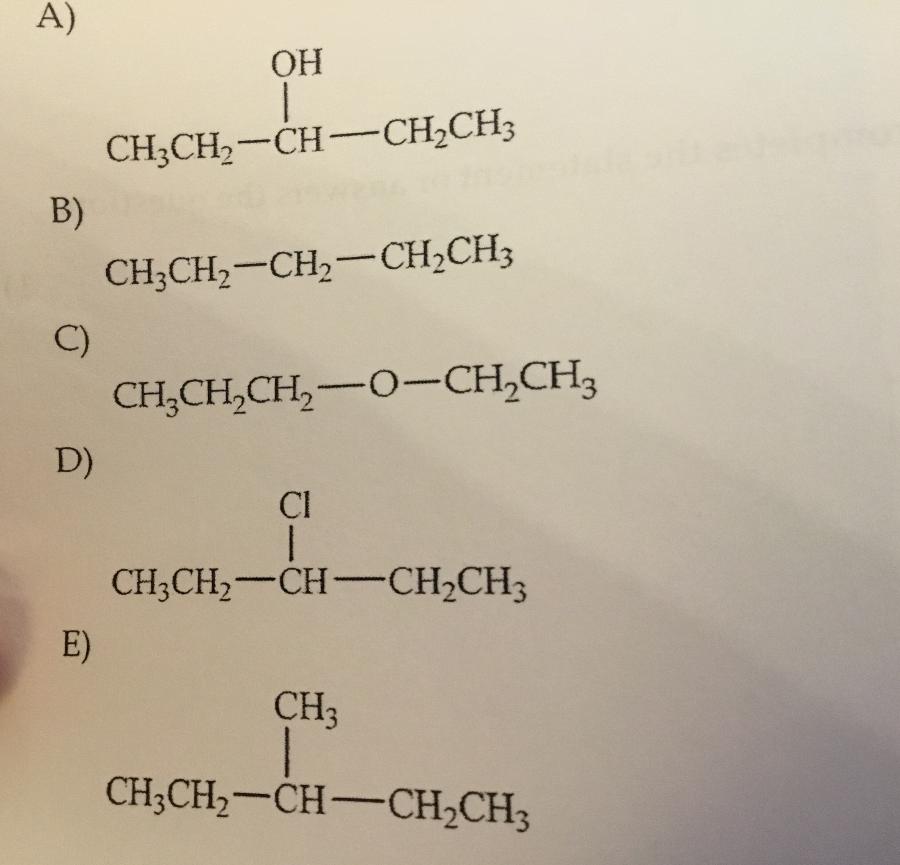
Which compound shown has the highest boiling point?
A.
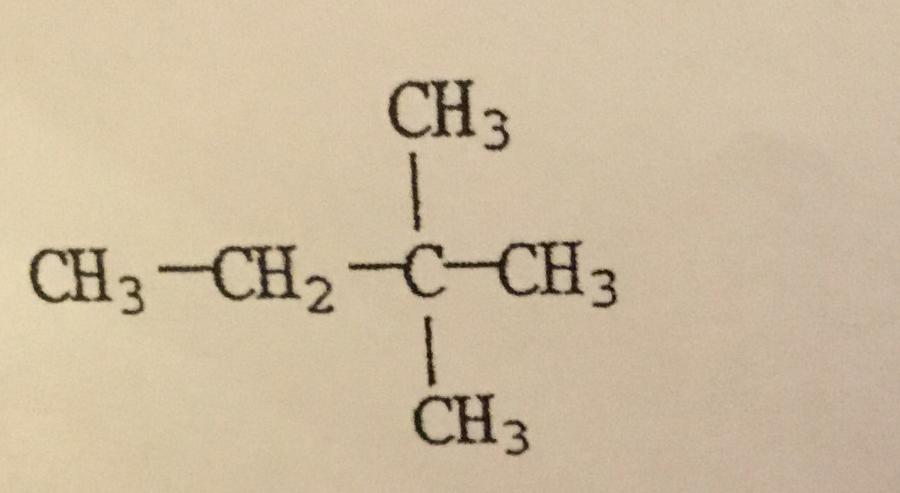
What is the IUPAC name of the compound shown?
A. Hexane
B. 2,2-dimethylbutane
C. Isohexane
D. Ethylmethylpropane
E. Dimethylbutane
B. 2,2-dimethylbutane
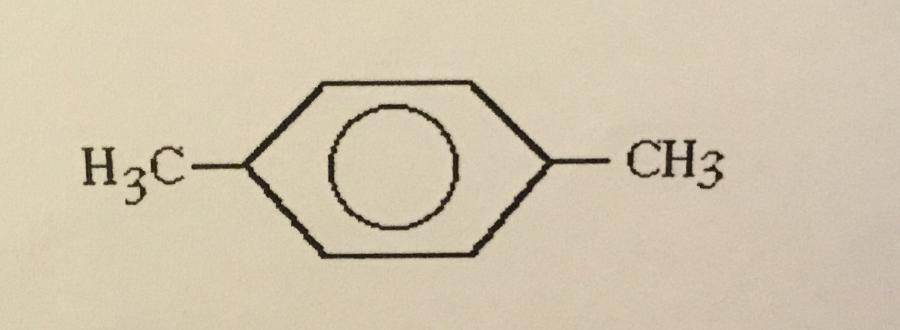
What is the systematic name of the structure shown?
A. 1,3-dimethylbenzene
B. Ortho-dimethylbenzene
C. Meta-dimethylbenzene
D. 1,2-dimethylbenzene
E. Para-dimethylbenzene
E. Para-dimethylbenzene
The relatively high boiling point of alcohols in relation to their molecular weight is the result of _______.
A. Hydrogen bonding
B. Diplomat forces
C. Ionic bonding
D. London forces
E. Covalent bonding
A. Hydrogen bonding.
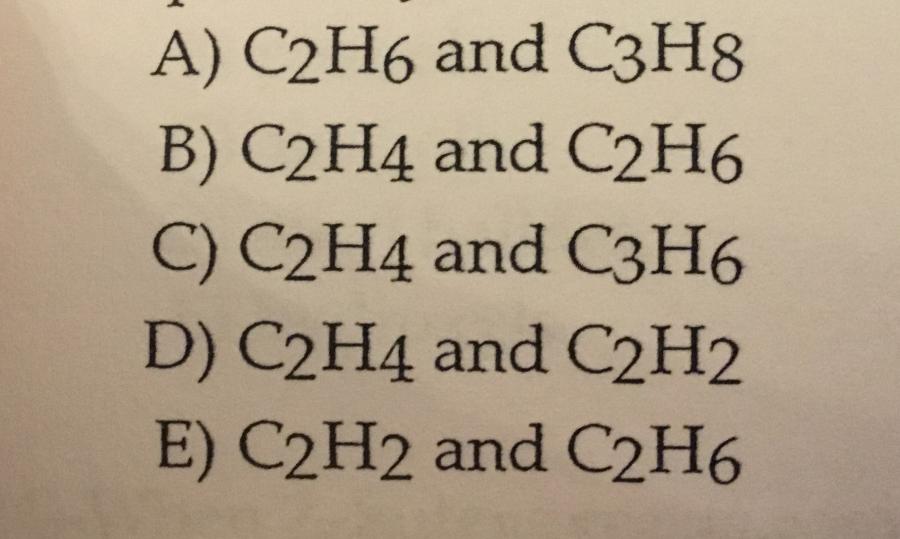
Ethylene and acetylene are the common names of the molecules _______ and ________.
D.
How many hydrogen atoms are contained in a molecule of cyclopentene?
A. 10
B. 8
C. 12
D. 5
E. 6
B. 8
When the aromatic ring is named as a side chain or functional group, it is referred to as the _______ group.
A. Xylyl
B. Benzyl
C. Toluyl
D. Phenyl
E. Benzoyl
D. Phenyl
Chemical reactions involving double bonds and generally referred to as ______ reactions.
A. Combustion
B. Oxidation
C. Reduction
D. Addition
E. Substitution
D. Addition reactions
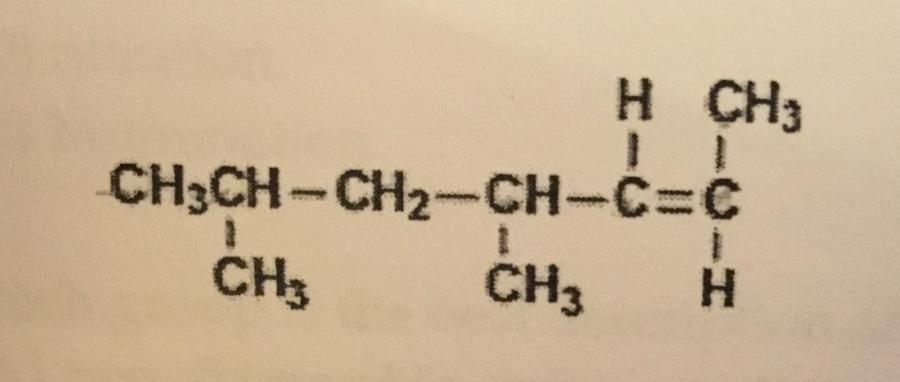
What is the IUPAC name of the compound shown?
A. Cis-4,6-dimethyl-2-heptene
B. Cis-2-nonene
C. Trans-4,6-dimethyl-2-heptene
D. Trans-2-nonene
E. Trans-2,4-dimethyl-5-heptene
C. Trans-4,6-dimethyl-2–heptene
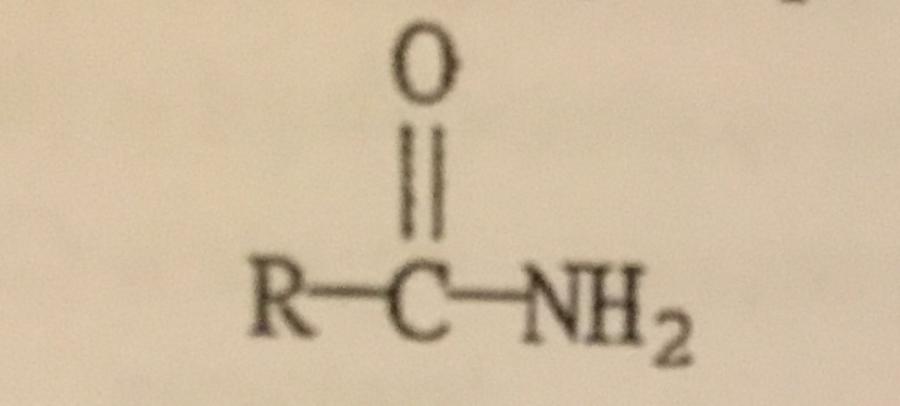
The functional group illustrated is an ______.
A. Alcohol
B. Amine
C. Ether
D. Amide
E. Ester
D. Amide
Which compound is a tertiary alcohol?
A. 3-methyl-2-hexanol
B. 3-hexanol
C. 2-methyl-1-hexanol
D. 2-methyl-2-hexanol
E. 1-propanol
D. 2-methyl-2-hexanol
Compounds with an oxygen atom bonded to two organic groups are known as _____.
A. Phenols
B. Hydroxides
C. Hydroxyls
D. Ethers
E. Alcohols
D. Ethers
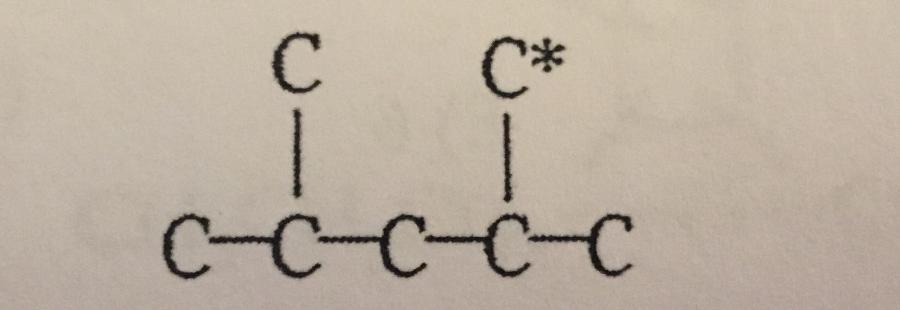
In the carbon skeleton shown, how many hydrogen atoms are bonded to the C* carbon?
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
E. 4
D. 3
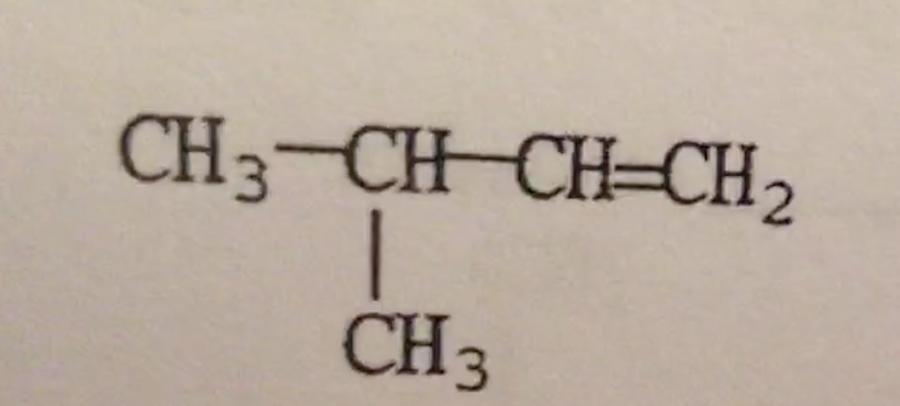
What is the IUPAC name of the compound shown?
A. 3-methyl-1,2-butene
B. 1,1-dimethyl-2-propene
C. Isopentene
D. 2-methyl-3-butene
E. 3-methyl-1-butene
E. 3-methyl-1-butene
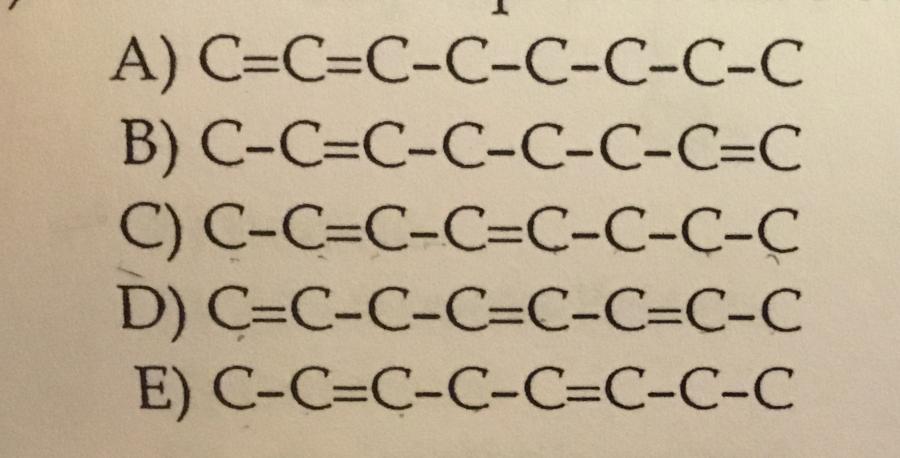
Which choice represents the carbon skeleton of 2,4-octadiene?
C.
Treatment of CH3CH2CH2OH with a limited amount of oxidizing agent will produce,
A. No reaction
B. An alkene
C. A crboxylic acid
D. A ketone
E. An aldehyde
E. An aldehyde
Which family of organic molecules is a hydrocarbon?
A. Aromatic
B. Aldehyde
C. Amine
D. Amide
E. Alcohol
A. Aromtic
The common name of CH2(OH)CH2OH is
A. Glycerol
B. Grain alcohol
C. Wood alcohol
D. Rubbing alcohol
E. Ethylene glycol (antifreeze)
E. Ethylene glycol
Compounds with the -OH group attached to a saturated alkane-like carbon are known as
A. Ethers
B. Phenols
C. Alcohols
D. Alkyl halides
E. Hydroxyls
C. Alcohols
When 2-butene reacts completely with bromine, the product is,
A. 1,3-dibromobutane
B. 1,2-dibromobutane
C. 2-bromobutane
D. 3-bromobutane
E.2,3-dibromobutane
E. 2,3-dibromobutane
When phenol acts as an acid, a _______ ion is produced.
A. Phenolic
B. Benzyl
C. Phenoxide
D. Phenyl
E. Phenolate
C. Phenoxide ion
The alcohol which contains two carbon atoms and has the common name of grain alcohol is,
A. Methanol
B. Glycol
C. Glycerol
D. Ethanol
E. Phenol
D. Ethanol alcohol
All of the following are common reactions of benzene except.
A. Sulfonation
B. Hydrogenation
C. Chlorination
D. Nitration
E. Bromination
B. Hydrogenation
Which best describes the properties of alkanes?
A. Non-flammable, polar, reactive
B. Flammable, reactive, water soluble
C. Flammable, non-reactive, insoluble in water
D. Non-flammable, non-polar, water soluble
E. None of the above.
C. Flammable, non-reactive, insoluble in water.
A substitution reaction can be best described as a reaction in which,
A. Two reactants combine to form one new product with no extra atoms.
B. A hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen to produce CO2, H2O and energy.
C. A single reactant undergoes reorganization of its chemical. Bonds, producing an isomer of the reactant.
D. Two reactants exchange atoms to give two new products.
E. A single reactant splits into two products.
D. Two reactants exchange atoms to give two new products
Which atom is MOST likely to form a polar covalent bond with carbon?
A. Na
B. O
C. S
D. C
E. H
B. O
All of the following are general properties of alkenes except.
A. Soluble in non-polar (organic) solvents.
B. May exist as cis-trans isomers.
C. Less reactive than the corresponding alkanes.
D. Low boiling points.
E. Flammable.
C. Less reactive
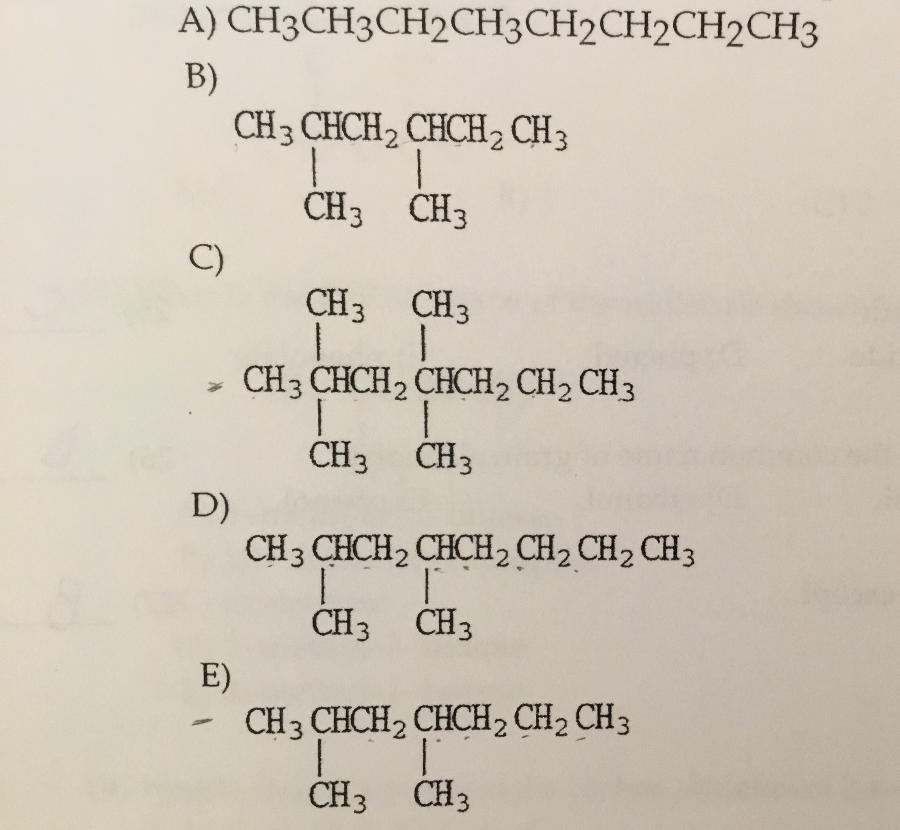
Which compound shown is the condensed structure of 2,4-diemethylheptane?
E.
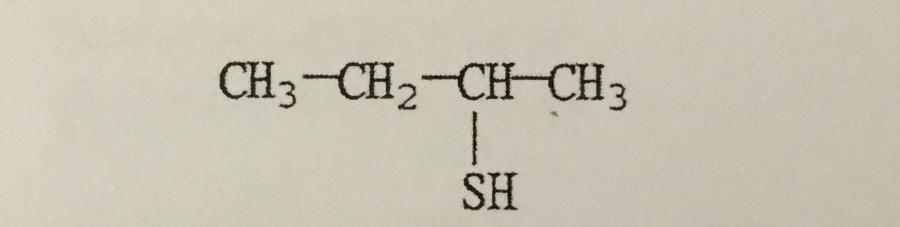
What is the IUPAC name of the compound shown?
A. 2-thiobutane
B. 3-thiobutanol
C. 1-methyl-1-propanethiol
D. 2-butanethiol
E. 1-methyl-1-thiopropane
D. 2-butanethiol
Alkanes are ______ in water and ______ than water.
A. Insoluble; less dense
B. Soluble; less dense
C. Soluble; more dense
D. Insoluble; more dense
A. Insoluble; less dense
All of the following statements are general properties of organic compounds except,
A. They have relatively low boiling points.
B. They have limited or no water solubility
C. They have relatively low melting points.
D. They usually behave as electrolytes in solution.
E. The bonds are covalent
D. They usually behave as electrolytes in solution.
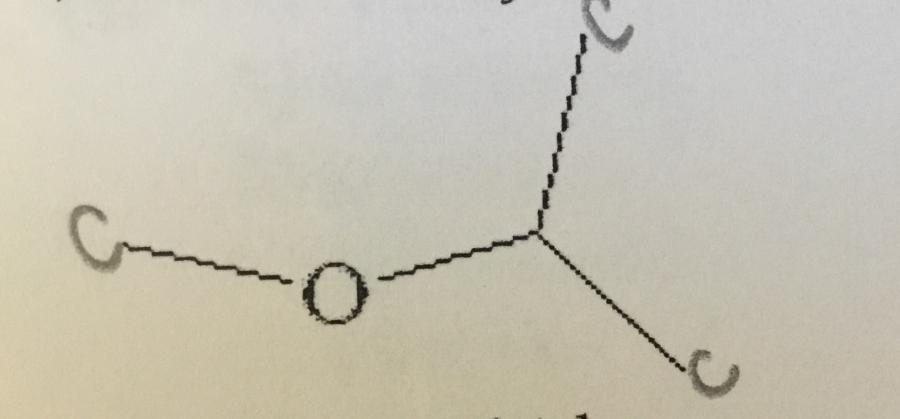
What is the systematic name of the compound shown.
A. Diethyl ether
B. 2-ethoxy propane
C. 2-methoxy propane
D. Ethyl methyl ether
C. 2-methoxy propane
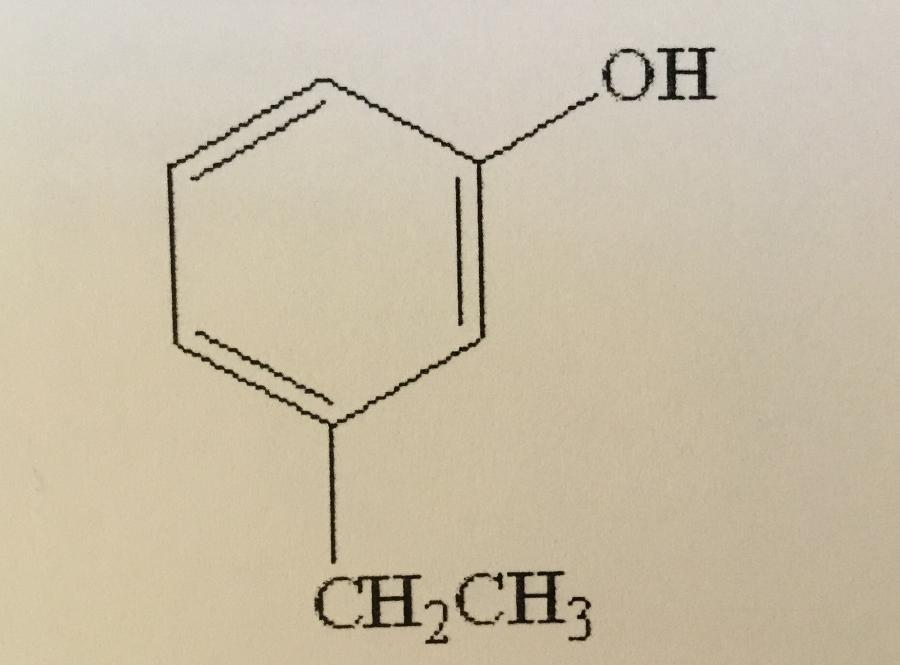
Name the compound shown.
A. M-ethylphenol
B. O-ethylphenol
C. P-ethylphenol
D. M-ethylbenzene
A. M-ethylphenol
In organic chemistry, the term ”unsaturated” means a molecule,
A. With a specific six-membered ring structure.
B. That is formed from many smaller molecules.
C. That contains one or more multiple bonds between carbon atoms.
D. That can reac by taking up one or more water molecules.
E. That has the maximum number of carbon-hydrogen bonds possible.
C.
When an alkene undergoes a hydration reaction the product is an,
A. Alkane
B. Aromatic
C. Alcohol
D. Ether
E. Alkyne
C. An alcohol
The major produc obtained from dehydration of 2-hexanol is,
A.2-hexanal
B. 2-hexene
C. 1-hexene
D. 3–hexene
E. 2-hexanone
B. 2-hexene
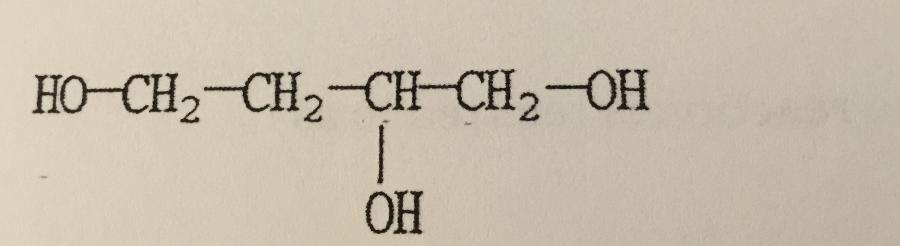
What is the IUPAC name of the compound shown?
A. Butanetriol
B. 1,2,4-butanetriol
C. 1,3,4-butanetriol
D. 2-hydroxy-1,4-butanediol
E. Butylene glycol
B. 1,2,4-butanetriol
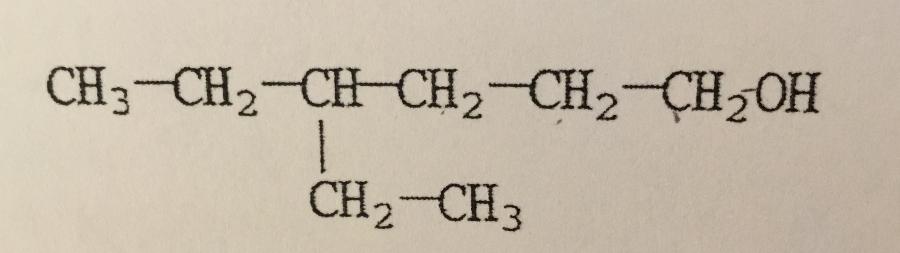
What is the IUPAC name of the compound shown?
A. 4,4-diethyl-1-butanol
B. 3-ethyl-1-hexanol
C. 3-ethyl-6-hexanol
D. Isooctanol
E. 4-ethyl-1-hexanol
E. 4-ethyl-1-hexanol
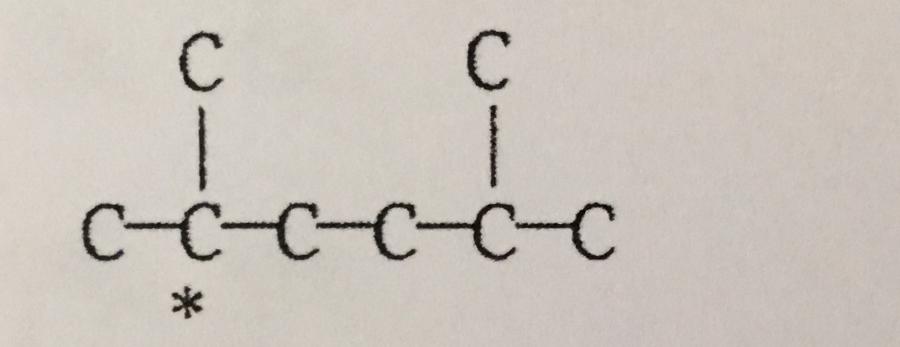
The C* is the ______ carbon atom.
A. Secondary
B. Tertiary
C. Primary
D. Quaternary
E. None of the above.
B. Tertiary.
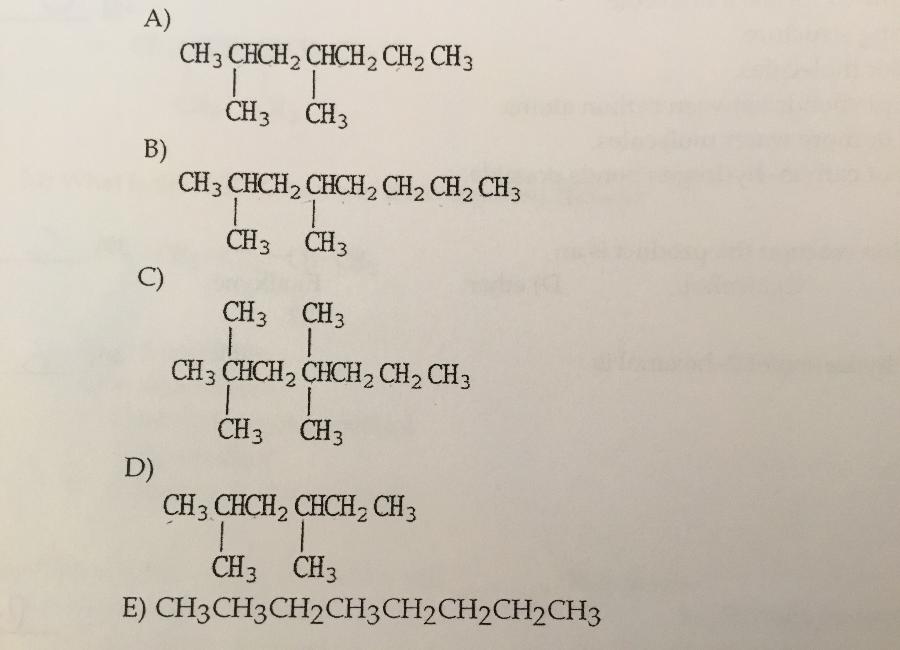
Which is the condensed structure of 2,4-diemethylhexane?
D.
When an alkane reacts with an element from group 7A, the reaction is referred to as,
A. Oxidation
B. Halogenation
C. Decomposition
D. Combustion
E. Displacement
B. Halogenation
When a think is oxidized the product is,
A. An aldehyde
B. A disulfide
C. Sulfuric acid
D. A ketone
E. An alkene
B. A disulfide
Organic compounds which are sulfur analogs of alcohols are referred to as,
A. Thiols
B. Sulfuric alcohols
C. Disulfides
D. Halides
E> carbonyls
A. Thiols